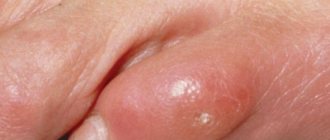
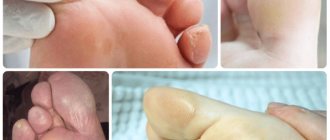
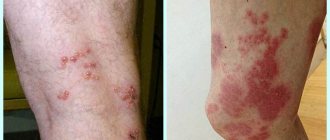
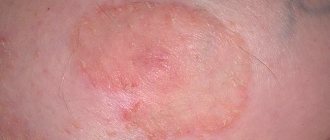
Types of calluses on the toes
Due to wearing shoes that are uncomfortable for the feet, a friction effect occurs. It is this that most often becomes the main cause of roughening of the skin and the appearance of calluses. But sometimes the reason lies much deeper - in poor metabolism, which manifests itself in this way.
There are two types of calluses that form on the big toe:
- soft, watery;
- dry, core.
When faced with any of these, the first thing you need to do for the comfort and healing of your toes is to change your shoes. At home, be sure to wear only soft slippers that will not compress the sore spot. When going outside, you should also try to wear your shoes as comfortably as possible.
You can remove these formations by going to a salon or hospital, or by yourself at home.
Prevention
It is not difficult to avoid the appearance of calluses if you take preventive measures:
- Wear only comfortable shoes. The pair should not be tight or, on the contrary, dangling on the leg. The material from which the shoes are made should be quite soft and preferably natural. Avoid wearing high heels or new shoes for too long.
- Maintain foot hygiene. It is necessary to remove rough areas of skin ahead of time to prevent the formation of calluses. It is recommended to visit a pedicure salon and use products to soften the skin of your feet.
- To prevent the formation of calluses, it is advisable to use special gel fixing pads. These pads help prevent your feet and toes from rubbing against the shoe material. Pads for the prevention of calluses are especially relevant for those who wear high-heeled shoes or narrowed models.
There is no 100% insurance against the formation of calluses. However, timely preventive measures can help avoid the appearance of neoplasms that cause discomfort.
How to get rid of calluses on your toes
Soft callus
The mistake many people make when removing it is to try to pierce it so that the liquid contained inside can flow out. This is strictly prohibited! There is a risk of infection and serious inflammation.
The best way to get rid of such a growth is considered to be daily treatment with one of the alcohol-containing solutions:
- brilliant green;
- iodine;
- propolis tincture;
- potassium permanganate solution.
The medicine should be generously lubricated with the growth itself and the area around it. These procedures need to be carried out until it “deflates.” If the callus does burst, lubricate the area with hydrogen peroxide and cover it with a band-aid.
Dry callus
The sooner you deal with it, the sooner you will get rid of it. If you do not pay attention to a dry callus, over time it will be very difficult to remove it yourself.
To get rid of dead skin using folk remedies, it needs to be softened regularly. To do this, you can use one of the following methods:
- Make baths. For them, warm water is collected, in which soap, salt and soda are diluted in small quantities. You can change the ingredients to pine extract or mustard powder. You need to keep your feet in the bath for 25-40 minutes.
- Another option for a steam bath is to add a little “% potassium permanganate” to the water.
- Lemon or aloe compress. A slice of lemon or an aloe leaf with the fleshy part should be wrapped with a plaster or bandage and left overnight.
- Potatoes can also be used as a compress. To do this, grind it to a pulp and also tie it to your leg. Before applying the bandage, place a piece of cellophane.
- For a vodka compress, you also need to use a bandage and cellophane. And a cotton wool soaked in vodka is applied to the rubbed area itself. Put a warm sock over the bandage.
- To soften the problem area, rub vegetable oil into it daily.
- If you are a fan of a variety of herbal treatments, use coltsfoot. You can make compresses, or steam your feet and rub the plant juice into the desired area throughout the day.
After baths, lubricate problem areas with baby or similar cream. Many people advise actively rubbing rough areas of skin with a pumice stone or brush. However, they must be used very carefully, removing particles that have separated after the procedures (for example, after a bath or in the morning, after removing the compress).
And if it’s not your style to be treated with so-called traditional methods and you trust modern medicine more, then you need to know how to remove a callus on a toe using modern methods - medications and salon procedures.
Cases requiring medical intervention
The main case that requires a trip to the doctor is callus . No matter how hard you try to dissolve the bone at home, nothing will come of it. The only way out of the situation is an operation in which the cartilaginous formation will be removed.
Another dangerous case is advanced cartilaginous callus . It will continue to grow into the tissue if proper measures are not taken. Another possible problem is relapse, even if the disease has been eliminated.
An equally dangerous situation is the appearance of pus in the area of the burst water callus . When the callus bursts, a wound opens. Through the blood and lymph, infection and contaminants instantly penetrate the body.
If you do not disinfect the wound in time and do not protect it, the consequences can be disastrous. Hurry to the doctor when the wound begins to fester !
Modern removal methods
At the pharmacy you can purchase various products for removing dead skin from fingers, such as:
- special patch with salicylic acid;
- keratolic gels, creams and ointments.
When using these products, be careful to ensure that the patch is applied exclusively to rough skin, without touching healthy areas. Same with creams and ointments. Before using these products, it will not be harmful to do any of the steaming baths described above. And then stick a patch or apply ointment on the wiped skin.
But these remedies are only relevant if the calluses on your feet have a short stem. If it is deep and long, you may need the help of specialists. Modern clinics and beauty salons offer the following methods for removing calluses:
- cryotherapy (cauterization with liquid nitrogen);
- laser elimination;
- hardware scraping.
Be sure to read the material: Calluses on the feet: photos, causes, removal and what to do if a callus bursts.
Using these methods, the outer layer of keratinized skin will be removed and the deep-seated root will be removed. Typically, clinics remove unpleasant growths in one or two procedures. After mechanical elimination using a laser or special discs, small wounds remain that will need to be looked after a little, using anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a specialist. If you decide to undergo cryotherapy, immediately after the procedure you will see smooth skin on your legs. But for some time you will still have to protect it with a band-aid so that the growth does not appear again.
Causes of inflammation
The appearance of inflamed calluses can be due to the following reasons:
- wearing uncomfortable shoes.
If the shoes are too narrow or wide, the foot will feel great discomfort, as strong friction occurs, which leads to the formation of calluses and its inflammation.
Foot deformities and various foot diseases.
If you have flat feet, bursitis (arthritis) of the foot joints and other diseases, then as a result, due to improper distribution of the load on the legs, calluses with thickened skin and an inflammatory process may form. Increased sweating of the feet.
Sweat softens the dead skin and a soft callus appears. Lymph can accumulate under a layer of thickened skin, which leads to inflammation of the water callus and its painful sensation. Poor quality hosiery.
If you have a hole in your toe and you are wearing shoes, this can also cause the appearance of an inflamed callus and lead to its suppuration. Excess weight.
A person who is overweight increases the load on the skin of the feet, resulting in not only corns, but also swelling of the feet, stagnation of blood and increased sweating of the feet, leading to bacterial contamination of callus areas.
Results
When your toes are hurt by uncomfortable shoes, don’t rush to get upset. Try to use one of the methods for removing rough particles as soon as possible. If you missed the moment when you can easily get rid of them, or they appear again suspiciously often, contact a specialist - a beauty salon or clinic. There they will help you identify the causes of calluses, advise you and offer various ways to eliminate them.
(
1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Causes and symptoms of suppuration
The causes of suppuration are the absence of adequate treatment for water callus or corns, which results in infection entering the wound. The site of the lesion begins to break out and purulent exudate appears, the immune system has turned on and leukocytes have begun to work. The process of suppuration occurs when there is insufficient antiseptic treatment of the wound.
Symptoms of suppuration:
- change in color of exudate (liquid). The contents of the callus become cloudy;
- the inflamed area hurts, turns red, there is swelling, itching;
- discharge of pus;
- increased body temperature;
- acute pain on palpation.
Localized on the fingertips
Calluses can appear on the outside of the fingers, on their pads. The formations cause pain while walking.
If uncomfortable shoes are to blame for the formation of such skin thickening (which happens more often), then they need to be changed. During treatment, you should choose shoes that are spacious enough and comfortable; they should not squeeze your toes.
Try to walk as little as possible until the callus heals. If the resulting growth is very painful, you can take a painkiller or anti-inflammatory drug.
These drugs include: ketanov, diclofenac and ibuprofen.
Such growths need to be treated with ointments or special patches that contain salicylic acid. They have a powerful softening effect. The ointments should be applied carefully, trying not to get on healthy skin.
Diagnosis of pathology
The callus that forms on the finger does not differ in structure from the formations that appear on other parts. It is not accompanied by pathological symptoms that worry the patient, since as the fragments are restored, the manifestations of the fracture subside. Externally, this formation may resemble a compaction, which is not accompanied by pain and signs of inflammation. Pathological manifestations are associated with disruption of the regeneration process.
The main diagnostic method is radiography; callus on x-ray is visualized as a slightly darkened spot. Gradually, the darkening undergoes calcification and modeling. On the x-ray it appears as a lighter area, which is due to its compaction. Within a year, a full-fledged bone is formed from soft structures.
Slow consolidation
This condition is diagnosed if, after a bruise or injury, the callus does not correspond to its stage. Its development is associated with a slowdown in the formation of bone tissue from fibrous tissue. Typically, delayed consolidation is diagnosed if about six months have passed since the injury. Deviation from the norm during the regeneration process is accompanied by elastic mobility in the affected area, pain that occurs with axial load, as well as redness of the skin.
Among the reasons that can lead to delayed consolidation include impaired treatment at the stage of callus formation after a fracture. Such errors are associated with problems of immobilization, tissue interposition and tissue regeneration.
The callus appears on an x-ray or x-ray in several projections with slow consolidation in the form of a gap between the fragments. Treatment after a fracture with delayed consolidation is predominantly conservative. To do this, lengthen the period of immobilization of the limb, and also give a moderate load on the limb.
Non-united fracture
Attention! This pathological condition is a violation of the process of restoration of fragments.
Changes can be diagnosed no earlier than two periods from the moment of injury to the process of complete healing. Symptoms characteristic of a non-united fracture include pain and pathological mobility in the injured area.
Bone callus in fractures that do not heal in a timely manner requires x-ray confirmation. On an x-ray, a callus looks like an area with a gap between the fragments, when the bone marrow cavities are still closed. If these cavities are overgrown with end plates, the patient is diagnosed with a pseudarthrosis. If a non-union fracture is suspected, it is necessary to regularly evaluate whether the callus is resolving and at what stage the regeneration process is. For recovery, it is important to achieve complete immobilization of the limb, blood circulation, and mineral metabolism.
False joint
This pathological condition occurs after a bone fracture and is accompanied by mobility in an area where it should not exist. Despite the fact that in clinical practice they account for no more than 3% of all fractures, they most often appear in the area of large tubular bones. A false joint can form if, after exposure to trauma, muscles, blood vessels, nerves or adipose tissue appear between hard structures. As a result, when a fracture occurs, the callus does not form correctly.
This condition is associated with early cessation of immobilization, technical errors when applying fixing bandages, as well as diseases that impair the process of tissue regeneration.
It is important for specialists to know what the callus looks like on an x-ray in this case in order to take timely steps to correct it and prevent the formation of a false joint. The resulting x-ray reveals that after the fracture the bone fragment is rounded, and the callus is completely absent or forms only in certain areas. There are soft tissues between the fragments. In this case, it is necessary to take into account how many stages the callus goes through and at what stage of recovery the patient should be. This is due to the fact that if the fusion period is exceeded by more than twice, we can conclude that a false joint has formed.
During diagnosis, it is necessary to rely on X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging data, since symptoms are sometimes completely absent or mild. Pain, as a rule, occurs only after loading the damaged area. Pseudarthrosis is treated only with surgical methods; conservative therapy is ineffective. In some cases, it is necessary to remove the ends of the fragments and subsequently lengthen them.
Types and stages
Callus is formed in several stages; in addition, it is divided into 5 types, among which are:
- Periosteal. This type begins to form immediately after injury. Periosteal callus formation involves complete limitation of motor activity in the damaged area. In the shortest possible time, compaction develops if there is an active blood supply in the area of the debris.
- Endosteal. The growth forms in the fracture zone, while the endosteal callus that forms appears on the inside. The appearance of a defect is typical for injuries in the area of the legs, metatarsal or radius bones.
- Intermediary. This structure is intermediate; it ensures the growth of hard tissue in the fracture site. It must be taken into account that such a formation as intermediary bone callus after a fracture is not detected on x-rays, and its treatment is prescribed in exceptional clinical cases.
- Periosteal. This type of callus forms when the area is not damaged and the fracture is not fixed, and the injury affects only soft tissue. The peri-spinous structure is characterized by the appearance of edema, swelling, pain and discomfort. These symptoms may bother the patient for a long time.
- Paraosseous. This callus in fractures of tubular or spongy bones leads to severe deformation of the structural elements. The appearance of a hard, brittle growth is considered a potentially dangerous neoplasm.
Types of callus vary depending on the type of fracture, its location or the nature of the traumatic impact.
Callus formed after a fracture of the clavicle or other structures occurs in several stages, which successively replace each other. Each stage requires specialist observation of the tissue condition, and, if necessary, therapy correction is carried out. The main stages of formation include:
- Autolysis. This stage begins from the moment of fracture, reaching its peak by 3-4 days. Against the background of tissue edema, leukocyte cells rush to the site of damage, processing the affected elements. Primary callus may appear in the scar, which can last up to 10 days. At this stage, signs of an inflammatory reaction may persist with tissue redness, swelling and pain on palpation.
- Proliferation. The connective tissue begins to actively grow and the formation of active substances occurs, which are necessary for the mineralization of bone structures that promote hardening. The proliferation stage can last up to one month.
- Restructuring of bone tissue. The formation of callus with the development of increased blood circulation at this stage leads to an increase in the density of cartilaginous structures and their replacement with bone ones. Mineral substances are deposited in the damaged area, which subsequently provide increased strength. Its duration can range from one month to six months. At these stages, it is important to prevent the formation of a false joint or other processes that impair regeneration.
- Complete healing stage. You can achieve full recovery after six months or a year from the injury. At this stage, the final formation of all structures, including the periosteum, occurs. In addition, functional activity and blood circulation are restored due to an increase in the number of blood vessels.
Treatment with patches
A patch designed to remove calluses is an effective, fairly convenient tool.
They come in different types:
- Silicone patch. It is intended for the treatment of both wet calluses and small corns. The composition contains colloidal substances, the task of which is to maintain a moist environment. This substance disinfects the wound and helps accelerate the growth of new skin. The advantage of such a patch is that it protects the wound from dirt, pathogens, and contaminated water.
- Salicylic patch. It is used to get rid of corns, both fresh and old. This patch contains salicylic acid, which helps to quickly soften the rough skin layer. It also has antimicrobial properties. The patch is applied to the problem area only when the feet are well steamed and wiped. It requires fixation with a simple plaster. After 2 days, the patch is removed. Several treatments may be required.
- Chinese patch. It contains salicylic acid and phenol. Thanks to the first substance, all pathogenic bacteria are killed, and the second helps to get rid of itching and pain. It should be applied to clean, pre-steamed skin. Changes once a day.