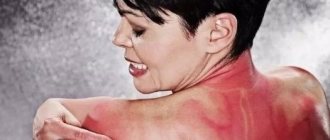
A 3rd degree burn is a very severe and extremely painful thermal injury, to one degree or another affecting all layers of the skin, and capable of causing irreversible changes in the damaged areas.
Photo 1. Third degree burns most often occur as a result of fire. Source: Flickr (ArSalles).
Causes and pathogenesis
A second degree burn is an injury that develops after exposure to external factors.
These factors include:
- thermal - upon contact with hot objects or boiling liquids;
- chemical - aggressive influence of salts, acids, alkalis of high concentration;
- electrical - careless handling of electrical devices or operation of faulty ones;
- radiation - the action of ultraviolet light or ionizing radiation.
With a 2nd degree burn, minor damage to the upper layer of the dermis and capillaries occurs.
What is a first degree burn?
The human body is designed in such a way that dermal cells are constantly renewed. A first stage burn can be treated in 3-5 days. The hyperemia gradually goes away, the swelling subsides, the skin becomes dry, wrinkled, then the outer layer comes off. It takes about a week to regenerate the epidermis.
Signs of the first stage are visible immediately after contact with the traumatic agent. A slight burning sensation and erythema appear at the site of the lesion. A slight swelling will form around the injury.
Such wounds most often occupy a small area and heal quickly. Rough scars and cicatrices are not preserved even in delicate areas.
1st degree burns result from:
- temperature exposure - boiling water, hot steam, hot objects;
- use of chemicals - acid, alkali, salt;
- electrical – touching exposed wires, damaged electrical appliances;
- radiation burn – excessive exposure to ultraviolet and radiation rays.
Minor irritation often appears due to prolonged exposure to the sun or injury at home (boiling water, hot appliances, electric current). If the skin is injured over a large area, this can cause poisoning by decay products or dehydration. To avoid complications, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Pain and redness of the skin.
- Dizziness and headache.
- Nausea, vomiting, chills.
- Rapid pulse.
First you need to remove the source of injury and cool the wound. Do not treat burned areas with ice - you can get frostbite.
It is advisable to treat the wound under medical supervision to avoid infection. If a child is injured, be sure to consult a doctor.
Clinical signs
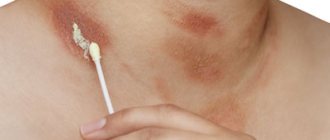
In the second stage, redness, hyperthermia of the affected area and swelling in this area occurs. Characteristic bubbles filled with tissue fluid also form.
After the fluid is released from the blisters, wounds remain in this area, which take about 2 weeks to heal. The clinic identifies several distinctive signs of a burn that are characteristic of this degree:
- redness;
- edema;
- severe pain syndrome;
- blistering;
- increased sensitivity of the affected area.
If a large area of skin is affected, the following symptoms are observed:
- general weakness;
- migraine and dizziness;
- urge to vomit;
- feverish condition.
This condition is especially difficult to tolerate in children. The baby, experiencing severe pain, becomes restless and whiny. There is also no appetite. The symptoms of general intoxication are much more pronounced than in adults.
Symptoms
A 3rd degree burn is divided conditionally into injuries “A” and “B” levels, depending on this, different signs of the wound area are characterized:
- A 3a degree burn is accompanied by burning of the entire top layer of skin, pain sensitivity is reduced. The surface of the epidermis has a heterogeneous structure, and bright hyperemia is observed. A 3rd degree burn is characterized by multiple blisters along the edges of the wound, with clear liquid. Immediately after the injury, the lesion appears as a black or brown scab;
- Type “B” is characterized by damage to nerve endings. If a 3b degree burn develops, there is no pain syndrome at all. The blisters are covered with dry scab, the edges of the wound are surrounded by hanging scraps of skin. Large-scale death of the dermis down to the subcutaneous fat.
Common symptoms of such damage include the following:
- Malaise, dizziness;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Lack of appetite;
- Headache;
- Increased body temperature.
Based on the level of severity, area of damage, depth of wounds, and general health of the patient, the treating specialist selects the necessary therapeutic regimen. With these symptoms, self-medication at home is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to tragic consequences.
First aid
So what to do if you get a burn? The speed of skin healing depends on competent assistance. Therefore, you need to know what you can do and what is prohibited. When providing assistance for a second degree burn, you must adhere to the following procedure:
- immediately remove the source of injury;
- the damaged area is washed with copious amounts of cold water. The cooling procedure helps prevent spread into the deeper layers of the skin;
- treatment with an antiseptic solution. Use medications that do not contain alcohol. It is better to do this with a peroxide solution;
- application of gauze. Dressings used at the pre-medical stage for 2nd degree burns must be sterile;
- If necessary, anesthesia is performed in any available way.
For second degree burns, it is strictly prohibited:
- tear off tissue adhering to the wound;
- soak the injured limb;
- use ice for the cooling procedure;
- apply cotton wool and tighten the bandage tightly;
- use alcohol solutions of iodine or brilliant green for treatment;
- treat the wound field with fat-like substances.
After providing first aid, you must consult a doctor to prescribe appropriate treatment. Typically, treatment for this degree of burn is carried out at home. The exception is internal burns. The speed of recovery depends on the correct provision of first aid and further care.
Recovery period
The main question that interests victims is how long it takes for 3rd degree burns to heal. It is definitely difficult to answer. As a rule, cell restoration begins only 3-4 weeks after damage.
At this time, qualified medical assistance is required. Unfortunately, even after prolonged treatment, deep scars and scars remain on the skin. Therefore, many victims have to resort to skin grafts and plastic surgery.
Skin grafting is a chance for many patients
Rehabilitation after burns is a long and very important process. Such injuries bring a person not only physical injuries, but also serious psychological trauma, requiring complex medical and psychotherapeutic measures. Their plan is developed individually by specialists.
Treatment and prevention of complications
Correctly selected therapy helps speed up healing. Treatment of 2nd degree burns involves the use of special means. The pharmaceutical market offers a variety of anti-burn and topical medications. But independent selection of these drugs is not always correct and may not bring the expected effect, so you should consult your doctor before use. So how to treat a 2nd degree burn? Antiseptic and drugs with anti-inflammatory effects are important in therapy.
Antiseptics are used in the first few days of treatment. Next, anti-inflammatory ointments are used. Medicines containing panthenol are very popular.
It is better to give preference to aerosol products when treating such injuries. They do not cause pain when used, even when treating a 2nd degree burn after opening the bladder.
Antihistamines are also prescribed. They help relieve swelling and relieve itching.
For severe pain, you can take any analgesic, and if there is such a need, the specialist will prescribe injections.
To accelerate tissue healing and the production of natural collagen, it is necessary to take fat-soluble vitamins and ascorbic acid. It is also important to adhere to the drinking regime and maintain a balanced diet to provide the body with resources for recovery.
Diagnostics
Burn injury has quite clear clinical manifestations, so its diagnosis is not difficult:
- Assessment of the depth of the lesion. Information about the damaging agent and the duration of its effect is of great importance. When assessing the degree, it is necessary to determine the presence of circulatory disorders, the temperature of the burned area, and pain sensitivity.
- Assessment of the affected area. The most commonly used methods are the “rule of nines” and “rule of palm”.
- Blood analysis. Detects leukocytosis, decreased magnesium and sodium, increased levels of potassium and albumin in the blood serum.
- Analysis of urine. Detects myo- and hemoglobinuria.
It is possible to accurately assess the depth and extent of damage only a week after injury.
Determination of the affected area
Further care
When further caring for the affected area, antiseptic measures must be observed. Is it possible to wet a burn? It is not advisable to wet the wound until it has completely healed. It is necessary to change dressings and treat with ointments on time.
When changing the dressing, it is important to pay attention to all changes that occur in the wound. Increasing pain, increased swelling and discharge of pus are signs indicating unfavorable dynamics. In this case, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
How long does it take for a burn to heal? Restoration of the skin occurs in 10-15 days. But for this you must follow all the doctor’s instructions. More serious lesions require hospital treatment.
Questions for the doctor
Harm of oil during burns
I remember when I was little, my grandmother always anointed her burns with oil. Now doctors say it is strictly prohibited. Explain why?
Hello! Indeed, treating a damaged surface with oil is not only useless, but can also aggravate the burn of the victim. Why is this happening?
The fact is that 80-85% of the human body consists of water, which, in addition to all other properties, has thermal conductivity. What happens during a burn?
Contact with a hot surface not only damages the skin, but also “transfers” a certain amount of energy to the tissues. The simplest way to level it is to hold the burned part of the body under cold running water for 10-15 minutes.
If you smear oil on a burn, a thick film is created on its surface, which prevents the energy from escaping outward, thereby directing it deeper and aggravating the damage.
Therefore, it is possible to treat the skin with any ointments (including regenerating ones based on dexpanthenol) only after thorough cooling and removal of energy.
Indications for antibiotic therapy
Not all degrees of burns require treatment with antibiotics. Mild lesions usually heal without these medications and are limited to the use of antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Antibiotics for burns are necessary in the treatment of deep, high-grade injuries. Drugs with this spectrum of action are prescribed in the presence of a chronic infectious process.
Also, streptocide for burns is prescribed if the patient is an elderly person or a child. A mandatory indication is diabetes mellitus. Antibiotics are sometimes necessary for extensive 2nd degree burns in a child.
Stages of healing
The rate of cell regeneration is individual for each person. Proper first aid is extremely important to alleviate the victim’s condition. A sequential algorithm of actions allows you to reduce the heating temperature in case of a thermal burn and neutralize the aggressive substance in case of chemical injury. This prevents deepening of the affected area and improves the prognosis for recovery.
First degree
Lesions of the 1st degree, in area not exceeding 5% of the skin, rarely provoke complications. The inflamed epidermis quickly recovers even without additional effort.
If you regularly treat it with products that can effectively heal damage, for example, Panthenol or Olazol, the symptoms disappear after 2-3 days. The redness subsides and peeling appears. The burn goes away without a trace, the skin is completely renewed.
Second degree
Stage 2 healing takes longer. If blisters have formed on the body, they should not be pierced. Inside there is a liquid containing white blood cells. They protect wounds from infection.
A burst bubble is an open gate for infection. Pathogenic microorganisms provoke inflammation and accumulation of pus. Such wounds take at least a month to heal and leave behind scars and scars.
Under normal conditions, recovery occurs within 2-3 weeks. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the doctor's instructions, regularly treat the blisters with antibacterial ointment, for example, Levomekol, and apply a sterile bandage. New skin forms under the blisters. Gradually they are blown away, the dead layer moves away, and in its place remains a pink spot of healthy epidermis.
Third degree
This degree of burn should only be treated in a hospital. Initially, severe inflammation develops. Necrosis and rejection of dead tissue is observed. To start the regeneration process, intensive therapy is needed, aimed at restoring immunity, suppressing infection, and relieving pain shock. A 3B burn requires surgery.
Only 20-30 days after injury, new cells begin to form, and healthy skin gradually appears . It may take several months to go through all stages of healing. Scars remain at the burn site, sometimes requiring plastic correction.
Fourth degree
Grade 4 damage is characterized by charring of tissue and death of all layers of the skin. They do not heal on their own. A person must lie in a room with a special microclimate and undergo complex treatment.
- In the first weeks, a scab appears in the affected area. It is important to avoid infection during this process.
- Granulation tissue slowly forms under the crust. This stage takes 1-2 months.
- When the granulation phase ends, skin grafting is prescribed. For transplantation, donor or the victim's own material is used.
The rehabilitation period after 4th degree burns lasts from 3 months to several years. The greatest danger is burn disease, damage to joints and bone tissue. Such patients often have impaired mobility and become disabled.
Any burns require the close attention of a specialist. Only a doctor can correctly assess the clinical picture and prescribe treatment that stimulates rapid healing.
Consequences
The consequences depend on the nature of the damaging factor. Each type of exposure leaves characteristic symptoms.
The most common causes are lack of water, dry skin and wound infection. Such complications are usually accompanied by large areas of injured skin.
Sometimes the blood supply is disrupted, and when nerve fibers are damaged, spasms occur.
Burn site infections are quite dangerous conditions and can cause skin infection. The environment created by a wound of this degree is favorable for most bacteria.
Forecast
Sometimes the consequences of burn injuries entail serious disruption of the functioning of internal organs, and sometimes even a threat to life. The prognosis is influenced not only by the degree of severity, but also by the patient’s age, as well as the quality and timeliness of therapy.
The main methods for determining the forecast are the “hundred rule” and the “Frank index”. With deep burns of 35-40% of the skin surface, it is impossible to help the victim.
The clinical picture, treatment tactics and prognosis for recovery after injury depend on the degree of thermal burn.