Causes of skin burns from liquid nitrogen
In most cases, freezing is used to remove papillomas and warts. Using a special nozzle, a chemical liquid is applied to the skin for 20 seconds. It is permissible to re-use freezing for severe skin imperfections. Failure to comply with one of the rules of use results in a nitrogen burn.
There are also some contraindications to the procedure. The chemical should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as for serious skin diseases. The main causes of skin burns with liquid nitrogen are also identified:
- careless handling of the reagent. When using loose fabric gloves, skin damage occurs;
- it is forbidden to touch cold objects that have come into contact with the substance;
- the vessel used must not be damaged so as not to cause leakage of the substance;
- When any materials are placed in the container, it causes the reagent to splash.
When performing cryotherapy in unventilated areas, the risk of injury increases. It is mandatory to use protective equipment, including a special suit, gloves designed for working with liquid substances, and strong shoes. Nitrogen burns can cause scarring or loss of vision, so it is important to take precautions.
Possible consequences and prevention of complications
The method of getting rid of warts using nitrogen has a significant drawback. During the procedure, it is not possible to take biomaterial from the tumor to perform a biopsy. The doctor cannot confidently reject its possible oncological nature. It is necessary to determine whether this tumor is malignant or not before the session.
Cauterizing warts with liquid nitrogen in rare cases leads to the following complications:
- local inflammation, causing pain and swelling of the affected epidermis;
- tissue necrosis.
Possible consequences and side effects can be warned by a qualified specialist who will remove the wart. To effectively remove the tumor, the doctor must choose the optimal temperature and freezing strength. If the impulse is too strong, a scar may remain on the dermis. Therefore, it is important to balance the cauterization force.
Cryodestruction is carried out painlessly if the person does not refuse anesthesia. The patient feels only a slight tingling and burning sensation. When a crust forms, itching may occur. A person should not feel any other uncomfortable sensations.
Cases when the site of a wart becomes inflamed are not uncommon. Patients are forced to relieve pain with painkillers. If such symptoms appear, we advise you to consult a dermatologist.
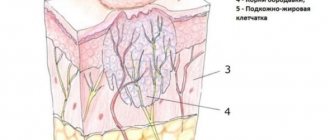
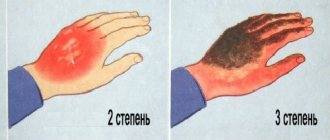
Degree of damage
When the first signs of tissue damage appear, the severity must be assessed. Depending on how extensive the lesion turned out to be, the following stages are distinguished:
- at grade 1, redness and swelling of the skin is observed. The injury is minor, heals without the use of potent drugs;
- Grade 2 is characterized by the appearance of blisters. Their contents are transparent, sometimes yellowish. At this stage, the top layer of skin exfoliates and peels off as a film;
- Grade 3-A represents damage to some skin layers, but deeper tissues remain unaffected;
- 3-B degree is characterized by tissue necrosis, in which a specific scab is formed;
- with the last, 4th degree, not only skin cells die, but also muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones, and joints.
For mild damage, doctors prescribe conservative treatment with medications. More extensive wounds require surgery.
First aid rules
When the first signs of thermal injury occur, a number of general measures are taken. First aid for a burn includes the following actions for the victim:
- any contact with the chemical reagent is stopped, the affected area is placed under cool running water. It is necessary to wash the wound for a long time (at least 20 minutes);
- if any clothing interferes with the provision of assistance, it is removed. If at the same time the fabric is stuck to the damaged area, it cannot be torn off, it is only allowed to carefully cut around the edges;
- a sterile bandage is applied to the affected area;
- in case of severe pain, the victim is given an anesthetic;
- if the burn is accompanied by fainting or a general deterioration in health, the person is provided with access to fresh air. If necessary, perform artificial respiration;
- If your hands are injured, remove the rings from your fingers, as they may swell.
In some cases, there are recommendations that call for piercing the resulting blisters with a sterile needle. Doctors advise against doing this, since infection penetrates into an open wound more quickly. After assistance is provided, doctors are called to hospitalize the victim.
Therapeutic measures
For degrees 1 and 2 damage, doctors in most cases prescribe treatment at home. Patients are prescribed a group of drugs that have an antiseptic, antibacterial, healing effect. Wounds are treated daily, several times a day, to avoid infection.
It is necessary to pierce blisters in a medical facility and not immediately after their occurrence. The recovery course will be selected by the attending physician. Depending on the extent of the injuries received, rehabilitation takes from 1 to 2 weeks. More serious burns take several months to heal.
The list of the most popular healing agents includes the following drugs:
- ointment or spray Panthenol. The method of application depends on the severity of the resulting lesions. When most of the skin surface has been damaged, an aerosol is used so as not to further injure the tissue;
- Bepanten. This ointment is similar in principle of action and composition to Panthenol. Provides anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect;
- Olazol spray has a complex effect. Anesthetizes and disinfects the surface, and also accelerates the process of cell restoration;
- Radevit ointment accelerates metabolism in the affected area, thereby reducing the rehabilitation period.
Additionally, the use of traditional methods is recommended, but before using them you must consult your doctor. In addition, the products can only be used for mild damage.
If you receive a burn during cryotherapy, you must provide first aid to the victim and call doctors. Liquid nitrogen can quickly destroy tissue, causing more extensive skin damage.
source
Traditional medicine recipes
It is important to use non-traditional remedies in combination with medications:
- When the injured area is very painful, a compress of chamomile and oak bark helps effectively. To do this, you need to mix the crushed raw materials 1 tbsp. pour 1 cup of boiling water. Leave the container for 30-40 minutes, cool to room temperature and apply compresses 3-4 times a day.
- Exposure to nitrogen can lead to the formation of a burn; in this case, applications of plantain juice are good for tissue regeneration.
- For better healing and recovery, aloe juice is used, which has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Causes of skin burns from liquid nitrogen
Careless handling of liquid nitrogen when performing medical or cosmetic procedures is a common cause of burns.
Liquid nitrogen rightfully belongs to the category of the most dangerous substances that can cause severe frostbite of the skin and severe damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes, so it is important to take precautions when working with such compounds:
- Do not use cloth gloves when it is necessary to pour or pour a substance, as in this case nitrogen burns very often occur;
- Do not touch materials that have been heavily cooled using liquid nitrogen;
- Do not tightly close the Dewar flask;
- Dewar vessels with obvious mechanical damage should not be used for work;
- Do not suddenly throw objects into a container filled with liquid nitrogen, as this may cause the formation of a large amount of splashes.
When to see a specialist
When carrying out procedures with liquid nitrogen, a burn remains in any case. But if the technique is followed, the burn will be shallow and will not cause major problems for the patient. In this case, the doctor or cosmetologist who performed the manipulation will give recommendations on caring for the wound.
But there are some cases when consultation and treatment under the supervision of a specialist is required:
- Inflammation of a burn wound;
- Self-opening of the blister;
- Deterioration in general health;
- Large burn;
- Severe pain in the wound;
- Increased body temperature;
- Burn at work.
In severe cases, you should call an ambulance, which will hospitalize the patient in a surgical hospital.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RoVPkoW2ToU
In other cases, you need to seek help from a surgeon at the clinic. If your skin is slightly damaged by nitrogen, you can seek help from a dermatologist.
Degree of damage
To know how to treat surfaces damaged by nitrogen, you need to correctly assess the extent of the damage:
- I degree – redness and swelling of the skin;
- II degree nitrogen burn – the appearance of blisters filled with a clear yellowish liquid. The epidermis peels off and the basal layer is exposed. There are no morphological changes in the skin, which determines the fundamental difference from deeper degrees of damage;
- III-A dermal degree - damage to not the entire thickness of the skin with preservation of the viability of the deep layers or appendages, represented by hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands, and their excretory ducts;
- III-B degree – necrosis of the skin followed by the formation of a characteristic necrotic scab;
- IV degree - accompanied by necrosis of the skin and deeper tissues, including muscles, tendons, bones and joints.
Features of nitrogen burn treatment suggest the division of lesions into two groups, represented by superficial and deep changes.
In the first case, only the upper layers of the skin die, so healing during conservative treatment is due to epithelization due to the preserved elements of the skin. With deep lesions, as a rule, there is a need for surgical treatment to restore lost skin.
First aid rules
The main condition is not to get confused, and also to know exactly what to do and how to properly provide assistance to the victim before contacting medical personnel:
- if there is dizziness, fainting, the victim must be taken out into fresh air as quickly as possible, if necessary, perform artificial respiration and immediately call emergency medical assistance;
- if liquid nitrogenous compounds come into contact with the surface of the skin, the affected area must be immediately and copiously rinsed with running water;
- if there is a very extensive burn surface, painkillers are administered;
- you need to remove all clothing that interferes with the activities and apply a sterile dressing to the wound;
- in case of carpal lesions, it is recommended to remove all rings, which will prevent the development of edema and subsequent ischemia of the fingers.
The depth of the burn can be preliminarily determined by identifying the level of pain sensitivity . Superficial burns are characterized by preservation or slight decrease in pain sensitivity. A reliable sign of a deep lesion is a scab with the presence of clearly visible thrombosed vessels.
Therapeutic measures
It is advisable to treat superficial burns without signs of shock at home. Toileting a burned surface involves removing particles of exfoliated epithelium and washing the lesion with any antiseptic solution that does not have an irritating or significant painful effect. At the next stage, the burn blisters need to be dissected and the contents carefully removed.
Excision of the exfoliated epithelium of the blisters is not required, since in this case the risk of wound infection significantly increases.
The burn bladder can be completely removed only when purulent contents appear .
A bandage with a standard antiseptic solution can be applied to dried surfaces, but for a small area of damage, an open method of treatment is most often used. The healing period for second-degree burns is approximately ten days. Healing of first degree burns usually takes less than a week. Treatment of more severe nitrogen burns will require serious therapeutic measures, which involve the use of the following medications:
- aerosol "Panthenol" with the active ingredient dexpanthenol has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, and upon penetration through the skin it synthesizes biologically active substances, thereby accelerating the wound healing process;
- Bepanten+ cream allows for complex treatment of burn surfaces, and also helps prevent bacterial infection of the wound;
- aerosol "Olazol" is a whole complex of active ingredients, represented by the antibiotic chloramphenicol, the anesthetic anesthesin, an effective stimulator of regeneration processes in the form of sea buckthorn oil;
- ointment "Radevit" with the main active components that stimulate the regeneration of the skin, allows you to stimulate metabolic processes in tissues, and accelerate healing.
In stationary conditions, therapy is carried out if the area of the skin lesion exceeds the size of the palm, the resulting burn is located on the face, genitals or mucous membrane, there are fragments of clothing at the burn site, the contents of the blisters contain inclusions of blood or pus.
Particular attention should be paid to burns that are accompanied by a significant increase in body temperature, severe nausea or vomiting, as well as confusion or loss of consciousness. The most severe consequence of a nitrogen burn can be burn disease, which is represented at different stages by a state of shock, acute toxemia and septicotoxemia, so severe lesions must be treated under the strict supervision of medical personnel.
source
Signs of enanthema - rashes on the oral mucosa
In some cases, malaise may be accompanied by rashes, the nature of which depends on the disease. Most often, enanthema is caused by bacteria or viruses. The baby's condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- he complains of a sore and itchy throat;
- he has difficulty breathing;
- it hurts for the baby to swallow;
- there is pain and aches in the body;
- In the morning and evening the baby is bothered by a dry cough;
- there is an increase in temperature and signs of intoxication.
First aid for burns
First aid should be provided immediately after a nitrogen burn occurs. If the burn occurs in a medical facility, then assistance and treatment is carried out by medical personnel. Actions to be taken in the event of a burn with liquid nitrogen outside of a medical setting should be considered in detail.
First aid for burns with liquid nitrogen:
- Stop exposure of the victim’s skin to liquid nitrogen;
- Rinse the affected skin area thoroughly with running water;
- Assess the condition of the victim and call an ambulance;
- If a person is unconscious or dizzy, provide access to fresh air (you can take it outside), unfasten tight clothing. Position the patient with the leg end elevated. This will ensure blood flow to the brain and prevent the development of fainting;
- In case of severe pain , give an anesthetic drug (Analgin, Baralgin, Ibuprofen and others);
- to the wound . If clothes get in the way, take them off. If clothes are stuck, carefully cut them off with scissors;
- If the patient is unconscious , then place him on his back with his legs elevated and turn his head to the side. Check for pulse and breathing. If respiratory and cardiac activity is preserved, then monitor the victim until doctors arrive. You can lubricate the skin of your temples with ammonia;
- If there is no pulse or breathing, immediately begin first aid (cardiopulmonary resuscitation). It is necessary to perform artificial respiration and chest compressions.
The difference between a wart and a tumor
Soft, large growths change color over time, becoming pinkish or purple. A slight redness is often mistaken for a malignant tumor, which causes panic in the common man.
An ordinary watery wart differs from a malignant neoplasm:
- light shade;
- lack of bleeding;
- painlessness when palpating the area of skin around it.
If the growth begins to bleed and turns blue, then there is a possibility that it has begun to degenerate into oncology.
What not to do when providing assistance
For first aid and ball therapy to be effective, it is necessary to know what actions will harm the patient. That is why it is necessary to separately consider the manipulations that cannot be performed during a nitrogen burn:
- Treat the burn surface with antiseptics containing alcohol. This will lead to increased inflammation and deeper tissue damage;
- and preparations based on them to treat burns The oil forms a dense film on the surface of the wound and creates a greenhouse effect, preventing the penetration of oxygen to the tissues. All this leads to a worsening of the wound;
- Apply a tight bandage . This contributes to increased pain and poor circulation;
- Puncture the resulting blisters yourself and remove the crust that covers the wound. The burn will become infected and suppuration will occur;
- Self-medicate , especially in case of inflammation and infection of the burn wound.
What can't you do?
Any burn can be treated with oil or any oily substance, for example sour cream.
But, if it’s good to spread sour cream on your sunburned back, this does not mean at all that the same method is also good for a serious chemical burn!
It is also simply unacceptable to use caustic products and, in particular, alcohol-containing tinctures for treatment. Today on the Internet you can find a lot of anti-burn folk recipes based on alcohol, onion and garlic. But all of them will only lead to even greater burns!
As noted above, you should not puncture a blister with a non-sterile needle. You should also make sure that no dirt gets on the wound.
It is not allowed to apply bandages that are too tight; they interfere with blood flow and prevent healing.
And finally, the last thing, you cannot remove the formed crust when the wound is just beginning to heal, this can only worsen the process.
If the burn does not get smaller within three days, and especially when the condition worsens, you should consult a dermatologist.
Severity of burn wounds
In case of a burn with liquid nitrogen, it is necessary to assess the severity of the damage to the skin. Because the severity of the burn will determine the method and extent of treatment, as well as the duration of recovery.
It is customary to distinguish 4 degrees of burn severity:
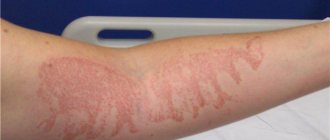
- 1st degree burn . Only the top layer of the epidermis is damaged. Therefore, only hyperemia of the skin and swelling at the burn site are observed;
- 2nd degree burn . The top layer of skin peels off, causing fluid-filled blisters to form. It may be clear, cloudy, yellowish or dark. The skin is red, the site of injury is sharply painful, swelling is observed beyond the wound;
- 3rd degree burn . In this case, grades 3A and 3B are distinguished. With a 3A degree burn, deep damage to the skin is observed, large blisters are observed that quickly burst. In their place there remains a large open wound. With a 3B degree burn, all of the listed symptoms are accompanied by necrosis of the affected tissue;
- Burn of 4th degree of severity. In this case, deep tissue damage down to the bones is diagnosed, and nerves are affected.
Possible consequences
Nitrogen burns can vary in severity. Complications after skin damage occurs are also varied:
- Blackening of the skin at the burn site. This is due to the death of the top layer of skin. In rare cases, even after treatment, the skin color at the burn site remains darker than in unburned areas;
- Changes in the eye due to burns of its mucous membrane. Often there is a significant decrease in visual acuity. In severe cases, there is complete loss of vision;
- Infection of the wound, which is manifested by severe throbbing pain, swelling, redness, local increase in temperature in the wound area;
- Sepsis occurs when an infection from a wound enters the general bloodstream and spreads throughout the body. In this case, general hyperthermia, deterioration of health, and multiple organ failure are noted;
- A state of shock develops with deep and extensive burns;
- Scarring. Hypertrophic, colloidal scars may remain.
Causes of burn injury
There are several reasons for this injury and they are all based on non-compliance with the rules for working with liquid nitrogen and non-compliance with safety rules. Actions that lead to burns:
- Touching exposed parts of the body to objects cooled with liquid nitrogen;
- Refusal to use personal protective equipment (gloves, mask, goggles). In this case, nitrogen, once on unprotected areas, quickly destroys tissue;
- Use of faulty equipment during cryotherapy. If there are chips or cracks, it is necessary to inform the person responsible for the equipment about this and draw up a written report or statement. It is dangerous to work on such equipment, since both the worker and the patient can get burned;
- Negligent attitude towards one’s duties and untimely inspection of equipment;
- Neglecting to ventilate the room where they work with nitrogen. This can cause damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes and upper respiratory tract$
- Violation of the technique of carrying out medical and cosmetic procedures.
Preventive measures
You can avoid the development of a burn with liquid nitrogen by following simple preventive measures:
- Compliance with safety rules when working with liquid nitrogen. This applies to both industry and medicine;
- Use of personal protective equipment (gloves, goggles, gas mask, mask, respirator);
- It is good to ventilate the room in which you work with liquid nitrogen;
- Contact a cosmetologist only in specialized clinics and salons. Only a good specialist will be able to carry out the procedure painlessly and without serious consequences;
- Seek help from a doctor in a timely manner. You can avoid complications after a burn only by following all the recommendations of a specialist;
- Monitor the serviceability of equipment;
- Compliance with cryotherapy techniques.
Treatment of burns with liquid nitrogen
Treatment can be carried out both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital setting. For burns of 1st and 2nd degree severity without signs of infection and shock, it is performed on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a surgeon. The patient treats and dresses the wound at home or in the clinic.
The attending physician prescribes medications for external use, painkillers and vitamins. For severe burns, shock, and intense inflammation, treatment is indicated in the burn department of a surgical hospital.
Medications
Various drugs for external use are used in treatment:
| Name and release form of the drug | Mode of application |
| Panthenol in aerosol form. It has anti-inflammatory and wound healing effects. | The aerosol is applied to a previously cleaned wound. The can of medicine must be shaken and held vertically while spraying. |
The aerosol is used up to 5 times a day, depending on the severity of the burn.
| Miramistin in the form of a spray. Has an antibacterial effect (non-alcoholic antiseptic). | Miramistin is used to treat wounds before applying medications. The drug has a wide spectrum of action. |
| Olazol in aerosol form. It has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and wound healing effects. | The aerosol is applied to the wound after pre-treatment with an antiseptic. Olazol is used up to 3 times a day, it is sprayed directly onto the wound surface. No bandage is required. |
| Levomekol in the form of an ointment. This is an antibacterial agent that is used for suppuration and infection of the wound. | The ointment is applied to the wound 2 - 3 times a day. It remains effective in the presence of purulent discharge and blood. |
How to care for your skin after the procedure
After cauterization of formations with nitrogen, a burn is formed, which must be carefully cared for. Rules for skin care after cryotherapy:
- Protect the resulting blister from damage. It cannot be torn, and even more so you should not open it yourself;
- Protect the wound from contamination with a gauze or bandage bandage;
- Use painkillers for severe pain at the wound site;
- Treat the burn with antiseptics that do not contain alcohol (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine);
- Use ointments and aerosols prescribed by the doctor to treat the wound. You cannot prescribe medications for yourself;
- Observe personal hygiene rules. This will reduce the risk of wound infection. You can shower, but the blister should not be damaged. Therefore, you need to wash carefully;
- You cannot cover the wound with a band-aid. This will damage the wound surface and may cause bleeding.