Potassium permanganate is a purple powder that, when diluted with water, changes color from faint pink to purple, and also becomes the most inexpensive and convenient antiseptic. A percentage solution of potassium permanganate has an anti-inflammatory effect, which makes it indispensable for various skin injuries, skin diseases and diseases of internal organs. In its own way, it is a panacea for all ills, if you know how to use it correctly.
Causes
The action of potassium permanganate is based on its strong oxidizing properties. In low concentrations, its solution has antiseptic properties, which is widely used in medicine: gargling, douching, gastric lavage, treating wounds and burns. Reduced manganese oxide forms albuminates with tissue proteins, which also produces an astringent effect.
If low concentrations of the drug have therapeutic properties, then high concentrations have a pronounced irritating, cauterizing and damaging effect on the skin and mucous membranes. Inept use of a solution or pure crystals of potassium permanganate leads to chemical burns. And when absorbed into the blood, potassium permanganate becomes a source of toxic damage to internal organs and disruption of the transport function of the blood (due to the formation of methemoglobin).
The causes of potassium permanganate burns lie in one thing - incorrect use of the drug. An antiseptic should be prescribed only by a doctor indicating the required concentration.
Burn from potassium permanganate: what to do and how to treat
A weak solution of potassium permanganate is widely used by people in everyday life for disinfection purposes. A few dark purple granules will provide a remedy for many problems. But if the concentration of the substance is incorrect, you can easily get a burn from potassium permanganate.
Properties and action of potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate, used exclusively in the form of an aqueous solution, is capable, due to its disinfectant and deodorizing properties:
- dry out skin inflammations and rashes;
- disinfect wounds, abrasions, cuts, ulcers, burns;
- sanitize the throat for purulent diseases;
- induce vomiting in case of oral poisoning;
- used for sanitation for gynecological and urological purposes.
Potassium permanganate is a powerful oxidizing agent, due to which its therapeutic effect is achieved. A weak concentration of the solution is used for bathing infants and treating tattoos during the healing process; a stronger solution is used for treating plumbing fixtures and common areas. But you need to monitor the concentration to avoid chemical burns.
Signs and danger
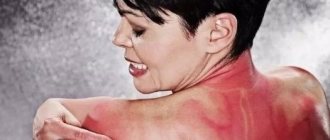
A burn from a strong solution of potassium permanganate occurs due to incorrect concentration or mistaken ingestion of crystals, which can happen to a small child due to his natural curiosity and the attractive color of the dry substance. Burns of the skin, eyes, mucous membranes, and digestive tract are types of injuries that have their own signs and, in the absence of emergency first aid, will bring serious health consequences.
| Type of chemical burn | Symptoms |
| Leather | With 1st degree burns, the site of injury appears swollen, reddened, and pain is present. A second-degree burn is expressed by the appearance of blisters at the site of injury with light contents, swelling, redness, and pain. Stage 3 is characterized by damage to the deep layers of the skin, blisters with dark contents appear. 4th degree is expressed by necrosis of tissues, subcutaneous tissue, muscles; damaged tissues are black from charring. It will take a long time to undergo treatment. |
| Eyes |
|
| Mucous membranes of the genital organs |
|
| Digestive organs |
|
The danger of chemical burns is fraught with serious health problems later. With severe skin lesions, scar tissue may form, which will entail the need for surgical intervention.
When the eyes are injured, their function suffers, vision deteriorates, dryness appears on the mucous membrane of the eyes, or vice versa, tear production increases. A burn to the mucous membranes of the genital organs will provoke vaginitis, erosion, endometriosis, and, during pregnancy, fetal rejection.
In case of a burn of the digestive organs and severe intoxication of the body, narrowing of the esophagus, stomach ulcer, kidney failure, and hepatitis are likely, which can significantly complicate the life of the victim.
Further treatment
After removing the toxic substance from the body or from the skin, patients undergo a course of treatment. For minor burns of the body, without consulting a doctor, it is allowed to use traditional medicine recipes, painkillers, and skin-regenerating drugs.
Complex burns are treated in a hospital after determining the depth of tissue damage.
Depending on the complexity of the injury, the patient is prescribed intravenous alkaline solutions, vitamin complexes, blood transfusions, painkillers, drugs to prevent liver and kidney failure.
The mucous membrane of the eyes is restored by injection, by introducing a 5% solution of vitamin C into the subconjunctival sacs, and steroid ointments and antimicrobial eye preparations are placed behind the eyelids.
Oral burns are treated comprehensively. The patient takes painkillers that block the development of bleeding, burn shock medications, and, if necessary, undergo plasma or blood transfusions, hemodialysis, and prescribe vitamin complexes intravenously.
Precautionary measures
Many people do not read the instructions for use of certain products, and this is a mistake. Proper dilution of potassium permanganate crystals consists of the initial dilution of the substance in a small container to a bright crimson color and its thorough dissolution.
The second stage is to add a strong liquid to the container where it is intended to be used, in a small amount. The process of dissolving manganese permanganate should be carried out with gloves; the residues should be disposed of or stored out of the reach of children, away from food products.
When adding a concentrated solution to a container for use, it must be filtered. Do not pour crystals directly into the bath or use concentrated liquid.
It is necessary to carry out explanatory work with children about the prohibition of trying unfamiliar liquids, substances and playing with them. All these rules are standard for working with all chemicals; if you remember them and follow them, the likelihood of getting a burn will be reduced to zero.
The article has been verified by the editors
Source: https://BezTravmy.ru/ozhogi/margantsovkoj.html
Symptoms
It is not difficult to identify a burn with potassium permanganate - this requires anamnestic data (the fact of using the drug) and clinical symptoms. The latter are typical for all burns. Based on external signs, the degree of damage can be determined:
- 1 – redness, swelling, burning.
- 2 – blisters on burned skin filled with clear liquid.
- 3 – the contents of the blisters are cloudy or bloody, the formation of a crust (scab).
- 4 – charring of tissues.
Very often there are burns from potassium permanganate in a child, since the skin of children is more delicate and sensitive to chemical damage. Rinsing the mouth with a concentrated solution leads to damage to the mucous membrane with brown-violet erosions. A burn to the esophagus can occur as a result of gastric lavage or ingestion of dissolved potassium permanganate. In this case, there are other symptoms:
- Burning and pain behind the sternum.
- Respiratory disorders (shortness of breath and suffocation).
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
- Increased salivation (hypersalivation).
- Vomiting blood.
Rinsing the eyes with potassium permanganate can cause burns to the cornea and conjunctiva. This situation is accompanied by pain and pain, lacrimation, spasm of the eyelids and increased sensitivity to light. The mucous membrane swells and turns brown, and the cornea becomes cloudy and rough.
Symptoms of burns with potassium permanganate are similar to signs of injury from other irritating chemicals.
Potassium permanganate burn - First Medical Aid, Symptoms
Potassium permanganate burns are classified as chemical burns.
Most often, the cause of such burns is accidents or failure to comply with safety precautions when working with acids or alkalis at home. Chemical burns are burns caused by contact with the skin or mucous membranes of an aggressive chemical reagent.
In this article we will talk about burns with potassium permanganate, burn treatment, and first aid.
Now potassium permanganate cannot be bought in pharmacies or hardware stores. The legislation of the Russian Federation prohibits the sale of it, as it was often used in the manufacture of explosives. However, many people still have supplies of this product at home.
It is a dark purple, almost black powder, which when dissolved in water becomes bright crimson and is most often used as an antiseptic or disinfectant.
These properties of potassium permanganate are explained by the high oxidizing ability of the substance.
Potassium permanganate is used in various areas of our lives.
We list the main ones:
- gargling for sore throats,
- washing wounds, abrasions, cuts,
- as an emetic for poisoning,
- antiseptic for washing eyes after being bitten by poisonous insects,
- treatment of ulcers and burns,
- douching for gynecological and urological diseases.
Potassium permanganate is potassium permanganate or potassium salt of permanganate acid. It can only be used in the form of an aqueous solution. The concentration and percentage should differ depending on the use of the antiseptic.
Important! Observe precautions when working with this substance and recommendations on the concentration of the potassium permanganate solution.
Treatment
In case of severe burns, under no circumstances should you wash the burned area with a strong solution of potassium permanganate. This may complicate further treatment of the burn with potassium permanganate or lead to a second burn, only now also a chemical one.
Potassium permanganate burn in a child
Children are most often at risk of getting burns. They are very curious and active. Bright manganese crystals or pink potassium permanganate solution can certainly attract their attention. In young children, the instinct of self-preservation is not well developed.
They may not understand cause and effect relationships and can easily become victims of potassium permanganate burns. Very often, children get burns from swallowing too concentrated a solution. In this case, you can get a burn from the potassium permanganate mucosa, as well as the esophagus and stomach.
Important!
- Store potassium permanganate solution or dry substance away from children - on the top shelves.
- If children are of a conscious age, explain the dangers of playing with potassium permanganate.
- When diluting an aqueous solution, it is necessary to work with gloves to prevent burns.
If a child receives a burn from potassium permanganate, immediate action must be taken. The degree of damage to the burn and further consequences depend on the speed and correctness of the first aid provided. The severity of the burn is determined by the concentration of the solution. The lower the concentration, the less the effects will be.
All burns are divided into four groups:
- First degree burns are characterized by redness of the skin at the site of the potassium permanganate burn. Such a burn is accompanied by itching, slight swelling, and unpleasant pain. This type of burn is considered the easiest and least painless.
- With second-degree burns, in addition to the previous symptoms, blisters form on the skin. If blisters form, you should never burst or pierce them.
- Third degree burns are skin necrosis with the formation of a gray crust. Such burns damage the integrity of the skin. Blisters with cloudy fluid and blood appear.
- The fourth degree is the most dangerous! It is characterized by necrosis or charring of not only the skin, but also muscle tissue, and sometimes even bone tissue. This is the most serious type of burn.
What to do if you are burned by potassium permanganate?
In case of a burn with potassium permanganate, first aid must be provided. It will depend on the location of the burn.
Attention! Do not panic! Panic never leads to anything good. Try to calm down and think soberly about the current situation.
If the burn is on the skin, then it is necessary to remove clothing from the area where the potassium permanganate came into contact. If the wound from a burn with potassium permanganate is small, it is necessary to rinse the burned area in running water at room temperature for 10 to 15 minutes.
To neutralize acid burns, use a two percent alkaline soda solution. To do this, two teaspoons need to be mixed with 1 liter of water. The solution must be applied as a compress with the solution to the burn site.
Then it is necessary to treat the burn wound after potassium permanganate with an anti-inflammatory or anti-infective agent.
If the esophagus is burned, then with such a chemical burn the person experiences severe pain. Symptoms of a burn include vomiting; if the larynx is damaged, the victim may begin to choke. In case of burns with potassium permanganate, it is necessary to rinse the stomach with a weak alkaline solution. The victim should be taken to a medical facility as soon as possible.
Women often get burns from potassium permanganate when douching. A vaginal burn with potassium permanganate is a very serious problem that occurs mainly due to the high concentration of the solution for treating the vagina. The first thing to do is rinse the affected areas with water at room temperature. To neutralize acid burns, use a two percent alkaline soda solution.
Important! After providing first aid, rest is a must. It is also necessary to take anti-shock measures.
These measures include warming the body. Our body’s defense mechanisms are designed in such a way that even in the warm season a person can experience cold and chills.
People who have experienced a stressful situation need time to come to their senses and calm down. It is best to take a horizontal position and relax. It is imperative to monitor the condition and, in cases of deterioration, call an ambulance.
For several weeks, pay attention to vitamins. They are needed for better recovery.
Loading…
Source: https://beauty-love.ru/travmyi/ozhogi/kak-izbezhat-ozhoga-margantsovkoy
Consequences
Negative consequences manifest themselves not only in damage to the skin or mucous membranes. A burn with potassium permanganate can trigger a mechanism for more serious changes:
- Collapse or shock.
- Liver failure.
- Toxic hepatitis.
- Methemoglobinemia.
- Hemorrhagic colitis.
- Laryngeal edema and asphyxia.
- Cramps.
Such troubles can be prevented only by timely identification of the source of the problem and provision of medical care. Any symptoms, especially in childhood, should be an unconditional signal to consult a doctor.
Potassium permanganate for newborns
It is mainly used for bathing and for treating the navel.
Bathing newborns with potassium permanganate
For bathing newborns, a very weak (pale pink solution) 0.02-0.05% solution of potassium permanganate is used. And to obtain it, you first need to prepare a 10% solution, as described above. Strain it through cheesecloth. And then add it to the bath, to 6-12 liters of warm (37°C) boiled water. Newborn babies are bathed in boiled water until the remainder of the umbilical cord falls off and the umbilical wound heals (up to about 1 month). The child is placed in a bath with potassium permanganate for 5-10 minutes and gently bathed. Wash your head, back, stomach, arms and legs with your palm or a soft cloth. After bathing, the baby is washed (rinsed) with boiled water without potassium permanganate.
Potassium permanganate for children Treatment of the navel
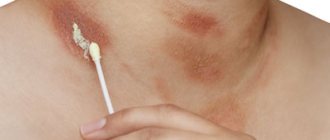
An intense pink 5% solution is used to treat the navel. To obtain it, 3 g of potassium permanganate is diluted in 60 ml of warm water. The solution must be filtered through cheesecloth. After that it can be used. It is recommended to treat the navel with potassium permanganate 2 times a day. In the morning after waking up and in the evening after swimming. Treatment of the umbilical cord or umbilical wound is carried out using a cotton swab.
Treatment
Only a specialist knows how to treat a burn correctly. Therefore, you should focus on the doctor’s recommendations. First aid consists primarily of removing potassium permanganate residues, which is done by washing and rinsing. Hydrogen peroxide, soda or acetic acid can be added to the water. When washing the stomach, activated carbon and sodium thiosulfate are also used.
Soda inhalation and drinking alkaline and oily solutions help prevent swelling of the larynx during burns of the mucous membrane. Often, a burn from potassium permanganate requires the use of medications:
- Local anesthetics.
- Painkillers.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Hemostatic.
- Infusion.
- Vitamins.
For methemoglobinemia, antidotes are needed (methylene blue, ascorbic acid), for renal failure, perinephric blockades with novocaine are performed, and shock requires plasma expanders, corticosteroids and sympathomimetics. To prevent secondary infection, early administration of antibiotics is indicated.
It is possible to cure burns and their consequences only with comprehensive correction of all disorders. This should be done by qualified healthcare professionals.
Potassium permanganate burn to skin and eyes (first aid)
Potassium permanganate (popularly “potassium permanganate”) is a dark purple powder that belongs to the group of strong oxidizing agents. A weakly concentrated aqueous solution is used for rinsing the mouth, washing wounds, treating trophic ulcers, etc.
If the proportions are not observed, it causes chemical burns. The degree of damage to mucous membranes and skin depends on the concentration of potassium permanganate in the water. First aid is to neutralize potassium permanganate with a two percent soda solution.
For shallow injuries, the wound is treated with anti-burn ointment.
Why is potassium permanganate dangerous for the skin?
Potassium permanganate is a strong oxidizing agent that interacts with many organic and inorganic substances:
- glycerin;
- tannins;
- potassium;
- gray;
- sugar.
During the chemical reaction, atomic oxygen is released, which has an irritating, cauterizing effect on the skin.
A burn with potassium permanganate is dangerous not only due to local, but also systemic complications. Absorbed into the blood, it has a toxic effect on the nervous system, kidneys, and liver tissue. During pregnancy, it provokes contractions of the uterus, which causes miscarriage or premature birth.
Degree of skin damage
Weak solutions containing 0.1% potassium permanganate do not cause irritation to mucous membranes or skin. At higher concentrations of the chemically active substance, a burn occurs. The degree of skin injury depends on three factors:
- forms of the chemical reagent (powder or aqueous solution);
- solution concentration;
- duration of contact of the reagent with soft tissues.
A burn from potassium permanganate is treated differently depending on the area and depth of the damage:
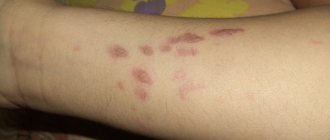
- 1st degree. Only the protective layer of the epidermis is affected. There is moderate swelling, redness, and burning. When using ointments with provitamin A, the burn goes away completely within 3-4 days.
- 2nd degree. The outer epithelium is damaged down to the germinal layer of the dermis. The skin becomes covered with blisters with cloudy contents. Healing occurs within 7-14 days due to cell division of the growth layer.
- 3rd degree. All layers of the epidermis are destroyed, partially (3A degree burn) or completely (3B degree burn) the dermis. The burn wound is covered with a dark brown scab. Pain sensations are reduced due to damage to the layer with sensory receptors.
- 4th degree. The epidermis, dermis, fiber, and partially muscles and bones are charred.
In 76% of cases, potassium permanganate leaves shallow burns. As the chemical penetrates the skin, dense scabs form. They prevent the irritating substance from entering the deeper layers of the dermis and muscles.
Severe 3rd and 4th degree burns are treated only in medical institutions! Traditional recipes are contraindicated.
Burns of 3B and 4 degrees are treated only in a hospital by specialists. Due to the total destruction of the skin, independent tissue restoration is impossible.
Signs of potassium permanganate burns
Superficial burns from potassium permanganate are manifested by redness, burning, and blistering rashes. With prolonged contact with the substance, characteristic brown scabs form. Severe pain when injured indicates shallow damage.
Ingestion of potassium permanganate crystals or liquid causes food poisoning and burns of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Typical symptoms of a burn injury include:
- painful swallowing;
- burning along the esophagus;
- nausea;
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- necrosis of the oral mucosa;
- labored breathing;
- excessive salivation;
- hemoptysis;
- unintelligible speech.
When highly concentrated solutions are swallowed, the laryngopharyngeal mucosa swells. Because of this, the respiratory channel narrows, which sometimes causes mechanical asphyxia, that is, suffocation.
The penetration of potassium permanganate into the conjunctiva of the eyes is indicated by the following symptoms:
- incessant tearing;
- darkening of the mucous membranes;
- acute pain in the eyes;
- decreased visual acuity;
- photophobia.
Burns of mucous membranes pose a serious danger to life. Potassium permanganate provokes spasms of smooth muscles. Because of this, breathing becomes difficult and the swallowing reflex is disrupted. If left untreated, intoxication occurs, which is indicated by constant nausea, headaches, vomiting, diarrhea, and weakness.
First aid
Methods for treating burn wounds are determined by the concentration of the potassium permanganate solution and the location of the damage.
Before the ambulance arrives, you must:
- remove clothing from damaged skin areas;
- rinse the wound with soda or running water;
- treat the burn with an antiseptic, burn ointment;
- apply a sterile bandage.
When it enters the blood, potassium permanganate destroys the parenchyma of the liver and kidneys. To neutralize its effect, take a 1% solution of ascorbic acid. This prevents hepatic-renal failure in the victim.
Skin injury
If crystals or a solution of potassium permanganate get on the skin, you must immediately wash the wound. Prolonged contact with soft tissues risks penetration of the chemical into the deep layers of the dermis.
First aid for skin injuries:
- Cleansing the wound. Damaged areas are freed from clothing. Potassium permanganate crystals are removed with napkins soaked in a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution.
- Washing. For 10-15 minutes, the skin wound is washed with running water at relatively low pressure. Injured tissues are blotted with sterile gauze and bandage.
- Neutralization of the chemical reagent. In case of a burn, you need to treat the skin with alkalis. To do this, dissolve 2 tsp in 1 liter of water. baking soda. Gauze is generously soaked in the liquid and applied to the burned skin.
- Disinfection. For shallow wounds, disinfectants and wound healing drugs are used - Dexpanthenol, Sulfargin, Radevit.
If blisters form on the body, they are covered with sterile bandages. The burn is pre-treated with drying ointments - Zinc, Boro Plus.
Burn of the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus
Damage to the esophagus with potassium permanganate is dangerous not only due to burns, but also severe poisoning. When providing emergency assistance you should:
- Neutralize the chemical reaction. The stomach is washed with a special liquid. Add 100 g of 3% hydrogen peroxide and 200 g of 3% ethanoic (acetic) acid to 2 liters of water. The medicinal liquid acts as an antidote to potassium permanganate. The procedure is performed until the vomit is discolored.
- Treat the oral cavity. The burned palate, gums, oral mucosa and tongue are wiped with a napkin soaked in a solution of ethanoic acid and hydrogen peroxide.
- Cleansing the gastrointestinal tract of toxins. The victim is given an aqueous 5% solution of sodium sulfate. Within 30-40 minutes, drink up to ½ liter of the product. To quickly remove potassium permanganate from the body, drink water with activated carbon. Up to 15 g of sorbent is added to 1 liter of boiled water.
To prevent irritation of the large intestine, castor oil is given to the victim after first aid. It acts as a mild laxative, which accelerates the removal of potassium permanganate from the body.
Eye damage
Delayed assistance for a burn in the eye area can lead to a decrease in visual acuity. To help the victim, you must:
- Rinse the mucous membrane. The eyes are rinsed with running water for 10 minutes.
- Antidote treatment. Damaged tissues are treated with a 5% tannin solution.
If there is a burn to the conjunctiva of the eyes, you must call a doctor at home. He will inject a solution of ascorbic acid into the affected tissue. To prevent bacterial complications, he will prescribe local antibacterial drugs.
Further treatment of burns
Self-treatment of burns is recommended only for relatively minor 1st and 2nd degree injuries. Local therapy consists of treating wounds with antiseptics and wound-healing ointments. The treatment regimen includes:
- Chlorhexidine – destroys pathogenic microbes, fungi, protozoa;
- Panthenol – stimulates the regeneration of damaged skin and mucous membranes;
- Levomekol – relieves inflammation, softens tissue, destroys infection and prevents purulent complications;
- Bepanten - acts like vitamin B5, accelerating the healing of wounds;
- Povidone-Iodine – destroys most pathogens of skin infections, stimulates the restoration of the epidermis;
- Radevit – reduces itching, moisturizes the skin, strengthens local immunity;
- Sulfargin – destroys bacterial infection, prevents purulent complications after skin transplantation.
To relieve pain, the doctor prescribes narcotic analgesics - Omnopon, Fentanyl, Dipidolor, Morphine. For a burn of the esophagus, patients take a 5% novocaine solution. To prevent internal bleeding, calcium preparations are used - Trenax, Etamzilat, Tranexam.
At the recovery stage, the main goals of therapy are to heal damaged skin and disinfect, as well as relieve painful or uncomfortable sensations.
If large areas of skin are damaged by potassium permanganate, a state of shock may occur. To improve the patient’s well-being, plasma transfusions are performed and vasoconstrictor drugs are administered.
In hospital settings, barbiturates are used to prevent muscle cramps.
Acute inflammation of the ocular mucosa is treated with corticosteroids:
- Dexamethasone;
- Paramethasone;
- Prenacid;
- Betamethasone.
Purulent complications are treated with antimicrobial drops - Levofloxacin, Tobrex, Fucitalmic. In severe cases, combination drugs with antibiotics and corticosteroids are prescribed - Tobradex or Maxitrol. Also, throughout the entire treatment period, intensive vitamin therapy with thiamine, retinol, ascorbic acid, and pyridoxine is carried out.
Complications
The consequences of burns with potassium permanganate depend on the concentration and location of the wounds. When swallowing the solution, the following are observed:
- vomiting blood;
- hemorrhagic colitis;
- general intoxication;
- diarrhea with blood.
If the eyes are damaged, visual acuity may decrease and complete blindness may occur. If potassium permanganate gets on large areas of the skin, burn shock, liver failure, and bronchopneumonia are diagnosed. In severe cases, anuria and toxic hepatitis occur. In the early stages of pregnancy, spontaneous abortion and fetal death are possible.
How to prevent chemical burns
To prevent a chemical burn, you must:
- store the powder in an airtight container out of the reach of children;
- use protective gloves and goggles when working with chemicals;
- prepare an antiseptic solution of the correct concentration - no more than 5 g of potassium permanganate per 100 ml of water.
When treating skin wounds, this antiseptic is pre-filtered. This prevents potassium permanganate crystals from entering injured tissue. Compliance with precautionary measures and proper first aid prevent serious complications when receiving a chemical burn.
Source: https://tden.ru/health/margantsovkoj
Prevention
Burns from potassium permanganate can be prevented only with proper preparation and use of solutions. The concentration of potassium permanganate in them should be as follows:
- Rinse the mouth and throat - from 0.01 to 0.1%.
- Lubrication of ulcers and burns - from 2 to 5%.
- Washing wounds - from 0.1 to 0.5%.
- Douching - from 0.02 to 0.1%.
When using the product for bathing small children, you need to dissolve the crystals in a separate container and then pour the resulting mixture into the bath. Otherwise, some particles may remain intact, and if they come into contact with the skin, they can cause a pinpoint burn.
Since potassium permanganate is used as an antiseptic in various branches of medicine, the relevance of the problem of burns with potassium permanganate remains quite high. A similar situation can arise if the solution is prepared and used incorrectly, when the skin or mucous membranes are exposed to a substance in high concentration. How to act to prevent injury and what to do for those who have already been burned are important issues that need to be addressed.
Degree of skin damage
Depending on the level of exposure, burns from potassium permanganate may differ in depth and severity of damage. When determining the degree of severity, you need to focus on the main factors:
- a type of potassium permanganate, which can be represented either as crystals or as a solution;
- the concentration of the potassium permanganate solution used;
- duration of traumatic impact.
Treatment of burns with potassium permanganate is based on correct determination of the degree of damage to the skin:
- in the first degree of a chemical burn, only the upper layers of the skin undergo changes, which is accompanied by slightly pronounced swelling and mild redness. There is mild pain in the burn area;
- in the second degree of a chemical burn, the damage spreads to the deeper layers of the skin with the appearance of relatively severe swelling and noticeable redness, as well as the formation of blisters filled with clear liquid;
- in the third degree of a chemical burn, the skin layers located in close proximity to the fatty tissues are affected, which is accompanied by the appearance of blisters filled with cloudy or bloody liquid;
- in the fourth degree, all tissues represented by the skin, muscles and tendons are affected.
Accidental ingestion of a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate is often observed, which provokes a chemical burn of the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach of varying severity. Among other things, the solution causes severe food poisoning.
How potassium permanganate helps with poisoning
Even a person who does not drink alcohol and tries to eat right can face poisoning. Potassium permanganate must be kept in your home first aid kit.
Having received poisoning, a person will immediately begin to wash out his stomach. In case of poisoning, it gives an antiseptic effect. This occurs due to the contact of oxygen with organic components, its active substance is released. Potassium permanganate does not cause vomiting on its own. It is caused by excessive fluid intake. And potassium permanganate serves to cleanse the wall of the gastric mucosa, thereby ridding it of poisonous and toxic substances in case of poisoning.
In addition to its low price, it is easy to prepare and effectively affects pathogenic bacteria:
- substances related to a number of chemicals, alcoholic beverages will enter a stage devoid of danger and activity;
- The microorganisms causing the poisoning die by combining with the antiseptic solution.
Powder diluted in water will help only if it is consumed fresh. After a short period of time, the solution will turn brown. This indicates its oxidation and loss of its auxiliary effect on toxic substances.
Potassium permanganate for diarrhea in adults is not recommended by doctors. With diarrhea, the intestines are exposed to toxic substances, and potassium permanganate can intensify this symptom. Which will lead to severe dehydration.
Rules for preparing a solution of potassium permanganate for gastric lavage
If a victim washes out the stomach due to potassium permanganate poisoning, you should take into account some rules indicating how to drink potassium permanganate during poisoning. This solution can have a negative effect on the body, including poisoning. These rules include:
- After opening a tube of potassium permanganate, do not inhale the crystals.
- Use glass containers to dissolve potassium permanganate.
- After stirring, carefully ensure that all crystals dissolve. To be safe, strain the colored water through cheesecloth folded in four. This will prevent the crystals from damaging your stomach.
- Store the powdered substance in protected places. If stored incorrectly, its explosive properties may be activated.
- If after use there is still potassium permanganate left in the container, it needs to be poured out. It will not bring any benefit if you repeatedly flush the gastrointestinal tract. Potassium permanganate oxidizes quickly.
- An allergic reaction to potassium permanganate is common. Therefore, testing should be done before use. Recommended for initial use.
- If drug poisoning is detected, the use of potassium permanganate will not bring any results.