Any changes located in the facial area bring anxiety to a person. Even pimples cause anxiety, not to mention the serious visible changes expressed by eczema on the face. Everyone knows that people meet people based on their appearance and it is extremely unpleasant if the impression is negative.
This disease is a real nuisance for both women and men. It causes serious psychological problems and complexes. If skin diseases on the body and limbs can be hidden in clothes, then the face remains visible.
It is impossible to hide flaws when going to work or to the store. Let's try to figure out what kind of disease eczema on the face is and what treatment modern medicine uses.
Eczema itself is an inflammatory change in the skin, when symptoms such as redness, peeling, crusts, vesicles, etc. develop. As a rule, the disease has an allergic or infectious origin. It is not life-threatening for the patient, but causes great discomfort, creating psychological problems.
Varieties and atypical forms
Eczema, which is classified as weeping, is several subtypes of the disease that have similar clinical signs, but are different diseases. There are four types of weeping eczema:
- Seborrheic is a disease provoked by disturbances in the working processes of the sebaceous glands of the human body. Clinical signs (rashes) have a characteristic localization and manifest themselves on the chest, shoulder blades or behind the ears.
- Microbial - is a complication during long-term treatment of mechanical damage to the skin, in case of infection with third-party pathogenic microorganisms. It is primarily localized on one or several edges of the wound, and in the absence of proper treatment it gradually grows. The process continues continuously until the start of treatment.
- True is the most difficult form of eczema from a treatment point of view. It is characterized by acute manifestations of clinical signs and short-term attenuation of the disease, without any systematics. The first signs are the appearance of erythema and swelling on the patient’s dermis, which gradually develop into vesicular rashes. If you scratch or otherwise damage the integrity of the resulting blisters, new foci of the disease will appear on the skin, looking like crusty, weeping erosions.
- Professional - fully corresponds to its name, because it develops only in representatives of certain professions who come into contact with physical and chemical irritants of the epidermis. It is localized exclusively in those areas of the skin that have been subjected to prolonged negative effects. Most often, cleaning professionals, construction workers, workers in chemical plants and other professions where constant contact with harmful substances is part of the job come to hospitals with this problem.
Causes
Dermatitis can be triggered by both external irritants and serious diseases.
It is the doctor’s task to look for the cause of the disease, but you can find out what common reasons the mentioned types of eczema occur:
- Mycotic. The trigger is allergic reactions to various fungal infections.
- Professional. Exposure to pathogenic factors of production, contact with chemicals.
- Varicose. The disease occurs in people with chronic varicose veins.
- Eczema of the nipples. A consequence of improper breastfeeding, one of the complications of scabies.
- Sycozyform eczema. Occurs due to microtraumas, chronic rhinitis, improper hair removal, etc.
To date, not all causes of the development of dermatitis have been established. The appearance of eczema can be influenced by disruptions of the nervous system, the development of endocrine and metabolic pathologies, a weak immune system and genetic factors, excess weight (varicose eczema), pregnancy and limb injuries. Infections and allergies play an important role in the formation of non-contagious inflammatory diseases.
How to treat
After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the most important thing is the timely administration of adequate treatment. Therapy will be aimed at eliminating the cause, as well as affecting the lesions.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment includes:
- depending on which particular causative agent of eczema was identified, antibiotics or antifungal drugs are prescribed;
- anti-allergy remedies;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antiseptics;
- hormonal drugs;
- agents that regulate the immune system;
- sedatives;
- vitamins and minerals.
Taking medications is aimed at eliminating pronounced symptoms. After completing such a course, it is necessary to use special ointments and creams - this will help prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Listerine is considered a highly effective external agent for this action. It is good because it does not contain hormones or any chemical components.
Zinc-naphthalene ointment can quickly relieve weeping, itching and inflammation, as well as heal foci of eczema. It is extremely effective due to its pronounced antibacterial and antiseptic effect.
Physiotherapeutic treatment methods
Physiotherapy is prescribed for infectious eczema on the legs and arms in conjunction with drug treatment:
- Laser therapy is the effect of light on the affected tissue. At the same time, biochemical processes in the skin are activated, which promotes wound healing.
- Magnetotherapy: the therapeutic effect is achieved by the action of a low-frequency magnetic field on the affected areas of the skin.
- Ultraviolet irradiation.
- Mud therapy.
All these manipulations are aimed at consolidating the results of drug therapy. It is also necessary to protect the skin from the negative effects of direct sunlight, snow, rain and frost .
Treatment and prevention
The above classification of eczema and description of the symptoms of the disease indicate the impossibility of self-treatment. Consultation with a dermatologist and consistent adherence to his recommendations remain the only way to relieve seasonal exacerbations. The key task of the doctor is to identify provoking factors. After this, a treatment strategy is formed - medications are prescribed to treat eczema. It may include systemic and local therapy. Physiotherapeutic procedures are an additional option.
Systemic therapy
The basis of drug treatment is antihistamines, which are designed to reduce the risk of developing acute allergic reactions of the patient to various internal and external factors. Sedatives are prescribed against the background of high psycho-emotional stress experienced by adults and children. Plasmapheresis and other types of hemocorrection are used in severe cases of the disease complicated by systemic pathologies.
If the effectiveness of the treatment is low, the doctor may prescribe the patient oral glucocorticosteroids. As the condition of the child or adult improves, the dose of hormonal drugs is reduced.
Local therapy
Retinol ointment is applied to local areas of inflammation. An alternative can be applications of pastes with keratolytic properties. Anti-inflammatory and antiseptic components contribute to the successful elimination of bacteria, viruses or fungal infections. If there are a significant number of vesicles, the patient is prescribed drugs with individually selected components. Their combination is based on the clinical picture of the pathology and the cause of inflammatory processes on the skin identified during diagnosis.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic complexes include:
- ozone therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser stimulation.
In difficult cases, a dermatologist may insist on treating eczema-affected skin areas using cryotherapy. After overcoming the acute phase of the disease, therapeutic and mud baths are recommended for children and adults. In some cases, irradiation of damaged skin areas with ultraviolet rays is prescribed. To determine the correct treatment, the dermatologist may refer the patient to a physical therapist.
Preventive measures
If signs of eczema are detected, patients should seek advice from a dermatologist. After confirming the diagnosis, you should follow a diet - you must exclude foods that can provoke allergic reactions from your diet. It is recommended to refrain from drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes.
Personal hygiene rules when treating eczema of the feet, hands, arms, legs or face include avoiding scented soaps. To moisturize the skin, it is permissible to use water-based creams.
Types of pathology
Depending on the causative factor and the nature of the manifestation, eczema on the hands is divided into several types. Below are the most common ones.
Table. Main types of eczema.
| Type of pathology | Description |
| Microbial | It occurs quite rarely on the skin of the fingers and hands. The main cause of the development of microbial eczema is an advanced form of mycosis of the palms. The pathology is accompanied by peeling of the skin, the appearance of a yellow crust and blisters with purulent fluid. |
| Professional | This type of eczema develops gradually and has a clear connection with the negative impact of external factors, including aggressive substances. In most cases, eczema affects only the fingertips, but sometimes the pathology can spread to the entire hand. |
| Dyshidrotic | Accompanied by a rash on the fingers or hands. In the absence of proper treatment, dyshidrotic eczema can become chronic, which will lead to the appearance of additional symptoms (burning and itching between the fingers). |
| True | The disease manifests itself acutely: vesicles, itchy cracks and redness appear on the affected areas of the patient’s skin. But when true hand eczema becomes chronic, the swelling intensifies, and ulcers appear on the affected areas. Without comprehensive treatment, the disease can bother a person for several years. |
| Fungal | In medicine, this form of eczema is also called mycoic. The main factor provoking the development of the disease is fungus in the nail area. Fungal eczema is infectious in nature, so it is easily transmitted to other people through contact. |
The main forms of eczema Depending on the nature of the rash and clinical manifestations between the fingers, eczema can be weeping or dry. Let's consider the types of pathology separately:
- getting wet. In addition to swelling and redness of the skin, small blisters appear on the hands, in the place of which, after opening, erosions remain - pathological foci on the skin from which purulent contents are released. Over time, crusts appear on the affected skin;
- dry. The affected areas of the skin thicken and become rough, causing small but very painful cracks to appear. Dry eczema is also accompanied by the appearance of papules - a rash in the form of nodules. As a rule, with dry eczema, no erosions or blisters occur, and the disease itself develops gradually. According to statistics, dry eczema on the hands is diagnosed much more often than wet eczema.
Features of the development of dry eczema
The classification into dry and weeping eczema is a conditional division, since many types of the disease at different stages of development can be dry or weeping.
About allergic eczema
Allergic eczema is one of the most common skin diseases, occurring equally often in both children and adults. It is characterized by a wide variety of skin elements of the rash and itching. It often becomes chronic with frequent relapses.
Allergic eczema is an unpleasant disease; a small rash appears on the human skin in various areas, then the disease develops in stages. Allergic eczema is a form of regular eczema. Allergic eczema is not an infectious disease; you cannot become infected with it. By the way, eczema in infants can go away on its own after reaching the age of three.
As for adults, eczema can appear in representatives of any gender, any age, often due to allergies. In adults, this form of eczema often develops into chronic eczema, and can go away and then suddenly appear again.
Symptoms and signs
Irritation can manifest itself in different ways depending on the reasons that caused it. When affected by a fungus (mycosis, candidiasis), pale rashes or redness and a powdery coating appear on the skin.
Fungal infections are characterized by a specific unpleasant odor. Bubbles form in the armpits, which burst, increasing the erosive area.
The patient feels itching, burning, pain. Shaving hair during this period becomes a painful procedure.
(Find out everything about fungal skin infections. Read about fungus on toenails here.
about athlete's foot in this article, about foot fungus here. about fungus on the hands on this page).
Characteristic symptoms
Weeping eczema always manifests itself in an acute form, then spontaneously subsides, and then begins an endless cycle of calm and exacerbation, which can only be stopped with the help of a qualified dermatologist. A sign of the most advanced stage is the formation of eczematous wells filled with exudate.
Clinical manifestations of weeping eczema are as follows:
- The first sign that distinguishes the weeping form from other eczemas is the appearance of vesicles and papules, which appear as fluid-filled bubbles standing on raised stands.
- Severe itching and redness - the patient constantly experiences sensations similar to a nettle burn, and the itching reaches such proportions that the patient’s sleep and mental well-being are disturbed.
- Localization - most often it is the hands, less often the legs. There are documented cases of weeping eczema even on the face, but this is an uncharacteristic manifestation of the disease and is quite rare.
- Signs of evolutionary morphism - any doctor in the process of diagnosing eczema always checks for the presence of this clinical sign. The bottom line is that all stages of eczema should appear in one area of the skin at once: crusts, erosions, papules and vesicles grow together and indicate a progressive disease.
- Spontaneous opening - manifested in the ability of papules to die off the skin and penetrate the exudate out. The dots may coalesce into areas, forming entire patches of oozing fluid from the skin.
- Weeping eczema is a symptom reflected in the English name of the disease weeping eczema. The formation of exudate into droplets similar to dew or tears is a characteristic feature of weeping eczema.
- Colored thickenings - if the disease has been advanced and has entered the chronic stage, then at the wound sites lumps will appear, rising above the surface of the skin. They are blue or red in color and are very flaky.
Depending on the pathogenesis and etiology, the clinical signs of eczema may vary, but despite this, there are classic symptoms of pathology that appear in any type of disease:
- burning and itching in the affected area of the skin;
- hyperemia (overflow of blood) and tissue swelling;
- the appearance of a rash (small blisters filled with liquid);
- the formation of dense crusts on the skin that occur when the blisters open;
- exfoliation of the stratum corneum of the dermis occurs and its further restoration.
Signs of eczema on the fingers Many patients notice disturbances in their mental state. This is due to the presence of an inferiority complex caused by a pathological skin condition. Most often, young women suffer from emotional shock, because the disease negatively affects their appearance (the manifestations of eczema cannot always be masked with the help of cosmetics).
Eczema between fingers
According to statistics, eczema on the hands is most often localized between the fingers or at their tips. The pathological process can also affect the thumb. Ignoring the symptoms of eczema can lead to serious consequences; for example, in the absence of timely treatment, blisters formed on the affected areas of the skin may burst, and purulent ulcers will appear in their place. This will cause even more discomfort.
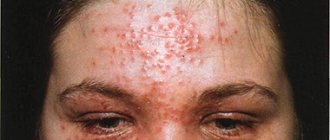
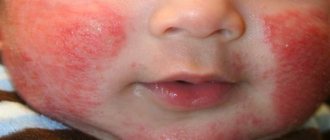
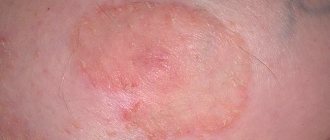
Eczema on the face photo with description 6 photos
Eczema on a person's face.
Photo 1. Eczema on a girl’s face. Photo 2.
Eczema on a person's face. Photo 3.
Eczema on a person's face. Photo 4.
Eczema on a person's face. Photo 5.
Eczema on a person's face. Photo 6.
For a better understanding, here are images of eczema on the face, photos of the initial stage and later forms. They will clearly make it clear what manifestations you should be wary of. Almost every type of lesion in the facial area has distinctive features, but only a dermatologist can diagnose it correctly. First, the doctor will examine the lesions and ask some questions. In thoughtful, thorough responses lies the possibility of rapid diagnosis. The collected anamnesis will reveal the diseases that the patient suffered during his life.
It is necessary to determine the factors due to which the signs presumably appeared. These could be possible allergens, the presence of wounds, etc. A scraping from the site of inflammation will reveal the pathogen. If there are no results, then most likely the problem is a reaction to allergens. Therefore, allergy and stress tests will be necessary.
Symptoms and forms
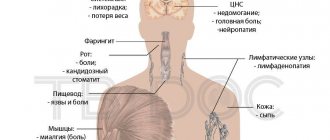
Depending on the cause, the rash may be red or white, the skin may become bumpy or pimply, it may have an odor, itching, swelling, discharge or pus, burning, tenderness or pain.
Sometimes armpit rash can also be accompanied by symptoms such as armpit swelling, runny nose, sweating, sore throat, headache, chills and fever, bone or joint pain and stiffness.
Eczema is a multifactorial chronic skin pathology that occurs with characteristic erythematous-vesicular rashes and serous inflammation of the papillary layer of the connective tissue part of the skin, itching and focal intercellular edema in the spinous layer of the dermis.
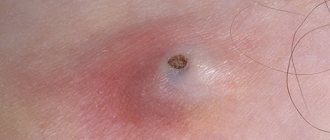
Acute form of eczema
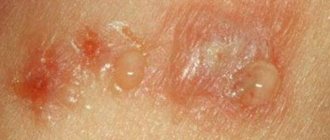
Photo of weeping eczema: what it looks like
In the initial stages of development, weeping eczema can look like a normal rash, so it is very easy to miss this stage, when it is most easily treated.
All stages flow from one another on one blister, which indicates the development of weeping eczema.
Content may be difficult to view
The basis for effective treatment of eczema is the elimination of the factors that caused it. Medicines for each stage are selected directly by the attending physician.
The general treatment regimen is as follows:
- Hyposensitizing therapy - it is aimed at restoring the basic functions of the body and maintaining it normal until the end of treatment for eczema. This stage includes intramuscular injection of one or more solutions: calcium chloride, sodium thiosulfate, magnesium sulfate or calcium gluconate.
- Antihistamine therapy is the second step on the road to recovery. Taking drugs in this group is aimed at reducing the activity of stimuli and stabilizing the patient’s general well-being. The doctor may prescribe to the patient: diazolin, tavegil, pipolfen, clarotadine, diphenhydramine, suprastin, sedatives, and sometimes corticosteroid medications.
- Immunocorrection - this stage involves restoring the proper functioning of the human body’s immune system. To do this, the doctor prescribes a combination of diuretics, vitamins and immunocorrectors: tactivin, thymalin, pentoxyl or decaris.
- External (local) treatment - this part of the treatment often includes a combination of classical and traditional medicine methods (in consultation with the doctor). The most common remedies are: salicylic, boric, ketoconozol ointments, boric acid, silver nitrate, resorcinol and potassium permanganate baths.
- All stages of treatment are accompanied by the exclusion of irritants that can lead to relapses of the disease: washing powders, detergents, etc. using a hypoallergenic diet.
Some stages of treatment deserve special attention, so it is worth talking about them in more detail.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy in the treatment of weeping eczema has a number of tasks that are achieved by different methods, such as:
- sedative methods are used to reduce central nervous system excitation;
- magnetic therapy and transcerebral UHF therapy are used for immunocorrection and solving problems of the endocrine system;
- laser therapy plays the role of anti-inflammatory treatment;
- electrophoresis and darsonvalization relieve itching and eliminate skin irritation.
The purpose of ointments, like all local therapy, is to soften the skin and restore its functions. At this stage, it is important to choose the right external products and take into account the tolerance of the patient’s inflamed skin to oily bases. If it is absent, the doctor will recommend diluting the medicinal ointments with nutritious pastes or oil, otherwise he will prescribe drugs based on glycerin, gelatin, starch, agar or casein.
Local therapy is introduced gradually:
- The first to be used are cooling anti-symptomatic compounds: based on tannin or resorcinol.
- After the inflammation is relieved, therapeutic agents are added: corticosteroids (Advantan, Elokom), antifungals, antimicrobials.
- External remedies against skin diseases of the Soviet school:
- Iricar,
- Ichthyol,
- Sulfuric.
Pills
In addition to medications aimed at treating accompanying ailments, medications will also be prescribed for eczema itself.
These include the following groups of drugs:
- Antihistamines are used to combat irritation and itching on the patient’s skin. This group includes: Loratadine, Zodak, Cetriliv, Suprastin and others. Anti-allergenic drugs should not be used before activities that require the patient to concentrate (driving a car, working day); they strongly induce sleep and can cause the patient to fall asleep involuntarily.
- Antimycotics - used when fungal and mycotic infections contribute to the development of eczema. The group includes: Fucis, Flucostat, Fluconazole and others.
- Antibiotics - these drugs are used for microbial damage to the patient’s tissues: Doxycycline, Loprax, Amoxil and others. Antibiotic therapy is always supplemented with medications that restore beneficial microflora: Acidolac, Hilak Forte and the like.
- Hormonal drugs are included in the treatment regimen during an exacerbation or if treatment is started when the disease has become chronic. These tablets are also available in the form factor of ointments, and the form of administration is chosen by the doctor. Hormonal drugs include: Carizon, Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, etc.
- Immunomodulators - used in parallel with vitamins to improve the general condition of the patient’s body. The most common are: Decamevit, Neurovit, Aevit, Supradin.
Eczema is an allergic type disease, so its treatment is accompanied by an appropriate diet. It is necessary to completely exclude food products that contributed to its occurrence, and if it is impossible to diagnose a specific group, exclude all possible irritants.
These include:
- honey,
- alcohol,
- cocoa products,
- citrus,
- smoked meats,
- sauces,
- coffee.
Sometimes the patient is prescribed a milk diet, in which the patient’s nutrition is limited to the following list of products:
- porridge;
- dairy products;
- green vegetables;
- fruits (except red and yellow);
- dietary meat.
Classical medicine cannot always solve all the problems that arise with weeping eczema, therefore, in consultation with your doctor, you can use folk remedies.
Proven recipes include:
- Cucumber brine with fir and sea buckthorn oils are mixed in equal parts and used as a lotion applied at night.
- Baths with herbal infusion. Dried chamomile, knotweed, yarrow, plantain, elderberry and Christmas tree needles are taken in the amount of 1 tbsp. each and cook in a 5 liter saucepan for 20 minutes, after which the strained mixture is added to the bath. Sometimes essential oils are added to such procedures, in particular: lavender, geranium, tea tree and others, which are selected taking into account the patient’s preferences.
- Lime mixture. To make the ointment, you need to boil a mixture of slaked lime and water in proportions 1:1 for 5 minutes, then cool and strain through cheesecloth. The resulting slurry is mixed with sunflower oil and rubbed on the affected areas three times a day.
- Birch buds. A glass of dried birch buds must be boiled in a liter of water for 20 minutes, then cooled and filtered with gauze. The infusion is used to lubricate sore spots three times a day.
- Powders and compresses. The simplest folk remedies are seashell flour or grated potatoes wrapped in gauze. Similar remedies are used before bedtime.
The main thing to remember is that you cannot be treated only with folk remedies, and their use in combination with classical medications should be supervised by a doctor.
Recommendations
For therapy to result in recovery, it is necessary:
- review your diet and follow the recommendations of a nutritionist;
- Eliminate stress from your life as much as possible;
- review your daily routine and balance your sleep schedule;
- get rid of all bad habits, without any exception.
Prevention of eczema on the face
The best prevention is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. High-quality nutrition should include a complex of substances necessary for the body. The main part of the diet should be vegetables, fruits and cereals. Lean meat, fish and dairy products are also important. Sweet, fried, smoked and various marinades have a bad effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Improper digestion and dysfunction of organs lead to allergic reactions.
Try to avoid stressful situations. Moisturize your skin with natural-based, hypoallergenic creams.
Physical activity and hygiene procedures are also necessary. It is important not to get carried away with detergents. They tend to be bad for the skin. If any manifestations occur, consult a doctor immediately. After all, it is better to prevent the disease than to allow complex forms that are difficult to treat.
Treatment of microbial eczema
Important! Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. When developing a treatment regimen, the presence and condition of injuries and cuts, as well as the degree of varicose veins, are important.
Local therapy with ointments
To disinfect the outbreak, make cold lotions: apply a gauze swab soaked in a cool 2% solution of boric acid to the affected skin. A thin layer of zinc paste dries up weeping eczema. Treatment of inflammatory changes is carried out using ointments:
- Triderm – 2 times a day for two weeks;
- Pimafukort – 2 to 4 times a day for two weeks;
- Lorinden A – 2 times a day for two weeks.
They can be combined with antibacterial ointments, which are also applied in a thin layer to the eczema lesion 2-3 times a day (Clindamycin gel, Tetracycline ointment, Erythromycin ointment). Zelenka, fucorcin and methylene blue will accelerate the drying of erosions and the formation of crusts, followed by healing.
Among the methods of physiotherapy in the treatment of microbial eczema, the following are used topically:
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- electrophoresis of drugs;
- laser therapy.
For eczema, it is useful to take warm baths with pine extracts for 15-20 minutes before bed. They will calm the nervous system and speed up the healing of the lesion.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics for microbial eczema are indicated if a bacterial infection is observed.
Signs of a bacterial infection:
- the appearance of a pustular rash;
- change in color of rashes and exudate;
- formation of erosive plaque;
- the appearance of a specific odor;
- fever and other signs of intoxication.
Also, with extensive skin lesions, papules and vesicles become gateways for any pathogenic microflora, and a weakened body is simply unable to fight active microorganisms. Antibacterial therapy must be preceded by a diagnosis of the pathogen, otherwise there is a risk of prescribing the wrong drug.
For microbial dermatosis, the following antibiotics are most often prescribed:
- Erythromycin,
- Oxacillin,
- Doxycycline,
- Ampicillin, etc.
Diagnostics
The examination includes:
- survey;
- inspection;
- laboratory methods (general blood test, search for specific antibodies of the IgE class);
- skin tests (applying a substance that is considered a potential allergen to the forearm or back and observing the reaction to it).
It may be necessary to culture discharge from foci of chronic infection onto nutrient media to identify the pathogen. It is also necessary to determine the pathologies of the nervous, endocrine and digestive systems, concomitant forms of allergies. It is important to find out sensitivity to medications, food, and professional provocateurs.