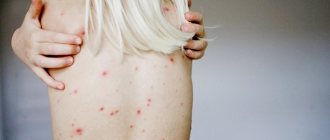
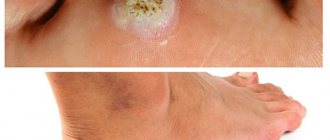
The fact that you should consult a doctor about a suspicious “mole” is indicated by 5 features of its appearance:
- it is asymmetrical
- it has jagged edges
- its diameter is more than 6 mm
- it is painted in several colors
- she's growing
In English, this combination is easier to remember: ABCDE - asymmetry, border, color, diameter, evolution - asymmetry, border, color, diameter, height. If you find yourself with such a formation, first find a good dermatologist or oncologist. Under no circumstances should you go to beauty salons, where they will most likely simply remove your “mole” and will not even suspect cancer.
A dermatologist or oncologist will find out how the formation has changed over time, whether there have been sunburns, whether anyone in the family has had skin cancer, etc. The doctor will also conduct an examination using a dermatoscope (a type of microscope). Thanks to this, the doctor can suspect cancer or make sure that there are no pathological changes.
Melanoma is a malignant tumor of the skin (less commonly, mucous membranes), which develops from cells that synthesize the pigment melanin. Sometimes it is also called "skin cancer", although this is not entirely correct. Melanoma often develops from black or dark brown moles (nevi) and age spots under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Up to 5% of all melanomas are formed from pigment cells of the retina and other elements of the eye. People with fair skin who burn easily in the sun have a much higher risk of developing melanoma than people who are naturally dark-skinned.
What are moles?
The scientific name for moles is nevus, or birthmark. It is difficult to find a person whose body is without a single pigment formation. From a medical point of view, moles are the localization of melanocyte cells consisting of melanin (a special pigment). In life processes, the protective function of melanin is noticeable, protecting a person from the effects of ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Thanks to the pigment, the skin acquires a tan.
Moles are often found on the body of a person who is predisposed to their appearance by genetic factors, as well as in people with the corresponding skin phototype.
Phototype is the skin's ability to perceive exposure to sunlight. There are six of them in total. They vary from the palest to the darkest. Understanding the skin phototype helps a person to better care for the skin and prevent unwanted pigment formations. The first and second phototypes are found among representatives of northern peoples, where exposure to the sun is not obvious. These are people with pale skin color. Basically, they easily get sunburned, the skin reacts with pain, peeling, and peeling. When exposed to the sun, people with this skin type are advised to use protective cream, wear closed clothing, and use hats, protecting their skin from the sun's rays.
There are three reasons for the appearance of moles:
- The main reason is the effect of sunlight on human skin if it is not ready for exposure.
- Hormonal changes in the body during growing up, in women during pregnancy or menopause.
- Constant trauma to the skin by mechanical action: cuts, bruises and even insect bites.
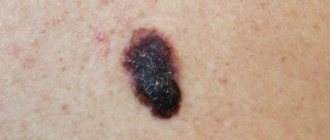
There are two types: malignant and benign moles. Benign ones do not pose a danger to human health and life. They have clear boundaries and no constant growth. Malignant moles are manifestations of skin cancer (tumors) – melanoma. This type of tumor disease is characterized by aggressiveness towards the patient and rapid spread.
Symptoms of a white mole
What is a white mole?
This is a benign formation that has:
- convex shape,
- soft base,
- color lighter than skin color,
- smooth edges,
- clear boundaries.
During its formation there are no signs of inflammation. At the same time, single elements or multiple formations may be present on the body. They quickly grow and increase in size, causing the head of the mole to overhang the skin over time. If you arm yourself with a magnifying glass and examine a white mole, you can easily notice a mesh pattern or brown dots inside it.
Types of malignant moles
There are two types of malignant moles:
- Melanoma is common. High degree of aggressiveness towards the patient. Nevus with jagged edges. The color scheme of the formation is expressed in the presence of shades of red and purple. The edges are blurred. Rapid spread of metastases.
- Carcinoma is a less aggressive growth of a neoplasm without the appearance of metastases, but deep damage to the skin.
Could the appendage be a cancerous tumor?
A malignant tumor that appears due to the activity of melanocytes can be recognized by its appearance:
- superficial location in the form of a process on the skin or mole;
- knotty - the most dangerous and aggressive. It looks like a nodule and can appear on a pigmented area of the skin;
- subungual melanoma - affects the lower extremities, in the area of the nail plate of the big toes, soles.
Any growth on the surface of a mole may turn out to be a cancerous tumor that requires immediate treatment.
Difference between malignant type of moles
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish malignant moles using the ACCORD distinction system. There are signs of malignancy:
- A – asymmetry of the mole. Refers to a gradual change in shape. Externally, upon visual inspection, the left half should be equal to the right, and the top should be equal to the bottom.
- K – contour, or edge. The edge of the nevus should be clear and even, without the feeling of a broken contour. If the edges are uneven, this is a sign of pathology.
- K – bleeding. A sign characterized by the fact that the mole should not emit discharge: bloody, mucous or purulent.
- O – coloring. The color of a benign skin lesion appears uniform. With a malignant nevus, inclusions of dots of a different color are likely - blue, yellow and others.
- R – size. Often large moles force a person to see a doctor. This indicator does not always characterize malignancy, but, according to statistics, large moles have the most negative potential for degeneration into melanoma.
- D – dynamics. It is important to monitor the growth rate of the nevus. Whether or not the tumor grows spasmodically is an important marker of the nature of the formation.
If you have at least one of the signs of malignancy, you should go to a dermatologist for an examination in order to distinguish a simple mole from a malignant one in time. Any form of cancer is a life-threatening risk. Timely provision of medical care will allow timely recognition and minimization of the risk of death as a result of the disease.
External signs of dangerous moles
What do nevi that are subject to pathological changes look like? Only a qualified doctor can accurately distinguish a safe neoplasm from a dangerous one. Other warning signs to watch out for:
- a blue lump under the skin, which has clear boundaries, no more than 10 mm in size;
- nodular dangerous moles, round, flat in shape, black or brown in color;
- skin dangerous neoplasms are convex, often pale;
- halo nevus, which is a pigment that is surrounded by a white ring;
- connecting dangerous moles that link individual formations into a whole;
- The Spitz, which looks like a pink, dome-shaped tumor, may have a hole through which fluid or blood comes out.
Other symptoms
In addition to the above-mentioned features of malignancy, oncology identifies a number of additional features. These include:
- redness, inflammation, burning, itching in the area where the nevus is located;
- peeling of the skin next to the mole;
- the structure is characterized by looseness;
- pimples and spots with blurred edges of pigmentation form next to the mole;
- Damage to moles causes prolonged bleeding.
It is impossible not to take into account additional symptoms that allow you to quickly understand the stage of malignancy of the tumor and determine the treatment procedure.
Particular attention is paid to the presence of tumors on the body in children. If a single symptom is detected, you should immediately contact a dermatologist for an examination.
The time interval between the initial stage of cancer and the appearance of metastases is short and takes a couple of months. Treatment to the degree of remission is complex; it is important to learn to recognize the pathology at the beginning.
Distinctive features of cancerous moles
Malignant moles are mutated cells of the birthmark - melanocytes. The degeneration of healthy melanocytes occurs simultaneously with rapid growth and invasion into neighboring tissues. The neoplasm spreads over the surface of the skin, goes deep into the epidermis, gradually penetrating into the deeper layers of the dermis.
The depth of penetration into adjacent tissue determines the stage of carcinoma. The higher, the more difficult the treatment, the worse the prognosis for the patient.
Characteristic signs of mole cancer:
- increasing the rate of growth of education;
- ulcers on the surface of the nevus;
- peeling;
- the neoplasm is dense, elastic;
- the integument is smooth, may resemble cauliflower;
- dark color of nevus;
- shiny surface;
- areas of necrosis may appear;
- the surrounding skin looks inflamed;
- bluish nodules may be visualized nearby - signs of active metastasis;
- asymmetry of the mole;
- the edges of the nevus are blurred;
- sometimes melanocytes begin to accumulate in one edge of the mole, so the nevus may be unevenly colored - black on one side, shades of brown on the opposite side.
Melanoma is dangerous due to rapid metastasis. The movement of malignant cells occurs by hematogenous, lymphogenous route. Any suspicious mole should be shown to an oncologist.
Classification of melanomas
The most common and dangerous type of melanoma is superficial. Accounts for 65% of the total number of diseases. The mole is located on the surface of the skin and tends to develop into the epidermis. This species is characterized by a deep black color.
In the acral form of the disease, the tissues of the palms, feet, and fingers and toes are affected. The described type of melanoma is rare. It is expressed in the appearance under the nails of an oblong dark spot that changes shape.
Nail melanoma
Nodular melanoma exhibits a reddish or pink tint. The main difference is the elevation above the skin level. Occurs in 15% of cases of skin pathologies.
The last type of melanoma is lentigo. Characteristic of the older age group of people. They grow from a nevus on the neck, arms or head. Despite its malignancy, it exhibits low aggressiveness and slow growth. Long process of metastasis.
Staging and choice of treatment tactics
To decide on treatment tactics, you need to determine the stage of melanoma. This takes into account the thickness of the tumor, whether there were ulcers on it, the rate of mitosis (the number of dividing cells), whether there are cancer cells in nearby lymph nodes, whether there are distant metastases (cancer cells not only in nearby lymph nodes). To determine this, you need to take into account the results of the examination and histological examination carried out at the first stage, take an x-ray and some blood tests. A CT scan may also be required.
If an enlarged lymph node is detected, it is removed and examined for the presence of tumor cells. In other cases, a biopsy (essentially, removal) of the sentinel lymph node (the first one in the path of lymph flow) is usually performed under local anesthesia. When the tumor thickness is less than 1 mm, there is no ulceration and the mitotic rate is low, this is not necessary. To understand which node is the sentinel node, a dye and a radioactive drug are used. They are injected into the tumor area and using a special sensor, and during the operation they look at where these substances are carried away by the lymph and where they accumulate. This procedure is called lymphoscintigraphy.
If cancer cells (micrometastases that are not visible on ultrasound or tomography) are detected in the sentinel lymph node, other lymph nodes located close to the tumor are removed. Unfortunately, this can cause pain, which sometimes takes a long time to go away. If lymph nodes are removed on the inside of the arm, shoulder stiffness may occur. If in the groin or armpit, there is a risk of developing swelling of the leg or arm (lymphedema). To control this condition, you need to perform certain exercises, massage and wear a sleeve or stocking made of compression stockings.
| Read more about dermatological research at the European Clinic | |
| Consultation with a dermatologist-oncologist | from 5100 rub. |
| Skin examination using the German FotoFinder device | 12100 rub. |
| Diagnosis of melanoma | from 5100 rub. |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Reasons for moles developing into cancer
The main factor influencing the disease is exposure to ultraviolet rays. The geographic dependence of the appearance of melanomas is associated with it. The further south a person lives, the higher the level of sun exposure, which means the risk of developing the disease increases. In this regard, doctors do not recommend prolonged exposure to the open sun.
If the sun causes a burn, this increases the risk of skin tumors degenerating into a malignant mole on the damaged area of the skin. The danger increases with each burn.
The risk group consists of people with burdened genetics. If relatives suffered from melanoma, then representatives of this kind are more likely to get sick. Injuries, thermal and chemical burns, and mechanical damage to moles cause the formation of cancer. Risk factors also include increased and uneven background radiation in the environment in the area where people live.
Possible complications
The most dangerous is the degeneration of a white mole into melanoma. This happens extremely rarely, but the risk of malignancy is still present. At risk are people who have a white nevus on their body after sixty years of age, in whom it is constantly growing and transforming into a large neoplasm, and in whom there are a large number of white moles on their body.
Risks also arise when a mole is constantly injured. You need to be wary of those growths whose edges are blurred and whose shape changes. The first sign of malignancy is the appearance of asymmetry in any plane (one edge is lower than the other, wider, more voluminous).
The appearance of a dot inside a white mole, the color of which is lighter than the color of the nevus, is considered dangerous. You should not delay visiting a doctor when the white growths begin to bleed and become uneven in color.
Diagnostics
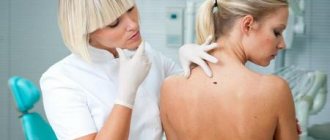
If signs of the disease are detected, you should contact a dermatologist for advice and a diagnostic test.
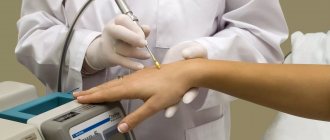
When performing a diagnosis, a dermatologist or derma-oncologist (a specialist in skin tumors) conducts research into possible melanomas and carcinomas. The initial method for diagnosing skin cancer is dermatoscopy. It consists of examining melanoma with a special optical device similar to a microscope. Allows you to determine cancer pathology by applying a special gel to the mole, which makes the stratum corneum of the skin transparent.
If signs of a malignant formation are detected during dermatoscopy, a biopsy is prescribed to identify the type of tumor. There are four biopsy methods. The specific method is prescribed by the attending physician. The method depends on the type of nevus and the risk of it developing into melanoma or carcinoma during the procedure: taking material for research involves physical damage.
Clinical signs
No other malignant neoplasm can compare with melanoma in the diversity of its course, clinical manifestations, and histological structure. It can develop primarily on unchanged skin or against the background of limited Dubreuil premelanosis, from congenital or acquired birthmarks. In all cases, the source of this tumor is melanocytes.
The clinical signs of a malignant mole are very diverse. This is manifested in size, shape, outline, surface character, consistency, color, and dynamics of change. Common to all forms is a set of characteristics, which is expressed by the initial letters by the abbreviation “AKORD”, developed by dermatologists and cosmetologists:
- Asymmetry (A) - lack of symmetry in the shape and contours of a spot, with the exception of birthmarks present on the child’s body at birth.
- Edges (K) are most often uneven and indistinct (blurry).
- Coloring (O) - uneven; The presence of dots and stripes of various tones of dark brown and black is noted.
- Size (P) - in diameter from 7 mm or more.
- Dynamics (D) of development - an increase in the previous birthmark or a rapid increase in the size of a new pigmented formation.
Signs 1, 2, 3, 5 are the main ones. Secondary clinical symptoms are in point 4, as well as:
- surface moisture, bleeding, ulceration, crusts; these phenomena can appear independently or as a result of light contact with clothing;
- softening of the tumor;
- presence of nodules;
- the presence of pink or pigmented dots or formations around the birthmark (satellites);
- redness and soreness of the surrounding skin surface as a result of the inflammatory reaction;
- signs of vertical growth.
Treatment
Methods of treating malignant skin tumors:
- Surgical intervention. Surgery is justified when removing large formations and when surrounding tissues are affected by metastases.
- Application of laser. This type of treatment allows you to burn out tumors to a residue with minimal blood loss to the patient, since the effect of the laser causes the blood vessels surrounding the wound to be sealed. The consequences of the procedure are minimal.
- Using electricity is the least used method. It is used as a last resort when there are appropriate indications in the patient’s medical history. This is due to the increased risk of injury of the procedure. The essence is burning with low-frequency current.
- Cryodestruction (destruction by low temperature). When prescribed, lidocaine is injected into the tumor for pain relief, then carbonic acid and liquid nitrogen. Thanks to its thermal properties, it destroys and stops the proliferation of cancer cells (cancerous epithelium).
- Radio waves. Prescribed for the lowest level of education. The procedure has no consequences and prolonged bleeding.
Treatment is prescribed when the mole turns out to be malignant, the nevus is large, and there is a high risk of mechanical damage.
Removal of a nevus with an increased ability to degenerate into cancer is also prescribed. Unaesthetic moles that spoil a person’s appearance (for example, a nevus on the face).
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate! Such games with life-threatening diseases are expensive.
How moles are checked: Yulia goes to see a dermatologist
Actually, I was going to publish this post last week so that everyone on May 25, Melanoma Diagnosis Day, could sign up for a free consultation with a dermatologist. This campaign is carried out in more than 30 countries, and we have been supported by the La Roche-Posay brand for several years.
But then I ended up in the hospital and all my plans went to waste - and therefore I’m telling you how such a consultation went for me after the fact.
For those who have long wanted to check their moles, but are afraid of everything in the world (and especially that they will tell him something wrong about his health), such a post can relieve possible fears. And maybe you, like me, finally go to the doctor -)) For reference: I have dozens of moles on my body. I have long wanted to find out how they are doing. Especially about a few specific ones. But while I usually don’t wait long for any ailment and go to the doctor, with moles I have a different story. Once I had an incomprehensible tumor itching and bleeding for six months, but I pushed the thought of going to check what it was as deeply as possible. It seems to me that we all have some kind of deep, semi-conscious fear about moles, which, frankly, does not help matters.
I went to the Yutskovskaya clinic for an appointment with Galina Aleksandrovna Naumchik, Ph.D., dermatovenerologist.
She surprised me by not only asking me to undress (the whole body needs to be examined for moles and tumors), but also to put on a hat.
It turned out that this is important so that the neck and face can be examined without problems. “What a strict approach,” I thought.
“Have you ever been examined by an oncologist or dermatologist to examine tumors?” I proudly tell you that after six months of suffering, I went to the dermatologist with my itchy neoplasm, which turned out to be a harmless keratoma and was immediately removed. But they never examined my whole body.
“Are you sunbathing?” Only on vacation and without fanaticism. “Did you have sunburns as a child? Before the bubbles? So I never burned out, but somehow I lay with a fever and a red back in the country.
The first questions are raised by my age spots on my face. And then the doctor draws attention to many red spots in the décolleté area. I knew for a long time that I had them, but I didn’t think about where from.
“But this mole periodically itches and seems to darken,” I share my suffering (pictured below).
“And another one is forming next to it,” notes Galina Aleksandrovna. “It has blood vessels and has a tendency to grow, so it needs to be removed, and with a histological examination - this is when the mole is completely excised and sent for study; all the cells need to be looked at under a microscope to determine that it is benign. Outwardly, she is like that, but we need to make sure.”
“Why are the moles nearby bright red?” — I’ve been asking a question that’s been troubling for a long time.
“Because these are not moles at all, they are dilated vessels - they are called hemangiomas. It is often believed that they appear due to dysfunction of the liver, but here you either had a skin injury or the blood vessels are generally fragile. Also, does this often happen due to biliary dyskinesia? (I have it - Author's note) However, you still need to take a blood clotting test from a therapist. In general, are bruises normal for you? Yes? This also confirms the pronounced fragility of blood vessels. You need drugs that improve the trophism of tissues and blood vessels.”
“Wow,” I think. For a thousand years I’ve been wanting to ask some doctor what to do to make the bruises heal faster, but here it is.
“Plus, I see a small vascular network on your décolleté area - this also confirms the fragility of the blood vessels. And obviously you sunbathe in this place more often - the mesh is localized here, and there is hyperpigmentation of the skin, a sign that there is photodamage here.”
I remember those sad two times when my chest burned badly on vacation - after which I began to smear it not just with sunscreen, but also with a stick on top.
“I hope you don’t go to the solarium? God bless. And never go. You are not allowed. In principle, it’s impossible,” continues Galina Aleksandrovna. Well, at least I'm doing something right -).
Let's move on to other parts of the body. I’m showing you a mole on my side that has been worrying me for a long time. At some point, it began to clearly stick out, then it came off halfway, covered it, and settled back in. Until that moment, I never knew that moles could do this -)
“Was there heavy bleeding? Oh, how beautiful, just cherry! This is not a mole, it is also a hemangioma, the same as the one on your chest, only ten times larger. This area is most often injured by jeans with a tight belt, or something else.”
Hemangioma
We are studying my beautiful hemangioma with a dermatoscope -))
“It’s also better to remove it, the main thing is don’t do it yourself! There is a very active feeding vessel here.”
I'm amazed, does anyone really do this on their own??
“Unfortunately, people often try to remove something themselves with “Clandestine” and “Supercleaner” - mothers for children or wives for husbands, and then a huge therapeutic correction is needed. At best, nothing happens; at worst, severe scarring remains.”
Let's move on to the back. There I have two problematic moles at once (although I am already beginning to understand that they, apparently, are not moles -)).
“This is a papilloma hanging on a stalk. Please note that it is brown, not red like hemangiomas. This is a benign skin tumor. It’s also better to remove it.”
We look with the photographer through the dermatoscope and at her:
Papilloma
“And here the keratoma is stunningly beautiful,” the doctor finds my last problematic “mole.” “Keratoma and a large number of sebaceous gland cysts on it.”
Keratoma with sebaceous cysts
“It’s all benign, but if left, it will grow, thicken, and its surface will become woody to the touch. Moreover, it is in your area of injury, near the bra strap - it is better to remove it.”
Keratoma
We carefully examine my legs. “You can’t sit cross-legged, do you know that?” - says the doctor. I remember coach Dima Stepin -) “This can also injure the delicate walls of your blood vessels, plus, when we sit like this, we squeeze our own popliteal vessels, this stimulates the formation of cellulite and venous insufficiency.” Again I remember coach Dima Stepin and say thank you to him in my head -)
This completes the inspection. As a result, it turns out that out of the entire set of spots on the skin of my body, I only have one really problematic mole, and the rest are not moles at all -).
“You have a tendency to form a large number of tumors,” the doctor sums up. - This is neither bad nor good, this is your feature, you know about it and therefore are armed. The main task is not to actively sunbathe, ALWAYS use sunscreen and not injure the formation. And once a year, come for an examination to an oncologist or dermatologist and remove those that require it.
— Which formations are most often recommended to be removed?
- Those that protrude above the skin. Those that may be injured. Those that are located in areas where they are actively exposed to solar radiation.
— If I play sports outside in Moscow in the summer, do I also need to apply products with SPF to my body? Although we are not in the tropics.
- Of course, we are not in the tropics, but we do have sun. It provokes both tanning and undesirable moments associated with the appearance of tumors. And these rays penetrate through the clouds on a cloudy day. So yes, you need it.
You also need to use some kind of body milk, light, melting, which is well absorbed - the skin of the body is dry. And for the same purposes, take a course of vitamin E and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids - this is what maintains the balance of the skin, its hydrolipid mantle from the inside. The skin is more protected, resulting in younger and healthier skin.
— What are the ways to remove formations?
— Surgical excision is when you need material for histology. If we talk about a less traumatic and invasive methodology, then there is radio wave destruction and electrocoagulation. Radio removal - uses a radio wave, it treats the skin quite correctly, removes gently and well, plus radio waves are used to treat conditions such as basal cell carcinoma, which is considered one of the cancers. Electrocoagulation and radio wave destruction also make it possible to send the material for histology. Some formations are also removed by cryodestruction - that is, using liquid nitrogen. But this is only in those areas where the skin is denser and thicker, for example, for plantar warts - nitrogen cannot be used on thin skin of the face, side surfaces of the body, décolleté, inner surfaces of the forearms and shoulders. On the back is conditionally possible. But with cryodestruction you can’t send anything for histology, so the method is chosen according to the tasks.
— Can a mole be removed immediately on the day of treatment?
— If there is no damage to the skin and inflammation around the formation, then yes.
— If a mole itches, what does it mean?
- This indicates that the skin is uncomfortable. There is no need to scratch it, it is better to go to the doctor right away!
— How often is such an examination of moles needed?
- For an ordinary person - once a year, if there are no aggravating factors, such as working in a hazardous industry, for example. Or if there were already educations - then once every six months.
- Who should you go to for such an examination?
— It is accepted that an oncologist makes a diagnosis, and a dermatologist or surgeon removes it. There are dermatologists-oncologists who do everything at once. But we must understand that when it comes to formations on the skin, this is a situation related to the oncologist.
I leave the doctor with a prescription for Detralex for the health of veins and blood vessels, advice to take a course of Omacor for three months (these are omega-3 acids) and simple vitamin E capsules for a month or two - and an instruction to see a therapist for blood clotting. Well, thoughts on who to go to to remove four of your moles, of which there is actually only one mole -).
When was the last time you checked your moles?
The day of melanoma diagnosis, when you could get examined for free, has already passed. But a list of clinics where you can go now is available on the website https://melanomaday.ru/.
Another useful service from La Roche-Posay is the interactive online educational platform Skin Checker. Here you can check your moles yourself + make a map of your own moles on your body.
Prevention
Tips for preventing skin cancer include:
- When the sun is highly active, its influence should be minimized by using appropriate cosmetics, sunscreens and closed clothing. Try not to go out into direct sunlight, be in the shade or closed area. Wear a hat.
- Try to avoid injuries, thermal or chemical burns. Avoid contact with skin of harmful chemicals and technical liquids (for example, exposure to gasoline, technical oil, chemical fertilizers and carcinogens).
- Eat foods enriched with vitamins E and D.
- Do not pick, cut or in any way mechanically damage emerging moles, regardless of type and shape (hanging, flat, convex, loose).
- If signs of malignancy appear, get diagnosed by a doctor.
By applying these tips, the risk of cancer is significantly reduced.
Who to contact and prognosis
What to do if a mole changes? Which doctor should I contact? First of all, it is worth visiting a dermatologist. In most cases, if there are suspicious signs, he will refer you to an oncologist. The specialist will prescribe the necessary tests and studies.
Forecast
What is the prognosis after removal of a malignant mole? With large metastases, a relapse may occur and the formation will appear again. A small mole after removal will not cause much trouble. After the operation, you should be constantly examined by a specialist. After removal, you should not go to the solarium, abuse the sun's rays, drink alcoholic beverages, or use cosmetics.
Forecast
After a mole has been removed, there are factors that make it possible to predict a cure:
- Stage. There are four stages of cancer. With the first, survival rate is more than 90%, with the fourth, less than 5%. Due to the danger of rapid development of skin cancer, timely treatment is the key to a favorable prognosis. Starting from the second stage, the prognosis is considered unfavorable.
- Degree of qualification of medical care, modern methods of treatment. The level of medical care differs in diagnostic centers of cities in relation to rural clinics. It is important to conduct a diagnosis and obtain treatment instructions from an experienced doctor using high-precision diagnostic equipment.
- Compliance with doctor's instructions before and after medical procedures.
- Changing the patient’s living conditions in order to eliminate the causes of cancer.
- The prognosis is influenced by the level of damage thickness. If it exceeds 10 millimeters, then the impact on surrounding tissues and lymph nodes begins, which significantly reduces the level of a favorable prognosis for the patient.
These factors together will determine the prognosis of survival.