- Types of skin cancer
- Who should be on guard?
- Skin cancer: first signs and symptoms
- Diagnostic methods
- Skin cancer treatment
Skin cancer is one of the most common cancer diseases.
Light-skinned people who have passed the age of 50 and live in southern latitudes are especially susceptible to it. The disease is manifested by changes in normal cells of the epidermis (upper part of the skin), hyperactive growth and reproduction of the resulting atypical cells, which causes serious pathological changes throughout the body. Timely diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer abroad significantly increases the chance of a full recovery or a significant extension of life.
Skin cancer classification
Skin cancer is classified into the following types: melanoma (a type of skin cancer that occurs due to the presence of pigment cells (melanocytes); today, many scientists tend not to classify melanoma as an oncological disease); squamous cell skin cancer (usually develops from flat cells belonging to the surface layer of the epidermis); basal cell skin cancer (formed in the case of atypical degeneration of basal type epidermal cells; such cells have a round shape, located under a layer of flat cells); adenocarcinoma (the rarest type of malignant tumor that develops from the sweat and sebaceous glands).
In order to assess the prevalence of cancer, as well as determine its stage, the international classification is used:
- T - indicates the prevalence of the tumor at the primary stage (it includes the following varieties: TO - when it is impossible to detect a tumor; TX - it is impossible to assess the condition of the found tumor; TI - tumor size is no more than 2 cm; T2 - tumor size - no more than 5 cm; TZ - tumor size more than 5 cm; T4 - stage of skin cancer, when the tumor reaches the underlying deep tissues, including muscles, bones and cartilage);
- N - a symbol indicating the condition of the lymph nodes (includes the following varieties: NX - inability to assess the shape of the lymph nodes due to lack of necessary data; N0 - an indicator that indicates that symptoms of metastases in the regional lymph nodes have not been identified; N1 - there are metastatic lesions of the regional lymph nodes ;
- M - symbol indicating the presence of metastasis (includes: MX - missing data regarding the presence of distant metastases; MO - symptom of distant metastases not detected; M1 - presence of distant metastases of skin cancer).
To assess the degree of differentiation of malignant cells, the following classification of skin cancer is carried out: G1 - indicates high differentiation of tumor cells; G2 - indicates an average degree of differentiation of malignant cells; G3 - low degree of tumor presence; G4 - skin cancer that cannot be differentiated; GX is a skin cancer that does not allow its degree of differentiation to be determined.
Early signs of skin cancer
Common first signs and symptoms of skin cancer:
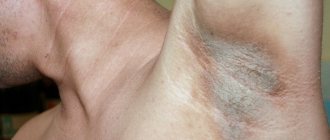
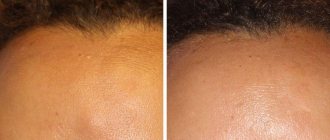
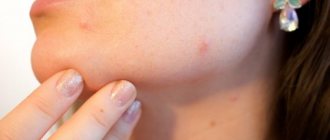
- A new mole, mark, or growth that looks different from other spots on your skin
- A mole that changes color, for example from brown to black.
- A mole with a vague border, asymmetry, or change in size
- A larger area of your skin darkens or changes color
- A wound or injury that does not heal within several months.
In Western medical practice, there are six signs that indicate that you may have a skin cancer.
“Ugly duckling sign”—new nodules, moles, spots, or other lesions
The most significant sign is any new permanent growth - a mole, nodule, or any growth on the skin that looks different from other spots on the skin. If a mole or mark stands out from other lesions, you need to pay closer attention to it.
New moles when you are over 35
Until the age of 35, it is completely normal to develop new moles. After that it becomes less common. In adults, 71% of melanomas show up as new moles or spots on the skin. Be especially aware of new spots if you're over 35, and be sure to check areas you don't often pay attention to, like your back. Photographing these difficult areas is recommended to detect any new lesions at an early stage.
ABCDE signs of Melanoma
If you notice a mole and it is of concern, it is useful to evaluate it using the ABCDE system of suspicious moles.
A - Asymmetry : The two halves of the mole look different.
If you draw a straight line through the middle of the spot, creating two halves and the halves don't match, then the mole is asymmetrical. Keep in mind that a typical mole may not always be completely symmetrical. If asymmetry is noticed, it may not be something serious in itself, but requires additional attention.
B - Border : Borders that are poorly defined or blurred. Ragged or jagged borders of a mole.
C - Color : Does color change from one area to another in the mole?
Melanomas can appear in shades of red, white or blue, but are usually shades of brown or black. And remember that changes in color, even if it's still just one color, such as a darkening mole, can also be a symptom of melanoma.
D - Diameter : Melanomas are typically larger than an eraser (about 6mm) at diagnosis, but may start smaller.
E - Development : If you notice that a mole is beginning to develop or find that the lesion is increasing in size or changing color, see your doctor to have it checked for possible degeneration. Any growing dome-shaped spots also require attention.
Any damage that rapidly changes shape, color or size
Note any damage, not just moles that increase in size or become raised above the skin. A typical sign to watch for is rapid growth.
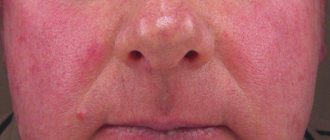
Sudden darkening of the skin area
If a separate area changes color or darkens, this may be the first sign of cancer.
Damage that won't heal
An important symptom of some skin tumors is a wound or lesion that does not heal for several months, including a lesion that itches or bleeds.
Melanoma or other types of skin tumors may look very different from the pictures above or any other pictures found on the Internet!
Causes of skin cancer
Among the causes of malignant tumors on the skin, the main one is considered to be prolonged exposure to open areas with ultraviolet radiation. The latter is proven by the fact that approximately 92% of all cancer cases are primarily affected by open areas of the body - the face and neck. People with fair skin are twice as likely to suffer from exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The formation of skin cancer is provoked by exposure to various chemicals that have a carcinogenic effect (lubricants, tobacco smoke, tar, arsenic). Thermal or radioactive factors that act on the skin also lead to cancer. Skin cancer can develop at the burn site, and also as a special case of complications after radiation dermatitis. Trauma to scars (moles) can cause them to degenerate into malignant formations.
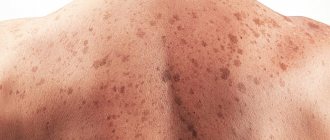
Heredity can be a precursor to cancer. If one of your family members has previously had a case of skin cancer, then the likelihood of it recurring is quite high. You should also remember about the existence of skin diseases that, after a certain period of time, can degenerate into malignant tumors, which are skin cancer. There is a list of diseases that can subsequently lead to a precancerous condition (Bowen’s disease, leukoplaxia, Queyra’s erythroplasia, xeroderma pigmentosum, senile keratoma, Dubreuil’s melanosis, cutaneous horn, various pigmented nevi (pigmented, blue, giant, nevus of Ota), as well as such chronic skin lesions such as tuberculosis, syphilis, trophic type ulcers.
Reasons affecting the production of anti-cancer proteins
The production of protein P15 is reduced or stopped for completely everyday reasons. In many cases, patients are to blame for their problems themselves. Mole cancer is caused by:
- Intense UV exposure - abuse of sunbathing and solarium;
- Traumatization of a mole by clothing, jewelry, accessories, etc.;
- Unsuccessful “information” with celandine, vinegar and other means that cause chemical burns;
- Trying to get a chocolate tan while having fair skin that doesn’t tolerate the sun’s rays well;
- Abuse of products containing carcinogens.
- Smoking and other bad habits that reduce immunity.
Genetic factors for mole cancer cannot be excluded. Sometimes the cancer defense system is weak from birth. Such people have numerous cases of cancer in relatives.
Knowing about bad heredity, you must be careful, excluding negative factors that provoke cancer. Examination of moles and birthmarks for patients at risk is strictly necessary.
Squamous cell skin cancer
The main manifestations of squamous cell skin cancer are rapid growth and rapid spread over the surface and in depth. The process of tumor growth into tissues located under the skin (bone, muscle or cartilage), as well as the emergence of new inflammation, occurs in parallel with the pain syndrome. This type of disease is expressed in the form of plaques, nodes or ulcers.
If we talk about the ulcerative version of squamous cell skin cancer, then it has the appearance of a crater-shaped ulcer, which is surrounded by a special ridge that has dense and raised edges. The ulcer is characterized by a rather uneven bottom, covered with a crust formed from dried serous-bloody fluid. The latter has a rather pungent and unpleasant odor.
As for the plaque of squamous cell skin cancer, it is distinguished by its bright red color, fairly dense consistency and special surface in the form of tubercles. Such a plaque can very often bleed, quickly increasing in size.
In the case of squamous cell skin cancer, the coarsely lumpy surface becomes cauliflower-like. It is characterized by high density, bright red or brown color. The surface may be eroded.
How a person dies: signs
Predicting the exact time of death is almost impossible.
Signs indicating that a person has only a few minutes left until the end of his life:
- Changing lifestyle, daily routine, behavior. These are early signs. Occurs several months before death.
- Impaired perception. Occurs 3-4 weeks before death.
- 3-4 weeks before death, people eat poorly, lose their appetite, and are unable to swallow (several days before death).
- Brain dysfunction. Happens in 10 days.
- A person sleeps more and stays awake less. When death is already close, he remains asleep for days. Such people do not live long. They are given only a few days.
- In most cases, 60-72 hours before death, a person is delirious, his consciousness is confused, he does not reflect reality. Can talk to dead people.
Symptoms that indicate the process of a person’s dying.
- Shortly before death, black vomit is observed. In the last hours of life, the patient may urinate or have bowel movements. If the biological fluid turns black, this indicates bleeding and is often observed in cancer patients.
- The cornea becomes cloudy.
- The lower jaw droops, the mouth is open.
- The pulse is too slow or cannot be felt.
- The pressure becomes minimal.
- The temperature readings are jumping.
- Noisy breathing and wheezing appear.
- At the moment of death, the pectoral muscles contract. Therefore, it may seem to relatives that the person continues to breathe.
- Cramps, convulsions, foam at the mouth.
- The limbs become cold, the legs and arms swell, the skin becomes covered with cadaverous spots.
Death occurs when there is an irreversible disruption of the vital systems of the body, followed by a cessation of the functioning of individual organs and tissues.
Most often, people die due to illness, injuries incompatible with life, drug addicts from an overdose of potent substances, alcoholics from toxic poisoning of the body. People die from old age much less often. Those who die from severe injuries or accidents experience quick death and do not experience the painful symptoms that sick people experience.
After a person passes away, an autopsy is required. This solves the question of how to find out the cause of death.
After the agony, clinical death occurs. The period for which the body lives after its onset is 4-6 minutes (until the cells of the cerebral cortex die), during which time it is possible to provide assistance to a person.
The main symptoms of clinical death.
- There are no signs of life.
- Cramps. There is involuntary urination, ejaculation, and defecation due to severe muscle spasm.
- Agonal breathing. 15 seconds after death, the chest is still moving. The so-called agonal breathing continues. The deceased breathes quickly and shallowly, sometimes wheezes, and foams at the mouth.
- No pulse.
- There is no reaction of the pupils to light. It is the main sign of the onset of clinical death.
If resuscitation measures are not started within 4-6 minutes, the person experiences biological death, in which the body is considered dead.
Progressive renal or heart failure provokes the appearance of edema - that is, the accumulation of fluid in the human body. Most often, it accumulates at a considerable distance from the heart - in the feet and hands. As a rule, such a symptom no longer requires any specific measures, since it is not the cause of dying, but only part of this process.
If we talk about natural death from old age, then people in old age often have problems with hearing and vision. Signs of death appear not only in the deterioration of the functioning of the senses, but in a change in the appearance of a person. “Cat's eye” is the name given to a visual change in the eye of a dying person, which is associated with a sharp drop in ocular pressure.
Decreased or complete loss of appetite. Since the dying person spends most of his time sleeping, the need for food decreases. The closer the end of life is, the more likely it is that the swallowing reflex is lost, and then the person receives nutrition through a tube or IV. It is quite difficult to say how long this condition can last in an elderly person.
Violation of thermoregulation. The body spends all its remaining energy to maintain the functioning of vital organs; as a result, the blood circulation decreases, which leads to paresis and paralysis.
General weakness
This symptom is directly related to the lack of nutrition of the body.
Just before death, a person cannot even get up.
The mood of the dying person can change from sentimentality to aggression. But most often a person becomes depressed - he stops reacting to events happening around him and to people. May perform inappropriate actions.
Predagonia
Before death, a person goes through three stages - pre-agony, terminal pause, agony. After which clinical death occurs.
Predagonia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- disorders of the nervous system;
- confusion and retardation of consciousness;
- drop in blood pressure;
- tachycardia, which is replaced by bradycardia;
- deep and frequent breathing, followed by rare and shallow breathing;
- increased heart rate;
- pallor and cyanosis of the skin;
- convulsions.
This is followed by a terminal pause, which is characterized by a slowing of the pulse, cessation of breathing, and temporary cessation of cardiac activity. This state can last from a few seconds to 5 minutes. Then agony sets in.
Basal cell skin cancer
The basal cell type of skin cancer is characterized by a benign and slow progression, in contrast to squamous cell cancer. In particularly advanced cases, it can grow into the tissue, which in turn causes pain. With this type, metastasis is usually absent. This type of cancer is characterized by large polymorphism. It often presents in one of the following forms: warty, scar-atrophic, nodular, nodular-ulcerative, pigmented, sclerodermiform and turban. At the beginning, basalioma develops with the formation of one small nodule. Sometimes there may be several nodules.
Complications of skin cancer
As skin cancer grows deeper, it destroys tissue. Typically, skin cancer is localized on the face, which means its prevalence can also affect the eyes, ears, paranasal sinuses and even the brain, leading to loss of vision, hearing, meningitis, malignant sinusitis, and damage to various parts of the brain. The latter often leads to death.
The spread of metastases occurs towards the lymphatic vessels with the further development of malignant formations of regional lymph nodes (inguinal or axillary). Induration may be detected, as well as enlargement of the affected area of the lymph nodes. When palpated, they may be painless, but at the same time mobile.
Over time, the lymph nodes may become fused with other surrounding tissues, causing their mobility to be lost and pain to appear. Subsequently, the lymph node may disintegrate, forming an ulcer-type defect. The spread of cancer cells with further blood flow can lead to the emergence of a secondary type of tumor focus occurring in the internal organs. The latter is often accompanied by the occurrence of stomach, liver, kidney, lung, and breast cancer.
Loss of energy
A person loses energy very quickly, so drips with glucose and vitamins are prescribed.
An elderly dying person experiences a loss of energy potential. This results in longer periods of sleep and shorter periods of wakefulness. He constantly wants to sleep. Simple actions, such as moving around the room, exhaust a person and he will soon go to bed to rest. It seems that he is constantly sleepy or in a state of permanent drowsiness.
The body's need for energy becomes less and less. A person may begin to resist eating and drinking or only eat certain foods (for example, cereal). First of all, a dying person refuses meat, since it is difficult for a weakened body to digest it. And then the most favorite foods no longer cause any appetite. At the end of his life, it happens that the patient is even physically unable to swallow what is in his mouth.
The body's need for energy becomes less and less. A person may begin to resist eating and drinking or only eat certain foods (for example, cereal). First of all, a dying person refuses meat, since it is difficult for a weakened body to digest it. And then even the most favorite foods no longer cause any appetite. At the end of his life, it happens that the patient is even physically unable to swallow what is in his mouth.
You cannot force feed a dying person, no matter how worried you may be that he does not eat. You can periodically offer the patient some water, ice or ice cream. To prevent his lips from drying out, moisten them with a damp cloth or moisturize them with lip balm.
Diagnosis of skin cancer
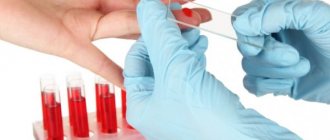
People who suspect skin cancer should consult a dermatologist, who will conduct the necessary examination of the tumor with further palpation of regional lymph nodes, as well as dermatoscopy. The depth of the sprouted tumor and the extent of the process can be determined using ultrasound. To study pigment formations, siascopy is performed.
Final confirmation or refutation of the diagnosis of skin cancer will be possible if a histological or cytological examination is carried out. The latter is carried out using microscopy, using specially colored smears taken from the surface of cancerous erosions. Histological examination is possible on the material obtained after removal of the resulting formation, as well as using a skin biopsy. If the skin located above the tumor node is not broken, then a biopsy can be taken using a puncture. Depending on the indications, a biopsy of the lymph nodes is performed. Histology can reveal the presence of atypical cells, determining their origin and degree of differentiation.
When diagnosing skin cancer, you will also need to exclude its secondary nature. The latter concerns primarily skin adenocarcinoma. To do this, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, X-ray of the lungs, CT scan of the kidneys, scintigraphy, CT and MRI of the brain, and contrast urography are performed. Such examinations will also be required to diagnose present but distant metastases or in case of deep germination of skin cancer.
Forecast
The prognosis for skin cancer and the results of its treatment depend on the stage, growth form, location, histological structure of the tumor and its treatment method.
In general, skin cancer in the initial and subsequent stages is more favorable than cancer of internal organs. Superficial forms of the tumor are more favorable for prognosis than deep-penetrating, infiltrating or papillary ones. Basal cell skin cancer has a better prognosis than squamous cell skin cancer.
In stage I-II of the disease, 80-100% cure for skin cancer is possible. With common forms of cancer (stage III) and especially with relapses, the results worsen significantly and amount to 40-50%. According to the summary data of oncologists, lasting recovery from skin cancer is achieved in 70-80% of cases.
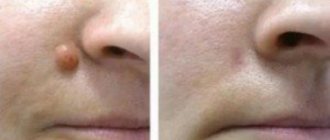
Surgical excision of skin cancer
The main goal in the treatment of skin cancer is radical removal of the tumor. Often removal is carried out using surgical excision of tissues that have already changed. The operation is carried out by capturing a couple of centimeters of healthy tissue.
The operation is performed, minimally involving healthy tissue, while maximally removing all tumor cells that have arisen. A microscopic intraoperative examination of the area of the removed formation helps to carry out this operation. Skin cancer can be eliminated using a carbon dioxide laser. The latter will reduce bleeding and give an excellent cosmetic result.
Preventing skin cancer
The best prevention of skin cancer is to protect the skin from exposure to adverse factors (ultraviolet rays, radiation, chemical, traumatic and thermal factors). Doctors strongly recommend avoiding direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation, and if exposed to the sun, it is necessary to use sunscreen. Workers in the chemical industry and persons who are directly involved with radioactive radiation must comply with safety rules, using all kinds of protective equipment.
Of great importance is monitoring the patients themselves who have a cancer predisposition or obvious precancerous skin diseases. Regular examinations by a dermatologist will be mandatory, as they allow timely detection of the possible occurrence of cancer cells. Choosing the right treatment therapy and method of tumor elimination is the surest way to prevent transforming melanoid nevi.
Prognosis for skin cancer
The mortality rate for skin cancer is very low compared to other types of cancer. The prognosis for recovery depends primarily on the type of skin cancer and the degree of differentiation of the tumor cells themselves. For example, basal cell skin cancer is characterized by a benign course (without metastasis). In case of timely treatment, survival rate after elimination of squamous cell skin cancer is about 96%. The most unfavorable prognosis is for those patients who suffer from melanoma. Among them, the survival rate is only 50-51%.
The cause of oncology of birthmarks is protein P15
The content of the article
Research conducted in Philadelphia confirmed the theory that moles and birthmarks (nevi) on the human body are formed in the womb and are probably genetic in nature. This means that it is impossible to prevent their occurrence, at least with the current level of progress. But stopping the degeneration of tumors into cancer is quite possible.
According to American researchers, birthmarks turn into cancer when the P15 protein, responsible for destroying cancer cells, disappears. The creation of drugs based on the protein compound P15 will help defeat not only skin cancer, but also other malignant tumors.
Scientist Toddy Ridkey found that the appearance of moles is caused by a mutation in the BRAF gene, to which the body responds with increased release of the P15 protein, which inhibits the development of tumors. Its concentration in a normal mole is 140 times higher than in the skin of a healthy person. Having implanted skin cancer (melanoma) cells into experimental mice, scientists discovered that tumors grew only in animals with reduced levels of P15. In other cases, the body destroyed the malignant cells, and melanoma did not develop.