Anyone can become infected with HPV or human papillomavirus. No one is immune from the virion entering the body. Considering the number of types of this virus and the frequency of its spread, we can say that almost every person on the planet has been infected with HPV at least once.
Important! If in men the human papillomavirus can manifest itself in the form of growths on the skin and mucous membranes or the infection will be completely asymptomatic, then women are at much greater risk when infected.
Etiology and pathogenesis
When infected, the human papillomavirus (HPV) invades epithelial cells. Ideal conditions for penetration are the presence of wounds on the skin or mucous membrane, microscopic cracks, abrasions, maceration. The course of inflammatory processes facilitates the penetration process. The mucous membrane under such conditions loses its protective factors. Having penetrated the donor cell, the pathogenic microorganism moves to its nucleus and remains in an inactive state for a long time. It undergoes adaptation, falls into a latent form and takes a wait-and-see attitude.
With a sharp decrease in immunity, it wakes up and begins to actively reproduce. The virus inserts its DNA into the nucleus of the donor cell, causing it to produce viral particles itself. An increase in their number promotes infection of neighboring cells and the formation of morphological changes in tissues. The number of virus replications has a limited number of reproduction cycles (about 400 copies per cell). Reproduced copies accumulate in the stratum corneum of the epidermis and are then released onto the surface of the skin. This is how a wart forms.
Once the viral DNA is inserted into the nucleus of the donor cell, it can exist in two forms. Episomal - exists separately from the DNA of the donor cell. This occurs when infected with strains that have low oncogenic risks. The integrated form is not capable of replication; the synthesized viral particles die and cause instability of the cellular genome. As a result, cell division is disrupted. Atypical processes lead to the growth of neoplasms that can degenerate into malignant ones. When the DNA of a virus is integrated into the DNA of a donor cell, the following precancerous diseases most often occur:
- Bowen's disease;
- Keir's erythroplasia;
- bowenoid papulosis;
- cervical cancer;
- focal hyperplasia of the oral mucosa;
- conjunctival papillomas;
- moderate and severe dysplasia.
Infection with a virus does not always lead to the development of dangerous processes. In young people under 25 years of age, cases of self-healing are often recorded. People of reproductive age are often diagnosed with infections caused by oncogenic strains. Their insidiousness lies in the fact that many diseases can occur without a pronounced clinical picture. Pathological conditions are discovered by chance, during routine examinations, when time is lost and nothing can be done. Therefore, if any types of warts appear on the body, it is important to seek help from a dermatologist and undergo all the necessary diagnostic examinations. They help determine the strain of the virus and take measures that can help contain the activity of the cellular parasite.
What can be the manifestation of HPV in men?
The presence of papilloma virus in the body can be indicated by various symptoms. More often these are neoplasms on the skin. It is difficult to say by the appearance of the formations how dangerous papillomas are in men. Much in this matter depends on the type of virus and the stage of the disease.
The main symptoms of this pathology are as follows:
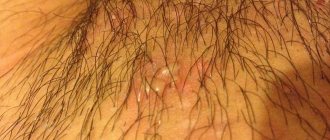
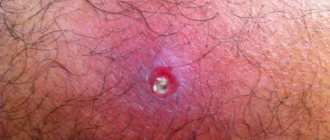
- Warts sometimes appear in a man's groin. These are round, convex formations that initially do not cause any concern. Their color is the same as that of the skin, so they are difficult to notice. More often they form on the feet and hands.
- Condylomas are genital warts. This papilloma in men is localized in the groin area, on the mucous membranes and genitals.
- Bowenoid papulosis is a characteristic rash on the skin of the genital organ. Essentially, these are pinkish plaques that rise above the surface of the skin. The danger of this type of HPV can only be judged after testing.
- This infection also causes Bowen's disease. These are reddish velvety plaques on the skin. Their shape is round and the edges are clearly defined. Plaques appear on the genitals if an infectious agent enters the body.
Risk factors
The virus is transmitted only from person to person. It can be contracted through sexual contact, through close contact with the skin of a patient, or through the use of shared washcloths, towels, or bath slippers. The risk group may include:
- people who often change sexual partners;
- lovers of unconventional sex;
- women and men who have sexual relationships with multiple people;
- regular visitors to public saunas, baths, swimming pools who neglect the rules of personal hygiene.
You can also become infected with the virus in a beauty salon while doing a manicure or pedicure.
Main directions of treatment
Many, having discovered a wart on their body, rush to remove it using traditional medicine recipes. It often happens that the chosen remedy is ineffective or provokes inflammation of the growth. It can become a catalyst for malignancy. To prevent complications from occurring, it is important to immediately consult a dermatologist.
At the appointment, he will definitely examine the growths, if necessary, perform a biopsy and send the material for histological examination. In order to prescribe tablets for papillomavirus, the doctor must know which strain caused the infection and how much virus is in the patient’s body. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and digest tests can answer these questions. Based on these laboratory tests, it is possible to draw up an effective treatment plan against papillomas. As a rule, it is carried out in two stages. First, the growth is removed, then complex drug therapy is used, aimed at fighting the virus and strengthening the immune system.
Preventing the disease and living with the virus
First of all, a young girl can and should protect herself during sexual intercourse. This is a fairly important way to prevent human papillomavirus. Protected sexual intercourse cannot provoke HPV type 18. In addition, you should stop using tobacco products, which contribute to the penetration of carcinogens into the human body.
To avoid becoming infected with HPV type 18, you need to carefully monitor your health, be more selective in your relationships, and follow all recommended precautions. If you have the slightest suspicion of a virus, visit a doctor.
Antiviral therapy
When treating papillomas, antiviral and immunomodulating agents are used only to improve the condition of the body and prevent the appearance of new growths. Today there are no universal drugs that can completely destroy the virus. Taking antiviral tablets can only suppress the reproduction of the cellular parasite. Each of them has its own principle of action, its own side effects, so the prescription must be given by the attending physician.
Alpizarin is most often used to treat infections caused by the human papillomavirus. Its active substance magniferin is extracted from the extract of kopeck (a medicinal plant). It destroys the DNA of the virus and inhibits the spread of infection. Herbal medicines are suitable for treating children. The dosage for a child is exactly half the dosage for an adult. The duration of the course of taking Alpizarin is three weeks. Violation of the rules of administration can provoke the development of an allergic reaction and the appearance of problems associated with digestive disorders.
There is another drug, Rimantadine. This is a more powerful drug, the main component of which destroys the shell of the papillomavirus. It is most often used to prevent relapses after removal of papillomas using hardware and surgical methods. The product is also suitable for preventing infection after contact with a carrier of the infection. The medicine has a large list of contraindications. "Rimantadine" should not be taken by those who have a history of severe pathologies of the liver, kidneys, or gastrointestinal tract. Side effects - tachycardia, increased nervous excitability, digestive disorders. Such symptoms quickly disappear after discontinuation of the drug.
Routes of infection, development features
After skin cells are exposed to the harmful effects of the human papillomavirus, a stratum corneum begins to form at the site of infection. In fact, this is a kind of defensive reaction of the body, which tries, with great speed, to reject “sick” cells. As a result, a woman witnesses the formation of an excessive number of various types of neoplasms, in particular warts, on her skin.
There are the following ways of infection with human papillomavirus type 18:
- Sexual path. It has long been proven that women who lead a fairly active sex life are most susceptible to developing this type of disease.
- Various types of domestic injuries and damages. Such injuries include, in particular, skin cuts. In this case, the infection can enter the blood and spread throughout the patient’s body.
- Vertical mode of infection, in which transmission of infection occurs from mother to child. Here we are talking about the genetic method of infecting the patient.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulators are natural or synthetic agents that help the body fight any types of infections by strengthening the immune system. Their intake stimulates the production of antibodies that can suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. There are four types of immunomodulators:
- immuno-strengthening;
- immunosupportive;
- antiviral;
- antitumor.
To combat infection, drugs of the third group are suitable. These include the following combination agents:
"Isoprinosine." It directly acts on the infectious agent and blocks the synthesis of viral particles. At the same time, it stimulates the production of immunoglobulin and leukocytes and allows them to destroy affected cells. The medicine is produced by manufacturers in the form of tablets. The dosage regimen is selected by the doctor individually. The patient's age and weight are taken into account. For adults, the standard dosage regimen is used: two tablets four times a day. Course duration is from 2 weeks to 1 month. If necessary, repeat the course of treatment, take a break of 30 days.
“Isoprinosine” is considered a universal remedy that fits very well into a comprehensive treatment regimen for papillomavirus. It can be used after surgical removal of papillomas to prevent relapse of the disease. It is well absorbed by the body and can be taken from the age of three. The safety of using the drug is ensured by a small list of side effects. An analogue of Isoprinosine is the drug Groprinosin.
"Acyclovir". Taking it helps block viral DNA synthesis and stimulate the production of antibodies. It is available in the form of tablets and ointments, so it is often prescribed when it is necessary to combine medicinal and local treatment. The drug can be used from the age of two. Children's doses are calculated taking into account the age and weight of the child. The prescription regimen for adults is standard (one tablet five times a day).
Acyclovir has a small list of contraindications. It should not be taken by people who have an individual intolerance to synthetic analogues of purine base, or by pregnant and breastfeeding women.
The drugs Cycloferon, Galavit, Arbidol have similar properties. "Acyclovir" is prescribed when a bacterial component or fungal infection is attached to a papillomavirus infection.
Vitamin complexes help to repeatedly strengthen the functioning of the immune system. The maximum therapeutic effect can be achieved by combining the use of antiviral drugs, immunomodulatory agents and pharmaceutical drugs intended for external use.
List of drugs
Drug treatment for HPV consists of antiviral and immunostimulating drugs. You can take two medications at the same time or replace them with one combined one. Combination drugs include an immunomodulator and an antiviral active substance.
Antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs
| Name | Category | Compound | Mechanism of action | Contraindications |
| Allokin-alpha | Combined drug |
|
|
|
| Immunomax | Immunomodulator |
|
|
|
| Isoprinosine | Combined remedy |
|
|
|
| Gepon | Combination drug |
|
|
|
| Galavit | Immunomodulator |
|
|
|
| Viferon | Combined remedy |
|
|
|
| Altevir | Combination drug |
|
|
|
| Roferon A | Combined remedy |
|
|
|
| Acyclovir | Antiviral drug |
|
|
|
| Interferon | Combination drug |
|
|
|
| Ribavirin | Antiviral |
|
|
|
Cauterizing drugs
Note! They are used locally on the area of papilloma to remove it.
| Name | Compound | Mechanism of action | Contraindications |
| Feresol |
|
|
|
| Verrucacid |
|
|
|
| Super clean |
|
|
|
| Podophyllin |
|
|
|
It is important! Remember that local treatment of papillomas alone is not enough. Regardless of their localization, you should undergo a full course of drug therapy until the viruses are eliminated from the body.
Means for cauterization of papillomas in the groin and face
The skin on the face and anogenital area is the thinnest and most sensitive.
Note! Self-use of chemicals to remove papillomas in the genital area and face is dangerous. It is recommended to undergo treatment by a dermatovenerologist.
Due to the danger of the drug getting on the mucous membranes, for papillomas of these localizations you cannot use Ferezol, Verrukacid and Supercelandine.
Of the listed drugs, only Podophyllin can be used, but very carefully. Condilin is also used, a stronger analogue of podophyllin, if the latter is ineffective.
Pharmaceutical products for external use
When choosing products for external use, it is important to understand that a wart is only an external manifestation of infection, indicating infection. If only local treatment is performed, the disease will certainly progress. Therefore, the use of funds should become part of complex therapy.
There are a large number of creams, ointments, and solutions that can be included in it. The choice of means largely depends on what goals are being pursued.
- If it is necessary to cauterize condylomas growing on the genitals, the patient is prescribed Veregen ointment. Its use causes necrosis of growth tissues and death of viral cells. After cauterization, the neoplasm dries out, turns into a crust, which then peels off on its own and falls off. The ointment should not be used on mucous membranes or skin that has any, even minor, damage.
- To cauterize small warts growing on other parts of the body, SAN FEN ZHONG ointment can be prescribed. It is applied directly to the growth for a week, after three to four minutes it is washed off with water. The effect occurs within a week.
- After radical removal of the wart, the patient may be prescribed “Oxolin” (an ointment with an antiviral effect) to treat the skin area. The duration of use is determined by the doctor.
- Viferon ointment is a product that has antiviral and immunomodulatory effects. Its use stimulates the flow of leukocytes to the affected area. It accelerates the natural fight against the pathogen and prevents the spread of infection to other areas of healthy skin.
- The composition of the ointment “Stefalin” consists entirely of extracts of medicinal plants. Its use becomes justified when it is necessary to activate the regenerative functions of the skin after removing warts.
Note! If you steam the tumor well in hot water before applying these products, the use of ointments will give a more positive result.
How to treat the virus?
Various methods are used for treatment. The most effective of them are presented below.
Antiviral therapy
To carry out antiviral therapy, a wide range of modern medications are used that can suppress the development of the virus. The drugs of choice are cycloferon and reaferon. If we talk about the first drug, it is a more expensive medicine than Reaferon, but it also has significantly greater antiviral activity.
The essence of the effect of this kind of drugs is that the cells of papilloma viruses are suppressed, which prevents the spread of infection throughout the body. As a result, the number of pathogens that provoke HPV types 16 and 18 is significantly reduced.
Surgical treatment
Quite often, it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment of human papillomavirus. If HPV manifests itself in the idea of genital candyloma on a woman’s genitals, then this is an absolute indication for removal of this type of neoplasm.
This is due to the fact that such candyloma quite often degenerates into oncology. If we are talking about warts, then only cosmetic procedures take place here. Using them, it is impossible to cure the carrier of the virus from this type of disease, but it is possible to improve the aesthetic condition of human skin.
Restoring the body's defenses
To restore the body's protective functions, drugs that can strengthen human immunity are often used. A woman’s strong immunity is the key to the fact that she will be able to defeat an insidious and oncologically dangerous disease much faster. To restore the body's protective functions, galavit becomes the drug of choice.
This is a very common medication that is used to “promote” the human immune system. It should be noted that these types of drugs hide a potential danger, which is that uncontrolled and frequent use of pills can lead to uncoordinated functioning of the human immune system.
Drugs prescribed for infection
It is necessary to highlight various types of drugs belonging to different classes that are used in the treatment of human papillomavirus:
- Galavit.
- Immunomax.
- Polyoxidonium.
- Viferon.
- Immunofan.
Listed above are drugs that have an immunomodulatory effect.
Antiviral drugs should also be highlighted:
- Acyclovir.
- Altevir.
- Reaferon.
- Cycloferon.
There is also a whole range of quite effective medications that have a destructive effect. These include:
- Solkovagin.
- Condelim.
Solutions and refrigerants
Often during outpatient treatment, solutions and refrigerants that have a cauterizing effect are used. They can be used to remove tumors. The three most popular products: “Ferezol”, “Verrukacid” and “Phenol” are based on the active ingredient phenol. Its improper use can cause severe chemical burns, so it is important to use the products strictly following the attached instructions.
Lapis pencil has similar properties (the main active substance - silver nitrate - causes tissue necrosis at the sites of exposure) and the Cryopharma refrigerant (its effect is similar to the cryodestruction procedure).
There are many pharmaceutical ointments and solutions that can eliminate the external symptoms of a viral infection and prevent its spread. But it is important to remember that all of the listed remedies are not intended for home treatment, but for outpatient treatment.
The effectiveness of laser removal of growths
Removal of papillomas is part of complex therapy. It can be implemented in different ways. One way is chemical exposure. It is used when you need to remove one small wart growing on invisible parts of the body. Carrying out cauterization of papilloma using solutions and refrigerants is associated with certain risks. This option cannot be used in the treatment of plantar growths and neoplasms with signs of malignancy.
But in the arsenal of modern medicine there are other, more effective treatment methods. Among them, laser removal of papillomas is considered the most advanced direction. Unlike surgical intervention, it does not apply to surgical methods of removal, so the recovery period after the procedure is short. Before the operation, local anesthesia is given. Then the doctor, using a special installation, turns on a nozzle capable of reproducing a thin beam. Its use allows you to remove the tumor layer by layer. It takes approximately four minutes to treat one papilloma.
The laser simultaneously burns and evaporates the tumor, coagulates the vessels that feed the wart, so during removal the risks of bleeding are minimized. After the session is completed, the wound does not leak; it quickly becomes covered with a crust, which disappears on its own within 8 days. If the crust is not removed prematurely, scars and scars will not remain on the skin. Before the procedure, the doctor makes settings in the device. It sets the penetration depth of the beam irradiation, the pulse of which should not penetrate deeper than required.
Complications after laser removal occur in 0.1% of cases. Most often, hyperemia is observed (slight swelling of the skin, as with a burn). If the equipment is used correctly, it is impossible to damage healthy tissue. The laser helps to disinfect the treated area. After its exposure, blood circulation increases, tissue nutrition improves, and regeneration is stimulated. Complex treatment helps to avoid relapse: parallel use of antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs. No special skin care is required after the procedure. The doctor recommends that the patient limit exposure to direct sunlight and high temperatures for two weeks.
Laser therapy has one drawback: during its implementation, tissue cannot be taken for histological examination. Therefore, this method cannot be used to remove growths with signs of malignancy.
Local and surgical treatment of HPV
When condylomas appear, many women attempt to get rid of them using folk remedies.
However, the mechanism of such treatment is exclusively the removal of local inflammation and an attempt to necrotize condylomas.
Folk remedies do not work on the virus!
This means that HPV will continue to multiply.
Which will lead to relapse of pointed neoplasms with a high risk of malignancy.
Therefore, attempts at uncontrolled use of herbal remedies for topical effects will lead to a direct threat to a woman’s life.
Traditional remedies for local use are mandatory.
They are used in combination with drugs prescribed orally.
The following medications are recommended for topical use:
- Miramistin
- chlorhexidine
- Panavir
- epigene
- geneferon
- verrucacid
- solcoderm
Topical medications are usually prescribed in suppositories.
In rectal or vaginal, depending on the location of the papillomavirus process.
The classic therapeutic regimen in gynecology for the elimination of HPV includes:
- ferrovir 10 ml per day intramuscularly in 2 injections for 10 days
- lykopid 6 capsules per day sublingually, divided into 3 doses
- chlorhexidine - irrigation or suppositories 4 times a day
- genferon - vaginal or rectal suppositories 2 times a day at different times with antiseptics
The full course of treatment is individual.
A clear deadline is set only for the administration of injections.
But according to the doctor’s decision, the duration of the course may increase or decrease.
The effectiveness of therapeutic measures for lesions of the cervix is very high.
And genital warts often have to be removed surgically.
Numerous reviews indicate that minimally invasive interventions significantly improve the rate of recovery from a viral infection.
Among the surgical techniques widely used are:
- electrocoagulation of condylomas
- laser vaporization
- mechanical removal with a scalpel
- cryodestruction using liquid nitrogen
- exposure to chemically active acids and alkalis
The above methods are highly effective.
But only with conservative support with antiviral drugs and immunomodulators.
If there is dysplasia in the cervix, extended surgical intervention is possible - laser or mechanical conization.
The procedure is also usually performed on an outpatient basis.
Since it is a small operation.
Thus, human papillomavirus is extremely common in the population.
When the gynecological tract is affected, HPV can bring a woman a lot of serious suffering.
Sometimes it provokes deadly diseases.
Modern medicine has a lot of possibilities to completely eradicate a microorganism.
Even in the absence of a clinical picture, and even more so after the appearance of genital warts, it is necessary to immediately contact a dermatovenerological clinic.
At the VDC, an accurate diagnosis of the type of virus is carried out, and all types of specialized treatment are prescribed.
Only a timely visit to a doctor will allow you to prevent in advance the dangerous effects of papillomavirus on a woman’s body.
ethnoscience
There are recipes in the arsenal of traditional medicine that can be used to remove warts at home.
The most popular of them is the use of celandine juice. It is prepared from the stems, branches and leaves of the plant. The raw materials are ground in a meat grinder, and the resulting pulp is squeezed through gauze folded in several layers. The juice is used to treat warts twice a day until the new growth turns black. After this, it will begin to dry, shrink and fall off on its own.
Our great-grandmothers in the villages used ash to treat warts. They took it out of the oven, ground it into powder, added a little water to it, kneaded it into a thick paste and applied it to the growth. After a few days, the wart began to dry out and fall off. Ash can also be made from burnt matches.
You can prepare a remedy for cauterizing warts from lemon peel. To do this, you need to peel two lemons, chop their peels, pour them into any glass container, add 100 grams of acetic acid and shake the contents thoroughly. The product should stand for a week in a dark place. It must be shaken periodically. To cauterize a wart, just drop one drop onto the head of the wart twice a day. This must be done until the wart turns black. Since acetic acid is used to prepare the tincture, it is important to treat papillomas carefully, avoiding contact of the product with healthy skin.
You can use folk remedies only if the growth of warts is provoked by a virus with low oncogenic risks.
Risks of degeneration of papillomas into cancer
Strains that can provoke malignancy processes most often cause the growth of genital warts. They appear on the genitals, around the anus, on the mucous membrane of internal organs (vagina, urethra, larynx). For example, if genital warts form on the cervix, it increases the risk of developing cancer by 60 times.
Oncogenic strains of the virus can provoke dysplasia (detachment of the epithelium). This process develops in three stages: the third stage is considered a precancerous condition. An ordinary brown wart located on the body can also mutate. Malignization becomes possible when there is mechanical damage to the integrity of the growth.
Any wart needs to be monitored to see how it grows and develops. If the papilloma suddenly changes its color, becomes larger, and its contours blur, then you should show the wart to a dermatologist. The growth, capable of degeneration, has a dense structure; it constantly increases in size, spreading across the skin. Processes are considered dangerous when papillomas begin to group and form one large neoplasm.
Prevention
The appearance of a wart on the body does not always lead to malignancy, but there is a risk of degeneration. Therefore, it is so important to use preventive measures aimed at combating the infectious agent when growths appear.
To do this you need:
- Constantly support your immune system - take vitamins regularly, give up bad habits, eat right, exercise, harden yourself, and treat any colds in a timely manner.
- Sunbathe less and avoid visiting the solarium.
- Wear clothes that fit, made from natural fabrics.
- Have one sexual partner for life.
- Use barrier contraceptives.
- Try to avoid close contact with infected people.
- Donate blood annually to identify strains of papillomavirus.
If possible, you should definitely be vaccinated against the most common types of the virus (6, 11, 16, 18). Vaccinations today are given to persons who have not started sexual activity (children from 9 to 12 years old). If you find warts on your body or mucous membranes, it is important not to self-medicate, but to seek medical help.
Forecast
The use of complex therapy makes it possible to make favorable prognoses for recovery. Warts may disappear completely, but no pill will help remove the virus from the body. Therefore, the risk of relapse will persist throughout life. In order for the immune system to restrain the activation of the cellular parasite, it must be constantly strengthened. To do this, it is important to protect yourself from severe stress. Women should constantly worry about their health, visit the gynecologist more often and carry out preventive examinations to detect cervical cancer in the early stages. Men should visit a urologist and monitor the condition of the reproductive system.
The danger of human papillomavirus for women
In general, HPV is a safe disease. However, some subtypes of the virus pose a serious danger to humans. In particular, we are talking about HPV types 16 and 18. For a long time it was believed that these types of viruses also did not pose any danger to humans. But several years ago, Harold Housen proved the excessive negative activity of HPV types 16 and 18. It turned out that these types of human papillomavirus can cause cancer. And in particular, cervical cancer in women.
In fairness, it should be noted that for women the human papillomavirus is much more dangerous than for men. This is due to the fact that some types of HPV can provoke cancer in women. We are talking about uterine cancer, as well as cancer of the vagina and anal area.
If we consider the age groups of women, then, most often, young girls are susceptible to the harmful effects of the virus. However, the disease can also develop in women of quite mature age. Often, the intensity of sexual life that a woman leads is of great importance.
In general, the danger for women is virus types 16 and 18. This is where the greatest danger lies. In addition to these types of viruses, there are other types (type 31, , 35, 45) that are also capable of causing cancer. However, these types of viruses pose a significantly less danger to women than viruses of types 16 and 18.