Herpes type 4 affects the human lymphatic system. The primary episode of the disease is accompanied by infectious mononucleosis: the palatine tonsils become inflamed and the size of the liver increases.
The most common is a mild form of the disease, but often the herpes virus type 4 in adults is in an inactive phase of development. The clinical picture of the disease may not be observed in an infected person, but he poses a danger to others. In most cases, transmission of the virus is through airborne droplets. It is important to consider what the symptoms of this type of herpetic infection are and how the disease is treated.
Routes of infection
Epstein-Barr virus can be transmitted in the following ways:
- airborne;
- contact;
- during blood transfusion;
- in case of unprotected sexual intercourse.
As a result of herpes entering the bloodstream, the body begins to counteract it. With a strong immune system, it can be suppressed. If the immune system is weak, this microorganism develops, up to the chronic form of the disease.
Causes
Having penetrated inside the body, the pathogen does not make itself known in any way for a long period of time until the appropriate conditions arise for its manifestation. First of all, the patient’s immune system, which controls the reproduction of the pathogen in the human body, weakens.
On this topic
- Herpes
All about herpes simplex
- Irina Nasredinovna Nachoeva
- September 24, 2020
The main factors for the penetration of the virus are:
- Deterioration in the functioning of the immune system.
- Overheating or hypothermia.
- Psycho-emotional stress.
- Unbalanced diet .
- suffered .
- Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
- Lack of vitamins.
- The period after surgery .
The main ways of spreading an infectious lesion:
- Airborne (via saliva).
- Infection through blood (for example, during a transfusion).
- Direct method (from the placenta of a pregnant mother to the fetus).
- Household (when consuming other people’s hygiene items).
- Contact method (during contact with a carrier of infection).
- Self- infection (in the process of scratching blisters/inadequate antiseptic treatment).
By observing precautionary measures, it is possible to significantly prevent infection with the causative agent of human herpes type 7.
Characteristic symptoms
The main signs of herpes in the initial stages are:
- sudden increase in body temperature;
- discomfort in muscles and joints;
- exhausted state;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
In this case, symptoms of tonsillitis and pharyngitis may appear:
- nasopharyngeal congestion;
- swelling of the tonsils and redness of the throat cavity;
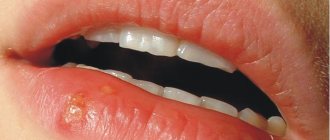
- the formation of purulent inflammations in the palate.
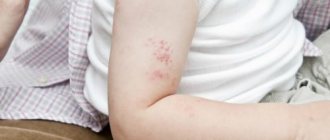
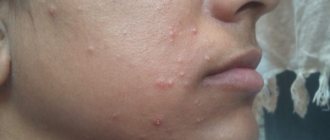
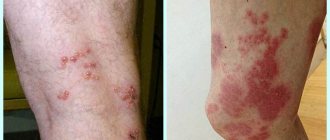
The following signs of pathology are periodically observed:
- formation of rashes, blisters;
- nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite;
- gastrointestinal disorder;
- enlarged liver, spleen.
If the infection spreads throughout the body, many internal organs can be affected.
After a month after the virus enters the body, the patient’s condition gradually improves. Subsequently, the manifestation of herpes type 4 is similar to an acute respiratory viral infection.
The Epstein-Barr virus leads to the activation of cancer cells in the patient's body. The following signs are characteristic of the formation of a malignant tumor:
- tinnitus;
- migraine;
- nasal purulent bleeding.
Asymptomatic progression of this disease is extremely rare.
How does it manifest?
The first symptoms of infectious mononucleosis resemble those of ARVI. There are some differences when affected by the fourth type of virus in children and adults.
In adults, the disease begins both against a background of fever up to 39C, and at normal body temperature. Weakness and high fatigue develop, against this background the following are noted:
- nasal congestion without severe runny nose;
- moderate redness of the oropharynx;
- prolonged hyperthermia, reaching in some cases up to 1 month.
At the peak of a herpetic infection, a characteristic triad occurs: fever without chills and sweating, enlarged and hardened lymph nodes and symptoms of sore throat.
Lymph nodes enlarge in the head (on the back of the neck, under the jaw, on the back of the head) and groin. The pain of the nodes is slight, sometimes the skin over them is swollen, there is no redness.
Symptoms of sore throat are more pronounced in adults than in children. I am concerned about a sore throat, a feeling of aching in the joints; upon examination, enlarged tonsils covered with a yellowish coating attract attention.
Newborns and breastfed children do not get sick; they are protected by their mother's antibodies. Until 2 years of age, symptoms resemble an erased picture of a respiratory infection. Older babies have a fever for up to 2 weeks, but their throat hurts longer.
Along with local manifestations, symptoms of damage to internal organs are noted:
- jaundice;
- an increase in the size of the spleen and liver;
- various rashes - from hemorrhagic (with small hemorrhages) to urticarial (itchy blisters);
- nausea and refusal to eat.
Such manifestations last up to 3 weeks, then the condition gradually improves. Immunity after infectious mononucleosis is stable, re-infection is impossible. The virus never leaves the body; a person remains a carrier for life. Among the adults examined, the carriage rate was 100%.
Diagnostics
To determine an accurate diagnosis, laboratory tests are required. These include:
- General blood analysis.
- Biochemical analysis.
- Enzyme immunoassay of blood serum.
- Polymerase chain reaction.
- Ultrasound examination of internal organs.
If cancer is suspected, a biopsy of tumor tissue is performed.
Treatment tactics
The course of therapy for type 4 herpes consists of a whole range of measures:
- suppression of infection;
- reduction and elimination of symptoms;
- restoration and strengthening of immunity;
- elimination of general intoxication of the body.
To suppress the development of the virus, antiviral drugs are prescribed, such as Acyclovir, Ganciclovir. When a bacterial infection is observed, antibiotics Metronidazole and Fluconazole are prescribed.
To eliminate general intoxication of the body, it is recommended to drink large amounts of water. In the acute course of the disease, a course of intravenous injections is carried out using a glucose solution or water-salt solution.
To reduce and eliminate signs of the disease, medications for fever and pain are used. In the presence of edema, hormonal medications and mouth rinses with various antiseptic drugs are prescribed.
Also, in the process of maintaining and restoring immune activity, a complex of drugs consisting of vitamins, immunomodulators, and immunoglobulins is used.
If a malignant tumor is diagnosed, chemotherapy and radiation treatment are used.
Treatment of herpes type 4 in children is carried out inpatiently. This is due to more severe symptoms of the disease.
Characteristics of the virus
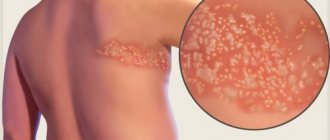
photo of roseola in children
HHV type 7 is a poorly studied member of the herpes virus family. It is ubiquitous, like all these viruses.
The seventh type belongs to betaherpesviruses, the genus Roseoloviruses. Type 8 also belongs to this genus. Type 7 virus has genetic, immunological and biological similarities to HHV-6.
Herpes type 7 was discovered relatively recently: in 1990 by isolating the virus from the blood of a donor. In 1996, its genome was completely studied. Herpes virus human type 7 is lymphotropic.
This means that the pathogen infects lymphocytes and monocytes, multiplying in them. Replication lasts 2-3 days.
Herpes virus type 7 can also cause activation of type 6, which often complicates diagnosis. But, unlike the sixth type of virus, the seventh type is not integrated into the chromosomal apparatus of the human cell.
It is noteworthy that HHV type 7 uses the same receptor for cell entry as HIV. After the herpes virus damages this receptor, its expression slows down, which makes it difficult for HIV to penetrate the cell.
This fact is used by scientists to develop new therapeutic approaches to treat the deadly infection.
Herpes type 7 is widespread. Approximately 95% of the entire population are asymptomatic carriers - in them the virus persists in affected lymphocytes.
About 75% of healthy virus carriers release the pathogen with saliva into the environment, due to this a certain level of morbidity is constantly maintained in groups and families.
Important!
Primary infection with herpesvirus type 7 occurs in childhood and occurs in the form of roseola or fever without a rash.
To a large extent, the cause of this childhood infection is HHV type 6, and in 10% of cases - type seven.
Reactivation of the infection does not lead to specific symptoms, so it is impossible to recognize the source of infection visually and clinically. The reason for the reactivation of herpes type 7 is a significant drop in immune activity.
A number of authors are of the opinion that the virus belongs to diseases such as pityriasis rosea, chronic fatigue syndrome, and mononucleosis-like syndrome.
Traditional medicine recipes
It must be remembered that the use of alternative methods of treating herpes must be agreed with the attending physician.
The most common methods of traditional medicine:
- The use of choleretic tinctures is recommended, since the virus lies dormant in the pancreas. To make the tincture, you need to take a teaspoon of one of the dry herbs: immortelle, tansy or corn silk, pour one glass of boiling water and let it cool. Strain the solution and warm it slightly before use. It is recommended to drink the tincture fifteen minutes before meals. The course of treatment should continue for a month;
- in case of exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to make a tincture of viburnum. It is necessary to chop four tablespoons of viburnum berries and add boiled water. Leave to infuse for four hours. Drink half a glass of the solution four times a day;
- Drinking fresh aloe juice also helps relieve exacerbation of the disease. To do this, you need to drink one teaspoon three times a day before meals. You can use the juice as an antiseptic to moisten inflamed areas. It is not recommended to use aloe juice if you have hemorrhoids, kidney failure, or during pregnancy.
Danger for a pregnant woman
Type 4 herpes poses the greatest danger to a pregnant woman and her fetus during initial infection. This is due to the lack of a developed immune defense in the body against this type of bacteria. This can lead to infection of the fetus through the placental barrier. The probability of such infection is sixty percent.
If there are repeated manifestations of the Epstein-Barr virus during pregnancy, the risk of illness in the child is reduced due to the developed immune defense. At the same time, the probability of infection of the fetus is present and amounts to five percent.
The presence of the virus in the mother’s blood contributes to the development of protection against infection in the baby. For several months after birth, the baby is protected from the effects of this virus.
Prevention
To prevent the disease, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Use condoms during sex.
- Treat the skin with antiseptics.
- Wash your hands frequently.
- Use only personal hygiene products.
- Periodically disinfect toilets.
- Avoid sexual intercourse if you have genital herpes.
- Limit contact with people who have recovered from this virus for a month.
Laboratory blood tests must be performed before transfusion or when using donor blood.
How is it dangerous for humans?
This virus, which makes up the fourth type of herpes, is suspected of being carcinogenic. There is no definitive evidence of this, but there is no doubt that the virus is associated with Burkitt's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal cancer, lymphogranulomatosis and complications after organ and tissue transplants, genital herpes, viral hepatitis, and herpetic sore throat. In recent years, there has been increasing evidence that the virus provokes the development of a formidable neurological disease - multiple sclerosis.
Burkitt's lymphoma has a high degree of malignancy. It begins its development in the lymphatic system, but very soon goes beyond it and affects other organs and systems - blood, cerebrospinal fluid and bone marrow. This disease affects young men in central African countries and is practically never found in our country.
With Burkitt's lymphoma, a person quickly loses weight due to fever, tumors appear on the jaw, teeth gradually fall out, and breathing and swallowing become difficult. The spine may be affected along with the spinal nerve roots. The abdominal form of lymphoma is manifested by tumors of the digestive canal, intestinal obstruction, and accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Nasopharyngeal cancer is manifested by bloody discharge from the nose, difficulty breathing, decreased hearing, and pain in the temporal region.
Multiple sclerosis, or exposed nerve disease, is the destruction of the myelin sheath of peripheral nerves and the formation of lesions in the brain. Symptoms depend on the location of the lesions.