Description of the disease
Idiopathic urticaria belongs to the group of allergic diseases. The problem is that it is not possible to identify the exact connection between exposure to certain negative factors and the manifestation of inflammation on the skin. The disease develops as a result of autoimmune disorders. The patient exhibits hypersensitivity to the cells of his own body.
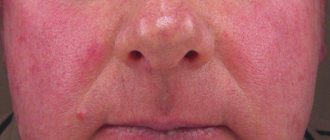
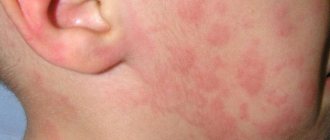
Inflammation can appear on any area of the skin
Skin inflammation often develops after contact with certain metals, eating chocolate, citrus fruits or brightly colored fruits. In this case, the irritants only serve as an impetus for the body’s allergic reaction. The root cause of the pathological process lies precisely in the malfunction of the immune system.
Experts distinguish three forms of idiopathic urticaria:
- True allergic urticaria. Skin inflammation develops as a reaction to a specific autoallergen (a substance secreted by the body itself).
- Pseudoallergic urticaria. The provoking factor is physical or chemical irritants (water, cold, sun, frost).
- Contact urticaria. An idiopathic reaction develops with prolonged contact of the skin with irritating substances (metals, cosmetics, synthetic clothing, etc.)
True idiopathic urticaria is a fairly rare pathology. It occurs in only 3% of the world's population. The disease can be diagnosed in people of any age and gender.
Idiopathic urticaria is a dermatological pathology of a chronic nature. If a person leads a healthy lifestyle, the disease may not make itself felt for a long time. At the slightest failure in the immune system, a pathological mechanism is triggered. Symptoms begin to appear, which are not always easy to get rid of.
Kinds
Based on developmental factors, excess sleep duration is divided into several types:
Pathological hypersomnia can appear as a result of a nervous disorder, as well as during sleep phenomena.
Idiopathic or psychophysiological hypersomnia occurs in completely healthy people aged 15-30 years against the background of chronic lack of sleep or constant stress. It is accompanied by “sleep intoxication,” a syndrome in which a person, after waking up, is confused, cannot orient himself in space, does not remember anything, and behaves strangely.
Post-traumatic hypersomnia is the consequences of mental and physical trauma, accompanied by stress. But its clinical manifestations are quite unpredictable, for example, “hysterical hibernation” - sleep for a long period with short awakenings. Infectious lesions of the brain and other pathologies can threaten lethargic (continuous multi-day) sleep.
Psychopathic hypersomnia is characteristic of patients with neurological disorders. It is unique in that an individual can sleep for several days, and the EEG shows that their brain is alert and active.
Narcolepsy is characterized by daytime sleep that is restless and does not bring rest. This is the most severe form of the disorder. At the same time, a person is not able to control himself; he can fall asleep in any position, anywhere. People who have long suffered from this disorder, sensing the approach of an attack, look for a comfortable place in advance and take a position that will allow them to sleep peacefully in comfortable conditions. When falling asleep and during sleep, the patient may experience hallucinations. His muscles relax so much that sometimes after waking up he is unable to move, sometimes even paralysis occurs for a long period.
Iatrogenic (drug-induced) hypersomnia develops after the use of certain medications.
Kleine-Levin syndrome or periodic hypersomnia - a drowsy state occurs from time to time along with an increased feeling of hunger. This is usually typical for young men (under 40 years old) and goes away on its own.
There are also species whose nature is unclear. As a rule, they are classified as idiopathic.
The disorder is also systematized according to its manifestations:
permanent hypersomnia – a monotonous desire to sleep. This condition is constant and accompanies the patient all day. Occurs as a result of injuries due to strong psychophysical stress, taking medications;
paroxysmal - attacks of drowsiness come suddenly and uncontrollably.
Causes
Idiopathic urticaria differs from a simple allergic skin reaction precisely in that it is not possible to accurately identify the cause of the pathological condition. This or that allergen is just a factor that provokes the inflammatory process of the epidermis. Mast cells play a leading role in the development of the disease. When damaged, they release substances that, upon contact with certain allergens, provoke inflammation of the skin.
In addition, the body's immune system begins to produce antibodies to substances secreted by mast cells. Sometimes this is enough to cause redness and blistering on the skin. The situation is aggravated by the addition of allergic factors.
Often ultraviolet rays provoke the development of inflammation
Idiopathic urticaria can be inherited . If one of the parents suffers from a pathology, there is a high probability that the child will also have to deal with the disease. Autoimmune disorders can be triggered by other factors. These include:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- oncological pathologies;
- infectious diseases;
- arthritis;
- metabolic failures;
- hormonal disorders;
- renal failure;
- drug and alcohol addiction;
- diabetes mellitus, etc.
Sjögren's syndrome is a disease characterized by damage to the exocrine glands. Idiopathic urticaria often develops against the background of a pathological process.
Damage to mast cells does not mean that you will have to experience unpleasant symptoms. The likelihood of developing idiopathic urticaria increases if the patient eats poorly, experiences strong emotional stress, and neglects proper sleep.
Characteristic
Idiopathic urticaria is a type of regular urticaria, but is distinguished by its vague appearance. It is difficult to determine what causes such rashes. They vary in extent: both small and large blisters are present.
The duration of such urticaria will last more than two months, which is why it is often called chronic. The blisters have clear boundaries and usually reach 2-4 centimeters.
In addition to being inconvenient from an aesthetic point of view, urticaria also causes inconvenience on a physical level. Constant itching prevents you from getting a good night's sleep and leads to irritability.
Symptoms
A person who develops idiopathic urticaria begins to experience the following symptoms:
- red blisters;
- itching;
- pain;
- insomnia;
- weakness;
- temperature.
Due to the itchy surface, a person begins to scratch the rash, causing the affected areas to become even larger and the blisters to swell. It is important not to introduce infection into such wounds and to constantly wipe with antiseptic agents, such as chlorhexidine.
Reasons for appearance
Before going for an examination, it is important to ask yourself a question and understand what new things have been used recently. At the moment, it is difficult to establish the true cause of the appearance of such rashes, but there are some factors that provoke the appearance:
- introduction of new drugs;
- insect bites;
- eating unfamiliar foods;
- diabetes;
- weakening of the immune system.
According to established studies, it is known that the cause of rashes is the activation of prostaglandins.
An increased concentration of histamines becomes the first cause of the appearance of a rash. If in addition to this there is another irritant, serotonin begins to be intensively produced, which will worsen the situation.
Symptoms
The manifestations of idiopathic urticaria are similar to inflammation of the skin of allergic origin. The difference is that in the second case it is enough to limit contact with the irritant and the condition of the epidermis is restored. Symptoms of idiopathic urticaria may remain unchanged for several weeks.
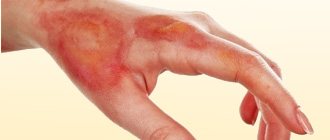
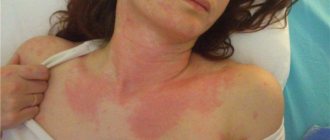
The disease begins to manifest itself with the appearance of small areas of redness on the skin that are not symmetrical. Skin inflammation can develop on the abdomen, arms, legs, back, face. After a few days, small red spots merge into larger ones, and bubbles filled with clear liquid appear on them. Blisters can vary in size (from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter).
Hives appear as red spots with blisters
A clear sign of idiopathic urticaria is itching, which is more pronounced at night. When scratching, the patient damages the upper layer of the epidermis, which performs a barrier function. As a result, pathogenic microflora can multiply in the area of inflammation, provoking the development of dangerous complications.
After 3–4 days, a crust forms at the site of the blister, which peels off after some time. If therapeutic measures are not carried out, some blisters are replaced by others.
Features of therapy
Treatment of urticaria is complex and must be done under the supervision of a doctor. This is due to the fact that it most often develops in people with allergies and can be accompanied by severe complications. These include angioedema and anaphylactic shock. These conditions pose a potential danger to the patient's life and can cause death if medical care is not provided in a timely manner .
Traditional methods
To get rid of allergy symptoms, the doctor prescribes local and systemic treatment. The selection of drugs is carried out taking into account the severity of the patient’s condition, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and the results of the tests performed. In most cases, patients are prescribed the following drugs:
- Antihistamines. In case of exacerbation of urticaria, first generation drugs are used - Suprastin or Diazolin. After this, they move on to more modern means that do not cause drowsiness (Zodak, Erius). In especially severe cases, hormonal antiallergic drugs (Mometasone, Prednisolone) are indicated.
- For gargling, use a 2% ephedrine solution if swelling affects the throat. The drug helps to constrict blood vessels, which will lead to a rapid improvement in well-being.
- Sorbents - Enterosgel, Polysorb. They free the body from dangerous toxins that accumulate as a result of the penetration of allergens. Take separately from food or other medications with an interval of 1.5 hours.
- Antihistamines for external use - Fenistil, Psilo-balm. Helps reduce rashes and relieve itching.
- Glucocorticoid ointments - hydrocortisone, Advantan. They are used in extreme cases when other means are ineffective.
- Digestive enzymes - Pancreatin. Often used for hives, since in many cases it occurs due to problems with digestion of food.
Sometimes patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory, antifungal, and sedative therapy, which helps speed up recovery and prevent the development of complications. After the acute period subsides, physiotherapy is used - electrophoresis, UHF, ultraviolet radiation.
Diet
A special diet must be followed throughout the entire treatment period. It involves avoiding foods that can trigger allergies . At the same time, nutrition should be balanced and nutritious. To achieve a positive result, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- You need to give up fatty meats, eggs, sausages, seafood and fish. They are replaced with veal or rabbit meat.
- Honey, any confectionery products and dishes containing large amounts of sugar should be removed from the diet.
- Nuts and flour products are mandatory. You are allowed to eat only whole grain bread or special bread.
- Patients are prohibited from drinking any alcohol. This is especially true for beer and wine.
- Chocolate, whole milk, tomatoes, strawberries and other red fruits are considered very strong allergens. They should be completely excluded from the diet.
- It is forbidden to use spices, hot sauces, and large amounts of salt.
During the treatment of urticaria, it is necessary to completely exclude all allergens in the form of foods from the diet. If they cannot be identified, it is recommended to keep a food diary, where you indicate the reaction to all the food you eat.
Traditional methods
The use of folk remedies for chronic urticaria will help cope with the disease without negative effects on the body. To achieve better results, you should use the following recipes:
- Application of milk of magnesia. The substance has a calming and protective effect in case of allergies. Milk of magnesia is applied to a cotton pad, which is applied to the blisters on the skin. The duration of the procedure is 10 minutes.
- Therapeutic baths and compresses. Half a cup of starch is mixed with the same amount of baking soda. The resulting mixture is poured with 300 ml of warm water. The bath is taken for 10-12 minutes, the procedure is carried out once a week. The compress is left on the skin for 30-40 minutes.
- Aloe ointment. A small amount of plant juice is mixed with oily vitamin E in a 1:1 ratio. The resulting mixture is applied to inflamed areas of the skin several times a day for a month.
- Herb tea. Two teaspoons of nettle are poured into 210 ml of boiling water and infused throughout the day. The strained infusion is drunk before bedtime. The course of treatment is 2-3 months.
- Green tea. This tasty drink can be an effective cure for hives. To achieve positive results, drink several cups of green tea every day before bed.
- Oatmeal medicine. Two glasses of flakes must be mixed with 3 tablespoons of starch. A little liquid is added to the mixture to obtain a paste-like substance. It is applied to the skin rashes for 20 minutes. This compress will help dry the epidermis and relieve inflammation.
Diagnosis of idiopathic urticaria
If characteristic rashes appear on the skin, the patient should seek help from a dermatologist or allergist. The diagnosis is made based on clinical manifestations and the duration of the disease. Urticaria is considered idiopathic if the exact cause of the pathological process cannot be determined.
Additionally, the following methods are used:
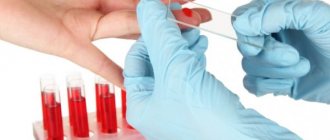
- Blood analysis. A change in blood composition may indicate the development of pathology. A study is carried out for the presence of sexually transmitted infections, and blood sugar levels are studied.
- General urine analysis. The study allows us to identify the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Bacteriological and parasitological examination of stool. The development of idiopathic urticaria can be caused by helminths.
- Allergy tests. During the research process, the specialist conducts testing to determine what substance is causing the hives. If inflammation of the skin is caused by a certain group of allergens, we are not talking about idiopathic urticaria.
- Skin biopsy. The study makes it possible to exclude urtical vasculitis.
A specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis already at the first examination.
To carry out differential diagnosis, you may need to consult with specialists of a narrow profile: endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, urologist, gynecologist, etc. During the study, in addition to urtical vasculitis, pathologies such as anaphylaxis, prurigo, erythema should be excluded.
What is idiopathic urticaria
Idiopathic urticaria is a term that combines a number of diseases that cause allergic red patches on the skin. If the allergen cannot be identified, a diagnosis of “idiopathic urticaria” is made. It can also be a consequence of other diseases. Most often women get sick, less often children.
When dealing with such symptoms, the doctor first of all refers to blood tests, urine tests, and detection of helminths. Having identified or ruled out concomitant diseases, allergy tests are performed.
For a complete medical history, an appointment with a gastroenterologist, dermatologist, etc. is required. Only after excluding the causes of such symptoms among other diseases is a diagnosis of “idiopathic urticaria” made.
How to distinguish from other species?
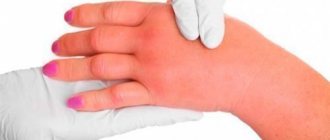
The main distinguishing feature of idiopathic urticaria is the unknown origin of the symptoms. Almost half of the cases of urticaria diagnosed are idiopathic. The rash looks like insect bites that are flat but raised above the surface of the skin and have a clear line. Their diameter varies from 1 mm to 5 cm. The rash appears spontaneously, changing color from red to lighter, and the rash is accompanied by itching.
Blisters appear on different parts of the skin and most often heal without a trace. The surrounding tissues are accompanied by angioedema. Swelling when damaged can begin to become inflamed, which brings additional discomfort. The rash can be caused by allergies, chemical or physical exposure.
Despite its chronic course, urticaria can be both constant and occasional. The rash may go away completely but return. Most often, the rash is provoked by stress, new food, or a different climate.
Chronic form
Urticaria that lasts more than six months is chronic. Blisters can appear on the body, be very itchy, and grow together. Allergy symptoms are not difficult to cure, but even the most experienced doctor cannot identify their cause.
To determine the cause, the patient undergoes sensitivity tests to various drugs containing the allergen. If it cannot be identified, immunomodulatory drugs are prescribed to relieve symptoms.
Non-allergic idiopathic urticaria
Symptoms of non-allergic urticaria also include itchy blisters that periodically appear in different places on the skin. The diagnosis is made in the absence of allergic reactions to the most common pathogens.
Angioedema occurs in 50% of patients with urticaria; they can also be of an allergic or non-allergic nature. Swelling does not cause itching, but a feeling of tension and discomfort in the places where it is localized. They last on the skin for up to 48 hours. Unlike urticaria, swelling affects a deeper layer of skin.
Non-allergic angioedema is caused by a deficiency of immunity, as well as the presence of the disease in the parents. In these cases, the swelling has a dense surface and does not cause itching or discomfort.
Treatment
The effectiveness of therapy directly depends on understanding the nature of the disease, as well as the factors that provoke the appearance of rashes. Unfortunately, in most cases it is not possible to determine with high accuracy what could lead to the development of pathology. Therefore, therapy includes a set of measures aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms and treating concomitant diseases.
Drug therapy for idiopathic urticaria may include the following groups of drugs:
- Antihistamines. Medicines from this group help relieve swelling and itching. The drugs Clemastine and Loratadine show good results.
- Sorbents. These products remove toxins from the body, as well as waste products of pathogenic microflora. You can use Activated carbon, Sorbex.
- Glucocorticoids. Drugs from this group are prescribed if the inflammatory process is localized on the face or other visible areas. Prednisolone and Hydrocortisone ointments can be used.
- Digestive enzymes. Drugs from this group normalize the digestion process and reduce the negative effects of certain nutrients. For idiopathic urticaria, the drugs Mezim and Festal can be prescribed.
Additionally, drugs aimed at treating concomitant pathologies can be used. These can be antifungal, sedatives, medications that normalize metabolic processes in the body.
Many antihistamines lead to side effects such as drowsiness and lethargy. In addition, the substances included in antiallergic medications negatively affect the liver. Therefore, you should never start taking this or that drug without consulting a doctor.
Drug therapy - gallery
Sorbex removes toxins from the body
Ointment helps relieve symptoms of urticaria
For urticaria, antihistamine therapy is mandatory.
Food enzyme normalizes the metabolic process
Diet for idiopathic urticaria
A patient with an inflammatory process on the skin needs to adjust his diet. First of all, you will have to give up foods that can provoke the development of allergies. These include:
- brightly colored fruits and vegetables;
- products with preservatives and dyes;
- coffee;
- chocolate;
- citrus;
- fresh milk;
- chicken eggs;
- smoked meats.
A hypoallergenic diet is the key to successful treatment of the disease
The diet is prepared by a specialist based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient. During the period of exacerbation of idiopathic urticaria, good results are shown by a dairy-vegetable diet, including:
- boiled or steamed vegetables;
- dairy products;
- neutral fruits (bananas, apples);
- milk porridge.
You can include boiled beef in the menu. You will have to reduce your consumption of salt and spices. But I recommend drinking more fluids. A person suffering from idiopathic urticaria needs to drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
It will not be possible to eliminate the cause of the pathological process with the help of physical influence. But some techniques can remove the unpleasant symptoms of urticaria and speed up the process of epidermal restoration. The following procedures show good results:
- UV therapy. Ultraviolet rays penetrate the affected tissues, providing a general strengthening, immunostimulating, anti-inflammatory effect.
- Electrophoresis. Medicinal substances are introduced into the body using an electric current.
- UHF therapy. An ultra-high frequency electric field has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
Electrophoresis helps eliminate the unpleasant manifestations of urticaria
Plasmapheresis shows good results for idiomatic urticaria. The technique involves plasma purification. Blood is drawn and biological material is purified from immune complexes, antibodies, and toxins. The purified plasma is reintroduced to the patient.
ethnoscience
There are many remedies that can eliminate the unpleasant manifestations of urticaria. In order not to aggravate the situation, the possibility of using one or another prescription should be discussed with your doctor.
Celery
Freshly squeezed celery juice is an excellent anti-allergy remedy. It can be taken orally (a tablespoon before meals) or wipe the affected areas with a swab dipped in the product.
Oak bark
Therapeutic baths help eliminate redness and swelling. Pour 250 g of oak bark into a liter of water, bring to a boil and cook for 20 minutes. Then the product must be filtered and poured into the bath. The treatment procedure is recommended to be carried out daily for 15 minutes.
Calming tinctures
In some cases, urticaria appears due to emotional overstrain or stress. Soothing tinctures based on valerian and hawthorn will help solve the problem. Ready-made medications can be purchased at the pharmacy. 15 drops of each tincture are combined with half a glass of water and drunk before bed.
Potato
The raw vegetable has excellent anti-inflammatory properties. The potatoes are grated on a fine grater, the juice is squeezed out a little, and the resulting pulp is applied to the inflamed areas. The compress can be secured with a gauze bandage. After 30 minutes, the product must be removed and the inflamed area should be rinsed with warm water. Skin with hives can also be treated with freshly squeezed potato juice.
Traditional medicine recipes - gallery
Grated fresh potatoes are used for medicinal compresses
Oak bark baths help relieve inflammation
Valerian tincture has a pronounced calming effect
Celery is a natural anti-allergy remedy
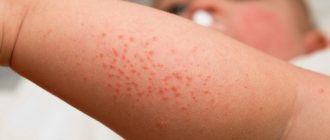
Idiopathic urticaria in children
Symptoms
In children, the disease may be accompanied by a number of others:
- digestive system problems;
- ENT organs;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diseases of the nervous system.
Children sleep restlessly; scratching the blisters often leads to their inflammation and a rise in temperature at night.
Photo
Treatment
Treatment is also aimed at strengthening the immune system and relieving symptoms. It is important to protect the child from provoking factors. It is necessary to limit contact of the child’s skin with synthetic fabrics and household chemicals. Many of your child's toys may contain allergens, which is important.
Choose clothes and bedding made from natural fabrics, replace soaps and shampoos with hypoallergenic ones. Parents should help the attending physician collect a complete picture of the disease, which will help identify the allergen. During treatment, it is necessary to protect the child from chocolate, allergenic fruits, and junk food.
Both children and adults can be referred to physiotherapy procedures - electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation, UHF therapy.
A doctor practicing dermatovenerologist talks about the causes, diagnosis, symptoms and treatment in the video:
Treatment prognosis and prevention
Unfortunately, it is not possible to get rid of idiopathic urticaria 100%. After complete elimination of unpleasant symptoms, they often appear again. The provoking factor may be certain medications, food, emotional stress, hypothermia, ultraviolet radiation, etc. Patients with recurrent idiopathic urticaria are not recommended to visit baths and saunas or take hot showers.
Simple preventive measures will allow you to lead a fulfilling lifestyle
Treatment of idiopathic urticaria cannot be neglected. First of all, because pathogenic microorganisms can easily penetrate the body through inflamed areas, provoking the development of serious life-threatening diseases. In addition, people with chronic idiopathic urticaria are at high risk of developing angioedema, which can lead to suffocation.
Patients with an unpleasant diagnosis have to follow simple preventive measures throughout their lives:
- adhere to a hypoallergenic diet;
- promptly treat any diseases of internal organs;
- stop using household chemicals;
- choose only hypoallergenic cosmetics;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- undergo an annual examination by a dermatologist.