What is chronic urticaria?
Chronic urticaria is a disease that is initiated by various causes, based on an allergen or other pathogen. As a result of the body's reaction, a rash appears on the skin. The course of the process for more than 6 months, as well as recurrent manifestations, characterizes the chronic form.
On this topic
- Hives
What are the dangers of mechanical urticaria?
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 17, 2020
It is possible to diagnose the disease using various studies, but it is not always possible to detect the pathogen. Therefore, for preventive purposes, people suffering from allergies are advised to reconsider their lifestyle and diet. These are the main ways to prevent periods of exacerbation and treatment.
According to statistics, children at an early age fall asleep due to improper selection of nutrition (formula). Among adults, cases of urticaria are more common in women than men.
Diagnostic measures
Before curing the disease, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis. This is done by a dermatologist or allergist. Despite the fact that the pathology does not pose a serious danger, it causes various inconveniences to the patient. In this regard, it is recommended to seek medical help as soon as possible.
It is unlikely that it will be possible to recover completely. However, with properly selected therapy, the duration of periods of remission can be significantly increased.
During an exacerbation of the disease, making a correct diagnosis is not difficult. To do this, the doctor will only need to assess the condition of the skin. During the period of remission, it is much more difficult to identify pathology.
An allergist may prescribe provocative skin tests. During their implementation, the integument is exposed to the intended irritant. For example, an ice cube, ultraviolet rays, water, and heat can act as a provoking factor.
Classification
Urticaria is classified according to the causative factors and pathogenetic mechanisms that provoke rashes on the skin:
- The autoimmune form is characterized by a long and severe course of the disease. Diagnosis is based on the lack of response to antihistamines.
- The idiopathic form is observed in chronic urticaria. A special feature is the inability to determine the allergen.
- The papular form is determined by the pathogen associated with an insect bite.
- The spontaneous form is characteristic of the chronic course of the disease. It appears for no apparent reason; it is not always possible to determine the causative agent due to the complex mechanism.
- The hereditary form is determined by the genetic tendency to react to an insect bite, flowering period or contact with some substance.
On this topic
- Hives
How to prevent an allergic reaction like hives
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 28, 2020
Physical form is determined by the body’s reaction to certain stimuli:
- due to mechanical effects (cholinergic type);
- after a sharp change in temperature (cold type);
- as a result of stress or deterioration of the psycho-emotional background (psychogenic type);
- after contact with an allergen (contact type).
Chronic disease occurs in different forms:
- recurrent (graphically the process is reflected by a peak curve that periodically changes the course of development);
- persistent (constant renewal of the skin rash).
acute and recurrent urticaria
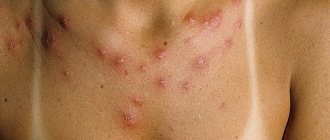
Urticaria is a skin disease associated with the appearance of an allergic rash. In shape and size, it resembles the blisters that appear after being struck by nettles, hence the name.
In the acute form, rashes appear literally in the first minutes after interaction with the provoking factor, they pass quickly - within a few hours. If the effect of the allergen is not eliminated, a recurrent form of the disease occurs.
A single episode does not require treatment, but chronic urticaria will not go away without treatment. If you experience symptoms of hives, you should definitely consult a doctor.
At CELT you can get advice from a gastroenterologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,200
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Mechanism of disease development
Urticaria differs from other dermatological and allergic diseases in the presence of a clear and understandable relationship between exposure to an allergen and the appearance of rashes.
Most often, patients can independently name the provoking agent - symptoms appear within a few minutes after contact with the provoking agent.
If the causes of urticaria are unknown, then first of all it is recommended to pay attention to contact with animals and diet.
An immediate allergic reaction develops as follows: the allergen enters the body, mast cells are immediately sent to it - they cause the release of immunoglobulin E.
When a mast cell is exposed to high levels of immunoglobulin, it produces histamines, substances that increase vascular permeability and cause swelling.
This is a protective mechanism that allows the body to block part of the allergen, and remove part as quickly as possible.
The provoking factor may not be a substance, but a physical effect - heat or cold, stress. Allergies can also be caused by the presence of a source of infection in the human body.
In clinical diagnosis, acute and chronic forms of urticaria differ in duration - if episodes of urticaria are present for 6 weeks and are interspersed with periods of remission, then a diagnosis of chronic urticaria is made.
Causes of development and forms of urticaria
The cause of urticaria is contact with an allergen. There are many factors that can provoke a pathological response of the immune system (this is an allergy). Most often, urticaria is caused by contact with such groups of substances as:
- Medicines, especially antibiotics and hormonal drugs.
- Dust.
- Animal fur or feathers.
- Plant pollen, poplar fluff.
- Substances that get under the skin from insect bites.
- Compounds that parasites secrete are most often caused by Giardia.
- Some substances contained in food products.
For the development of acute urticaria, short-term contact with the allergen is sufficient. The chronic form is characterized by frequent relapses and is associated with prolonged proximity to the substance causing the pathological reaction. Therefore, at the first manifestations of an allergy, it makes sense to conduct special tests, find out what exactly caused the rash, and exclude any contact with this substance.
In the chronic form, the rash and inflammation are less pronounced. After an exacerbation, the symptoms disappear for a while. Recurrent urticaria may be associated with the presence of a source of infection in the body and requires consultation with a specialist.
Symptoms of urticaria
The disease has specific manifestations, so there are usually no problems with making a diagnosis.
Specific symptoms of allergic urticaria:
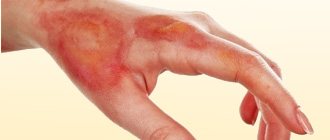
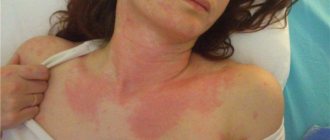
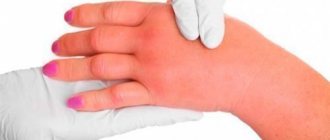
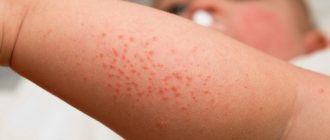
- Skin rashes resembling blisters from contact with nettles.
- When pressed, the blisters are white and lose color.
- Itching that leads to scratching.
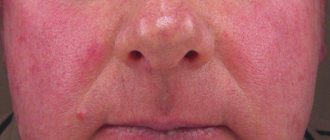
- The skin at the site of the lesion is swollen and red.
- The rash can appear on any part of the body in its acute form; sometimes urticaria even affects the mucous membranes.
- In chronic pathology, the rash often appears on the bends of the arms and legs.
With direct contact with the allergen, rashes appear quickly, within a few minutes, and disappear without a trace in a maximum of 2 days. The rash subsides within 3-6 hours.
If complications develop, skin symptoms may be accompanied by swelling of the larynx, fever, weakness, headache, nausea, and difficulty breathing.
If life-threatening complications occur, you must take any antihistamine and call a doctor. If allergy symptoms only include hives, then emergency care is not required. In this case, it is worth making an appointment with an allergist to establish a diagnosis and avoid chronicity of the disease.
Diagnosis of urticaria
Diagnosis begins with an examination by a medical specialist and most often ends at the stage of collecting an anamnesis. Typical urticaria is associated with the presence of a specific allergen. Most patients had atopic reactions in childhood. Visual assessment of the skin helps to make a final diagnosis - urticaria can be easily distinguished from other skin diseases.
If there are symptoms, but the patient finds it difficult to name the reason for the development of the pathological reaction, a number of specific tests are performed.
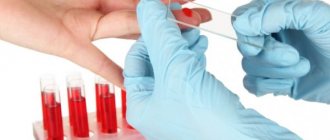
Laboratory tests include determination of general and specific immunoglobulin E, as well as a general blood test. Special provocative tests allow you to identify a fairly specific allergy provocateur.
If the cause is not established, further diagnosis involves testing for parasitic infestations.
Treatment of the disease
If the allergen is known, then the main recommendation is to avoid, if possible, contact with the substance that provokes hives.
That is why accurate diagnosis is important - it is necessary to understand which group of chemical compounds can lead to the development of urticaria. It often happens that the same substance is found in different foods or in different pharmaceuticals.
And an allergy to pets can affect only one breed or spread to almost all pets, from cats to hamsters.
Therapy is needed if the disease has become a recurrent form - this happens if it is impossible to stop contact with the provocateur. In a situation where test results show the presence of an infectious focus, it is necessary to determine the infectious disease. It is likely that the urticaria will go away after healing.
If a patient is diagnosed with an allergy to dust, food or plants, then lifestyle changes are required: frequent wet cleaning, following a proper diet and avoiding walking during the flowering period of plants. Concomitant treatment is designed to alleviate symptoms when they reappear.
Factors that initiate the development of urticaria
The causes of the disease are divided into two categories.
Endogenous, resulting from disruption of internal organs:
- gastritis;
- pancreatitis;
- helminths;
- diseases ;
- inflammation of various types in the oral cavity (on the gums, teeth), etc.
On this topic
- Hives
The best treatments for generalized urticaria
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 18, 2020
Exogenous, associated with exposure to external factors:
- reaction to chemicals ;
- hypothermia or overheating;
- friction or vibration.
The presence of chronic inflammation in the body provokes bacterial infection, resulting in chronic urticaria.
ROLE OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF ALLERGY.
Clinical and experimental studies show that changes in the body's hormonal levels can That is, it is an interconnected process.
Activation of the pituitary-adrenal and sympathetic-adrenal systems under stressful conditions inhibits in some cases the development of allergic reactions and inflammation. Against the background of adrenalectomy, on the contrary, anaphylactic shock and a number of other allergic reactions in animals are more severe.
Allergic processes cause activation of the pituitary-adrenal system. This activation is nonspecific, secondary and is a response to damage. At the same time, allergic changes occurring in the adrenal glands themselves block the synthesis of cortisol to one degree or another and often enhance the formation of corticosterone. Repeated exacerbations of allergic processes lead to depletion of this system. Therefore, in patients with long-term allergic diseases, a certain degree of insufficiency of the adrenal cortex is always detected.
Symptoms
Among the main manifestations of the disease is a pink rash. Cavityless elements can be of different shapes with a diameter from 0.5 to 15 cm. The central part of the affected area may have a slightly pale tint.
A characteristic feature of blisters is their ability to change, merging with each other and rising above the surface of the skin.
The spread of the focal zone throughout the epidermis affects the subcutaneous fat, resulting in the development of Quincke's edema. Localization of swelling is most often observed on the face (in particular on the lips, tongue), as well as the genitals.
On this topic
- Hives
How to cure water urticaria permanently
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 13, 2020
Sometimes other parts of the body become affected:
- neck;
- limbs;
- palms and soles;
- torso.
The progressive form of the disease poses a great danger to the larynx area. There is a spontaneous deterioration in general condition due to lack of breathing. In such cases, immediate medical attention cannot be avoided.
The chronic course of the disease differs from ordinary urticaria in less severe rashes and periodic exacerbations. Pinkish lesions appear on any area of the skin. Often the process is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, headaches, weakness, and aching pain in the joints.
In case of damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive system, the following may occur: nausea, vomiting, loose stools. Among the most unpleasant sensations is an obsessive and increasing itching, which causes nervous breakdown and insomnia.
Based on the results of a blood test, thrombocytopenia and eosinophilia are diagnosed.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that there are many causes of the disease, different diagnostic methods are used. Sometimes it is enough for the attending physician to examine the patient and study the history of his card.
On this topic
- Hives
How to avoid cold urticaria
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 12, 2020
The final diagnosis is made after laboratory tests, which include tests:
- blood (CBC, biochemical);
- urine (OAM);
- feces (coprogram).
Data from blood tests do not show any significant changes in urticaria, with the exception of an increase in the level of eosinophils. If other indicators deviate significantly from the norm, then the cause of the characteristic symptoms may be another disease.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following may also be prescribed:
- blood test for RW and antibodies to HIV infection (if necessary, to helminths);
- coprogram (stool examination), etc.
To conduct an extensive examination, we recommend:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- radiography (chest);
- Ultrasound (abdominal cavity);
- biopsy (immunofluorescent method).
It is worth noting that an impressive list of studies is carried out to diagnose the chronic form of urticaria, since other types are determined by a different algorithm.
The course of the disease in a recurrent form or the unclear picture based on the results of the tests given gives grounds for the doctor to prescribe a full medical examination.
This will help identify foci of chronic infection that has developed as a result of an allergic reaction to microorganisms and their metabolic products.
On this topic
- Hives
How to prevent the development of cholinergic urticaria
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 12, 2020
On the recommendation of the attending physician, the patient can be referred to specialized specialists: gynecologist, otolaryngologist, oncologist.
Different types of diets are used for diagnosis:
- elimination, which involves the consistent exclusion of products from the menu that are suspected of having an allergic reaction;
- provocative, in which ingredients with allergenic properties are sequentially added to the diet.
Dietary techniques are based on monitoring the body in order to identify the pathogen.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of symptoms of dermographic urticaria, adherence to the prevention of exacerbations helps:
- Clothing must be loose, without elastic bands, narrow straps, or rough seams;
- You cannot wear tight, constricting socks or tights;
- It is not recommended to carry bags and backpacks on your shoulders;
- When washing your body, you should use only soft washcloths;
- It is not advisable to take long walks, especially in high-heeled shoes;
- When working sedentarily, you need to get up and stretch once every half hour;
- Sports training should be chosen that avoids impacts, pressure on the body and falls.
You also need to learn not to react violently to stress. The severity of symptoms is partially reduced by following a hypoallergenic diet and strengthening the body's defenses.
Dermographic urticaria is not a fatal disease, but the pathology can negatively affect both personal life and work.
Therefore, it is necessary to choose the most optimal therapy and follow all the doctor’s advice. In most cases, the disease completely stops within a few years of its onset.
Treatment
There are different methods of treating chronic urticaria, but they all have a common first stage, which is to remove the allergen from everyday life or diet.
The medical approach involves the use of drugs. But first the patient undergoes an examination in order to exclude any inflammatory processes. Deworming is also performed to prepare the body for treatment.
Pharmacological drugs are prescribed individually. The following groups of products are most often recommended:
- antihistamines;
- magnesium sulfate;
- hyposulfite ;
- desensitizing (calcium-based);
- sedatives (calming the nervous system).
On this topic
- Hives
How to prevent the development of hives from the sun
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 11, 2020
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the severity of the disease. In severe cases, 1st generation antihistamines (intramuscular injections) are used. In some cases, intravenous administration of the drug is prescribed.
It sometimes takes quite a long time to identify the cause. However, common factors in the mechanism of development of chronic urticaria make it possible to quickly begin treatment, thereby localizing the spread of lesions.
Reasons for development
Recurrent urticaria is the most common type of the disease. The development of numerous red rashes on the skin indicates that the body is exposed to a certain allergen, which causes organ cells to begin to produce a beneficial protein called histamine. After the release of this substance, liquid seeps through small capillaries, which over time accumulates in the layers of the epidermis and causes urticaria.
Dermatologists note that the mechanism of development of the chronic form of the disease is autoimmune in nature. All patients in this category contain LgG antibodies. It is they who activate even dormant mastocytes of the skin, thereby forcing them to attack healthy cells of the body. As a result, a severe allergic reaction develops. The main causes of recurrent urticaria can be safely called lupus erythematosus, damage to the thyroid gland, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes mellitus.
The chronic form of the disease is closely related to menopause, since it is during this period that natural hormonal changes occur, which can provoke activation of the pathology. In addition, urticaria can also occur under the influence of other pathologies:
- Helminthiasis.
- Viral type hepatitis.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Dental problems (caries).
- Hypothyroidism.
- Vitiligo (the appearance of multiple white spots on the skin).
- Inflammation of the appendages in women.
Do not forget that not only diseases, but also allergens (triggers) can provoke the development of urticaria. Against this background, a person may encounter unpleasant symptoms and complications. Most often, multiple red rashes on the skin appear under the influence of the following factors:
- Drinking drinks that contain caffeine.
- Exhaustion of the nervous system due to frequent stress and depression.
- Alcoholic drinks.
- Excessive pressure on the epidermis (wearing clothes and shoes that are smaller).
- Medications (aspirin, various painkillers, opiates).
- A sharp decrease/increase in temperature.
- Consumption of food additives (specific salicylates contained in dyes, tomatoes, orange juice).
- Skin exposure to hard, chlorinated water.
- Various insect bites.
- Regular use of ACE inhibitors, which are effective in combating hypertension. In some cases, angioedema may occur.
Diet
Dietary nutrition is prescribed in cases where the cause of the disease is a food allergen. The menu is quite varied, but requires strict adherence to restrictions.
Recommended ingredients for the diet table:
- types of meat - turkey, rabbit;
- porridge – buckwheat, rice, corn;
- oils (moderate amount) – vegetable, butter;
- bakery products – hypoallergenic cookies, yeast-free bread;
- vegetable set - zucchini, broccoli, dill, salad, potatoes (let sit in water for 15-20 minutes before cooking);
- milk derivatives - kefir, cottage cheese (homemade, but not too fatty).
Sugar should be replaced with fructose, the amount of salt should be reduced by 3 times or completely abandoned during treatment. If you include fish dishes in the menu, then preference should be given to freshwater varieties; seafood contains pronounced allergenic properties.
Complication
The most dangerous complication of chronic urticaria is swelling of the throat and tongue, which causes breathing problems and even anaphylactic shock. Without emergency medical care, a person may die. Manifestations of Quincke's edema disappear on their own within three days.
In almost 30% of patients, urticaria becomes chronic. The duration of treatment in some cases leads to depression. If your psycho-emotional background worsens, you should seek advice from a psychotherapist; using the latest techniques you will be able to cope with this complication.
Chronic urticaria can also signal other diseases, such as cancer. Forecasts in such cases are unforeseen.
The development of various complications occurs in young children who have not been treated for urticaria provoked by baby food (formula or cereals). Timely refusal of a product with an allergen can literally save a child’s life.
Key Features
In the first stages of development, urticaria is accompanied by multiple red blisters that can affect different areas of the skin. Externally, such rashes are very similar to burn marks. These formations are accompanied by severe itching and burning. Over time, they merge into larger lesions or appear as separate spots. Dermatologists have found that individual rashes can appear within a month. The longer the blisters remain on the skin, the greater the likelihood that the disease has become chronic.
The patient may experience periodic exacerbations, which are necessarily replaced by remissions. Repeated relapse always occurs when the disease is first activated. But this pathology has a main feature - all symptoms are eliminated immediately after the acute stage is stopped.
Depending on the causes of exacerbation of the disease, experts are accustomed to distinguishing between several main forms of the disease. Practice shows that papular urticaria is the most difficult to treat. But during diagnosis, another type of disease can be determined:
- Physical. The disease occurs as a result of the development of an allergic reaction to unfavorable external factors: direct sunlight, cold, vibration, heat. In addition, numerous rashes can be triggered by mechanical or physiological effects on the surface of the skin.
- Chronic urticaria. The reasons for the development of this form of the disease are very diverse. In some cases, a combination of several unfavorable factors may occur. Blisters always have clear boundaries and rise above the surface of the skin. Often the rash is accompanied by severe swelling. Patients experience malaise and a critical increase in temperature. In the absence of quality treatment, a person’s quality of life may deteriorate.
- Infectious. Pathology develops after the penetration of pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasitic infections into the body. Once the underlying cause is eliminated, the disease can be treated.
- Papular. This disease is characterized by a certain seasonality. Most often, rashes appear after a wasp, mosquito or bee bite. Small blisters may appear on the skin, which gradually turn into papules. This form of the disease is diagnosed in the summer in 99% of all cases. The limbs, face, and neck are most affected.
- Nervous urticaria. This disease most often develops into a chronic stage. Rashes develop against a background of nervous experiences and emotional instability. The disease can recur after increased stress, tension and depression.