Definition of disease
Heat urticaria and its antipode, cold urticaria, are considered types of temperature urticaria, which affects about 7% of the world's population. It most often occurs among children and young people, although many cases have been recorded among older people.
Dermatologists distinguish two forms of heat urticaria:
- local. Occurs at the site of direct skin contact with a heat source.
- cholinergic. It is a non-standard reaction of the body to an increase in internal temperature and can appear in the following situations:
- when visiting a sauna or steam bath;
- after a hot bath or shower;
- while walking in hot weather;
- after sports or other physical activity;
- when consuming hot foods and drinks or alcohol;
- for various diseases accompanied by increased body temperature;
- as a result of severe nervous excitement or stress.
Skin rashes can appear in women during menopause against the background of periodically occurring “hot flashes”, accompanied by increased sweating.
In what cases is it necessary to reduce a child’s temperature?
This question is a stumbling block for pediatricians. Some insist on starting to treat hives as soon as they reach 38°C. Their arguments include depression of the child’s general condition, a malfunction of the immune system, and the body’s inability to cope with both the allergen and its own reaction to it.
Other pediatricians, and it should be noted that there are many more of them, on the contrary, prohibit lowering the temperature during urticaria until it reaches 39°C. In this case, the arguments are completely different:
- Most microbes and viruses, if we are talking about a secondary infection or disease, stop reproducing at temperatures above 37°C
- Interferon is produced in the body only at 38 degrees and above. The amount of interferon reaches its maximum on the second or third day after the temperature rises and that is why most infectious diseases, including acute respiratory viral infections, end safely on the third day.
The task of parents is to provide the body with the opportunity to lose heat, which occurs when sweat evaporates and when the inhaled air warms. That is, the room should be relatively cool, the air humid. The child needs to be given as much liquid as possible - teas, compotes, fruit drinks, water, etc. It no longer matters what he drinks, the main thing is how much.
The truth, as usual, is somewhere in the middle and you should always focus on the child’s condition and well-being.
Reasons for appearance
To date, the etiology of thermal urticaria has not been clarified. According to dermatologists, the trigger of the disease is the organic substance acetylcholine, released in large quantities by the body when exposed to high temperatures.
Under the influence of acetylcholine, the so-called mast cells located in the subcutaneous layer release histamine into the blood, which is a mediator of allergic reactions. As a result, the permeability of the capillary walls increases, through which liquid leaks and blisters appear on the body.
Factors that can trigger heat urticaria include:
- the presence of autoimmune diseases (diabetes mellitus, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, systemic lupus and others);
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- excessive wrapping in cold weather, leading to increased sweating;
- insufficient development of the immune system;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- nervous and emotional instability.
In most cases, heat urticaria occurs against the background of other allergic diseases. At the same time, the risk group includes people with a hereditary predisposition to allergies.
What antipyretic drugs can be taken for urticaria?
The choice of drug depends on the patient's age and the active substance. As for age - up to a year it is better to choose rectal suppositories, up to 5-6 years - syrups and suspensions, over 6 years - tablets, lozenges, etc.
There are 2 groups of active substances that are used to make antipyretic drugs for children - ibuprofen and paracetamol. The principle of action is the same, but every 3rd patient experiences an allergic reaction to paracetamol.
Based on paracetamol the following are produced:
- Cefekon;
- Calpol; Paracetamol;
- Panadol;
- Efferalgan.
Based on ibuprofen:
- Ibuefen;
- Nurofen;
- Motrin.
It is strictly forbidden to wipe children with alcohol and vinegar solutions to reduce the temperature of urticaria. Not only does the child already feel bad, but the parents additionally poison his body through such activities.
Symptoms
Heat urticaria, like other varieties, can occur in acute or chronic form.
- spicy. Symptoms appear suddenly and “gain in intensity” over a short period of time. Duration of the disease – no more than 6 weeks;
- chronic. It is characterized by relapses that can bother a person for months and even years. It is possible that the intensity of manifestations may increase with each new attack.
In the acute form, the likelihood of dangerous complications such as anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema is several times higher than in the chronic form.
The main signs of heat urticaria include the following:
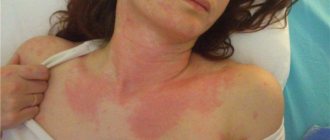
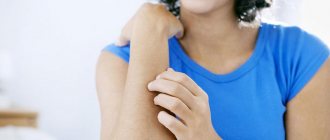
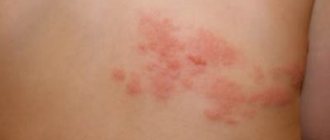
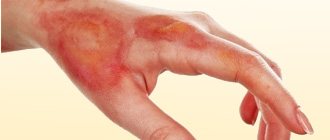
- the appearance on the body of bright pink voluminous blisters, similar to traces of nettle burns;
- redness and swelling;
- severe itching;
- a feeling of skin tightness and burning when touched.
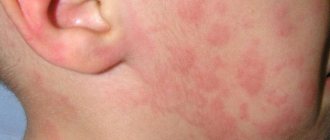
With the cholinergic variety, the blisters are smaller (up to 2 mm in diameter) and have a bright red color in the center and pale pink at the edges. In the generalized form, the rashes can merge, covering large areas of the body.
Some patients with thermal urticaria experience the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- nausea, vomiting;
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- headache;
- increased salivation;
- general malaise.
If in the local form the rashes usually appear on the area of the skin that was in direct contact with the thermal irritant, then in the cholinergic form the blisters often form on the chest, neck, forearms, face, and can spread throughout the body.
Can there be a fever with urticaria in adults?
In an adult, urticaria itself does not provoke fever. The maximum is up to 37°C, and even then, this is rather a statistical error. The temperature rises with complications and repeated infections - in this case the mark reaches 39-40°C.
Interestingly, high temperature can also lead to the appearance of urticaria; it is called allergic urticarial dermatosis. This is how the body reacts to the release of interferon. And this form of urticaria is accompanied by itching, hyperemia and the formation of monomorphic blisters. Symptoms usually go away within 24 hours.
If even with a single episode of urticaria the temperature rises sharply, the patient has an underlying disease. Most often this is:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- fungal and bacterial infections;
- diseases of the endocrine system and disorders of the thyroid gland;
- problems of the lymphatic system.
Be sure to contact your physician to schedule an examination. Urticaria very rarely acts as an independent symptom; it is rather an indicator of the disease.
Diagnostics
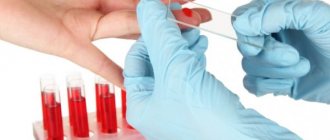
If you experience symptoms of heat urticaria, you should make an appointment with a dermatologist or allergist. After a visual examination and questioning of the patient, the doctor will prescribe a series of tests that will help identify the cause of urticaria.
These include:
- the patient’s hand is lowered into a bath of hot (48-500C) water for 3-5 minutes or a glass with liquid heated to the same temperature is applied to the forearm;
- a person is asked to exercise for 20-30 minutes on an exercise bike or treadmill to provoke sweating and an increase in body temperature;
- Acetylcholine is injected subcutaneously, which in the presence of cholinergic urticaria gives a reaction within 20 minutes.
To identify concomitant diseases, the doctor may give a referral for blood, urine, stool, and ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. In some cases, consultations with other specialists are required: gastroenterologist, immunologist, endocrinologist, neurologist.
Based on the research results, the dermatologist makes a final diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Mechanism of occurrence
When urticaria jumped up, symptoms in children appear due to the high sensitivity of the immediate appearance. In this case, the body responds inadequately to some influence coming from within. It begins to produce histamine , which causes inflammation.
A skin reaction indicates that the body is trying to reduce the concentration of harmful elements.
Urticaria is divided into two forms :
- acute course;
- chronic course.
The mechanism of occurrence of acute urticaria is associated with medications, food factors, insect bites, inhalation of pollen, and blood transfusions.
Research shows that 50% of patients with acute illness most often have other allergic reactions and diseases , in particular bronchial asthma and atopic dermatitis.
Treatment
The effectiveness of treatment for thermal urticaria depends on accurately identifying the causes that provoked it and stopping the sick person from contacting them.
The main recommendations are as follows:
- do not visit saunas and baths;
- swim and shower at a water temperature not exceeding 400C;
- do not take long walks in hot weather;
- do not consume excessively hot food and drinks;
- give up alcohol;
- during vacation, travel to countries with temperate or cold climates;
- do not abuse physical activity, which can cause the body to overheat.
In addition, it is necessary to follow a hypoallergenic diet so as not to provoke allergic reactions.
Traditional therapy
The difficulty in treating thermal and cholinergic urticaria lies in the low effectiveness of antihistamines, which is caused by an excess of acetylcholine in the body. Second generation antihistamines “work best” for this disease:
- Claritin;
- Erius;
- Cetrin;
- Zodak.
In addition, to treat affected areas of the skin, external preparations are used, which include atropine and belladonna extract, as well as the following ointments:
- Fenistil gel;
- Psilo balm;
- La Cree;
- Nesulin.
The last two remedies can be used to treat young children and women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
In severe cases, when the rash spreads to large areas of the body, ointments containing corticosteroids are used:
- Triderm;
- Advantan;
- Akriderm;
- Celestoderm.
A cool shower or bath, ice packs, and rest in a cool room will help improve a person’s condition.
In case of nervous excitement, which can also provoke an attack of thermal urticaria, the use of sedatives is indicated - Notta, valerian tincture, Motherwort-Forte, Novopassit.
If you follow all the doctor’s prescriptions and recommendations, the symptoms of acute heat urticaria can be cured within a few days. The chronic form of the disease, if preventive measures are taken, goes away in 6-10 months.
When and how to reduce the fever?
Temperatures up to +38°C indicate the development of an inflammatory process. The hypothalamus specifically causes hyperthermia to facilitate the destruction of pathogens. In this case, you should not take medications. If the temperature rises to +38.5...+40°C, immediate use of antipyretics, application of cold compresses and ice baths are required.
In what cases is it necessary to reduce a child’s temperature?
When there is a fever against the background of urticaria, it is necessary to pay attention to the cause of the inadequate immune response. If hyperthermia was caused by an infectious agent, the fever should not be reduced to +38°C. When the reading is above +37°C with simple allergies, it is necessary to take antipyretic drugs.
In the latter case, indicators should not be allowed to increase above +38°C. Otherwise, interferon will begin to be produced, and the patient’s condition will worsen. The body cannot cope with the fever on its own, since the immune system is impaired.
What does official medicine offer?
If the cause of the development of high temperature was urticaria, antihistamines are prescribed:
- Zyrteca;
- Suprastina;
- Citrina;
- Erius;
- Tavegila.
If allergies occur as a result of infection, antipyretic medications such as Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are used. It is forbidden to give Aspirin to children to avoid the development of bleeding from blisters.
Traditional methods
At a temperature of +38°C, you can use traditional methods of treatment:
- Regularly ventilate the room where the patient is located to ensure access to fresh air.
- Give plenty of water. You need to drink 3-4 sips of liquid every half hour. It is not recommended to replace water with juices, compotes and tea. If desired, you can add 1 tbsp to the water. l. lemon or honey.
- A decoction of chamomile and linden helps reduce fever. 1 tsp. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over each ingredient and leave for 2 hours. Give the patient 3 times a day 150 ml.
- Do not force a person to eat.
- Avoid using warm blankets. They disrupt heat exchange.
The patient is provided with complete rest. He must remain in bed. Physical activity can lead to recurrent hyperthermia.
Complications
Neglect of treatment for urticaria and ignoring the dermatologist’s instructions can cause serious and dangerous complications.
These include:
- angioedema angioedema - spread of rashes and swelling to the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, oral surface, and larynx. May cause respiratory failure and asphyxia;
- anaphylactic shock, in which a decrease in blood pressure and loss of consciousness occurs in a matter of minutes. If emergency care is not provided, it leads to death.
There is also a danger of secondary infection of the affected areas of the skin with pathogenic bacteria that enter the subcutaneous layer through wounds from scratching. As a result, a person may develop symptoms of a serious purulent-inflammatory disease - pyoderma.
Everything you need to know about nettle fever
Rash and fever are nonspecific, that is, symptoms characteristic of various pathologies. When they appear, you need to think not only about allergies, but also about infection, intoxication (poisoning) and a number of other diseases. Therefore, it is important to know the characteristics of nettle fever to avoid confusion during diagnosis.
Reasons for development
The temperature reaction with urticaria is most often a consequence of allergies. If the body comes into contact with a substance that the immune system perceives as foreign, and therefore dangerous, protective reactions are triggered with the participation of special protein complexes - antibodies and biologically active substances - histamine, bradykinin, etc. The following may act as a provocateur:
- Food product.
- Medicine.
- Chemical.
- Juice, pollen and plant extracts.
- Insect poison.
The development of fever in urticaria may also be based on autoimmune reactions and exposure to physical stimuli (vibration, pressure, heat). Sometimes the frequency of exacerbations depends on climate conditions. Thus, heat is dangerous for patients sensitive to the sun, and low temperatures will lead to a rash in the cold form of the disease.
Features of hyperthermia in adults
Patients most often experience so-called low-grade fever – an increase in temperature within the range of 37.1 to 37.9 °C. They tolerate it relatively easily; if the area of skin damage is small, hyperthermia may not occur at all. If it occurs, then, as a rule, there are accompanying symptoms:
- general weakness;
- chills;
- skin itching;
- muscle and joint pain;
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- poor tolerance to physical activity.
The condition improves after the rash disappears. Fever due to urticaria usually does not pose any serious threat to adult patients; it appears, like blisters, suddenly, grows quickly, but is most pronounced at the initial stage of development of an acute reaction.