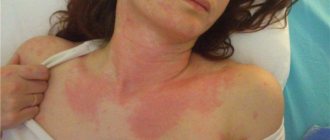
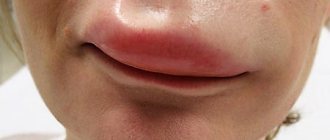
Consequences of urticaria in adults.
Urticaria often occurs in young children when transitioning from breastfeeding to a regular diet, but in them it resolves with fewer complications than in adults.
After 16 years of age, its occurrence is fraught with very dangerous consequences, even death, if urgent measures are not taken. We will consider the consequences of urticaria in adults below.
What it is?
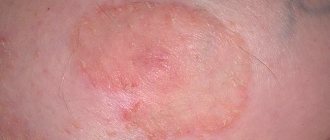
Urticaria is an allergic disease, the main manifestation of which is the appearance of blisters .
Such a reaction of the body occurs as a result of a certain irritation. Urticaria is a group of diseases that have one common symptom - blisters that are constantly itchy and have a clear demarcation. They rise above the surface of the reddened skin; the size of such blisters can be several millimeters or several centimeters. The main feature of this disease is that urticaria, the symptoms of which appear very quickly, can disappear equally quickly with adequate treatment. Thus, the disease sometimes manages to develop and disappear within a few hours.
Types of the disease and their external manifestations
The disease is distinguished by the nature of the disease.
There are several types of classification of cirrhosis. According to the etiological factor, they are divided into those whose causes have been established, those with questionable or unknown origin. According to the clinical course, biliary, portal, hypertrophic and mixed types are distinguished. All of them are manifested by general and local symptoms.
In liver cirrhosis, the nervous system is the first to be affected, so initial symptoms such as fatigue, drowsiness, irritability, forgetfulness, and others are nonspecific. Specific symptoms increase and appear gradually. When examining a patient, the doctor pays attention to small signs of the disease, including:
- The tongue and mucous membrane of the mouth are bright red, swollen and shiny.
- Redness of the palms, hands, or entire arm.
- Angiomas on the face.
- Spider veins. Localized on the stomach, above the navel.
- Atrophy of the genital organs.
- Gynecomastia and erectile dysfunction in men, menstrual irregularities in women.
- Swelling of the lower extremities and muscle atrophy.
- General malaise, fatigue, weakness.
- Nosebleeds.
Minor signs of the disease do not differentiate its type and do not indicate the etiological factor that provoked the development of the disease. They cannot determine the stage of the disease. Signs only indicate the presence of a problem, and laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods, as well as specific symptoms, make it possible to more accurately determine the type of cirrhosis.
Biliary type of disease
The skin and eyes take on a yellowish tint.
This type of disease is caused by stagnation of bile. Externally it manifests itself as dark yellowness of the skin, severe itching and the formation of yellow plaques on the eyelids, chest and face, pain and hardening of the organ, darkening of urine and discoloration of feces. Swelling, which is not relieved by antihistamines, is explained by an excess of bile acids in the blood, which enter the subcutaneous tissue and irritate the nerve endings.
A decrease in itching occurs with the development of hepatocellular failure.
Alcoholic cirrhosis
The pathology develops after prolonged liver poisoning with alcohol-containing substances. The signs of such cirrhosis are especially significant in the last stages of organ destruction. Among them:
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- dry jaundiced skin with stars;
- itching;
- yellowness of the sclera;
- weight loss;
- hyperthermia.
Cirrhosis of viral etiology
The pathology is caused by a virus.
Its development is facilitated by viral hepatitis of various forms, the presence of which a person may not even know. Infection occurs mainly through the blood and leads to impaired liver function and inflammation. The development of cirrhosis of viral etiology is accompanied by a sharp increase in the size of the gland and abdomen, the skin and sclera become bright yellow. Complications such as bleeding into the abdominal cavity and peritonitis are common.
Types of urticaria
Experts distinguish several different types of this disease, guided by the reasons that provoked its development. If a person prone to allergic reactions has had a disrupted diet , it means there is a food allergy. Separately, doctors distinguish cold, mechanical, and solar forms of urticaria. Cholinergic urticaria develops as a reaction of the autonomic nervous system to exposure to heat or physical activity. The term “demographic urticaria” is also used, which also develops under the influence of etiopathogenetic factors and is a physical form of the disease.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the course of the disease, doctors distinguish acute and chronic forms. Chronic recurrent urticaria develops against the background of infection. Urticaria pigmentosa is the result of pathological processes of skin cells. What urticaria looks like in this case depends on the intensity of the processes occurring. Sometimes these can be very pronounced spots of a blue-red hue.
Trying to determine what urticaria is and how this disease occurs in humans, experts sometimes make a diagnosis of “idiopathic urticaria.” Such an allergic reaction occurs for no apparent reason, and this situation occurs quite often. At the same time, medications (ointments, creams, etc.) may not have a positive effect on the patient’s condition.
Urticaria also occurs relatively often during pregnancy. Such an allergy in pregnant women can be either a result of exposure to the allergen described above, or a reaction to hormonal changes in the body of the expectant mother.
Consequences of urticaria
According to statistics, every fourth person on the planet has suffered from urticaria at least once in their life.
The disease itself does not seem to be the most terrible, but it causes a lot of trouble for its “lucky” owners.
Causes and symptoms
Urticaria is a special form of dermatitis. When talking about this unpleasant illness, people mean a skin disease in which severely itchy pale pink blisters appear on the surface of the body. Outwardly, it resembles a burn from contact of an open area of skin with nettles. It is customary to divide urticaria into acute and chronic forms.
Causes of acute urticaria:
- allergies to food (it can be caused by fruits and vegetables of red or orange color, chicken eggs, honey, nuts, chocolate, caviar, and less often - fish);
- allergic reaction to insect bites (bees, wasps, hornets and even mosquitoes);
- allergies to various medications (antipyretics, antibiotics, phytotherapeutic products);
- allergic reaction to blood products (this is possible with blood transfusion, as well as its components);
- Oddly enough, stress can cause hives. In this case, it is curable only if a person achieves a certain mental balance. As for the chronic form, allergens have nothing to do with it;
- it sometimes occurs as a result of a malfunction of the immune system, when the body mistakes its own cells for foreign ones and tries to fight them. It also happens that chronic urticaria appears after exposure to high or low temperatures, as well as due to ultraviolet irradiation (including in a solarium);
- Sometimes a hormonal imbalance can trigger hives in women.
People suffering from chronic hives are advised to check their blood sugar levels to rule out diabetes. In addition, the doctor may prescribe an examination for carriage of helminths, because the waste products of parasites can cause skin rashes.
Consequences of urticaria in adults
Is hives dangerous? Yes, definitely. People suffering from acute urticaria should listen very carefully to their feelings, because in some cases angioedema may begin.
This most terrible consequence of the allergic form of the disease often develops rapidly. The swelling spreads to the larynx, the person feels an acute lack of oxygen.
Probability of death
Can you die from hives? Yes, such a severe allergic reaction as swelling of the throat and tongue impairs breathing.
As a result, a person may die from anaphylactic shock if he does not receive emergency medical care.
Conclusion
To urgently temporarily relieve the extremely unpleasant symptoms of urticaria, you can take one of the antihistamines available on hand.
But it is not recommended to treat this insidious disease on your own.
He will prescribe comprehensive treatment, and, if necessary, give a referral for additional examination. It should be remembered that urticaria can be a manifestation of various serious diseases, including cancer.
What consequences may appear in adults after urticaria?
Urticaria often occurs in young children when transitioning from breastfeeding to a regular diet, but in them it resolves with fewer complications than in adults.
After 16 years of age, its occurrence is fraught with very dangerous consequences, even death, if urgent measures are not taken. We will consider the consequences of urticaria in adults below.
What causes urticaria in adults?
In adults, urticaria is less common than in children, but the consequences can be very dangerous. After all, it occurs against the background of various disturbances in the functioning of the body. This is what this disease leads to if you don't take action.
Reasons for appearance
In adulthood, this disease rarely occurs in a completely healthy body. Most often, it indicates immune disorders as a result of existing diseases. The following factors can provoke urticaria:
- poisoning and the presence of parasites in the body;
- drug intolerance;
- neoplasms;
- food allergies;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- insect bites;
- reaction to organ transport or blood transfusion.
Causes of urticaria
An allergen that provokes the development of urticaria can be any substance. This could be food, flower pollen, or medicine. Also, urticaria in children and adults sometimes appears after an insect bite or as a consequence of exposure to an infection on the human body. Even waste products of microorganisms can trigger the development of urticaria. To prevent the occurrence of such an allergic reaction in the future, it is important to determine what exactly caused the hives. In some cases, simple observation will be effective, but sometimes the patient needs to undergo a series of laboratory tests.
The development of acute urticaria most often occurs as a result of exposure to drugs, food, insect bites or infections. The chronic form of urticaria manifests itself as a consequence of certain pathological processes that occur in the internal organs of the patient. Also, the chronic form of urticaria occurs with disorders of the nervous system. In the classification of forms of the disease, physical urticaria , which occurs as a reaction to heat, cold, pressure, exposure to sunlight, vibration, and physical activity.
Due to some etiological factors, chemically active substances accumulate in human tissues, for example, histamine , which increases the permeability of vascular walls. Accordingly, the capillaries , swelling of the papillary dermis occurs, and as a result, blisters appear on the patient’s skin.
Allergens are sometimes incompletely broken down protein products, which, penetrating into the blood, induce the production of antibodies to certain foods. Also, an allergic reaction can be triggered by toxins that contain spoiled food, toxic substances that are formed in the body of patients with colitis , as well as in people with insufficient kidney function. Bacterial allergies may also occur. In the process of the occurrence of urticaria, an important factor is functional disorders of the nervous system. Thus, cholinergic urticaria manifests itself during nervous excitement due to the release of acetylcholine .
Urticaria develops as a result of increased vascular permeability of the microvasculature and the subsequent development of edema around the vessels. Blisters with urticaria are a consequence of hypersensitivity, which occurs against the background of an increased level of concentration of biologically active substances.
Urticaria is a toxic-allergic dermatosis , which has a polyetiological genesis.
As factors that have pathogenetic significance, concomitant diseases should be noted - chronic focal infection , helminthic infestation , biliary dyskinesia , gastrointestinal disorders , allergies to medications .
In medicine, the causes of urticaria are divided into exogenous (pharmacological, nutritional, physical, temperature) and endogenous (pathology of internal organs).
Urticaria - symptoms and treatment
Diagnosing urticaria does not require specific laboratory diagnostics, although identifying the causes of the disease may require it.[3]
First of all, you need to see an allergist-immunologist as soon as possible. If there are no rashes at the time of the visit, try to provide the doctor with photographs of the rashes/swelling for maximum information (provided that the clinical manifestations were not severe and did not require emergency assistance during photographic recording).
During the appointment, the allergist-immunologist will collect a detailed medical history, life history, allergy history, and conduct a physical examination (examination, measurement of blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature, listen to the heart and lungs, palpate peripheral lymph nodes, abdomen). In most cases, this diagnostic complex will be sufficient to make a diagnosis and select therapy.[2]
In more than 90% of cases, acute urticaria resolves within two weeks and does not require special examination, unless the triggering agent is identified.[1]
If there are frequent relapses of acute urticaria or there is a chronic disease, you will need:
- general blood test with leukocyte formula and ESR calculation;
- study of some biochemical blood parameters;
- examination for the presence of viral hepatitis B, C;
- conducting provocative tests (ice cube for suspected cold urticaria, hot heating pad for thermal urticaria, water compress for aquagenic urticaria, exercise test for suspected cholinergic urticaria, etc.);
- determination of antibody levels to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin with an intradermal test with autologous serum;
- scratch tests with non-infectious allergens and/or the presence of specific immunoglobulin E in the blood for any allergen.[2]
If further diagnostic search is necessary, it would be advisable to:
- Ultrasound of internal organs (thyroid gland, abdominal cavity, pelvis);
- FGDS or fluoroscopy of the stomach;
- X-ray examination of the chest organs and paranasal sinuses;
- virological or bacteriological examination for the presence of infectious agents;
- analysis of the level of antibodies to the Cag A protein of Helicobacter, Giardia, helminths;
- rheumatic tests (ANF, AT to DNA, CRP);
- studies of complement components C3, C4, etc. [3]
An important diagnostic test in patients with urticaria is skin testing.[9] They are informative in patients with atopic urticaria and negative in patients with pseudoallergic urticaria (subject to the timing of the tests and the accompanying preparation for testing).[5] The bilirubin test against the background of an elimination test is also informative (carried out in a hospital, therapeutic fasting is prescribed with the intake of only water, showers and cleansing enemas). If the result of elimination, reduction or relief of symptoms is positive, the allergic genesis of urticaria is confirmed. In patients with allergic urticaria, the bilirubin level is reduced or within normal limits, in patients with pseudoallergic urticaria it is increased.[4]
Symptoms of urticaria
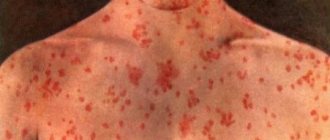
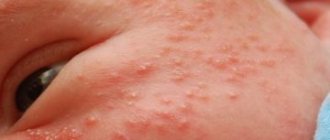
Symptoms of urticaria are mainly manifested by pathological formations on the skin. In more rare cases, such formations appear on the mucous membranes. These can be blisters of different sizes, which rise above the skin level, have a pink tint, and are swollen and dense. The outlines of the blisters can be either round or large scalloped, sometimes they are pale in the center.
It is common to distinguish several different types of urticaria. In the acute form of the disease, urticaria suddenly affects a person, and he develops urticarial rashes and very severe itching. The blisters that appear are pale pink in color and vary in size. At the same time, in the center the blister is matte, and at the edges it has a pink color. The shape of the blisters can be either round or completely uneven. In some cases, such blisters may merge into a single area. Such a process for the patient is fraught with a general deterioration of his condition: so-called nettle fever occurs. Acute urticaria can appear on the mucous membranes of the palate, tongue, larynx, and lips. As a rule, this form of the disease occurs as an allergic reaction to certain foods or medications. In some cases, urticaria, the symptoms of which appear very sharply, occurs after vaccinations, the administration of certain medications, or blood transfusions.
The so-called artificial urticaria is an atypical form of this disease, which is characterized by the appearance of rashes on the skin that have a linear shape. In this case, patients do not complain of itching. This form of urticaria occurs in humans mainly as a consequence of mechanical irritations.
If the patient has a high sensitivity of the body to allergens, then he may experience chronic recurrent urticaria . This form of urticaria is provoked by a chronic infection, problems in the digestive tract, or other reasons. It often develops against the background of chronic infectious diseases - cholecystitis , tonsillitis , etc.
Periodically, relapses of the disease, in which blisters appear on the skin, alternate with remissions that last for different periods of time. When blisters appear, a person suffers from itching, his temperature may increase, and headaches may occur. The itching is sometimes so severe that the patient suffers from sleep disorders and neurotic disorders.
With acute limited Quincke's edema (the so-called giant urticaria ), a sharp development of limited swelling of the skin, as well as the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the face, occurs. A person’s cheeks, lips, eyelids suddenly swell, and the genitals may also swell. The general appearance of the skin changes: it becomes white or pink and becomes densely elastic. During the development of Quincke's edema, stenosis and asphyxia may occur.
If a person suffers from solar urticaria , the symptoms of this disease appear in the summer. This disease mainly manifests itself in women. Especially often, solar urticaria accompanies liver disease , and also occurs in people who suffer from disorders of porphyrin metabolism and have high sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. With solar urticaria, urticarial rashes appear on areas of the skin that remain exposed to direct sunlight. Basically, in this case, the hands and face are affected. Solar urticaria is a type of photodermatosis . If a person suffering from this disease stays under the sun's rays for a long time, then in addition to rashes, he sometimes also develops a general reaction of the body, in which cardiac activity and breathing are disrupted. Shock may occur.
Another type of disease is cold urticaria (another name is cold allergy ). In this case, skin damage occurs after a person has been exposed to the cold for a long time. The cause of the rash is too much cryoglobulin . These are antibodies that accumulate in the body.
secondary are divided into primary and cold urticaria. The secondary form of urticaria occurs as a consequence of an allergic reaction to metabolic that appear in the skin due to exposure to low temperature. Also, cold urticaria occurs due to the individual characteristics of the body constitution.
To confirm the diagnosis of both solar and cold urticaria, an exposure test is taken from the skin.
In contact urticaria, which is a type of allergic dermatitis , a person develops blisters immediately after coming into contact with certain antigens. In some cases, the body reacts to such contact with a generalized urticarial rash.
Is urticaria dangerous and what will happen to the patient without treatment?
Many people have heard about hives, as well as the fact that in most cases it is associated with an allergic reaction.
A food product, an insect bite, washing powder - this is not the entire list of likely triggers for the occurrence of itchy blisters. But is urticaria dangerous to health and life? What are the consequences for a patient who does not receive treatment? Read about all this in the article.
This term refers to a group of diseases that, despite different causes, development mechanisms and provoking factors, have a common feature: the presence of an itchy, uniform rash in the form of blisters on the skin.
Elements (urticaria) appear suddenly and disappear without leaving traces; exist no longer than 24 hours. In this case, episodes of the reaction can be repeated (that is, recur) for 6 weeks (acute form) or more (chronic course).
People at risk of developing urticaria:
- people with a hereditary predisposition to allergies;
- patients with autoimmune disorders;
- patients with pathologies of the endocrine, digestive, and nervous systems, including those with intestinal dysbiosis syndrome;
- persons who abuse or for some reason are forced to take many medications;
- patients suffering from infections (bacterial, viral, fungal).
The development of the disease is promoted by stress, poor diet, and lack of breastfeeding. Provocateurs (triggers), contact with which triggers a skin reaction, are various substances (allergens). These are food products, medicines, insect poison, chemicals, cosmetics. There is a possibility of sensitivity to physical influences - vibration, pressure, heat, cold.
Thus, urticaria can occur not only as a form of allergy; sometimes it can also be provoked by physical factors (non-immune variant).
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Both patients and their families have legitimate concerns about whether urticaria may pose a serious health threat. Let's try to figure this out.
Why is urticaria dangerous?
The rash itself does not have a poor long-term prognosis. A blister is an element without a cavity, resulting from swelling of the papillary layer of skin. It disappears, as it appears, quite quickly and without traces - without forming any erosions or wounds. Therefore, with isolated urticaria, although the patient is irritated and frightened due to the rash, there is no direct threat to health and life.
At the same time, one should ask the question: why did the urticaria make itself felt? What disease led to its development? After all, if you do not pay attention to episodes of rash, over time they may become more frequent, and the underlying pathology (for example, intestinal damage accompanied by dysbacteriosis) worsens.
You should also remember the risk of developing Quincke's edema. This is a swelling of dense consistency that can be localized externally (cheeks, eyelids, lips), in the digestive and respiratory tract, and affect the nervous system. Because of it, there is a risk of asphyxia (suffocation), due to the blocking of the lumen for the passage of air in the larynx area.
In addition to what has already been listed, it is worth keeping in mind that urticaria can be part of the clinical picture of dangerous immediate hypersensitivity reactions due to allergies.
In addition to Quincke's edema, these are bronchospasm (narrowing of the airway due to muscle contraction) and anaphylactic shock (a critical drop in blood pressure, leading to oxygen starvation - hypoxia; has a high risk of mortality).
What complications exist in adults?
If the reaction is mild and limited to blisters that last a few hours on isolated areas of the skin, usually no adverse effects should be expected. The greatest danger in such cases is scratching: due to increased friction of itchy areas, tissue trauma occurs and infection can penetrate into the resulting “entrance gate” (scratches, wounds).
If we are talking about a severe course, the consequences of urticaria in adults may include such conditions as:
- development of respiratory failure and asphyxia (suffocation) with swelling of the larynx, bronchospasm;
- injuries and neurological disorders as a result of a seizure;
- anaphylactic shock.
Such disorders are usually associated with allergies. It is very difficult to predict how severe an exacerbation episode will be, but in all cases attention must be paid to prevention.
Possible complications in children
A child, like an adult, can suffer reactions of varying severity. Most often they are caused by allergic sensitivity to foods, insects and other provocateurs. Possible consequences for urticaria in children are:
- Asphyxia (suffocation) with bronchospasm, laryngeal edema;
- Trauma, neurological symptoms after a seizure attack;
- Infection as a result of active scratching;
- Dehydration (dehydration) due to frequent vomiting, diarrhea, high body temperature.
The younger the child, the more severely any complications of the reaction affect him. The lumen of the respiratory tract in children is narrow, so the development of life-threatening respiratory failure with laryngeal edema occurs faster than in adults.
The danger of dehydration should also not be underestimated: with fluid, the patient loses electrolytes - substances necessary for the normal functioning of the body.
As a result, heart rhythm disturbances and other secondary pathological conditions may occur.
What happens if the disease is not treated?
If the question relates to the period of acute reaction, there are two main scenarios:
- cessation of an episode of disturbances several hours (up to a day) from the onset of symptoms;
- the occurrence of complications, the formation of secondary pathological conditions and, possibly, death.
The prognosis must take into account the likelihood of the worst ending - if the disease is not treated, there is always a danger to life. In the period between attacks there is no cause for concern, but after provoking a reaction, the patient should be treated immediately - the risk is too obvious to ignore even a mild form of the course. In addition, urticaria can be combined with other allergic diseases:
- Hay fever;
- Allergic dermatitis;
- Bronchial asthma.
It may also be a precursor to their development. Not the cause, since there is no direct connection, but the primary pathology in the “allergic chain” or “march” in a particular patient. However, reasonable treatment in combination with prevention helps prevent the formation of such unfavorable links.
Is the disease curable?
It is difficult to completely get rid of this disease, especially if its development is associated with the presence of chronic pathologies of the functional systems of the body. But with adequate therapy and compliance with preventive measures, there is every chance of transferring the patient to a state of remission. In a broad sense, this is recovery, and in a narrow sense, it is the absence of symptoms until new contact with the trigger.
Currently, there is a way to reduce sensitivity to provoking substances - allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT).
The patient is sequentially administered increasing doses of the potential trigger, and if the outcome is successful, he develops tolerance (immunity) to it.
This means that repeated contact will not trigger a reaction involving antibodies (protective complexes) of the IgE class - and, accordingly, there will be no symptoms either.
The method is not 100% effective, requires a long course of treatment, and has contraindications (childhood, pregnancy, presence of a tumor, etc.). May be dangerous for patients with a history of anaphylactic reactions, including shock.
How to recognize?
In order not to confuse this pathology with another, similar disease, you should have an idea of the main clinical signs. Urticaria in adults and children is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the presence of a rash in the form of blisters - red, porcelain, plain or with a border;
- absence of exudate (liquid) in the elements;
- itching of varying degrees of intensity;
- the possibility of damage to absolutely any area of the skin;
- the risk of the formation of Quincke's edema in the lips, cheeks, external genitalia, mucous membranes.
These are all local symptoms; Both the patient and the attending physician can be confused by the so-called systemic, or general manifestations:
- Weakness;
- Headache;
- Chills;
- Fever;
- Flatulence;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Diarrhea;
- Runny nose;
- Cough.
The combination of manifestations resembles an infection, and with severe abdominal pain, even surgical pathology may be suspected. Therefore, vigilance and attentiveness are required.
Blisters with urticaria disappear within 24 hours and are not combined with other types of rashes.
However, there are exceptions (usually typical for children). This is the presence of small bubbles on the surface of the elements, the appearance of spots and nodules. However, blisters still predominate; careful differential diagnosis is needed.
How to treat ?
Various methods of therapy are used, which are also measures to prevent exacerbations:
- diet;
- elimination (limiting contact with the provocateur);
- taking medications.
During the acute period of the reaction, you should not eat foods that cause symptoms and those types of food that have a high allergen-provoking potential:
- Citrus;
- Tomatoes;
- Mushrooms;
- Shrimps;
- Crabs;
- Eggs;
- Milk;
- Chocolate;
- Coffee;
- Nuts;
- Peanut.
Elimination is determined by the type of provocateur; Diet is one example of restrictive measures. Urticaria can also be treated with pharmacological drugs:
- antihistamines (“Cetrin”, “Zyrtec”, “Erius”);
- glucocorticosteroids (“Prednisolone”, “Dexamethasone”).
They are used in a course to provide routine and emergency care to patients of different ages.
Tatyana Torsunova
Sources: medscape.com, mdlinx.com, health.harvard.edu.
Source: //roddom32.ru/krapivnitsa/chem-opasna.html
Diagnosis of urticaria
As a rule, diagnosing acute urticaria is quite simple; this can be done by both an allergist-immunologist and a general practitioner. But in some cases, to select the correct therapy, it is necessary to determine the allergen. It can be identified using a number of special studies. Autoantibodies can be isolated using markers for Epstein-Barr and hepatitis B . The patient also undergoes a general and detailed blood test, urine test, skin test, and liver tests. biopsy is required .
If the patient has signs of systemic pathology, then he needs to undergo rheumatological tests. The fact is that urticarial and urticarial elements can also occur in other diseases, so a thorough examination of the patient is important.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with Dühring's dermatosis , since similar symptoms are observed with this disease.
Increased life expectancy in liver cirrhosis
Following an effective treatment plan that can slow or stop liver damage and manage complications is the main way that people with cirrhosis can increase their life expectancy.
Treating the underlying cause of cirrhosis is also critical. Although alcohol abuse is not always the cause, patients with cirrhosis may benefit from abstaining from alcohol altogether, as doctors recommend. Antiviral drugs can prevent additional liver damage if viral hepatitis is the cause.
Patients with cirrhosis should see their doctors regularly to find out how their condition is progressing. Medicines and treatments to treat symptoms of cirrhosis include:
- diuretics to reduce excess free fluid
- laxatives to reduce toxins
- beta blockers to reduce portal hypertension
- shunting to reduce blood pressure
- liver transplantation
Prevention of urticaria
As measures to prevent the development of urticaria, it is important to treat gastrointestinal diseases, eliminate foci of chronic infection, and exclude all factors that can provoke allergies. It is necessary to maintain a balanced diet.
Prevention of urticaria in children requires a very careful attitude to all irritants. Therefore, all new foods should be introduced into the diet carefully and gradually. It is important to take measures to strengthen the child’s immune system. If your baby is prone to frequent allergies, he should be periodically taken to see an allergist.
The use of preventive measures is available if the cause of urticaria is precisely known. So, with cold urticaria, you need to avoid hypothermia, with solar urticaria, you need to hide from direct rays of the sun. You should also avoid taking medications, eating foods that cause such reactions, etc. It is currently impossible to prevent the chronic form of the disease.