Flat condylomas are one of the types of HPV with endophytic growth. The main difference between this type of neoplasm is that, unlike genital warts, flat condylomas grow deep into the tissue, causing structural changes that are invisible to the naked eye . May be located on the cervix in women.
Condylomas appear due to the penetration of the human papillomavirus (HPV) into the body. As a rule, their formation is caused by oncogenic types of HPV , which can often be subject to the process of malignancy (malignant degeneration).
What is the danger of flat condylomas
Flat condylomas in most cases develop in women on the cervix and arise due to invasion of oncogenic types of HPV into the body. Such conditions can develop with decreased immunity or with prolonged absence of treatment.
Both options are dangerous due to the high risk of damage to the cervix and the subsequent development of precancerous conditions and cancer .
Even non-oncogenic types of HPV that abundantly affect the cervix will lead to the development of constant bleeding, menstrual irregularities, and painful sexual intercourse. And constant injuries to flat condylomas can lead not only to infection, but also to malignancy, despite the absence of dangerous strains of papillomavirus.
Development of the disease
The incubation period of the pathogen can be up to several years
. In general, if we talk about the pathogen of the disease, we can note the simplicity of its occurrence. The virus, which causes the growth of condylomas, penetrates one of the epithelial cells. After this, it begins to exist in it, not always immediately provoking any process.
The incubation period of the pathogen can be quite long – up to several years. In rare cases, the disease appears immediately. Symptoms appear after the virus penetrates the nucleus of a human cell, changing its DNA structure. This leads to the fact that this small particle of the body begins to work incorrectly. It produces its own division, thereby provoking the formation of formations on the mucous membrane. This process spreads over time to several cells. If they are located nearby, the condyloma becomes quite large. In the case when they are localized in different parts of the cervix, several not very large papillomatous formations appear on the organ.
Causes of formation of flat condylomas
Flat condylomas, like genital warts, develop in connection with HPV infection . The virus penetrates epithelial cells, causing their increased division.
For unknown reasons, flat condylomas begin to grow not outward, like other papillomas, but deep into the tissue.
It is paradoxical that, with a seemingly almost complete absence of external manifestations, the endophytic growth of condylomas is much more dangerous and more often ends in the malignancy of neoplasms.
Causes of growths
The presence of human papillomavirus in the body does not guarantee that growths will begin to appear. Some people are carriers, but throughout their lives they do not encounter external manifestations of the disease.
For the progression of the disease, provoking factors are necessary, which are:
- stress and conflict situations at home or at work;
- hormonal contraceptive pills and other drugs that change human hormonal levels;
- hormonal imbalance caused by various diseases;
- viral or infectious diseases of chronic course;
- a pathological process leading to a weakening of the functions of the immune system.
Children most often become infected with the human papillomavirus during childbirth from the mother or poorly disinfected medical supplies.
Symptoms and signs of development
In some cases, flat condylomas can manifest themselves as cervical erosion , sometimes they can be completely asymptomatic.
Although women may complain of pain during intercourse and spotting at different periods of the cycle.
The main diagnosis is made during a gynecological examination and a series of tests. If necessary, a biopsy is performed for histological examination.
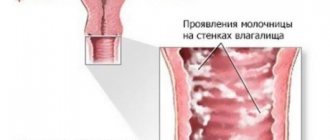
Cervical condylomas
The development of cervical condylomas is quite rare and should always be differentiated from polyps, erosions, endometriosis, cancer and some other conditions.
These tumors are detected only during a gynecological examination. Women may consult a doctor due to long or painful periods, complain of pain during sexual intercourse, as well as bleeding that occurs after sex or spontaneously.
Photo 1. Sudden gynecological bleeding may be a sign of the proliferation of condylomas. Source: Flickr (Francisco Sosa Lemus).
Flat condylomas during pregnancy
During pregnancy, physiological immunosuppression (decreased immunity) develops, associated with a high concentration of estrogens and the prevention of the development of an immune response aimed at the fetus.
This condition allows all previously dormant infections to manifest themselves. HPV is no exception and its manifestations can develop in any trimester of pregnancy.
The formation of flat condylomas occurs , as a rule, with manifestations of papillomavirus already existing before pregnancy . They must be removed due to two factors:
- During the process of a child passing through the natural birth canal, he can become infected with papillomavirus, which will negatively affect his health in the first years of life;
- The presence of any neoplasms of the cervix can serve as an obstacle to its normal opening during childbirth;
- Due to physiological immunosuppression, the already significant risk of malignancy of flat condylomas increases.
Course of the disease
The human papillomavirus can be stored for a long time in the genital epithelium. Despite all attempts, experts have not yet been able to determine the exact cause of this phenomenon. In addition, in some cases, neoplasms in different parts of the body and mucous membranes may not manifest themselves for several decades. But under the influence of various unfavorable factors, a kind of degeneration of flat papillomas into dangerous malignant neoplasms can occur.
Other carriers of HPV infection may experience a fairly rapid growth of condylomas, which is why all therapeutic measures should be taken as quickly as possible. It takes 3-5 years for a benign tumor to degenerate into a malignant tumor. If activation of the virus occurs in a young person, then the reproductive system may be seriously affected. Any transformation of condyloma can develop into cancer.
As metastases grow, there is a rapid deterioration in health, due to which a person loses his ability to work, his body temperature rises, there is acute pain in the affected area, as well as physical and nervous exhaustion. In an advanced stage, condylomatosis can affect the anal area. The whole danger is that at the initial stage, papillomas are invisible. Only after the rapid growth of growths does the patient experience severe itching and burning during bowel movements.
The process of wart formation itself takes only a few hours; there are no vessels inside them, which is why such papillomas are rarely large. Sometimes there are situations when, after a short period of time, the growths dry out and fall off on their own, due to which there is no need to undergo drug therapy.
Diagnosis of flat condylomas
Diagnosis of these formations is carried out during a gynecological examination . , areas of altered mucous membrane, disruption of the integrity of the epithelium, and minor bruising can be detected on the cervix .
To differentiate flat condylomas from other formations, two methods are used :
- When flat condylomas are moistened with 3% acetic acid, white granules or spots appear on their surface;
- When Lugol's solution is applied, flat condylomas absorb it unevenly, different from the surrounding healthy tissue.
It is mandatory to take a test to determine the HPV type .
Carrying out a PCR or Digene test allows you to accurately determine the presence or absence of oncogenic strains of the virus.
This study is especially important for cases of benign or malignant neoplasms in the female reproductive system that have already existed in the past.
Genital warts of the cervix
These are genital warts on a relatively short stalk or wide base, which can constantly grow, or appear in single “inflorescences”. On the mucous membrane of the cervix they are visible as pale pink, pointed multiple formations of irregular shape. Unlike flat condylomas, these forms are usually clearly visible when examining the cervix in women, even with the naked eye.
Routes of transmission of the virus:
- During unprotected sexual contact.
- From mother to child during childbirth.
- Through general hygiene supplies.
- Contaminated objects inserted into the vagina.
- Not sterile instruments in honey. institutions.
Risk factors:
- Immune deficiency.
- Prolonged stress.
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Having 2 or more STDs.
- Early start of intimate relationships.
Symptoms:
- Burning, itching in the vagina.
- Unhealthy discharge.
- Unpleasant sensations during sex.
- Contact bleeding.
- Foul odor (in advanced cases).
Being a clinically obvious manifestation of human papillomavirus infection, if left untreated, cervical warts can quite successfully spread to other parts of the reproductive system. Most often they appear on the labia, vaginal walls and, with known sexual preferences, in the anus and oropharynx. If condylomas grow in the urethra, the person will experience discomfort when urinating.
Diagnostic measures are similar to those for detecting flat warts. A full examination of the genital organs, urethra and anal canal to identify possible “daughter” lesions, colposcopy and a Digen test are mandatory.
Treatment options
Due to the fact that flat condylomas occupy rather inaccessible areas of the mucous membrane and are difficult to detect with the naked eye, it is not possible to remove them using a laser, liquid nitrogen, electrocoagulation or radio wave method. The most optimal way to get rid of them is surgical excision within healthy tissue.
Surgical removal
The operation can be performed under local or general anesthesia , which depends on the size of the tumors and the wishes of the patient.
The presence of flat condylomas on the cervix is an absolute indication for surgery due to the need for histological examination. Among other things, removing such a tumor helps prevent its malignancy in the future.
Drug treatment
In addition to surgery, a course of drug therapy is carried out. Antiviral and immunostimulating agents are used for oral administration and keratolytics locally.
To stimulate the immune system, preparations of echinacea, ginseng, thymogen, vitamins C, E are used. To combat papillomavirus, immunoglobulins and Acyclovir are used.
Features of removal during pregnancy
The decision to remove flat condylomas during pregnancy should be made together with the expectant mother, an obstetrician-gynecologist and a dermatovenerologist. If there are indications for a cesarean section, the removal of tumors should be postponed until the postpartum period. In addition, large flat condylomas of the cervix can serve as an indication for cesarean section , since they will interfere with its normal opening. Carrying out operations on the cervix, especially in the second half of pregnancy, can have an extremely adverse effect on the course of both pregnancy itself and childbirth.
Photo 2. Removal of condylomas in pregnant women is a question for discussion with the patient herself and her obstetrician. Source: Flickr (Dirk Houbrechts).
Prevention of flat condylomas
Due to the fact that flat condylomas occur due to infection with papillomavirus, you should avoid contact with people who have all kinds of papillomas , which are determined visually.
Transmission of both genital and flat condylomas occurs during sexual intercourse, even when using contraception.
To avoid the development of the virus and the appearance of flat condylomas, limit relationships with infected people, do not have sexual contact with persons who have any manifestations of the papillomavirus.
Carry out timely treatment and removal of any warts and papillomas.
Unsafe HPV vaccination
Vaccines used include Gardasil and Cervarix. But not all gynecologists approve of them, because there is no accurate data that these vaccines protect against the disease. Vaccines are valid for 8 years from the date of administration. They prevent infection with HPV types 16 and 18. But there are many more types, as we noted above. There is currently no vaccine against other HPV viruses.
Some doctors believe that this type of vaccination may affect a woman's ability to conceive and carry a child to term. But this has not been proven by research. Vaccines have side effects:
- menstrual irregularities (which can cause infertility)
- hormonal imbalance
- inflammatory process in the uterus
- dysfunction of the ovaries, etc.