What's happened
The papilloma has a round or slightly elongated shape, can be light or dark in color (depending on the pigmentation of the location), has a wide or thin stalk through which it is fed.
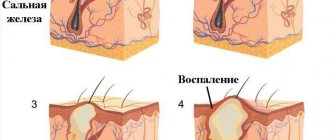
- Papillomas growing on mucous membranes usually have an outer epithelial layer and an inner submucosa.
- Individual growths resemble a pea in appearance, and multiple papillomas (papillomatosis) look like cauliflower.
- Most of the formations on the organs of the digestive tract and respiratory tract are benign, that is, they cannot cause cancer.
But there is a high risk of degeneration of the growth when it becomes oncogenic.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vtdaI_JqQAA
That is why such papillomas must be removed by a specialist, after careful examination and diagnosis.
The formation of papilloma in the throat is due to the active activity of the papilloma virus in the human body. The pathological focus looks like a wart-like growth and is located on the tonsils and their arches, on the soft palate. Papillomas rarely appear on the uvula. Localization of growths in these places is less dangerous than in the larynx and trachea - here they create obstacles to normal breathing.
A benign neoplasm is attached to the mucosa with a thin or wide stalk. Its body is covered with epithelium, under which there is a submucosa. Why does papillomatosis of the throat develop?
Causes of papillomatosis in the throat
In children, infection occurs perinatally, that is, at birth by a mother who is a carrier of the papillomavirus. In this case, the disease becomes respiratory in nature. In adults, the main channel of transmission of the HPV strain is sexual intercourse.
The risk group includes 2 categories of people:
- children under 5 years of age;
- men and women whose age falls within the range of 20 – 40 years.
Factors that provoke the sudden appearance of papillomas may be:
- smoking;
- suppression of the immune system;
- infectious diseases characteristic of childhood (measles and scarlet fever);
- diseases of the organs of perception with a chronic course (chain “ear – throat – nose”);
- promiscuity;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, including in public places.
Laryngeal papillomatosis in adults can develop into cancer. Therefore, it is necessary to approach its treatment responsibly. If the doctor offers a histological examination of the tumor, you should not refuse the procedure.
Clinical picture characteristic of the disease
If there is a small papilloma in the throat, there may be no symptoms. But if a person opens his mouth and looks in the mirror, he will notice a formation. As it grows, the following changes appear:
- feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- difficulty breathing;
- speech disorders;
- difficulty swallowing food;
- feeling as if choking while eating.
Also, a person should be wary of the frequent incidence of sore throat, because papillomas on the tonsils often develop as a result of chronic tonsillitis. During the examination, the doctor observes swelling of the tonsils or fusion of the arches with the tonsils.
In children, the clinical picture of papillomatosis can be expressed through signs of degenerative changes in organs if the baby suffers from renal or liver failure and other similar ailments. Parents should also pay attention to the child’s frequent coughing for no reason, hoarseness and loss of voice, and difficulty breathing in the baby, similar to suffocation.
An alarming symptom of laryngeal papilloma in childhood is a developmental delay - both mental and physical. This is due to oxygen starvation, which developed against the background of impaired breathing. Very often, papillomatosis appears due to a tendency to diseases of the respiratory system (ARVI, pneumonia, bronchitis).
The photo (above) shows papillomas in the throat. A massive accumulation of neoplasms is characteristic of childhood. Single elements are typical for adult patients.
Overgrowths of papillomas look like cauliflower. They are visible in the vestibular part of the larynx, trachea and subglottic space. In childhood, they are dangerous due to myocardial dystrophy and inhibition of the activity of the endocrine and nervous systems.
Methods for treating papillomas formed in the throat
Drug therapy for papillomatosis is based on the prescription of antiviral drugs and drugs with an immunostimulating effect. The first group of drugs is taken for prevention in order to avoid further spread of growths and to suppress the activity of HPV.
Conservative treatment of papillomas is carried out using the following means:
- magnesia;
- arsenic;
- trichloroacetic acid;
- potassium iodide;
- podophyllin in the form of a 10% solution;
- complex of inosine and dimethylamino-2-propanol p-acetamide-benzoate from TEVA Corporation.
Papillomas growing on mucous membranes usually have an outer epithelial layer and an inner submucosa. Individual growths resemble a pea in appearance, and multiple papillomas (papillomatosis) look like cauliflower. Most of the formations on the organs of the digestive tract and respiratory tract are benign, that is, they cannot cause cancer.
Causes of papillomas in the throat.
Papilloma is a benign formation arising from transitional or squamous epithelium. The growth in question has a stem and a head and resembles a mushroom. The blood supply to papilloma occurs due to small vessels that supply the cells with oxygen. The size of the neoplasm is usually small, but it can grow over time.
Papilloma in the throat, depending on its anatomical location, can pose a serious danger to human health. As a rule, the neoplasms are multiple and located close to each other. Possible localizations of growths:
- Cheek mucosa.
- Tongue.
- Tonsils and their arches.
- Larynx.
- Vocal cords.
- Trachea.
About 80% of the world's population is infected with papillomavirus, but not everyone has manifestations of the disease. There are two routes of infection:
- Sexual – transmitted through sexual contact. Infection can also occur when vaginal secretions or semen get on the mucous membranes. It is the latter variant of infection that often provokes papillomatosis in the oropharynx.
- Postnatal – infection occurs at the time of birth of a child by a mother carrying the virus. Infection can occur during passage through the birth canal or during surgical delivery.
Children under five years of age and men are most susceptible to the appearance of benign growths in the throat (due to the increased content of androgens in the body). Congenital papillomatosis is rare.
Carrying HPV does not mean having the disease. This pathology occurs in a latent form in most people. Certain risk factors can trigger the onset of symptoms, including:
- Frequent diseases of the ENT organs of a viral and bacterial nature.
- Consumption of corrosive substances (smoking, alcohol-containing drinks, drugs).
- Contacts with harmful carcinogenic compounds.
- Diseases and conditions that inhibit the activity of the immune system.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Past herpes virus infections.
- Artificial feeding of newborns.
Reasons for appearance
Papilloma in the throat. This is a fairly common complaint with which patients turn to an otolaryngologist. This pathological formation in the form of a papilla on the mucous membrane of the throat causes severe discomfort.
Multiple growths rarely occur; as a rule, the formation occurs in a single variant.
First signs
Spreads to lips, tonsils, trachea. A person infected with papilloma may complain of the following symptoms:
- difficulty swallowing;
- severe sore throat;
- discomfort due to the sensation of a foreign body.
Frequent inflammatory processes in the pharynx, especially on the tonsils, due to exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis lead to the appearance of growths.
Is it necessary to remove papilloma?
The peculiarity of papillomas is their unpredictability. In 40% of cases this is a harmless skin formation. In some cases, they contribute to degeneration into warts or malignant neoplasms.
Symptoms at the initial stage of the disease:
- slight discomfort in the throat;
- sensation of a foreign object;
- cough;
- frequent sore throats.
When the tonsils are affected by papilloma, sore throats are more severe: with swelling that blocks the airways.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Dentist-therapist | What diseases does it treat and when should you contact a dentist? | Competently about health on iLive
As the growth increases, the patient’s well-being worsens due to constant coughing. Papilloma makes breathing difficult and interferes with speaking.
But why tonsils in the holes can appear after a sore throat and what medications can cope with such a problem is described here.
In the video - is it necessary to carry out operations:
According to the degree of growth, papillomatosis is divided into:
- defeat in a separate area;
- on several;
- obstructive, blocking the windpipe.
Papilloma requires removal if there is a risk of its increase in size or the appearance of new growths.
You may also be interested in information about what stomatitis on the tonsils looks like and what pharmaceutical drugs should be used first.
The immune system can overcome single, small papillomas on its own within one to two years. In other cases, treatment is prescribed.
Kinds
There are many varieties and classifications of papillomas.
Only with a visual examination can a doctor determine what kind of tumor it is and prescribe the correct treatment.
Age classification of papillomatosis:
- congenital or intrauterine;
- acquired through domestic or sexual contact;
- children's (juvenile);
- recurrent;
- adult, which occurs more often in men when the production of sex hormones decreases.
By degree of growth:
- in a certain area of the throat - limited appearance;
- in multiple areas - widespread;
- obstructive type, disrupting the air flow through the respiratory tract.
According to symptoms and state of respiratory tract functions:
- it is slightly difficult to inhale and exhale if there is hoarseness and noise during breathing - this is the first compensatory degree;
- shortness of breath, lack of oxygen, bluish skin, anxiety, cold sweat are characteristic of the second degree of decompensation;
- complete cessation of breathing, loss of consciousness occurs due to asphyxia in the third degree of papillomatosis.
Based on the presence of oncogenic properties, papillomas are divided into:
- benign;
- malignant.
congenital or intrauterine; acquired through domestic or sexual contact; children's (juvenile); recurrent; adult, which occurs more often in men when the production of sex hormones decreases.
in a certain area of the throat - limited appearance; in multiple areas - widespread; obstructive type, disrupting the air flow through the respiratory tract.
it is slightly difficult to inhale and exhale if hoarseness and noise appear during breathing - this is the first compensatory degree; shortness of breath, lack of oxygen, bluish skin, anxiety, cold sweat are characteristic of the second degree of decompensation; complete cessation of breathing, loss of consciousness occurs due to asphyxia in the third degree of papillomatosis.
benign; malignant.
The classification of papillomas is varied. Depending on the degree of growth, growths in the larynx can be limited, widespread and obstructive (limiting air access). Depending on the moment of infection, children's (juvenile) and adult papillomatosis are distinguished.
Based on the appearance of the formations, they are distinguished:
- Pointed - growths that tend to merge to form a single bumpy surface.
- Flat – areas with a grainy surface and unchanged color.
- Thread-like - easily injured formations on a thin stalk.
- Simple - pineal-shaped mobile papillomas with a flat base.
- Epithelial hyperplasias are small, soft and mobile growths of a reddish hue.
Classification
There are three types of condylomas of the anogenital area:
- Genital condylomas - this group includes formations of this type that have a low level of oncogenicity. The incubation period can last from 2-3 weeks to six months. Such formations in intimate places look like warts on a thin stalk of flesh-colored or red color. Their structure is similar to cauliflower. They can be either single or multiple. If such a growth is located in a place where it is constantly injured (on the labia, in the anus, etc.), then the growth increases. In addition, secondary infection and subsequent ulceration of condylomas may occur.
- Flat condylomas - such formations mainly appear in the area of the cervix and its thickness. They can also be localized in the vagina in women. From the point of view of potential malignant degeneration, flat condyloma is the most dangerous formation, since it is most often caused by papillomavirus types 16 and 18.
- Lata or papular condylomas are warty-type formations on a wide stalk, which are characterized by a tendency to macerate. This formation is a secondary manifestation of syphilis and is not associated with HPV.
In addition, there is a rare form of this disease - giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma . It develops in the anogenital area and is also provoked by the human papillomavirus. Buschke-Loewenstein condyloma is benign histologically, but clinically demonstrates malignant properties. The formation grows into surrounding tissues and is highly likely to recur.
Removal in children
In children, surgery to remove growths is performed under local anesthesia.
To eliminate papillomas, use:
- cryogenic method;
- electrocoagulation;
- ultrasound.
These methods are the least traumatic, painless, and heal quickly.
Contraindications for treatment:
- presence of open wounds in the mouth;
- temperature;
- cold intolerance;
- blood diseases.
Removal by chemical means is not prescribed. The use of the radiofrequency method, laser and conventional scalpel is limited.
But how the vacuum rinsing of the tonsils occurs and what the price of such a procedure is, is described here.
Folk remedies
Carry out the procedure three times a day until the warts completely disappear. If the wart has just started to grow, try removing it with the white of a chicken egg. Pour the egg, for example, into a frying pan, and apply the white that remains on the walls of the shell to the wart or papilloma.
To boost immunity and get rid of papilloma, traditional healers advise drinking a special healing infusion for papilloma. Mix equal parts of nettle and plantain leaves, horsetail herb, lemon balm and dandelion root, after thoroughly chopping all the plants. Take 3 tablespoons of the mixture and pour 4 glasses of cold water, put on the stove and boil for 7-10 minutes.
Then leave for 2-3 hours, letting it brew. Drink 3 tablespoons of the infusion 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 7 days. You need to take 1 teaspoon of chopped garlic and mix with 2 teaspoons of any base cream. Apply this product to gauze and apply to the papilloma. You can secure the bandage with a bandage.
This compress should be left for 3-5 hours, then wash the area with warm water and soap. Literally within a month the papillomas disappear. Infusion of herbs and ointment with garlic will help reduce papillomas. Infusion. Chop nettle and plantain leaves, horsetail herb, lemon balm and dandelion root and mix in equal parts.
Ointment 1 tsp. mix chopped garlic with 2 tsp. any base cream, apply to gauze and bandage it to the formation on the skin or fix it with an adhesive plaster. Leave for 3-5 hours, then wash off with warm water and soap. And within a month the papillomas will disappear. Take green walnuts of milky ripeness, cut them into slices and grind in a meat grinder.
Fill a liter jar about 2/3 full with this slurry. Add the rest of the volume with purified kerosene. Now you should close the composition with a tight polyethylene lid and leave for 21 days (always in a dark place!). After three weeks, the resulting product should be filtered through 4 layers of gauze, and the remainder should be squeezed out thoroughly.
Pour the resulting liquid into a dark glass bottle, close tightly and place in a dark, cool place. Actually, you need to lubricate papillomas with this product 1-2 times a day until they go away. The healing process can be accelerated by taking freshly squeezed potato juice orally. You need to drink it twice a day, half an hour before meals. The course of treatment is 2 months.
And one more thing: the removal of papillomas is facilitated by increased immunity. For this, you can drink rosehip infusion or the well-known “Immunal”, which, in fact, is an alcohol tincture of Echinacea. A glass jar is loosely filled 1/3 with green sprouts from potato tubers.
Young spring celandine grass (possibly with roots) is washed, slightly air-dried and placed in the same jar up to 2/3 of the volume, about another 1/3 is filled with young shoots of thuja. Fill the contents with pure alcohol so that the alcohol level is higher than the collection, and leave for 10-15 days under a lid in a dark place. It is not necessary to strain the finished product.
The color of the tincture is dark green, almost black. The wart or papilloma is lubricated with the composition three times a day, three times each time. That is, having smeared the wart once, let it dry for one minute, then smear it again, and so on - three times in the morning, at lunch and in the evening. The course of treatment for one papilloma is 5-12 days.
But be careful not to let the tincture get into your eyes or mucous membranes. It is better to start treatment on the waning moon. All components are highly poisonous plants, so keep them out of the reach of children. Mix 100 ml of alcohol, 2.5 g of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), 2 g of boric acid and 2.5 ml of 5% iodine.
After this, the papilloma will fall off. If you apply an ice cube made from an infusion of string, chaga and celandine to the papilloma for 3-5 minutes three times a day, it will gradually fall off by itself. Papillomas - even numerous ones - can be removed with an egg. Take the shells of two eggs, place them on a baking sheet and place them in an oven preheated to 250°C for 30 minutes.
Then, once the eggshells had cooled, she ground them in a coffee grinder until they were powdered. Pour the powder into a glass container and close the lid tightly. Tear the cotton wool into small pieces.
Sprinkle each papilloma generously with egg powder, cover with cotton wool on top and secure with adhesive tape. Wear this bandage for about 2-3 weeks, changing it once every three days. Papillomas will disappear after the first course of treatment.
Removal in adults
Methods for removing papilloma are prescribed depending on the patient’s health condition.
Pregnant women are contraindicated:
- use of radiofrequency method;
- ultrasound;
- chemical means.
Radiotherapy is not used if there are:
- cardiovascular disorders;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- malignant neoplasms.
Additional contraindications for prescribing electrocoagulation include blood clotting disorders and individual intolerance to electrical procedures.
But what a tonsil abscess without fever looks like and what can be done about such a problem is indicated here.
Genital warts: symptoms and treatment
Most often, human papillomavirus spreads through direct contact. It is transmitted during sexual intercourse in the anus and genital area, mouth or throat. Genital warts in the mouth or throat are extremely rare. Using condoms can significantly reduce your risk of contracting this virus. After contracting human papillomavirus infection, the disease often spreads to the genitals and anus.
Often, genital warts are transmitted from partners when the sick person does not even have visible signs of the disease. The first symptoms may appear when the infection has been “successfully” transmitted to another sexual partner.
Experts say that the likelihood of transmission of this virus from a sick pregnant woman to a newborn baby is very small, although it does exist. It has not yet been established at what point (during pregnancy or childbirth) human papillomavirus infection is transmitted from mother to child. It is not recommended for women with genital warts to give birth by cesarean section. Only if condylomas are present in the vagina, the doctor recommends a cesarean section.
Infection with papillomavirus usually does not cause symptoms, and not all cases cause visible genital warts. Visible symptoms of the disease usually appear two to three months after infection. In exceptional cases, they occur as early as 4 weeks of illness. In other situations, symptoms of infection may not appear for many years. By and large, everything happens purely individually, namely depending on the state of immunity of a particular person.
Symptoms of this infection include irritation, bleeding and itching. Genital warts come in a variety of sizes and shapes. They can be very large or, conversely, microscopic. Some appear in groups, others individually. Condylomas often resemble the head of a cauliflower in appearance. Sometimes they are white and flat, so they are practically invisible. In men and women, condylomas appear in the groin area, around the genitals, in the rectum, near the urethra, and on the anus.
This is interesting: What happens if you tear off a condyloma
Genital warts appear in women on the genitals and vagina. They are often discovered by a gynecologist during an examination.
In men, condylomas appear on the scrotum and genitals. Sometimes only a doctor can detect genital warts. Often the symptoms of this disease are very similar to the symptoms of completely different diseases. To establish a diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination by a specialist.
Treatment of condylomas is carried out using several methods: surgical, in which they are removed mechanically; therapeutic, in which medications are taken that destroy these formations; biological, based on limiting the activity of the virus.
Laser removal of condylomas is considered the most advanced method to date for getting rid of the manifestations of this unpleasant disease. After this procedure, there is practically no trace of condyloma left.
No less popular and not too expensive is cryotherapy - removal of condylomas with liquid nitrogen. During this procedure, they are frozen with a special applicator for a few seconds. After some time they disappear on their own. After 10 days, the condyloma mark disappears. This procedure is effective, painless, safe and generally available. After it, no marks remain, unlike other surgical methods. Before carrying out treatment, it is necessary to consult with specialists.
Symptoms
A small papilloma in the throat often has no symptoms at all, but only when it grows do the following appear:
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat and tonsil area;
- sore throat, discomfort for no reason;
- violation of swallowing functions;
- labored breathing;
- speech impairment, if the warts are localized on the vocal cords, complete loss of voice;
- cough, and with multiple growths, coughing up pieces of papillomas.
At the onset of the disease, mild hoarseness and slight shortness of breath usually appear.
In children, papillomatosis can lead to:
- to disruption of mental and physical development;
- endocrine disorders;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx;
- to disruption of the nervous system.
Papilloma in the throat is a benign growth. The pathology is caused by a viral pathogen; you can catch it during normal communication, but it is not always accompanied by the development of a clinical picture. Those most at risk are men, preschool children and the elderly.
sensation of a foreign body in the throat and tonsil area; sore throat, discomfort for no reason; violation of swallowing functions; labored breathing; speech impairment, if the warts are localized on the vocal cords, complete loss of voice; cough, and with multiple growths, coughing up pieces of papillomas.
to disruption of mental and physical development; endocrine disorders; chronic diseases of the nasopharynx; to disruption of the nervous system.
Papillomatous growths on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity can grow in almost any area. Most papillomas are found on the palate, palatine sacs, followed by the prevalence of the process on the inner surface of the cheeks, gums, and tongue. Changes in the mucous layer under the influence of the virus are found in the throat and larynx.
Reviews - how is life with laryngeal papillomatosis?
Most people suffering from laryngeal papillomatosis note that the presence of epithelial growths of various shapes and localization densities in the throat and oral cavity as a whole significantly reduces their quality of life. Papillomas interfere with eating and food products with a rough surface often cling to benign formations, causing pain.
In patients whose oral cavity contains papillomas in the area of the palate, in most cases there is practically no discomfort in terms of unpleasant sensations and they do not use a surgical method to remove tumors. Thus, the quality of life of patients with laryngeal papillomatosis directly depends on which part of the throat the epithelial growth is located. Based on this, a treatment protocol, recommendations for removing papilloma and methods for further rehabilitation of the patient are developed.
Diagnostics
Papillomatosis is diagnosed using several methods at once, allowing not only to determine the presence of growths, but also the location of their distribution, the degree of organ damage and size.
Diagnostic methods:
- visual examination by an otolaryngologist using a laryngoscope - a special device for examining the throat;
- examination of the throat using an operating microscope - microlaryngoscopy;
- radiography and computed tomography;
- to identify disturbances in the functioning of the vocal apparatus, in particular, the ligaments, laryngostroboscopy and electroglottography are used;
- analysis of material obtained from biopsy of growths;
- removed papillomas are examined for histology - the presence of cancer cells.
Blood must be taken for analysis.
Papilloma in the throat is detected by a doctor during a visual examination. To clarify the extent of the spread of the disease, it may be necessary to examine the larynx using a laryngoscope.
Infectious granulomas and malignant neoplasms give a similar visual picture, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy of the affected tissue is performed, followed by histological examination of the material. The patient may also be prescribed a blood test for HPV to determine the strain of the virus.
Basic methods of combating condylomas in the mouth
These growths themselves create discomfort and therefore it is necessary to get rid of them as carefully as possible. They are not always treated, even if the person has no other health problems.
If a patient has single condylomas, then complex treatment can be carried out and the outcome of the disease can be monitored. If you notice a growth in the mouth or condylomas in the throat, you should immediately contact a specialist (dentist).
The doctor will tell you in detail how to treat condylomas, but the methods are as follows:
- Strengthening the immune system through the use of medications: “Cycloferon”, “Kipferon”, “Timalin”, “Echinacea”.
- Comprehensive fight against viruses and infection with the help of the medicine “Panavir”.
- Toxins can be removed from the human body using the drug “Prospidin”. This drug specifically targets viruses and stops the spread of infection throughout the body.
- This method involves physically removing the condyloma. The growth can be removed using a laser, radio waves, or photodynamic therapy.
Drugs can also be prescribed before physical removal of the condyloma.
It should be remembered that the infection quickly spreads to healthy human tissue, so proper treatment is the key to future health.
Each person is given an individual course of treatment, taking into account a number of factors.
The specialist considers factors such as:
- age;
- stage of the disease;
- forms and types of condylomas.
To completely get rid of condylomas, it is necessary to complete the entire course of step-by-step treatment, and only then can you get rid of the growth and the discomfort it causes.
After removing the growth, the doctor prescribes Imudon to speed up the healing of the wound. Treatment with the medical drug “Solcoserite” is recommended against the occurrence of infection. Sea buckthorn oil is also used to treat the affected area. You need to maintain oral hygiene, consume plenty of vitamins, and adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
Strengthening the body's immune system is very important, but first of all you need to monitor the condition of your oral cavity and lifestyle. With the right lifestyle, the likelihood of developing condylomas is minimal.
Routes of infection
The viral infection is transmitted from person to person through close contact:
- sexually (the risk of getting the virus triples with promiscuity);
- through kisses;
- by household means (in public places);
- through the birth canal to the newborn from the mother;
- for injuries, microcracks and other damage (self-infection).
sexually (the risk of getting the virus triples with promiscuity); through kisses; by household means (in public places); through the birth canal to the newborn from the mother; for injuries, microcracks and other damage (self-infection).
It is impossible to become infected with papilloma, you can only become infected with a virus, and how it behaves in the future depends on many external and internal factors.
Conducted research has helped to reveal that HPV is present in the body of almost 90% of the population of the entire planet. Infection is possible at any age and in several ways.
If we are talking about the development of papillomas in the mouth of children, then infection most often at this age occurs through vertical and household contact.
The vertical route is the transmission of the virus from a sick mother to her newborn child as it passes through the birth canal. At this time, the microorganism is able to get on the skin of the face, mucous membranes of the mouth and throat.
Among children, the most common route of transmission of HPV is still considered to be through household contact - transmission occurs through close contact, through toys, and when using the same hygiene items. Children often drink from the same cup, use the same spoon or fork, and can eat the same piece of fruit for several people - HPV is found in saliva and therefore in such cases it easily spreads and leads to infection.
HPV is transmitted through touch. Ways of infection with papillomavirus:
- sexual, regardless of the type of sexual contact (if the infected partner has warts located in the perineal area, using a condom does not exclude transmission of the virus);
- from mother to child during childbirth;
- household (general hygiene and household items);
- self-infection during depilation or shaving;
- through handshakes, kisses (if the papillomas are located in the contact zone).
Please tell us about laryngeal papillomatosis.
The fact is that my fifteen-year-old daughter was diagnosed with papillomas in her throat. They offer surgery. Or maybe there are folk remedies for this disease?
Raisa DEREVYAKO
Glussky district
Alexander BIZUNKOV, assistant at the Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Vitebsk State Medical University, Candidate of Medical Sciences:
– Laryngeal papillomatosis is one of the most problematic diseases in otorhinolaryngology. What is papilloma? This is a common wart, which is often found on various parts of the skin and is removed by cauterization with liquid nitrogen in beauty salons. These also develop in the larynx. Only here the voice suffers and even breathing becomes difficult.
Effective treatment is achieved only when it is reasonable to combine various methods. The most common means of helping a child with papillomatosis is surgery. But, unfortunately, such intervention does not cure the disease and is always associated with additional tissue trauma. Which, in turn, leads to two unpleasant consequences: firstly, the growth of new papillomas is often activated, and secondly, the formation of scar tissue occurs, which impairs voice and breathing.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Cyst of the left maxillary sinus
Therefore, it is necessary to use more gentle methods. For example, removal of papillomas using laser surgery – it causes much less trauma to the larynx.
In recent years, more and more attention has been paid to drug treatment of this disease. The use of modern medications allows some patients to refuse surgery altogether.
Successes in drug therapy became possible after the causative agent of the disease was isolated. It turned out to be the human papillomavirus, namely its varieties - types 6 and 11. It is known that, for example, the 16th and 18th types of this virus are the causative agents of certain sexually transmitted infections and are considered as one of the most significant causes of the development of cervical cancer. In this regard, experts believe that a child may become infected with the papilloma virus during childbirth.
Interferons, an important component of antiviral immunity, are most widely used today to treat the disease. Medicines are also used to help the body produce its own interferons.
Another group of drugs is antiviral. Drugs that slow down cell proliferation are also used. The most widely used for this purpose is podophyllin, which is a herbal preparation - a mixture of various compounds obtained from the rhizomes and roots of podophyllum thyroid. Kalanchoe juice is also used to lubricate the vocal folds.
In recent years, a new group of drugs – cytokine therapy – has become increasingly widespread. At the end of the last century, small protein molecules (cytokines) were isolated and studied, which cells responsible for immunity use to “communicate” with each other. Some of these protein molecules have been learned to be made artificially using genetic engineering.
Drug therapy can replace surgical treatment. There is evidence that almost 50 percent can avoid surgery. sick. But we specifically do not give the names of medications in order to exclude self-medication. All medications should be prescribed by a doctor and the patient’s well-being should be constantly monitored.
For inhalations for papillomatosis, you can also use herbs, for example, celandine juice. However, we must remember that this toxic substance will be absorbed into the lungs and enter the blood. Therefore, a doctor’s consultation is necessary here. An infusion of celandine (8 g per 200 ml of water) is less dangerous, but you should also be wary of its toxic effects, since the treatment is long-term.
We can recommend a mixture of two infusions for use after removing papillomas: St. John's wort herb and calendula flowers. To prepare it, you need to take 10 g of each herb and leave it in 200 ml of boiling water for 2 hours. Filter the resulting liquid. By the way, if there is a family member with laryngeal papillomatosis, an inhaler is an irreplaceable thing.
Treatment
Papilloma on the palatine arch, tonsils or uvula requires complex treatment. It includes taking antiviral drugs, immune-stimulating drugs and direct removal of tumors.
Each stage is an important component of the fight against viral infection. If you ignore at least one of the components, any action will not bring the desired result.
Without medication, the risk of relapse increases significantly.
We recommend reading: Papilloma on the tongue The wart has turned black Papilloma on the lip
After a detailed diagnostic study, the doctor prescribes the necessary medications aimed at weakening HPV and restoring the function of natural defense. Such drugs include Viferon, Interferon, Allokin Alpha, Cycloferon.
It is important to understand that such drugs have many contraindications and side effects. Purchasing them without a medical prescription is extremely dangerous to human health.
Excision of formations can occur using special procedures. The most appropriate method is selected by the doctor, based on the patient’s condition, the degree of damage by growths, physiological characteristics and the wishes of the patient himself. To remove tumors in the throat, use:
- cryodestruction – freezing with liquid nitrogen;
- electrocoagulation – evaporation by electric current;
- radio wave exposure – removal by converted high frequency waves;
- laser excision - burning with a special laser;
- surgical intervention - an operation using general anesthesia.
During treatment in small areas of the oral cavity, preference is given to radioknife and electrocoagulation. Both methods allow the operation to be performed bloodlessly. If exposure to current allows small blood vessels to be sealed, then radio waves are completely contactless.
Adherents of alternative treatment have their own recipes for getting rid of growths in the throat and uvula. The most famous method is the use of celandine juice.
The liquid contained in the plant stem is used to treat the affected area. You need to be especially careful with this procedure.
Swallowing celandine juice is extremely dangerous. Traditional healers also use castor oil, tea tree oil, soda, garlic, nuts with gasoline, iodine, peroxide, ammonia and potatoes.
You can see a photo of the problem above.
Complex therapy is effective, including removal of growths and prescription of medications.
The doctor decides what removal methods to use and how to treat papillomatosis.
The following methods exist for removing papillomas:
- chemical, during which acid, salts of lead or silver nitrate, solutions of perhydrol and potassium permanganate are applied to the warts. This method is contraindicated for use in children and persons with hypersensitivity to chemicals;
- Radiotherapy is the safest way to get rid of papillomas, leaving no scars or cuts, and almost completely eliminating the occurrence of relapses.
Surgical removal of papillomas is carried out using a scalpel, laser, exposure to liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy), electrocoagulation (use of electric current) and ultrasonic disintegration.
- In hard-to-reach places (in the larynx, on the tongue), laser removal is most effective. After removal, your health quickly returns to normal, and the crusts formed at the cut sites fall off on their own.
- New growths inside the larynx are removed without external skin incisions using laryngoscopy or a special mirror. Papillomas in the esophagus are cut off using forceps.
- Removal of extralaryngeal growths occurs through an incision in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, trachea and the application of a tracheostomy - a tube through which the patient breathes during surgery.
After removal of the papilloma, new layers of epidermis are transplanted onto the affected vocal cord.
After surgery, the use of antitumor ointments and injectable drugs (Prospidin) is effective.
Human papillomavirus infection sooner or later manifests itself as growths on the body or mucous membranes.
But if warts on the skin can still exist asymptomatically, then papilloma in the mouth causes significant physical discomfort and disrupts the functions of the body.
In addition, such growths are unsafe for health in general due to the risk of degeneration into malignant tumors.
How to recognize, or better yet, prevent danger in time?
Papillomas in the mouth appear only in cases of human infection with the papilloma virus.
It is very common, so it is almost impossible not to become infected with it, especially considering that one of the ways of its transmission is through household contact.
But how often do papillomas occur on the oral mucosa? This is not uncommon for doctors.
Moreover, they encounter such cases not only in adults, but also in children and adolescents, in whom the activation of the virus occurs against the background of hormonal changes.
The papilloma virus can enter the oral mucosa in the following cases:
- using other people's personal hygiene items (toothbrush, towel);
- insufficiently thorough processing of dishes when they are used together with a virus carrier (especially in catering establishments);
- kissing a carrier of the virus (if the virus is localized in the oral cavity);
- unprotected oral sex.
In a child, infection can occur during birth if the mother is infected with the papilloma virus.
It is in such cases that growths appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth, nasopharynx or in the eye area.
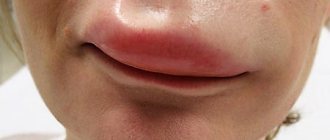
Photo: HPV infection can occur through kissing
Answer to the question: “Is it possible to kiss a carrier of the papilloma virus?” is obvious - the risk of infection is very high.
And if one of the kissers already has growths in their mouth, then the transmission of the virus will definitely take place.
When they appear
From the moment the virus enters the body until the growths appear, a lot of time can pass, during which a person is a carrier of the infection without knowing it.
It all depends on the state of his immunity.
- If the body's natural defenses are strong enough, the incubation period can even last several years.
- In other cases, growths can be detected after two months.
Photo: pregnancy is a provoking factor for the manifestation of HPV
Reduce immunity and promote activation of the virus:
- colds and infectious diseases;
- chronic inflammatory processes;
- bad habits;
- stress and physical fatigue;
- hormonal imbalances;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and antibiotic therapy;
- pregnancy period.
Not any of these conditions will necessarily lead to the formation of papillomas, but they all significantly increase this risk.
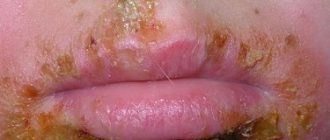
What they look like
Papilloma in the mouth (the photo shows the types of growths) has its own characteristic features, which make it easy to diagnose even independently.
- Usually these are small formations (no more than 1 cm) of a nodular type with a bumpy surface.
- Sometimes they have a thinner base (pedicle), but sometimes they grow in width, resembling a cockscomb or cauliflower.
- The color of these growths is similar to the surrounding mucous membrane, but may be darker (redder) or have a whitish tint.
- To the touch, all formations are soft, elastic, elastic.
- They do not cause pain or cause other unpleasant sensations. But at the same time, of course, they cause inconvenience, interfere with eating and even during conversation.
Specific symptoms may depend on the location of the papillomas in the oral cavity.
It is unreasonable to diagnose yourself only from photographs and personal observations. Only a specialist can most accurately determine what a growth in the mouth is and the degree of its danger. Therefore, there is no need to delay your visit to him.
Locations of papillomas in the mouth
The entire oral cavity is lined with mucous membrane, so growths can form on any part of it:
- on the tongue, mainly on its lateral surfaces;
- in the larynx, tonsils and vocal cords;
- on the hard palate;
- on the cheek;
- on the inside of the lips and gums.
In the larynx
Photo: localization in the larynx
Tonsil cancer is a malignant disease. It is characterized by the formation of a tumor. This disease is considered to be a rare type of oncology. In this case, it is most often the tonsils that suffer in men. Cancer is diagnosed, according to statistics, in elderly men (over 60 years old), and this type of oncology occurs in this group almost 10 times more often than in women.
Brief description of the pathology
Tonsil cancer develops in the oropharynx. The formation increases in size and over time develops into a malignant tumor without borders. Tonsils in their biology are considered lymphoid tissues. There are six types of tonsils in humans:
- two palatines (located above the palate in the oral cavity);
- two pipes;
- pharyngeal;
- lingual.
Of course, oncology can affect any of these types. However, cancer of the palatine tonsil is most often diagnosed.
Initially, the disease manifests itself as enlarged lymph nodes, compaction, tumor, and ulcer. Then metastases begin to develop. This pathology is a rapidly progressing disease. Doctors detect the disease by examining the mouth and lymph nodes.
chemical, during which acid, salts of lead or silver nitrate, solutions of perhydrol and potassium permanganate are applied to the warts. This method is contraindicated for use in children and persons with hypersensitivity to chemicals; Radiotherapy is the safest way to get rid of papillomas, leaving no scars or cuts, and almost completely eliminating the occurrence of relapses.
In hard-to-reach places (in the larynx, on the tongue), laser removal is most effective. After removal, your health quickly returns to normal, and the crusts formed at the cut sites fall off on their own.
New growths inside the larynx are removed without external skin incisions using laryngoscopy or a special mirror. Papillomas in the esophagus are cut off using forceps.
Removal of extralaryngeal growths occurs through an incision in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, trachea and the application of a tracheostomy - a tube through which the patient breathes during surgery.
The opinion of most doctors regarding the treatment of tumors of viral etiology in the mouth is clear - such growths must be removed.
The localization of tumors in the oral cavity creates all the prerequisites for its infection; such growths are also characterized by increased pain due to the close location of nerve endings in the mucous layer. Growing papillomas in some cases negatively affect not only chewing and the entire meal, but also change diction for the worse.
Constant trauma with the development of an inflammatory reaction increases the risk of degeneration of virus-affected cells into malignant ones.
To remove papillomas in the mouth, most doctors use laser destruction. The method is characterized by painlessness, absence of scars and the smallest number of relapses. The possibility of reappearance of papillomas in the mouth can be reduced by prescribing a course of antiviral treatment, immunomodulators and vitamin complexes.
The use of folk remedies is recommended only if the formation in the oral cavity is single, is not prone to the appearance of lesions and does not cause much concern to the person. If an increase in the number of papillomas is detected, with their rapid growth and the appearance of ulcers, you should urgently contact your dentist first, who will prescribe a series of examinations.
You can often hear the question, how to treat growths on the oral mucosa? Doctors' opinions on the treatment of papilloma tumors almost always agree - this is the removal of papillomas in the throat or any other areas of the skin where they are often injured, inflamed and infected.
chemical method; radiotherapy; using a scalpel; laser removal; cryotherapy; electrocoagulation; removal using liquid nitrogen.
After removing tumors in the throat, in order to avoid the appearance of new growths, antiviral medications are prescribed, immunomodulators, and a complex of vitamins are recommended.
Treatment at home
Treatment with folk remedies is effective if papillomas in the throat are single, and their appearance is not accompanied by severe discomfort.
Important! If the tumors grow, their number rapidly increases, and ulcers begin to form, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor for qualified medical help.
Peel a clove of garlic, cut it in half and rub the cut side onto the new growths several times a day; A tincture of green walnut peel will help (dried walnut leaves will also work). To prepare it, fill the raw materials with alcohol, seal the container, place in a dark place to infuse for two weeks, shake from time to time.
The prepared tincture should be lubricated on papillomas several times a day; Buy castor oil, soak a small cotton swab in it and apply it to the growth for a couple of minutes. The procedure must be carried out twice a day until the papilloma disappears; The white of a raw egg helps a lot, which should be used to lubricate the growth daily. .
Attention! When using traditional methods of treatment, do not forget about oral hygiene. In addition to brushing your teeth daily, rinse your mouth regularly with mouthwash. After undergoing treatment procedures, try not to eat food for an hour after they are performed.
If you decide to start self-treatment with traditional methods, first consult with your doctor. Perhaps he will recommend removal as the best way out of the situation and for the safety of your health.
Characteristic features of condyloma
Condylomas are growths that can appear in the human oral cavity; they are usually located on the tongue, but there are also condylomas under the tongue. Condylomas on the mucous membrane are considered a common occurrence.
The growths appear due to the entry of the papilloma virus into the body, which can penetrate during direct contact with an infected person. Condyloma is a dangerous formation, because it may not appear for a long time, which is why the patient will not even know about the presence of infection in his body and will be dangerous to the healthy people around him.
This is interesting: HPV and condylomas are the same thing
They have a very interesting structure and shape; sizes can vary and even reach the size of a walnut. Characteristic color and shape of the formation: the growth secretes an unpleasant liquid and has an odor. If you do not get rid of the growths in time, then in the future you will have to deal with the consequences of an acute infection, which is often accompanied by the spread of infection in the larynx and genitals; curing warts and growths from which is just as difficult as from the oral cavity.
You should refrain from treating the consequences of infections at home, as this may aggravate the situation and lead to an increase in the disease. Treatment should not only be timely, but also under the supervision of a specialist.
Condylomas can spread throughout the larynx
Therapy after the removal procedure
After excision of tonsil papilloma, the patient must complete full treatment to the end to prevent the risk of reappearance of growths. To do this, you should take a course of anti-HPV medications.
Until the surgical wound is completely healed, a person needs to limit his intake of spicy and hot foods. If necessary, rinse the mouth with chamomile decoctions or other disinfectants.
The International Body of Disease Classification classifies papilloma on the uvula and throat as benign formations. However, the risk of developing cancer is still present. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of illness, you must seek help. The sooner this happens, the more effective the treatment will be.
When to delete
Removal of condylomas is especially necessary in the following cases:
- growths interfere with the full functioning of the body;
- symptoms of the disease intensify;
- there is a suspicion of an oncological process;
- there is a threat to the patient's life.
This is interesting: What is genital warts confused with?
The decision on the need for removal is made solely by the attending physician. You should not try to get rid of tumors on your own. This can lead to hazardous consequences for health and significantly complicate the existing situation.
Condylomas that occur inside the throat are a dangerous phenomenon that can significantly affect the patient’s quality of life. Therefore, the sooner you visit a doctor, the fewer problems will arise in the future.
Risk factors
In children, risk factors are frequent infections of the ENT organs:
- chronic tonsillitis (angina);
- laryngitis, tracheitis, pharyngitis;
- acute and purulent otitis media.
The disease papillomatosis is common in people aged 20 to 40 years, who lead an inappropriate lifestyle, are subject to stress, and have bad habits.
There are indirect factors that can affect the activity of the virus:
- taking hormonal contraceptives by women;
- passive smoking;
- air pollution from exhaust gases and industrial emissions;
- improper oral care;
- heredity;
- age and associated hormonal imbalances (children under two years of age, adolescents during puberty, women during menopause, pregnant women are most at risk);
- stress.
chronic tonsillitis (angina); laryngitis, tracheitis, pharyngitis; acute and purulent otitis media.
taking hormonal contraceptives by women; passive smoking; air pollution from exhaust gases and industrial emissions; improper oral care; heredity; age and associated hormonal imbalances (children under two years of age, adolescents during puberty, women during menopause, pregnant women are most at risk); stress.
Causes and methods of getting rid of warts in the mouth
As a rule, viruses and infections attack the oral cavity, so condylomas in the mouth best signal the onset of a serious illness. If such formations appear, you need to consult a specialist and carry out timely treatment.
Mouth condylomas are a serious disease.
There are many types of them, but the greatest harm to a person can be caused by genital warts on the tongue. To effectively fight the disease, it is necessary to determine the type of condylomas.
Reviews
- Svetlana F.: “After a sore throat, a child developed a papilloma on his tonsil. At first it was the size of a small pea, and then it became the size of a bean. The son began to eat poorly, be capricious, and cough frequently. Electric cauterization was prescribed. Everything went very quickly. My throat tingled a little after the operation. The child spat out the papilloma the next day. A week later we saw a doctor. Everything has healed. I hope she doesn't grow any bigger."
- Tatyana K.: “When I swallowed, I felt something was bothering me. She didn’t see anything in the mirror herself. I contacted an ENT doctor. He said it was papilloma and advised me to do cryotherapy. The procedure itself is painless. But after it, I initially felt worse. There was a feeling that the tonsil was swollen. A day later everything returned to normal. When the wound healed, there was also slight discomfort. Now everything has healed, but you need to see a doctor in a month so that there is no relapse.”
You may also be interested in information about what reviews there are about purulent plaque on the tonsils without fever and what can be done about such a problem.
It is impossible to get rid of the papilloma virus that has entered the human body. Decreased immunity activates the bacillus. The appearance of a growth on the tonsil causes discomfort, can cause shortness of breath, and provoke an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis. Modern treatment methods make it possible to remove papilloma painlessly, without relapses.
Manifestation of condylomas
During the initial stage, which lasts at least a month, growths appear on the tongue, cheeks, gums and even the roof of the mouth. These growths have a certain shape and can be round or pointed.
The growths vary in color: the base has a pinkish tint, but the top of the formation is white. The color of the growth depends on the location in the human oral cavity.
Growths always cause discomfort, so it is quite difficult not to see them. They can itch and cause burning and itching. In advanced situations, condylomas appear not only in the oral cavity, but also in the human throat.
Such growths can cause serious illnesses, so you need to carefully monitor your health and, at the slightest suspicion or symptoms, consult a doctor, and then, during treatment, follow a clear course and instructions: getting rid of condylomas is not so easy.
Genital warts in the mouth are especially dangerous because another person can become infected even through a kiss.
Only with serious treatment and careful attention to your health can you achieve a complete recovery.
The danger of condylomas lies in their reappearance. You need to realize that if condylomas appear in the pharynx, the infection has spread and the situation has become more complicated. In addition, condylomas in the larynx cause discomfort when eating, which can lead to stomach problems.
Discomfort when swallowing is one of the manifestations of condylomas
What is squamous cell papilloma and its structure
What is squamous cell papilloma and its structure
? The answer to the question: what is this can be answered - it is a benign neoplasm. The main places of localization include the face, neck, and mucous membranes. If the pathology is not treated for a long time, it can become malignant. Externally, a flat papilloma resembles a mole in the shape of a circle. Color can vary from flesh to deep brown. Doctors call squamous cell papilloma with hyperkeratosis the most common. It mainly occurs in older people, sometimes in individuals 30-35 years old.