One of the most severe signs of allergy is angioedema. In medicine it is also called angioedema . The development of pathology is observed in 2% of patients with a tendency to an allergic reaction. The disease is characterized by rapid development, as a result of which a person requires emergency medical care. Under the influence of certain factors that are not fully understood, women and children are more susceptible to this condition.
Angineurotic edema - what is it?
Quincke's edema is a pathology of an allergic nature, the main symptom of which is rapid and sharp swelling of the skin, subcutaneous tissue and mucous membranes. Most often, swelling occurs in the face, neck, hands, upper body and feet. Much less often it affects the insides, joints and membranes of the brain, although such cases are possible.
The disease can appear at any age, but most often it is diagnosed in young women and children older than the first year of life. In young men and the older generation, angioedema can also develop, but in a much smaller percentage. The risk group primarily includes people who have a pronounced allergy to any allergen.
More than 90% of all cases of giant urticaria are associated with the use of medications, especially ACE inhibitors. These include Captopril or Enalapril, but there is also a hereditary type of pathology.
Development mechanism
One of the most important components of primary and acquired immunity takes part in the formation of angioedema - a cascade system of proteolytic enzymes, which is formed by a complex of complex proteins.
Thanks to it, the immune response is realized, and the body is protected from the influence of foreign agents. A system of complex proteins is directly involved in inflammatory and allergic reactions. When the system is activated, bioactive enzymes are produced from special immune cells of mastocytes - histamine, bradykinin, etc., thereby stimulating inflammation and the development of an allergic reaction. Activation of this system leads to the fact that the vessels dilate, and their walls become more permeable to liquid components of the blood, while blood pressure drops, this symptomatology is accompanied by the appearance of various rashes and swelling.
In the angioedema form, the quantity and quality of the C1 inhibitor plays an important role. This is a specific enzyme that is regulated by the complement system. The main function of a C1 inhibitor is to inhibit and control the activation of this system. With a lack of this enzyme, the compliment system can start uncontrollably, with a massive release of bioactive substances from mast cells, an allergic reaction is triggered and edema develops.
Swelling is provoked by bradykinin and histamine; it is these substances that help dilate blood vessels and increase their permeability to liquid components of the blood, as a result of which the tissues of the deep layers of subcutaneous fatty tissue and mucous membranes accumulate interstitial fluid, which forms edema. The mechanism of development of this pathology is similar to urticaria, only in the case of anaphylaxis, the vessels dilate and become more permeable in the superficial layers of the skin.
Causes
If there is a hereditary disease, most often its first manifestations occur during puberty, and there are many factors that can provoke the development of edema. These include:
- stressful situations;
- infectious pathologies;
- various damages;
- surgical and dental interventions;
- menstrual changes;
- the onset of pregnancy;
- estrogen-based oral contraception.
If acquired angioedema is a consequence of an allergic reaction of the body, then it can be triggered by the following allergen:
- a certain type of food - seafood, especially red sea fish, caviar, citrus fruits, nuts, chocolate;
- preservatives and coloring substances found in food, most often in sausages and cheeses;
- plant pollen;
- animal fur, bird down and feathers;
- toxic substances and saliva that enter the victim’s body during an insect bite - wasps, bees, mosquitoes, mosquitoes, etc.;
- ordinary dust.
In addition, angioedema also occurs due to the influence of other factors:
- helminthic infestation or viral infection;
- pseudo-allergic reaction, which is a reflection of another somatic disease, for example, a functional disorder of the digestive system;
- a tendency to form swelling, which can occur in people against the background of problems with the endocrine system, and in particular with the thyroid gland;
- oncology and blood pathologies;
- exposure to chemical and physical factors, including medications. Most often, this reaction is caused by painkillers, sulfonamide drugs, antibiotics from the penicillin group, and in rare cases, cephalosporins.
In 1/3 of cases, it is not possible to find out the exact reasons why the swelling appears, and an idiopathic form of the pathology is diagnosed.
Why does pathology develop?
The development of the syndrome occurs in the form of a response to irritants that have entered the body, as is the case with allergies. This reaction can be formed under the influence of:
- substances that contain food, especially nuts and fruits, egg whites and lactose, fish, honey, chocolate products, all kinds of food additives;
- medications, especially antimicrobials, painkillers, B vitamins, drugs containing bromine and iodine, acetylsalicylic acid, antihypertensive drugs;
- toxic substances, mainly insect poisons;
- pollen of grasses, flowers and trees;
- pet hair;
- household chemicals or industrial chemical substances - phenol, turpentine, etc.
- dust and dandruff;
- microscopic organisms: fungi, bacteria, viruses.
The irritant for each patient is its own substance, harmless to other people. But the development of a particularly pronounced and immediate response of the body is observed to the venom of a snake or insect.
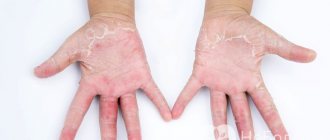
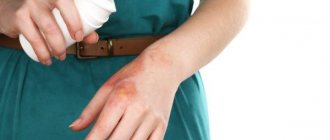
Allergic swelling of the hand in an adult after exposure to insect venom
Among the indirect factors, the impact of which ends in Quincke's edema, it should be noted diseases of the internal systems, infection with worms, and problems with the thyroid gland.
Some patients have a congenital tendency to this disease. With this type of pathology, the formation of edema occurs regardless of the influence of irritants, for example, due to hypothermia or stress.
Classification
| Variety | Development mechanism and features |
| Hereditary angioedema | Any part of the body can swell, but there is no urticaria. The first manifestations of the pathology occur in early childhood, the condition can greatly worsen during puberty. The presence of a hereditary disease is indicated if angioedema has already been diagnosed in the family. This is an often recurrent type of disease. |
| Acquired | This type of pathology develops in middle age and is also not accompanied by urticaria. There are no documented cases of angioedema among the victim's relatives. |
| Swelling caused by taking ACE inhibitors | The most common diagnosis is facial swelling, but in principle it can occur on any part of the body without being accompanied by urticaria. Such swelling may occur in the first three months of therapy with ACE inhibitors. |
| Allergic edema | This type of pathology is complemented by urticaria and itching, and it can also often develop together with anaphylactic reactions. Swelling appears immediately after contact with the allergen and lasts on average 1-2 days. |
| Idiopathic edema | With this type of Quincke's edema, specialists cannot determine the exact cause of the development of the disease. In half of such cases, swelling is accompanied by urticaria. It is more often diagnosed in women, although the number of such episodes usually does not exceed 3 cases per year. |
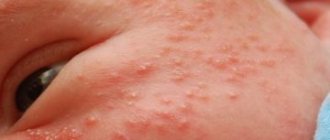
Quincke's edema, symptoms in children
Parents of children who are hypersensitive to allergic reactions need to know everything about the pathology of Quincke's edema: what kind of disease it is, and most importantly, how it manifests itself and what to do if such situations arise. Children suffer from this disease quite often. The risk of its occurrence increases in the following cases:
- If a newborn baby is constantly given artificial food
- When early cessation of breastfeeding occurs and its replacement with cow's milk protein
- Using aggressive agents when washing and rinsing children's clothing and soft toys
- Frequent use of antibiotics, multivitamins
Signs of this pathology in a child can appear from birth. For children under four years of age, the non-allergic nature of the edema is more typical, due to heredity and the complement reaction. It is noted that the death of children due to laryngeal edema occurs in 20% of all cases of its occurrence. The difference between the manifestations of pathology in children and adults is that:
- They are more often diagnosed with cases of gastrointestinal and brain lesions
- Articular syndrome is not observed in childhood
- The allergic form of this disease often occurs along with symptoms of urticaria and asthma.
Depending on the degree of inflammation of the mucous membranes, subcutaneous tissue, larynx, neurological abnormalities and abdominal syndrome, Quincke's edema in children can be represented by multiple varieties.
Note: ∗ Rapid development of symptoms when the larynx is affected often requires urgent tracheostomy to prevent the death of the child. ∗∗ With angioedema in children, abdominal syndrome is caused by damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and intestines.
In rare cases, there may be urinary retention, tachycardia, fever . If symptoms of swelling occur, you should call an ambulance as quickly as possible, and before they arrive, you should try to alleviate the child’s condition. Knowing how to provide emergency care , what angioedema is, symptoms in children, photos of manifestations of the disease is necessary for all parents who are concerned about the health of their children.
How it manifests itself
The clinic is quite diverse; the first signs of pathology appear within half an hour after contact with the allergen. First, a burning and tingling sensation is felt at the site where swelling develops. Then, about 35% of patients notice pinkness or redness of the skin on the torso or legs. This can happen both before and during swelling.
Depending on the type of edema and its location, symptoms can vary greatly, so we will consider all the signs of the disease that are characteristic of a particular type and location of swelling.
Depending on the type
| Type of pathology | Symptoms | |||
| Onset and duration of swelling | Localization | Characteristic signs | Peculiarities | |
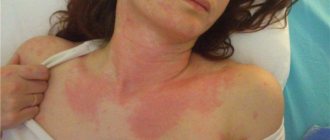
| Allergic edema | It can last from a few minutes to an hour. Most often, 5-30 minutes pass before the first signs appear. The reaction is completed after a couple of hours, maximum after 2-3 hours. | Swelling usually develops in the face and neck. First, swelling of the lips, eyelids, and cheeks appears, then it spreads to the upper and lower extremities and genitals. Swelling occurs on any part of the body. | The swelling area is dense, no pits appear on it after pressing. The color of the swelling is slightly reddish with pallor. | In addition to the main symptoms, urticaria, itching and rashes may occur. |
| Hereditary, acquired and edema associated with treatment with ACE inhibitors | The onset of symptoms in adults begins within 2-3 hours; in most cases, swelling goes away within 2-3 days. In some patients, swelling lasts about a week. | At the initial stage, the eyes, lips, and tongue swell, then swelling may appear in the genital area. This pathology can develop in any part of the body. | Swelling is characterized by pallor and tension of the skin, lack of itching and redness. When you press on the swelling, there are no pits left on it. | Does not combine with urticaria. |
| Idiopathic edema | Manifestations, duration and place of formation may be the same as in all the cases listed above. | In half of the cases it is accompanied by urticaria. | ||
Depending on the place of origin
| Localization | Symptoms |
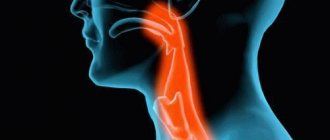
| Swelling of the respiratory organs and oral cavity (larynx, tongue) | This is the most dangerous place for swelling to occur, as it can cause trouble swallowing, a sore throat, a barking cough, increasing hoarseness, difficulty breathing, and respiratory failure. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner in case of this reaction, a person may well die. |
| Lung swelling | Exudation of liquid substances into the pleural cavity, coughing, chest pain. |
| Swelling of the digestive organs | When the intestinal walls swell, the stomach begins to ache, vomiting and diarrhea appear, dyspeptic disorders, signs of an “acute” abdomen, peristalsis increases, and peritonitis develops. |
| Swelling of the urinary tract | Urine output is delayed and symptoms of cystitis appear. |
| Swelling of the brain | Headaches, convulsions occur, consciousness is impaired, and other neurological disorders of various types may appear. |
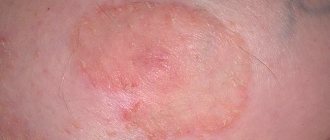
| Swelling on the face | The eyelids, lips and cheeks may swell locally. If the oral mucosa is affected, the tonsils, soft palate, and tongue swell, which causes breathing to worsen and asphyxia may begin. Swelling from the face can spread to the meninges, which can be fatal. |
Symptoms of angioedema
The worst thing about this disease is its suddenness . Swelling on the face, arms, and neck can form within half an hour and develop further if urgent measures are not taken.
First, local swelling of the mucous membranes is observed, which is not accompanied by pain. According to patients, there is heaviness throughout the body, a desire to lie down, and weakness. When you feel Quincke's edema, palpation is painless, and there is no depression left at the point of pressure, the skin is leveled to its previous state.
It is worth remembering that at the initial stage of Quincke's edema in the face area, difficulty breathing, coughing, lack of oxygen, swelling of the tongue, and numbness of the parts of the face affected by edema may be pronounced. With swelling of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, there is a feeling of heaviness in the internal organs, pain, possibly upset stool or nausea.
The most common places for swelling to develop are the lips, nose, larynx, tongue, and eyelids. The most dangerous are swelling of the tongue and larynx, as this can lead to difficulty breathing and asphyxia.
Angioedema can last for several days and disappear on its own , but sometimes requires complex medical intervention. It is worth remembering that this disease is recurrent in 80% of cases, so those who encounter it once should keep medications with them in case of a repeat reaction.
Help at the first signs
At the first symptoms, you should immediately use emergency ambulance services.
Before the arrival of specialists, first aid at home should be provided without fail, which may include the following activities:
- if swelling is an allergic reaction, then first of all you need to protect the victim from contact with the allergen, for example, after a wasp or bee sting, you need to remove the sting;
- the room in which the victim is located must be ventilated and maintain a constant flow of fresh air;
- the victim must be reassured;
- the victim should not be constrained by his clothes; his belt, tie or girdle should be removed;
- in order to remove the allergen from the body as quickly as possible, you need to make the person drink plenty of fluids and give sorbent preparations, like activated carbon;
- Any vasoconstrictor drops should be instilled into both nostrils of the victim;
- Apply a cold compress to the swollen area;
- if swelling begins to develop after an injection of medication or an insect bite, you need to tie a tourniquet above the place where the bite or injection was;
- you need to give the victim an antihistamine.
Upon arrival of the ambulance, the following actions will be carried out on site:
- detoxification;
- intravenous or intramuscular administration of prednisone;
- intramuscular injection of suprastin;
- use of diuretics (diuretics);
- use of protease inhibitors.
After emergency care, the patient is hospitalized in the allergy department, since giant urticaria, especially in severe form, requires urgent and qualified help.
Antishock therapy
In case of anaphylactic shock, Epinephrine is used. If necessary, you can repeat the injection. The break between injections should be at least 20 minutes. In case of unstable dynamics and risk of death, intravenous use of Epinephrine is possible (1 ml of 0.1% Epinephrine per 0.1 L of saline solution).
In parallel with the administration of Epinephrine, blood pressure, respiration, and heart rate are monitored. In adults, blood pressure should exceed 100 mm Hg. Art. In children, the indicator is 50 mm Hg. Art.
Providing emergency care for anaphylactic shock requires compliance with a number of rules:
- the patient must lie down;
- the head should be turned to the side and located below the legs;
- the lower jaw is extended, and all removable dentures are removed from the oral cavity.
Necessary medications in the first aid kit
Allergy sufferers and people prone to recurrent angioedema should always have 3 main medications in their first aid kit: adrenaline, hormones and an antihistamine. If giant urticaria develops, they should be administered in the same sequence:
- First, an adrenaline solution is injected intramuscularly into the thigh, delta of the shoulder or buttock. If the effect does not appear, the injection will be repeated after a quarter of an hour. The drug prevents the release of substances that provoke allergic reactions, increases blood pressure, relieves spasms, improves heart function;
- then intramuscularly, but better intravenously, you need to administer a hormonal drug - dexamethasone, prednisone or hydrocortisone. If there is no syringe, the contents of the ampoules can simply be held under the tongue; the drug is absorbed more quickly through the veins under the tongue and begins to act, bypassing the liver barrier. The dosage depends on the form of release, since hormones can be in the form of an injection solution or in the form of tablets. These drugs relieve swelling, eliminate itching, stop the release of substances that contribute to the development of an allergic reaction, and eliminate bronchospasm;
- The first aid kit should contain antihistamines that block H1 receptors and H2 histamine blockers. The first type of drugs includes Loratadine, Cetirizine, Clemastine, Suprastin. H2 receptor blockers - famotidine, ranitidine, etc. It is better to inject the drugs into the muscle, since the tablet form has a later effect. These drugs stop the release of histamine, bradykinin and other substances that trigger allergies, eliminate swelling, itching and redness.
Symptomatic therapy
Colloidal and saline solutions are administered to prevent a decrease in pressure, as well as normalize the volume of blood in the bloodstream. Most often, 0.5–1.0 l of saline solution, 0.5 l of hydroxyethyl starch, and 0.4 l of polyglucin are used.
After achieving normal circulating blood values, it is possible to use vasopressor amines:
- 0.2–2 ml of norepinephrine per 0.5 l of 5% glucose;
- 400 mg of Dopamine per 0.5 l of 5% glucose.
The dose is adjusted until the systolic pressure reaches 90 mmHg. Art.
In case of bradycardia, subcutaneous injections of atropine (0.3–0.5 mg) are recommended. If necessary, atropine can be administered every 10 minutes.
When bronchospasm develops, agonists and other anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator drugs are used through a nebulizer.
Dyspnea, dry rales and cyanosis are indications for the use of oxygen therapy.
Sometimes it is possible to use catecholamines - adrenaline and ephedrine.
Diagnostics
To understand how to relieve swelling, the doctor initially examines the patient and studies the existing symptoms, taking into account the reaction of swelling to the administration of adrenaline.
Further diagnosis involves establishing the cause of the development of the pathology. Usually, to do this, it is enough to ask the victim about allergic diseases in his anamnesis or in the medical histories of his closest relatives.
Information about how the patient’s body reacts to taking different foods, administering certain medications, and contact with various animals is important. In some cases, special blood tests and allergy tests may be needed.
Quincke's edema, photo
The external signs of this disease are very noticeable . This is because most often they are located on open areas of the body. The instant change and appearance of puffiness of the skin immediately catches the eye of others.
In order to know how to act in situations where you or your loved ones suddenly show signs of illness, you need to clearly understand what angioedema is, its symptoms and treatment. Photos of its manifestations will help to accurately recognize the symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment of Quincke's edema is carried out in two stages. First, the acute process is stopped, then the cause that caused the pathology is eliminated.
Treatment at home is unacceptable; you can only provide first aid until the ambulance arrives, provides emergency treatment and takes the victim to the hospital.
The doctor will make a decision on how to treat the disease based on an examination and interview of the patient, as well as depending on the nature and severity.
If the patient has severe anaphylactic shock, swelling will be treated in intensive care. If there is swelling of the larynx, the victim may be in the intensive care unit or in the ENT department. In case of abdominal syndrome, the patient is placed in surgery. If there is no threat to life, then the swelling can be treated in an allergy or therapeutic department. In each specific case, the attending physician will prescribe individual drug therapy, which will help not only relieve swelling, but also remove accompanying symptoms.
If angioedema is of an allergic nature and is an anaphylactic reaction, then adrenaline, glucocorticoid hormones and antihistamines are first prescribed.
Detoxification must be carried out; for this, saline solution, reoplyuglyukin, ringer lactate or other solutions of similar action are injected intravenously.
In case of an allergic reaction to food, you need to drink enterosorbents - activated carbon, Sorbex, Enterosgel, etc. If you have difficulty breathing, you need to take antispasmodics that widen the airways and relieve spasms from the bronchi - Eufilin, Salbutamol, etc.
During the acute period of edema development and between its episodic recurrences, modern medicine uses several generations of anti-allergy drugs:
- 1st generation antihistamines: Suprastina, Pipolfen, Diprazin, Khifenadine, Avil, Omeril, Dazolin, etc. They begin to act within 20 minutes. These drugs are very effective in treating angioedema, but cause drowsiness and weaken the reaction, therefore they are contraindicated for drivers and operators of various equipment. Affects H1 histamine receptors;
- 2nd generation antihistamines block histamine receptors and normalize the functioning of mast cells, from which biologically active substances enter the blood. Zaditen will help to effectively cope with spasms of the respiratory tract; it is prescribed in addition to angioedema with bronchial asthma or broncho-obstructive pathologies;
- 3rd generation antihistamines do not have an inhibitory effect on the central nervous system, but they also block histamine receptors and normalize the functions of mast cells. These drugs include Loratadine, Astemizole, Semprex, Allergodil, Zyrtec, Cetrin and many others.
When a non-allergic form of the disease is diagnosed, in which the concentration of C1 inhibitor in the blood decreases, the treatment regimen will be slightly different. In this case, adrenaline, hormones and antihistamines are relegated to the background, since they have low effectiveness in combating this type of pathology. First of all, medications are prescribed that increase the concentration of the deficient enzyme in the blood, C1 inhibitor:
- purified concentrated C1 inhibitor;
- fresh frozen plasma;
- Danazol, Stanazolol – male sex hormones;
- Aminocaproic and tranexamic acid are antifibrinolytics.
In cases of severe swelling of the larynx, which completely blocks the airway, an incision is made in the cricothyroid ligament, and a special tube is inserted into the resulting hole for an alternative method of breathing. More severe patients are connected to a ventilator.
Quincke's edema in children, emergency care
There are a number of activities that have been developed to inform parents about what to do if Quincke's edema suddenly appears in their child. First of all, experts advise adults not to panic, calm the child down and call an ambulance, explaining over the phone what happened. Next, they advise you to act clearly and quickly, according to the instructions.
Upon arrival, doctors assess the situation and, accordingly, select medications and methods to alleviate the child’s condition. If there is laryngeal edema:
- Stop exposure to allergen
- Do oxygen inhalations
- Instill saline solution into a vein
- Adrenaline and Prednisolone are administered
- If previous methods of therapy are unsuccessful, tracheal intubation is performed.
- The upper respiratory tract is sanitized
- Conicotomy (surgical incision of the ligament between the cartilages) and artificial ventilation
It is noted that quickly and correctly provided assistance can greatly improve the condition of children and contribute to a speedy recovery. But even when the signs of the disease are neutralized, doctors will insist on urgently transferring the child to a hospital.
After a detailed examination and diagnosis in the hospital, the doctor prescribes measures aimed at neutralizing the factor that provoked the onset of the disease. In case of food allergies , a hypoallergenic diet is recommended: food that can provoke repeated negative symptoms is removed from the diet of the mother (if breastfeeding) or the child.
are also selected taking into account the baby’s age . To reduce susceptibility to food irritants, enzyme agents are often used in therapy: Creon, Festal. An important point in neutralizing edema and preventing its subsequent appearance is the treatment of foci of chronic infection: elimination of infectious diseases, helminthic infestations, and disturbances of intestinal microflora.
PS When a child develops this disease, face, hands, genitals, feet, mucous membranes of the mouth and throat often swell quickly Therefore, parents should be very careful and carefully monitor the baby’s skin and health. You especially need to be on guard in cases where the child has previously shown signs of allergies. Also at risk are children to whom this disease could be inherited.
Complications and consequences
People who do not know why angioedema is dangerous can treat it carelessly, and meanwhile, if the larynx or trachea swells, this can lead to asphyxia, followed by coma, disability and even death.
Edema in other organs also causes undesirable consequences. When the pathology is localized in the digestive system, peritonitis may develop, intestinal motility increases, and dyspeptic disorders may appear. When the genitourinary system is damaged, acute cystitis and urinary retention develop.
The greatest concern is swelling of the face, since it can lead to damage to the brain and its membranes, and labyrinthine systems and symptoms of meningitis may occur, which poses a direct threat to the patient’s life.
Nutrition Basics
When the swelling is of an allergic nature, it is very important to know exactly what you can and cannot eat. The diet should be developed taking into account the following rules:
- From the menu you need to exclude all products that can cause a direct or cross allergic reaction, that have a high content of amines and histamines, as well as foods that have high sensitizing properties. Products should not contain synthetic additives, dyes or preservatives;
- it is important that the diet is well thought out and balanced; excluded products must be replaced with analogues that are harmless to the patient;
- All food should be beneficial to a person, increase the body’s protective properties and improve health.
Here is a list of foods that can cause various allergic reactions, including giant urticaria:
- seafood, chicken eggs, soy, peanuts, milk, cocoa. Among plant foods, tomatoes, spinach, strawberries, grapes, bananas can cause allergies;
- a pseudo-allergic reaction can be caused not only by the products from the previous paragraph, but also by pineapples, chocolate and spices;
- Allergy sufferers should exclude wine from their diet;
- with caution you can eat foods high in biogenic amines and histamines - cod, tuna, herring, cheese, sauerkraut;
- you need to exclude gas-forming foods from the menu - legumes, black tea, coffee drinks, stewed and fried meat or fish.
The following products can cause cross-allergy:
- nuts during the hazel blossom period;
- apples when eaten together with pears, cherries, cherries and quince;
- taking certain foods with certain medications, such as aspirin with grapes, raspberries, apricots, etc. A reaction may occur when consuming chicken eggs with interferon and lysozyme or kefir with drugs of the penicillin group;
- bread and cereal dishes during the flowering period of cereal crops;
- kefir together with moldy cheese;
- cow's milk with veal and beef dishes;
- cow's milk with goat's milk;
- sea fish with seafood (crabs, shrimp, shellfish, caviar).
By choosing the right diet, you can minimize the risk of developing the disease.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of edema may include the following rules:
- adhere to a proper diet, and if you are prone to allergic reactions, follow a gentle diet;
- strengthen the immune system with vitamin and mineral complexes;
- eliminating foods that cause allergies from the diet;
- if you are allergic to certain medications, you need to warn your doctor about this and, if possible, replace them with other medications;
- When taking new antibiotics, you should always have antihistamines on hand;
- people with a hereditary form of edema should avoid surgery and injury.
To prevent harmful consequences, you need to seek help from a doctor at the first symptoms.
Examination for Quincke's edema
The main and decisive direction of the examination is to determine the cause and predisposition. If the swelling is caused by a hereditary factor, it is necessary to determine what disease or environmental reagent caused its manifestation.
Typically, angioedema occurs with prolonged exposure to an allergen: medication overdose, active spread of pollen, paint smell, food allergen. The patient may have previously had a mild allergic reaction to some foods or substances. It is very good if the patient remembers where and when, then it will be easier for the doctor to identify the allergen and prescribe treatment.