Weeping eczema is a dermatological disease that develops against the background of impaired immunity and neuroendocrine regulation of the body. Its main manifestations are the presence of skin rashes in the form of bubbles (vesicles) with serous contents. It occurs in an acute form, affecting the arms and legs, but in severe cases of the disease with relapses it can affect other areas of the body.
Types of eczema
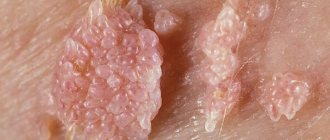
Manifestations of true eczema are always acute: it can begin in a person of any age, and the course of the disease will be jerky: frequent relapses, after which the disease becomes chronic, in which exacerbations periodically appear. The acute stage is characterized by the formation of multiple blisters, and after they open, weeping erosions . At the acute stage of the disease, a person suffers from severe burning and itching. When inflammation subsides, the total number of blisters decreases, the skin becomes dry and begins to peel. The size of the foci of true eczema can vary, the contours are often blurred, and the affected areas alternate with healthy areas of the skin. Such lesions usually occur symmetrically on the feet, forearms, and hands. The disease in children often affects the face, buttocks, limbs, and chest.
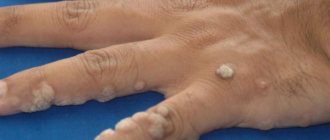
One of the subtypes of true eczema is dyshidrotic eczema , which, as a rule, develops on the soles, on the sides of the fingers, on the skin of the hands and palms. Symptoms of this form of the disease are the appearance of a large number of small blisters that have dense covers. The size of such bubbles is small - from 1 to 3 mm in diameter. The foci of the disease are easily distinguished, since they are surrounded by a rim of the stratum corneum, which peels off in the process. In the center of the formation, scales, crusts, and small erosions are noticeable. Treatment of dyshidrotic eczema should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor, and even any folk remedies can be practiced only after its permission.
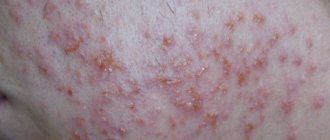
In microbial eczema, the lesions are located asymmetrically; as a rule, they occur on the human limbs and have a rounded outline. There are also ulcers and clearly defined boundaries of the stratum corneum. Often, with the development of this form of the disease, the patient eventually develops fistulas, trophic ulcers, and wounds that do not heal for a long time. Microvesicles are visible near the main focus of the disease . At the same time, far from the source of the disease, allergic rashes sometimes appear. A variety of this form of the disease is nummular eczema , in which the patient develops round lesions with clear boundaries. They have a diameter of no more than 3 cm, a blue-red hue, and scales are noticeable on the surface. Most often, such lesions are localized on the back of the hand, as well as on the extensor surface.
Seborrheic eczema develops on the scalp . Such a lesion can also involve the ears, shoulder blades and sternum area. In this case, it has a yellowish tint, the fatty scales are layered, and there is no weeping. Such foci are characterized by gradual regression in the central part with parallel growth on the periphery.
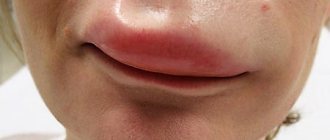
Occupational eczema is an ailment of an allergic nature, which manifests itself as a consequence of human contact with certain substances that irritate the skin. In this case, damage to exposed areas of the skin most often occurs: eczema can appear on the face, hands, neck, and forearm. In more rare cases, the feet and legs are affected. At the site of the disease, the presence of edema, vesicles, and periodic itching and weeping are noted. After some time, signs that are characteristic of true eczema begin to be noted. The disease lasts a long time, but if the patient no longer comes into contact with the allergen, which caused the development of the disease, then regression quickly occurs. The patient must realize that with each new exacerbation the disease will become more severe. Skin tests are used to determine the presence of high sensitivity to allergens.
The mycotic form of the disease manifests itself in the patient in the event of a fungal infection . In this case, eczema often develops on the legs. This form of lesions is characterized by significant peeling and round lesions. Treatment of eczema on the legs is carried out comprehensively: the use of antifungal drugs is mandatory.
In the paratraumatic form of the disease, rashes appear where there was previously an injury.
The development of varicose eczema is facilitated by the presence of varicose symptom complex of the legs. In this case, medications that are used to treat varicose veins .
Effective and popular drugs for dermatosis with blisters
The prescription of hormonal ointments or creams for eczema with blisters can be explained by the high efficiency and potency of the drug, which helps relieve inflammation and stop the rapid progression of the disease. Such medications can only be used after medical consultation. In addition, the doctor must monitor the progress of treatment. Corticosteroid drugs have a lot of contraindications and are highly likely to develop side effects. As a rule, medications of this group are applied to the inflamed areas for a week. Otherwise, the medications may become addictive to the body. Most often, hormonal treatment of vesicular eczema involves the use of the following drugs:
- Lokoid;
- Elokom;
- Triderm;
- Advantan;
- Sinaflan;
- Celestoderm.
In parallel with the external use of hormonal ointments, antiallergic drugs are taken orally, which are necessary to desensitize the diseased epidermis and eliminate symptoms. Antihistamine therapy usually lasts about a month. Mostly for eczema, doctors prescribe:
- Tavegil;
- Suprastin;
- Lorantadine;
- Cetrin.
Absorbing drugs have a good effect, cleansing the body, thereby helping to speed up the process of removing toxins from its limits. The easiest way to combat harmful waste and toxins is to use activated carbon. A similar, but more effective principle of operation has:
- Multisorb;
- Atoxyl;
- Enterosgel.
Antiseptic solutions prevent the entry of pathogenic agents and disinfect the epidermis. The treatment is carried out before the direct application of external hormonal ointments. Zelenka, Fukortsin or Bactoderm do not contribute to cauterization or opening of the vesicles. In no case should you puncture blisters, wishing for a speedy recovery.
For microbial eczema with blisters, antibacterial treatment will be a mandatory addition to general drug therapy. Among the external preparations, it is worth noting tetracycline ointment, Sintomycin, Levomekol. Antibiotics from the category of cephalosporins, macrolides, and aminoglycosides are prescribed in tablets. In case of fungal infection of tissues, the dermatologist will prescribe appropriate antimycotic treatment.
For eczema, hormonal ointments or creams are prescribed due to their high efficiency and potency.
Causes of eczema
This disease is also called weeping lichen . Eczema is of a neuro-allergic nature. As a rule, during the development of the disease, redness and swelling of the skin appear, after which cracks and very small blisters gradually form, which are difficult to distinguish with the naked eye or in a photo. At first, the skin in the affected area is dry, but later ulcers or wet skin appear in place of the blisters. Most often, this disease develops in children, and if proper treatment is not provided, the disease gradually becomes chronic.
A number of factors, both internal and external, are identified as the causes of the disease. This is a genetic predisposition, disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems, secondary immunodeficiency , infections, allergic reactions. Sometimes the occurrence of eczema is associated with dysfunction of the central nervous system, as well as damage to peripheral nerves.
Nutrition
Diet plays a very important role in the treatment of this form of eczema.
Patients need to exclude any fried, spicy, fatty or smoked foods from their diet. Sweets and products from the group of potential allergens (citrus fruits, etc.) are prohibited. You should give preference to steamed plant foods. In the chronic form of weeping eczema, such a diet is followed for life, otherwise the patient experiences a large number of relapses.
Symptoms of eczema
A characteristic feature of the disease is the symmetry of the manifested processes. In children, eczema often develops on the face, chin, and less commonly on the head, back, chest, knees and elbows. In adult patients, eczema is often diagnosed on the arms, neck, ankles, as well as in bends - on the inside of the elbow or on the outside of the knee. To determine how to treat a disease, it is important to initially attribute the manifested disease to a specific type.
However, there are a number of symptoms characteristic of all types of the disease: redness of the skin, the appearance of blisters, crusts, cracks, the presence of peeling and scratching. Also, spots appear on the affected areas, the color of which can vary from pink to bluish. It is important to treat eczema on the hands, as well as on other parts of the body, in such a way as to reduce the manifestations of another symptom - attacks of severe itching, which most often appear in the evenings, as well as immediately after contact of the affected area of the body with water.
Treatment with folk remedies
You can learn how to cure eczema from traditional medicine recipes that have survived to this day. An effective ointment, which includes 20 g of burdock leaves, chamomile flowers, coffin root, and fireweed herb. All these components are used in dried form. Water is added to this mixture and the herbs are simmered over low heat. Later you need to add a tablespoon of oil to them. Once the mixture has thickened enough, it is filtered and mixed halfway with glycerin.
You can also prepare an ordinary decoction of burdock root for external use, for the preparation of which you need to add 15 g of crushed dry burdock root to one glass of water and boil for ten minutes. Compresses for the affected areas are also made from fresh strawberries, previously well crushed.
Traditional medicine also recommends decoctions and infusions for internal use. In this case, you can undergo treatment with a decoction of dead nettle flowers, which is consumed several times a day half an hour before meals. Similarly, you can take a decoction of wheatgrass root and verbena tea. It is also recommended to drink tea from dried viburnum fruits, and also take 2 ml of sea buckthorn oil for several days.
Recommendations for eczema
On days when the disease worsens, you should definitely follow a diet, eliminating all allergens from the diet. There is no need to allow affected areas of the body to come into contact with water or household chemicals. You should also limit contact with allergens, which at one time have already caused the development of the disease. It is important to prevent infections from entering the body, in particular the herpes .
It is imperative to sanitize foci of infection, which are giardiasis of the biliary tract , acute pyoderma , varicose veins , and intestinal dysbiosis .
Treatment of eczema in children requires mandatory deworming . During treatment, the child should receive a large amount of natural vitamins from vegetables and fruits.
What is weeping
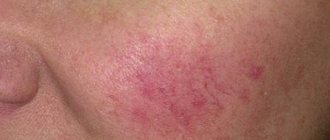
Weeping is a weeping area on the skin that occurs as a result of an abnormal process, which is expressed in the exudation (secretion) of serous, bloody or purulent fluid (exudate) through small erosions (damages) of the epidermis (the upper layer of the skin). Weeping is not a disease, it is a sign of a pathological process occurring in a separate area of the skin or a symptom of internal disorders and dermatological diseases.
Serous exudate looks like a transparent whitish liquid containing proteins, leukocytes (white blood cells), breakdown products, and toxins.
The leading factors in the manifestation of weeping erosions due to exudation are considered to be:
- increased permeability of blood vessels (capillaries, venules - small veins) as a result of inflammation or aggression of allergens;
- as well as an increase in pressure in the vessels of affected tissues due to hyperemia (overflow of blood).
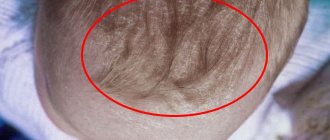
Weeping behind the ears of a child (photo)
Eczema in children
Weeping lichen in children manifests itself with the presence of signs of seborrheic , true and microbial eczema. The symptoms of these forms of the disease are combined in different ways and can be combined on different parts of the body. The first symptoms of the disease may appear in children who are three months old. The disease is mainly typical for babies who are artificially fed. Initially, the child’s forehead may be affected, then the cheeks. After this, the lesion gradually affects the scalp, neck, ears, limbs, torso, and buttocks. The child is worried about insomnia, as he feels severe itching. Seborrheic eczema can appear as early as the second week of a child’s life. In this case, a rash appears in the hair, on the cheeks and forehead, on the ears and on the folds of the neck. Sometimes children also have signs of microbial eczema.
Eczema can sometimes be accompanied by asthma and occur against the background of exudative diathesis . Often the tendency to eczema is observed throughout life. Children suffering from this disease are often allergic to certain foods, smells, dust, and medications. Any allergic reaction can become a kind of impetus for the development of eczema.
It is important to pay close attention to this problem in infants. It is imperative to consult a doctor regarding feeding such children. Babies with eczema should not be swaddled tightly, nor should they wear clothes made from non-natural fabrics. When bathing your baby, you can add string, chamomile, or oak bark to the water.