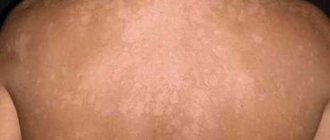
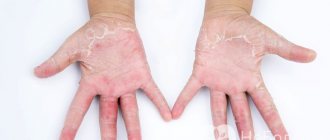
A clean and healthy dermis is the dream of many people. Often patients turn to the doctor asking: dark spots on the skin, what are they? Defects can be caused by different pathogens. They indicate a disruption in the functioning of internal organs, but sometimes arise due to external factors. Dermatologists will explain how to get rid of unpleasant formations.
Dark spots on the skin
The appearance of dark spots on the face or body always upsets us.
This seemingly only aesthetic problem makes you feel embarrassed in front of others and look for various cosmetic methods to eliminate hated dark pigmentation. However, dark spots on the skin are not only an external defect.
Their appearance in many cases signals malfunctions in the functioning of various systems or organs and requires a comprehensive examination and observation by a specialist.
Treatment
The therapy is prescribed by doctors, but if the defects are caused by external factors, then you can use the advice of traditional medicine. The following recipes are common among them:
- Lemon juice will help people who don’t know how to remove dark spots under their arms. You need to take a piece of citrus and rub it on the problem area of the skin. After twenty minutes, wash the cavities with warm water and lubricate with nourishing cream.
- Mix a little water with two teaspoons of baking soda until you get a paste. Apply the scrub to problem areas. Massage for 2 minutes, then rinse.
- For people who are looking for ways to get rid of dark spots under their arms, juice from raw potatoes will help. You need to soak a compress in it, apply it to the pigmented area for half an hour, then rinse it off.
Before using the advice of traditional medicine, you should consult a doctor. This treatment is combined with traditional therapy. Initially, you should make sure that there are no allergic reactions to the ingredients of masks and scrubs.
Causes
There are many reasons why dark spots appear on the skin. Among them:
- bad heredity,
- pregnancy and hormonal changes in the body,
- diseases of internal organs, for example, adrenal glands (Addison and Cushing syndrome),
- age,
- excessive exposure to the sun or solarium,
- skin damage (burn or mechanical impact),
- incorrectly selected drugs,
- constant stress,
- gynecological diseases,
- lack of ascorbic acid, etc.
Prevention measures
The likelihood of any type of pigmentation can be reduced by following preventive measures:
- In summer, do not go outside without sunscreen applied to your body.
- Avoid visiting a solarium, especially if your skin is light or prone to pigmentation.
- Do not use dubious creams, lotions and other products to care for the epidermis.
- Try to stay out of the sun from 11:00 to 16:00.
- Never take antibiotics or hormonal pills without a doctor's prescription.
Monitor your diet:
- exclude all semi-finished products;
- do not drink soda, alcohol and coffee;
- eat seasonal fruits and vegetables;
- consume a minimum of smoked meats, pickles and sweets.
Important: to improve skin color and normalize melanin production, you should drink 2–3 liters of clean water per day.
Age spots appear on various parts of the body and can be of any shape or color. They can be dealt with using many methods, ranging from laser removal to folk remedies.
The main thing is to coordinate any option for eliminating skin changes with your doctor and listen to all his recommendations.
Blitz tips:
- visit a medical office as soon as pigment spots begin to form;
- Make sure that on a sunny day the skin is protected from ultraviolet rays;
- if after any treatment option side effects begin or there is a deterioration in the skin condition, you need to visit a doctor and choose a different method of therapy;
- Do not start any salon procedures to lighten the epidermis without first consulting a dermatologist.
Causes and main symptoms of melanosis
Many long-term or severe chronic pathologies can lead to excessive melanin deposition in the skin.
Melanoses in diseases of internal organs
Such pigmentation disorders can be caused by the following pathologies:
- Endocrine melanosis. This pathology is observed with congenital or acquired dysfunctions of the endocrine system. The cause of the appearance of dark spots on the skin can be the following pathologies: insufficiency of the adrenal cortex, dysfunction of the gonads, the synthesis of melanophore hormone by the pituitary gland, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, Sape-Lawrence syndrome, etc.
- Hepatic melanosis. The cause of dark spots on the skin is liver dysfunction caused by cirrhosis and other diseases.
- Uremic melanosis. The cause of dark spots on the skin is chronic renal failure, leading to pigmentation disorders.
- Cachectic melanosis. The cause of dark spots on the skin is severe forms of tuberculosis.
Toxic reticular melanosis
This disorder of skin pigmentation develops as a result of chronic poisoning of the body, which develops during prolonged contact with various lubricants, coal, machine oil, tar, oil or resins. In addition to the development of melanosis, patients experience symptoms of general health problems.
Arsenic melanosis
This disorder of skin pigmentation develops as a result of chronic poisoning of the body with arsenic. This chemical can enter the body when taking arsenic preparations (Osarol, Miarsenol, Novareslon, etc.) or when working with certain agricultural preparations or in hazardous industries.
Melanosis (nevus) of Becker
Becker's nevus most often appears in boys 10-15 years old. This pigmentation disorder can occur in men and, sometimes, in women. A nevus looks like a yellowish or dark brown spot of irregular shape. Its edges are uneven or scalloped, and there is increased hair growth on the surface.
The location of Becker's nevus can vary, but most often it is observed on the shoulders, forearms, chest, back or legs. At first it looks like a small island, but gradually increases in size (sometimes more than 20 cm in diameter).
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
The exact reasons for the development of Becker's nevus remain unclear. However, the fact that it is more often observed in males and is accompanied by pronounced hair growth indicates an important role in its formation of male sex hormones.
Other assumptions link its development to exposure to ultraviolet rays, since its appearance can often be associated with the presence of insolation. A possible hereditary predisposition to this type of pigmentation disorder cannot be ruled out, since familial cases of Becker melanosis are often identified.
Dubreuil's melanosis
This pigmentation disorder is considered a precancerous condition. It appears as a small, flat, but slightly raised dark spot of irregular shape. Its dimensions initially reach 2-5 cm, but over time (after several years) they can increase to 8-10 cm.
The contours of the spot resemble a geographical map, and the color can vary from light or dark brown to black. As precancerous Dubreuil's melanosis progresses, it may be accompanied by the appearance of papillomatous, papular and nodular elements on the surface of the spot.
The spot becomes darker, and areas of compaction, peeling and erosion may be observed on it. Redness, freckles, telangiectasia, and keratosis may appear around the hyperpigmented area. Such changes in the spot in Dubreuil's melanosis may indicate its transformation into a malignant tumor (melanoma).
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
This disease is not common. It can be observed in both men and women, and is more often detected in adulthood (after 50 years). According to some experts, this pigmentation disorder is more often observed in women.
Various factors can contribute to the development of precancerous melanosis Dubreuil:
- age;
- race (pathology is extremely rare among representatives of the Negroid race);
- skin photosensitivity;
- frequent skin trauma;
- tanning abuse;
- overdrying of the skin.
The transformation of Dubreuil's melanosis into a cancerous tumor can occur after 2-30 years (on average 10-15 years). According to some statistics, malignant melanoma in 20-30% of cases develops against the background of such a pigmentation disorder. The transformation of Dubreuil's melanosis (in 40-75% of cases) into cancer is especially likely if left untreated.
Acanthosis nigricans
This rare skin disease can occur in a benign or malignant form. The clinical picture of acanthosis nigricans is accompanied by the appearance of black or dark brown spots with hyperkeratosis and papillomatosis.
They are most often located in large natural folds (under the mammary glands, armpits, intergluteal region, under the knees, between the back of the head and neck, etc.) or on the elbows. The severity of symptoms depends on the form of the disease - with a malignant course, changes in the skin are more pronounced and progress faster.
Various factors can cause the development of acanthosis nigricans:
- genetic predisposition;
- malignant tumors;
- endocrine diseases;
- taking hormonal medications;
- long-term use of certain medications.
In young people, this disease often develops due to a genetic predisposition or endocrine diseases, and in older people, it often becomes a sign of the formation of a malignant neoplasm. Sometimes the symptoms of acanthosis nigricans become harbingers of cancer.
Urticaria pigmentosa (mastocytosis)
https://youtu.be/f7JJa0FomSM
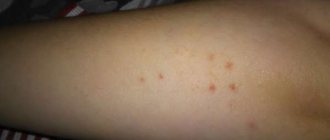
Urticaria pigmentosa is a form of mastocytosis and is observed in 75% of cases in children. Itchy red-pink spots appear on the body of a sick child, which transform into blisters filled with clear liquid (sometimes mixed with blood).
After opening such skin changes, brownish-brown pigmentation remains on the skin (in some cases, the blisters leave no traces). In 70% of cases, during or after puberty, areas of hyperpigmentation resolve on their own.
In adults, urticaria pigmentosa does not proceed as favorably as in children, and is often complicated by systemic mastocytosis, which leads to disability and death of the patient. The reasons for the development of urticaria pigmentosa and mastocytosis have not yet been sufficiently studied.
Scientists suggest that these pathologies can be provoked by the following factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- inflammatory processes caused by toxic lesions or infections;
- immune reactions;
- stress;
- climate change;
- insolation, etc.
Nevus spilus (coffee stain)
This type of hyperpigmentation is accompanied by the appearance of one or several spots with uniform coloring and clear contours. They can be localized on any part of the skin, are present from birth or appear spontaneously. The sizes of coffee stains can vary and increase as they grow.
Their shade can range from light to dark brown. Darker or black dots are sometimes observed on the surface of the spots and there is never any hair growth.
The reasons for the appearance of Nevus spilus are not yet well understood. There are suggestions that their formation is provoked by a hereditary predisposition.
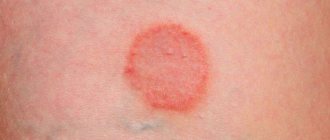
Lentigo
These dark, smooth spots on the skin are benign hyperpigmentations that are yellowish-brown or dark brown in color. Their sizes can reach 1-2 cm in diameter. The spots can be localized on the face, neck, or the surfaces of the arms and legs.
They are characterized by a chronic course, slow progression and extremely rare degeneration into malignant melanoma (the risk of malignancy increases with frequent trauma to the skin in the area of the spot).
Lentigo can occur among patients of any age group. Among the reasons for their appearance are the following factors:
- gene mutations;
- genetic predisposition (heredity, phonotype);
- hormonal imbalance (puberty, pregnancy, menopause, hormonal disorders, taking hormonal medications);
- long-term insolation;
- hypersensitivity to ultraviolet rays;
- sunburn in childhood;
- long-term exposure to artificial sources of learning;
- age;
- immune disorders;
- AIDS;
- immunosuppression after organ transplantation;
- carriage of human papillomavirus.
Lentigo is often provoked by a combination of several of the factors described above.
LEOPARD syndrome
This pathology is characterized by the appearance at a young age of hundreds of lentigines on the surface of the skin of the trunk, face and limbs.
It is always accompanied by disorders in other organs and systems: valvular stenosis of the pulmonary artery, impaired cardiac conduction, growth retardation, mild mental retardation, hypospadias and other pathologies of the genital organs, late onset of menstruation, sensorineural deafness and widely spaced eyes.
LEOPARD syndrome is always caused by gene mutations:
- PTPN11;
- RAF.
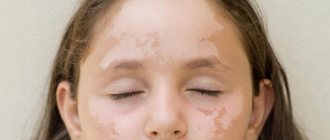
Chloasma
These multiple or single dark spots appear in women and are irregularly shaped areas of hyperpigmentation that are yellow-brown (sometimes darker) in color. In some cases they are large in size, and their outlines resemble a geographical map.
The location of chloasma can be different: face, nipples, torso (along the white line of the abdomen), genitals. In winter and autumn, hyperpigmentation may fade.
The reason for the appearance of such dark spots is always associated with hormonal imbalance (increased estrogen levels):
- ovarian dysfunction;
- pregnancy;
- menopause period.
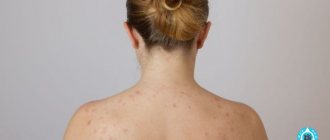
Freckles
These small, dark patches of light yellow or deeper brown skin may appear on the face or body. They often appear in children, become more noticeable in spring and summer (during periods of greater solar activity) and may disappear completely with age.
Most often, freckles appear in people of phototypes I-II (blond hair and skin, blue or green eyes) after exposure to ultraviolet rays. Scientists have proven a hereditary predisposition to this type of hyperpigmentation.
Poikiloderma
This type of dark spots is a special type of skin atrophy that is accompanied by patchy or reticular hyperpigmentation and telangiectasia. Dermatologists distinguish congenital (Thomson syndrome) and acquired types of poikiloderma. Pathologies are accompanied by the appearance of redness and swelling on the skin.
Subsequently, skin atrophy develops and telangiectasia, hyperpigmentation and depigmentation appear. Patients have hypersensitivity to ultraviolet rays. Skin changes can be observed on the face, neck, arms, legs and buttocks.
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
With congenital poikiloderma, which is more often observed in women, other pathologies are present: underdevelopment of the genital organs, cataracts, abnormalities of hair, teeth, nails and bones.
The following factors can cause the development of poikiloderma:
- pathological gene on chromosome 8 (with congenital pathology);
- frequent and prolonged exposure to sunlight on the neck and chest;
- ionizing radiation;
- some cosmetics;
- endocrine disorders;
- oncological diseases;
- connective tissue pathologies;
- muscle tissue diseases;
- dermatological diseases;
- other unknown reasons.
Recklinghausen's disease
With Recklinghausen's disease (or neurofibromatosis type I), dark café-au-lait spots appear on the skin, rashes in the form of "clusters" of freckles (in atypical places) and neurofibromas.
Hyperpigmented spots may be present on the body from birth or appear during childhood. The intensity of their color can vary and is usually represented by brown shades, but in some cases they can have a gray-blue color. They are usually located on the surface of the limbs or torso, and there are at least five of them.
With age, their number may increase. Neurofibromas appear on the patient's body. And subsequently they appear in other systems and organs (on nervous tissue, adrenal glands, etc.). In 3-15% of cases they can degenerate into cancerous tumors.
As the disease progresses, the nervous system and musculoskeletal system are involved in the pathological process. Patients exhibit varying degrees of mental retardation, epileptic seizures, depression and psychological disorders.
On the bone side, patients with neurofibromatosis exhibit various anomalies: kyphosis, defects of the vertebral bodies, cysts in the long bones, etc.
Also, with Recklinghausen's disease, the following disorders are detected:
- Lisch nodules (hamarthromas on the iris of the eye);
- premature puberty;
- gynecomastia;
- growth disorders;
- syringomyelia (a disease accompanied by the appearance of cavities in the spinal cord);
- pulmonary and renal artery stenosis;
- formation of cysts in the lungs.
The cause of Recklinghausen's disease is a mutation in the gene of chromosome 17, which manifests itself in 100% of cases and cannot go unnoticed throughout life. This severe disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner and increases the risk of developing malignant neoplasms.
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
With Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, small lentigine-shaped spots of brownish-yellow, brown or dark brown color appear on the skin and mucous membranes of the patient. On the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, nasopharynx, sclera and red border of the lips they have a blue-brown color. The size of pigmentation can reach 1-4 mm.
On the face they are most often localized around the lips and eyes or around the nostrils, and on the body - on the back of the hands and forearms, chest, abdomen and palms. Less commonly, hyperpigmentation is observed on the forehead, chin, external genitalia, or around the anus.
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
In patients with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, polyps form in the intestinal lumen. These neoplasms lead to the periodic appearance of abdominal pain, dyspeptic disorders, diarrhea, rumbling in the abdomen and flatulence. Subsequently, they can degenerate into malignant tumors.
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner and is often observed in several family members. This pathology is common on all continents and is somewhat more common in women. In some cases, the pathology occurs without the appearance of dark spots on the skin and mucous membranes and is accompanied only by the development of intestinal polyposis. Causes and main symptoms of blue-gray dispigmentation
Nevus Ota
Nevus of Ota is a unilateral single spot of black-bluish or dark blue color, which is located in the area of the eye, upper jaw and cheek. Sometimes such a pigmentation disorder consists of several spots merging with each other. In rare cases, this dyspigmentation can be bilateral.
Such a dark spot can spread to the sclera and mucous membranes of the eye, pharynx and nose. The intensity of its color can vary - from slightly noticeable to ugly saturated. The spot is present from birth or appears during adolescence and does not disappear on its own. Sometimes nevus of Ota transforms into melanoma of the skin.
Scientists do not yet know the exact reasons for the appearance of such blue-gray dispigmentation. Presumably the formation of nevus of Ota is due to hereditary factors, but this theory has not yet received substantiated confirmation.
In most cases, such dark spots appear in people of the Mongoloid race. In isolated cases, nevus of Ota is detected in people of European or Negroid races.
Nevus Ita
The symptoms of nevus of Ita are in many ways similar to the symptoms of nevus of Ota. The only difference between such a dark spot is its location - the area of hyperpigmentation is localized on the neck, in the chest or shoulder blade area, or under the collarbone.
Mongolian spot
With a Mongolian spot, an area of gray-blue, bluish or bluish-brown pigmentation of an irregular or round shape is found on the skin of a newborn. Its size can vary (from 1-2 to 10 or more centimeters in diameter).
It is usually located in the lumbosacral region, but can also be localized in other parts of the body (back, buttocks, back of the lower leg, etc.). Sometimes migration of the area of dyspigmentation may be observed, i.e. displacement (for example, from the lumbar region to the buttock).
In most cases, the Mongolian spot is single, but multiple dispigmentations of this type also occur. There have been no cases of such dark spots transforming into skin cancer.
At first, the dispigmentation has a rich color, but with age it becomes pale and gradually decreases in size. More often, the spot completely disappears by 4-5 years, but sometimes it can be observed up to 7-13 years. In rare cases, the Mongolian spot is also present in adults.
Scientists believe that such dyspigmentation develops with incomplete migration of melanocytes from the deeper layers of the skin into the epidermis. The exact reason for this incomplete process is still unknown. The Mongolian spot is observed in 90% of cases in children of the Mongoloid race, often detected in the Negroid race and only in 1% of cases among Caucasians.
Pharmacy products
Vitamin F99 fatty
- Fastest acting
- Country Russia
- Price: 117 RUR
- Rating (2020): 9.5
This cream contains vitamin F, which is one of the most important components for maintaining healthy skin. With its deficiency, poor healing of even small wounds is observed, ulcers may occur that leave scars, the skin begins to peel off severely, and pigmentation is disturbed. Therefore, additional use of products containing this vitamin prevents possible problems. In addition, vitamin F restores the walls of blood vessels, improves their permeability and blood flow, resulting in an improved complexion.
- Advantages
- Evens out facial tone
- Promotes a healthy glow
- No smell
- Effect in the first days of use
- Several forms of cream depending on skin type
Retinoic ointment
- Improves skin smoothness
- Country Russia
- Price: 270 RUR
- Rating (2020): 9
The main active ingredient of retinoic ointment is a synthetic analogue of vitamin A, which is a powerful antioxidant, prevents the proliferation of melanin cells, normalizes the functioning of the sebaceous glands, increases the protective properties of the skin and promotes exfoliation of the epidermis.
- Advantages
- Helps in the fight against wrinkles
- Accelerates regeneration processes
- Can be used for a long time (up to 12 months)
BTpeel lactic acid
- Complex action
- Country Russia
- Price: 590 RUR
- Rating (2020): 9
Did you think that hyperpigmentation can only be removed with professional and expensive means? But no! Simple pharmaceutical products are in no way inferior to professional ones. For example, lactic acid has an exfoliating effect, stimulates the formation of new cells that no longer contain melanin, and blocks the action of pigment, preventing the reappearance of age spots.
- Advantages
- Mild healing effect
- Stimulates the formation of hyaluronic acid
- Lots of good reviews
- Included in cosmetics
- Suitable for sensitive skin
Badyaga
- Helps in treating bruises
- Country Russia
- Price: 68 R
- Rating (2020): 9.5
Another well-known natural-based product, the main active component of which is the extract of badyagi - a freshwater sponge, which is included in many cosmetics. Creams based on it have the consistency of a scrub and exfoliate the skin well, removing cells with pigment. In addition, this consistency has an irritating effect, increasing blood flow and nutrition of dermal cells, due to which age spots gradually lighten.
- Advantages
- Helps tighten pores
- Accelerates wound healing
- Reduces the activity of the sebaceous glands
Liquorice root
- Wide range of applications
- Country Russia
- Price: 21 R
- Rating (2020): 9.5
Licorice root is not a new cough medicine known to many, but that is not why it was included in our selection. The fact is that licorice root extract can be used not only internally, but also externally. Licorice contains a very large amount of antioxidants, vitamins, has an anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effect, and gently whitens stains without causing excessive irritation. Interestingly, you can use not only syrup for skin care, but also a self-prepared infusion.
- Advantages
- Suitable for age-related pigmentation
- Can be applied to scalp and hair
- Can be used as a mask
- Can be combined with other products
Diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis, if spots appear on the skin, you need to contact a dermatologist.
Considering the variety of causes that cause skin pigmentation disorders, the doctor can prescribe consultations with various specialized specialists: endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, geneticist, urologist, phthisiatrician, occupational pathologist, oncologist, allergist, immunologist, cosmetologist, neurologist, orthopedist, surgeon.
Sometimes only treatment under the supervision of several doctors helps to get rid of the disease.