Growing moles are an increase in the size of formations that previously had a flat appearance or small diameter. The condition is provoked by inflammatory processes and various internal health problems. Formations appear in a person several months after birth and increase in number and change throughout life. The process is influenced by various factors, most of which are negative for the skin.
The mechanism of appearance of moles
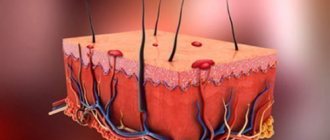
A mole is an area of accumulation of melanocytes. A nevus consists of skin cells containing an excess amount of pigment. The first birthmark appears in a child between the ages of 6 months and 1 year.
The first spots are difficult to notice; they are transparent and have not yet had time to color. Over time, their color becomes brighter and darker.
The formation of moles occurs before the age of 24. In older age, the appearance of new elements is associated with various external and internal factors. By the age of 70-80, all neoplasms disappear and are replaced by senile pigmentation.
Nevi come in different types. The evaluation criteria are shape, size, shade. The palette is wide, you can find red, blue, pink, brown. The tone may become darker after tanning or lighter after cosmetic procedures.
Main types of moles:
- flat, located in the upper layer of the skin, safe;
- hemangioma - a small red nodule, slightly hanging;
- blue, characterized by a smooth surface, hemispherical shape;
- convex, grow from the deep layers of the dermis, have a small diameter, hairs often grow through them;
- large pigment spots are congenital formations that grow with a person.
Causes
There is nothing dangerous or frightening about the formation of new moles. For some people, it is difficult to determine the cause, the source of pigmentation.
Appearance in childhood is a normal, natural process.
The location and type of spot were determined at the genetic level and are passed on from parent to child. You can often find identical nevi in close relatives. Caution should be exercised in case of an unreasonable increase in the number of spots or their unusual appearance.
Acquired growths tend to degenerate into malignant cancer. It is important to know the reason for their growth and to protect against the consequences in time.
Internal factors
If, after 25 years, pigmented neoplasms begin to actively appear on the body, it is necessary to pay attention to the state of health. Often the reason lies inside; to find it, you need to seek medical help and get tested.
- Changes in hormonal levels. If there is an imbalance in the body, the pituitary gland begins to actively produce a hormone that increases the amount of melanin in skin cells. The body becomes covered with pigment spots, and the size of existing elements changes. A surge can be triggered by pregnancy, abortion, menopause, adolescence, and disturbances in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
- Stress, long-term depression.
- Lack of ascorbic acid, vitamin K or iron in the body.
- Pathologies of the pancreas, causing complications such as diabetes and other serious diseases.
- Problems in the functioning of the liver.
- Exacerbations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Bad habits.
- Problems of a dermatological nature.
By eliminating the source of the problem in time, you can stop the process of abnormal pigmentation.
In most cases, after restoration of hormonal balance and treatment of diseases, acquired nevi disappear or lighten on their own.
External factors
The skin protects the body from environmental influences. New spots are a possible signal of the emergence of dangerous internal processes. If the problem is detected in a timely manner, many unpleasant consequences can be prevented, including cosmetic defects and melanoma.
The main reasons for the appearance of moles:
- ultraviolet radiation. Under the influence of the sun or rays in a solarium, the production of the coloring substance – melanin – increases. The main factor provoking the appearance of new nevi. Melanin accumulates in excess and comes out. A scattering of freckles and large elements can be observed after intense tanning. The spots are dangerous and can cause skin cancer. Excess sun can cause degeneration of any benign formation;
- change in radioactive background. Dermatologists often indicate an increase in the number of birthmarks after patients undergo fluorography or other radiation-related examinations;
- injuries. After burns, cuts, surgical interventions, the injured area is covered with young skin, which reacts sharply to exposure to direct sunlight and other negative factors;
- poor environmental situation. Toxic substances and radiation negatively affect the condition of the skin. The pregnant body with weakened immune defense reacts sharply.
It is important to eliminate the dangerous factor, long-term exposure to which provokes changes in information in cells and the emergence of a cancerous tumor.
Where do moles most often grow?
The appearance of nevi is facilitated by various internal and external factors; they determine the location of their localization.
A dark birthmark can form on any part of the body: leg, buttock, foot, elbow. The formation is not dangerous and is often inherited from parents; during life it can change shade, shape and size for no apparent reason.
The neck, face, head, ear tend to become covered with red moles, which is caused by vasodilation, small pigments and papillomas (a hanging convex growth that has a thin stalk). These manifestations become malignant as a result of injuries or excessive exposure to the sun, and can remain for a long time or disappear on their own. Papillomas tend to grow and multiply. It is necessary to get rid of them in time before healthy skin becomes infected or inflammation begins.
Mongolid spots are characteristic of people with dark skin. Location: buttock or lower back. It is often diagnosed in childhood and goes away by age 15.
Flat convex hemangiomas form during the period of waiting for a child or after childbirth, due to hormonal imbalances. If growth and change in shape are observed, removal is recommended. The older the age, the more education.
Light moles matching the color of the skin can appear in different places: stomach, back, face. If the amount increases noticeably, consult a dermatologist.
The largest number of nevi is observed in people with fair skin, blond or red hair. Often spots are found on exposed parts of the body - face, shoulders, arms. This is how the skin is protected from ultraviolet radiation.
Alarm Signals
The following signs may indicate the probable onset of malignant processes in a skin growth:
- increase in size to 6 mm or more;
- uneven color with the presence of several shades;
- roughness, uneven surface, presence of cracks;
- lack of clear boundaries, their unevenness;
- constant modification of education;
- itching, bleeding, swelling, redness or darkening.
Any of the described phenomena should cause concern. For example, if a red mole has increased in size, you should immediately visit a dermatologist. Only a doctor is able to assess the condition of the growth and determine the level of risk of malignant degeneration.
Why do moles get bigger?
Nevus tends to change size, color and shape. In some cases, the process occurs unnoticed and takes several years; in other situations, changes occur in just a few months.
Reasons for enlarging moles:
- Thyroid diseases. Due to improper production of hormones, lack of vitamins and minerals, the growth of pigmented tumors increases.
- Hormonal changes. The growth and thickening of a mole is a serious pathological process that indicates problems within the body. Hormone imbalance occurs unexpectedly and sharply, internal organs, tissues and systems react with the appearance of moles.
- Injury. Regular or single friction, disruption of the integrity of the nevus leads to cell division and proliferation.
- Ultraviolet exposure. Solarium and sun negatively affect moles, provoking changes.
- Papillomavirus. For a long time, the viral element may look like a mole, but as immunity decreases, it begins to darken and increase in diameter.
Be sure to consult a doctor if suspicious changes are observed.
Is the rapid growth and enlargement of nevi safe?
Rapid growth is considered to be an increase of 1-2 mm per year. If the speed is less and there are no other symptoms of degeneration, then the process is caused by physiological factors and is not dangerous to health or life.
A simple home method will help you accurately determine the change in size. Apply a ruler with millimeter markings to the growth and take a clear photograph. After a period of time, repeat the action and compare the results.
If the growth is rapid, you should immediately contact a specialist. An oncologist will come to your aid and perform diagnostics using modern equipment and a microscope.
What to do if it becomes voluminous?
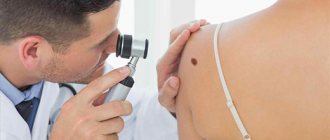
If the nevus becomes voluminous, it would be a good idea to show it to the doctor. A specialist will examine the mole using a special device (dermatoscope) and draw conclusions about its potential danger. Your doctor may advise:
- Observe the nevus and avoid injuring it.
- Remove a mole.
Doctor's recommendations
Doctors strongly recommend that their patients be vigilant, because even absolutely safe nevi will need to be monitored subsequently so as not to miss the possible development of cancer. You may be concerned about:
- Rapid and sudden growth.
- Asymmetry.
- Changing the edge.
- Change in color.
- Ulceration and bleeding.
If any of the warning signs appear or if a raised mole is accidentally injured, it is better to seek medical help at a dermatological clinic.
Should I delete it?
There is no need to remove ordinary raised moles that are not suspicious and do not bring any discomfort to their owner. The patient can get rid of the nevus at his own request if he simply does not like such a formation. Contrary to popular belief, removing a mole cannot trigger the development of cancer.
Sometimes doctors strongly recommend removing raised moles, especially if they grow large (more than 6 mm) and are constantly injured. Most often, before getting rid of a nevus, the patient is recommended to undergo a series of tests, but they can be performed after the intervention.
Potentially dangerous moles must be removed in any case, but only under the supervision of an experienced specialist and with mandatory histological examination of the removed material.
Is removal on the face dangerous?
Modern methods of dermatology and aesthetic cosmetology surgery make it possible to get rid of nevi on the face reliably and permanently without negative consequences for appearance. But at the same time, experienced doctors strongly do not recommend vaporizing a mole with a laser. It is very important to remove the tumor in such a way that it can subsequently be examined for the presence of pathologically changed cells (possible signs of malignancy). Such manipulation can be performed not only with an ordinary scalpel, after which scars remain on the body. In some clinics, patients are offered the use of the same laser, radio waves or electrocoagulator to cut out the nevus without damaging it. Such elimination techniques are considered the most suitable for removing moles on the face, since they:
- At a minimum, tissue damage occurs.
- Does not cause bleeding.
- They are not complicated by infection.
- Allows you to remain without scars or with small, unnoticeable scars.
- Allows you to recover as quickly as possible.
- They are painless and quick.
The removed nevus must be sent for histological examination. The doctor will tell you how best to do this at the stage of preparation for the intervention.
When to see a doctor
Moles do not cause harm to health unless abnormal transformation occurs in them. Melanoma or skin cancer is a dangerous consequence of injury and the influence of negative factors. The development of the disease does not go unnoticed; it is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the nevus thickens;
- the shape changes to asymmetrical;
- throbbing or sharp pain appears;
- sharp pigmentation is observed;
- peeling;
- cracks;
- the areola may become swollen and itchy;
- blood or ichor is released;
- coarse hair becomes thinner or falls out;
- the surface pattern is disrupted.
If you notice one or more symptoms, get examined immediately to prevent unwanted consequences.
When a pigment spot appears on the body, many people perceive it as a new key to their destiny. Medicine is far from esoteric and believes that such a phenomenon is preceded by a certain event or unfavorable condition. A mole appears or begins to increase in size as a response to an injury, burn, or other exposure. Dangerous and may harm your health.
Why are they dangerous?
Convex moles are considered potentially more dangerous in terms of malignancy, which is explained solely by their unfortunate location. Such neoplasms are easily injured by clothing, nails, and simply random movements. They can be torn off in falls and other accidents. In addition, such moles are more susceptible to the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation, since they have a larger area compared to flat ones.
But surprisingly, according to statistics, cancer much more often develops from flat nevi. Perhaps this feature is explained by the fact that convex tumors initially attract more attention to themselves, so patients notice any changes in them much earlier, and have time to take treatment (removal) measures before the progression of cancer processes.
If a convex mole (large or small) is located in an inconvenient place, is constantly injured or is simply caught by clothing, doctors strongly recommend removing it and not assessing the possible risks of malignancy in your own practice.