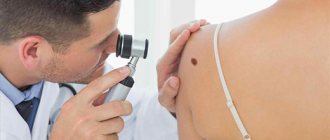
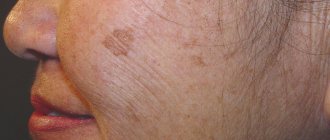
Many people perceive the appearance of red moles on the body as a signal from the body of some kind of illness. Red moles on the body are benign formations - angiomas, which are the result of the work of the vascular system. They can appear absolutely anywhere. What causes them, what to do if a red mole appears and whether it is possible to get rid of it - these are the main questions to which many want clear answers.
Red growth, vascular neoplasm
What are moles?
Experts distinguish the two most common groups of moles - pigmented and vascular.
There are many classifications of moles, and all of their components have their own medical term or name. But still, experts distinguish the two most common groups - pigmented moles and vascular ones. The former are formed due to an excess of melanin, the latter – due to problems with blood vessels (in particular with capillaries). Moles can also be congenital or acquired. Moreover, congenital ones are not always visible immediately; their pigmentation appears only after some time.
Large moles are the most dangerous, so you need to monitor them constantly and consult a doctor if there is the slightest change. Large formations can quickly transform into malignant tumors, which can negatively affect not only the skin, but also internal organs, and also contribute to the development of various diseases.
Preventive measures
In the vast majority of cases, the formation of moles is due to hereditary predisposition. Therefore, it is impossible to prevent the appearance of nevi and limit their number.
However, it is possible to prevent the development of moles provoked by external factors. To prevent nevi from appearing in large numbers, the following preventive measures must be observed:
- avoid damage to the skin;
- do not stay in direct sunlight for a long time;
- wear comfortable and loose clothing without cutting or chafing straps, belts, or underwires;
- when visiting the beach, use sunscreen;
- control hormonal levels, especially during adolescence and pregnancy;
- monitor the condition of the body, maintain health;
- undergo preventive medical examinations annually.
Causes of red moles on the body
By its nature, a red mole is a cluster of blood vessels and capillaries
By its nature, a red mole is a cluster of vessels and capillaries, which normally perform the function of oxygen and nutritional supply to the epidermal structures. With the development of any internal pathological process or under the influence of exogenous factors, small vessels can connect, forming a kind of bundle, which in medicine is often called an angioma.
When asked by a patient regarding small red moles, “What is this?”, the specialist will most often answer – angioma. Typically, these pigmented formations are formed during the period of active growth of the body, that is, in early childhood, which is associated with a serious transformation of the human vascular system at this age.
A distinctive feature of red pigmented nevi is the loss of color intensity of the formation when pressing on it, which is associated with a vascular reaction. In addition, red moles normally do not hurt or itch, and do not change their shape and size over time.
The following etiotropic factors may be the causes of angiomas in adult patients::
- Excessive sun exposure (excessive ultraviolet radiation);
- Hormonal imbalance (puberty, pregnancy, menopause, etc.);
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the pancreas;
- Injuries and mechanical damage to the epidermal integument;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Violation of the formation or destruction of pigmented cells.
Today, doctors do not give a clear answer regarding the causes of red moles on the body, however, the factors listed above can become a provoking condition for their appearance.
Why do hanging moles appear?
Hanging moles are a consequence of infection of the body with papillomavirus.
Skin formations on a thin stalk are called papillomas. These nevi are easily damaged by awkward movements and touches, so it is better to get rid of them in advance. After removing the papilloma, the doctor prescribes drug therapy to the patient aimed at destroying the virus. In some cases, hanging moles appear not due to papillomavirus, but due to other factors:
- hormonal fluctuations during puberty or after childbirth;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- hereditary predisposition.
Types of red moles
Red star-shaped mole
The appearance of red moles on the body can be accompanied by various visual characteristics of the defect. Such epidermal formations can be either flat, forming in the deep dermal layers, or have a superficial nature, protruding above the skin. Moreover, according to the nature of the visual picture, all angiomas are usually divided into two groups:
- Spot. The pigmented area has clear red borders and is a point at which a collection of vessels and capillaries is concentrated. Often, punctate angiomas are multiple in nature, manifesting themselves in the form of specific “rashes” on the patient’s skin.
- Star-shaped. Such moles are a collection of tiny thin vessels that are visible through the epidermis and converge at a central point, forming a kind of star. These structures are also associated with diseases such as rosacea.
In addition, a separate group includes especially large red moles on the body - hemangiomas, which usually significantly spoil the patient’s appearance and require cosmetic correction.
Structural features
Angiomas come in various shapes - they can be completely flat and slightly convex. The sizes of pigment spots also differ. They can appear on the body in the form of small pink, red dots and large spots that occupy the entire limb (arm or leg).
Simple (capillary) angiomas are smooth or convex spots of pink, purple, bright red color that turn pale when pressed. Some of them are formations with a bright red dot in the middle. From it, along the radius, the vessels diverge in the form of an asterisk.
In people, a raised pink mole may appear on the body - one of the plaques of psoriasis or elements of lichen planus. A single plaque of a reddish-brown color, already basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma at the initial stage. It peels off and has raised edges. Basalioma is characterized by a shiny surface.
Red moles in newborns
During the neonatal period and infancy, red moles in children are very noticeable, but they often disappear by the age of 5.
Such benign tumors do not pose a danger if they:
- They do not itch, do not hurt, do not cause any concern;
- They do not become larger, for example, in a few months they do not increase in size by 3 times or more;
- Not located under the eye, on the nose, on the face or on the genitals.
It is known that hemangiomas can rapidly grow along the periphery, this is especially true for the first months of a child’s life. Therefore, in 10-12% of cases they are removed, since there are indications for this.
The fact is that as the mole grows, it will destroy nearby tissues, causing defects not only cosmetic, but also functional. This is relevant in the case when hemangiomas are located on the ears, under the eyes, etc. Normal functioning of organs becomes impossible due to compression by the overgrown formation.
Many moles - is it good or bad?
In fact, there is nothing good about having too many moles. There are many legends that: a person who has many birthmarks will become happy; such a person is spiritually multifaceted and intellectually gifted; moles attract good luck and repel bad luck... There are a lot of options, but all of this is just wishful thinking. In fact, there is nothing good about a large number of moles. On the contrary, British scientists have recently proven that an abundance of age spots doubles the risk of developing skin cancer for their carrier.
The same pair of genes in the human body is responsible for both the formation of moles and the risk of developing cancer. People who do not have a large number of birthmarks do not have a trace of any of these genes. Thus, you need to fight the abundance of moles, so to speak, from the inside.
However, they have one advantage. Quite a dubious plus, I must say, but scientists seem to have proven it. The fact is that a huge number of birthmarks have a beneficial effect on a person’s biological age, reducing it by 5-7 years. As a result, people with nevi are more active and internally young. Even if this theory has a scientific basis, it is unlikely that its results should be taken as an axiom. It is unlikely that they apply to everyone.
Features of red moles in adults
Red moles, as primary formations, do not appear in adulthood. They arise from previously undetected vascular proliferations. Most often, they are treated before the child enters school, so if a hemangioma is present in adulthood, this means that it was either not treated, or the tumor is located on internal organs.
The most dangerous location of a red mole is considered to be the vertebral body. As the tumor grows, the structures of the spine will weaken, which contributes to the occurrence of fractures.
Prevalence and localization
According to available statistics, hemangiomas are detected immediately after the birth of a child. This happens in 87% of cases. Girls are at risk; they account for about 70% of all diagnosed red moles. By the way, it is hemangiomas that make up up to 48% of all soft tissue formations that are detected in childhood.
A red mole can be found in any part of the body, but 80% of all such defects are localized in the upper part of the body. It is also possible to detect hemangiomas, although extremely rarely, on the bones, in the brain, lungs, and liver.
- 95% of all hemangiomas are simple formations;
- 3% – cavernous formations;
- 2% – mixed type formations.
The most common are red moles on the skin. But angiomas can also be located on the mucous membranes and even in internal organs. Red moles are especially common on the face and neck.
Red moles on the body do not appear so often, but they are also not uncommon. Red moles often appear on the stomach.
Red dots on the body are often discovered at birth or in early childhood, and they increase as the body grows. Small red dots can appear at any age throughout life.
Red moles, or so-called port-wine stains, can be significant in size and cover most of the face, leading to pronounced cosmetic imperfections. But more often there are small formations in the form of small red dots. Red moles on the chest appear more often in women. And in men, red dots most often appear on or near the nose.
Causes
No doctor can still give an exact answer as to why these formations appear. Why there are many red moles in the facial area is also difficult to explain. This is probably due to the abundant vascular network of facial tissues.
In children
It is generally accepted that a congenital tumor develops as a result of an intrauterine disorder in the formation of vascular tissue, which occurs against the background of failure of the processes of development and growth.
How does this happen? During the formation of organs and systems, vascular tissue penetrates all parts of the body without exception along a certain chain of pericytic cells. These cells, being a kind of conductors of information, react to the slightest lack of oxygen: if the fetal tissues experience hypoxia, the synthesis of special proteins that attract pericyte cells is immediately launched. These cells begin to pave new blood supply routes, thus eliminating hypoxia. In some cases, even after the cessation of hypoxia, the synthesis of specific proteins does not stop; the vascular system continues to develop, turning into voluminous tumor-like formations.
The second name for red moles is vascular hyperplasia. This means that the tumor arises as a result of disruption of the growth processes of vascular tissue, which lead to an increase in its quantity. How and in what way this process occurs is difficult to answer with 100% accuracy, since this requires monitoring the characteristics of intrauterine tissue development. The data presented are based on autopsy results of aborted and stillborn fetuses.
In adults
- Acquired pathology is associated with hormonal disorders, explaining the appearance of hemangiomas in adults (pregnancy, menopause, diseases of the endocrine system, as well as hormonal therapy or oral contraception).
- There are suggestions about the negative effects of ultraviolet and radiation exposure, viruses and chemicals that provoke tumor growth in adults.
- Microtraumas and skin cracks with permanent damage to the capillary network lead to such neoplasms.
- Long-term and uncompensated hypovitaminosis C, leading to thinning and fragility of capillaries, is also relevant among the causes.
- Red moles accompany the course of other diseases (for example, diseases of the liver, pancreas, cancer of internal organs). It is not uncommon for a cluster of red moles in a certain area of the body to indicate a predisposition to cancer in this area, a nearby organ.
Why are red moles dangerous?
Many doctors believe that red moles do not pose any danger, despite the fact that they are benign tumors
Many doctors believe that red moles do not pose any danger, despite the fact that they are benign tumors. For many people, it is simply a matter of beauty and external aesthetics. Of course, red moles cause some concern, but often their owners simply do not notice angiomas on their body and do not attach much importance to their appearance. However, there is an opinion that red moles can directly affect the health of internal organs.
In particular, with diseases of the pancreas and liver, red dots are localized only on the upper part of the body, mostly on the arms. The more intense the localization of red moles, the more the disease worsens. Red moles can also indicate the presence of rheumatic diseases, such as lupus, dermatomyositis or arthritis. But in this case there is no clear location of the angiomas. They can be of various shapes and sizes.
If a red mole does not bother its owner and does not change its external characteristics, it can be argued that such a formation does not pose a significant threat to the health and life of the patient. At the same time, you should get professional medical advice and resort to modern therapeutic methods if you have the following manifestations:
- The red mole grows or changes its shape;
- The patient experiences pain, itching or burning in the area where the pigmented formation is located;
- The mole is bleeding;
- Superficial structures or ulcerations appear;
- There are more than 6 small red dots in one area of the body.
All these symptoms may indicate the development of an oncological process. In addition, the category of dangerous moles includes angiomas located in places where they can be easily injured when wearing clothes, shoes, jewelry, etc. Mechanical damage to such a formation can provoke the appearance of new red moles on the body, activate malignant transformation and leave scars or scars on the skin.
Prevention of angioma
- Careful handling of the mole, protection from mechanical influences.
- Drink at least two liters of fluid per day.
- Including foods rich in vitamins E and D in your diet. For example, avocados and olive oil.
- Regular bowel cleansing. You can eat spirulina algae, which removes toxins from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Protect yourself from excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays. This is especially true for white-skinned people with red or blond hair. If you stay in the sun for a long time, you must use sunscreen.
- Moisturize skin as needed.
Red moles on the body are usually not dangerous. They are benign formations. You should consult a doctor only if the angioma causes discomfort or spoils the aesthetic appearance. Modern medicine offers several quick and painless ways to get rid of this disease.
What to do if a red mole appears on the body
An indication for immediate consultation with a doctor is the growth of angioma
Since red moles tend to go away on their own, specialists usually do not prescribe a special course of treatment. If an angioma does not grow and does not bother a person in any way, then it does not pose a danger. It is not recommended to touch neoplasms in closed areas of the body. Removal may be approved by a specialist if the mole is located, for example, on the face, i.e. for cosmetic purposes. An indication for immediate consultation with a doctor is the growth of angioma.
There are several treatment options for red moles, and it should only be chosen by a medical specialist after conducting a series of studies. Among the most popular and effective methods of treating angiomas is laser surgery: vascular sclerosis, X-ray therapy, infrared or light coagulation. Flat red moles are treated much faster and easier than raised ones. The operations are performed without anesthesia, although they are quite unpleasant in sensation. Sometimes after the procedure it is necessary to use a numbing cream. After removal of the angioma, it is recommended to avoid visits to the solarium and prolonged exposure to sunlight for several months.
Complications
Hemangiomas (red moles) can disrupt the functioning of organs that are located next to them. This is especially dangerous if they grow in the liver, near the eyes, or in the brain.
- Inflammation and the appearance of ulcers on the mole are possible. As the pathological process fades, spontaneous disappearance of the mole is not excluded.
- Bleeding from a mole as a result of its traumatization. Bleeding is dangerous if there is a large mole, if it is a cavernous or combined formation localized on the internal organs.
- Infection.
How to get rid of red moles
Removal of small red moles is usually carried out for aesthetic reasons. If red dots on the hands rarely bother you, then a red dot on the face does not look aesthetically pleasing and attracts attention. Treatment for red moles involves removing them.
Removing red moles is not difficult, but the procedure must be carried out only in a clinic equipped with modern high-quality equipment.
And, most importantly, the removal of the tumor should be carried out by a dermato-oncologist. He will be able not only to correctly diagnose, but also to carefully rid you of red moles and dots.
Diagnosis of the disease
People who have any moles on their body require systematic consultations with a dermatologist. During the examination, the specialist assesses the condition of all neoplasms, since any of them can be dangerous. With special attention, the doctor will examine those that have visual differences from the rest.
Even a doctor with extensive professional experience cannot always identify the process of degeneration of a tumor into malignant at an early stage. This is the main reason for performing a biopsy and subsequent histological analysis.
Sometimes computer dermatoscopy of pink moles may be required - the latest technique to diagnose degeneration. With its help, you can not only look at superficial changes, but also see what is happening more deeply.
In this case, the tissues are not injured. The obtained data is transmitted to the attending physician, who analyzes it and determines the degree of risk.
Only after this does he prescribe treatment or make a radical decision to remove the mole.
This diagnosis is carried out to determine whether malignant cells are present in the tumor. For this purpose, they are removed and sent for further biopsy - a study that allows for an accurate diagnosis.
Examination is also possible using a dermatoscope - the device detects malignant growths at an early stage.
Medical correction of red moles
The doctor, after conducting an initial examination and the necessary diagnostic measures, will make a conclusion regarding the likelihood of malignancy of the red mole. Based on this diagnosis, a strategy for further therapeutic actions is developed. If a red mole does not pose an oncological threat and is located in a closed area of the body, its removal is not necessary.
In cases where the red nevus causes aesthetic or physiological discomfort to the patient, it can be removed using modern hardware techniques, the priority among which is laser destruction.
This method of removing red moles guarantees painlessness and safety for the patient, and also has a low level of trauma.
Should I be afraid?
Small red moles are safe, but under the influence of constant mechanical factors they can degenerate. Moreover, the impact can be not only traumatic, but also invisible - ultraviolet. If the nevus's halo is damaged, heavy bleeding will occur, and the mole itself may increase in size after healing.
The most dangerous are angiomas located on the neck, abdomen, shoulders and chest. The formations that are most susceptible to injury are those located on the scalp. Moles on the lips, face, and oral mucosa can be called a cosmetic defect that causes discomfort. Due to constant mechanical stress, these formations quickly increase.
You should not worry too much about the appearance of red spots, because stress and anxiety can worsen the situation. The best way to get rid of fears is to get tested.
So, how to remove a red mole
The least traumatic and most effective method is the removal of red moles using the Surgitron radio wave device
The least traumatic and most effective method is removal using the Surgitron radio wave device. Using the radio wave method is the best choice for removing red spots and moles on the face and other open areas of the body, since the surrounding tissues are not injured. After healing, as a rule, no trace remains. Using the Surgitron radio wave device (made in the USA), it is possible to remove red dots without leaving a trace, since the radio wave does not damage surrounding tissues. If you are deciding where to remove a red mole in Moscow, pay attention to the method that the clinic offers and the qualifications of the doctors.
Classification
According to morphology
Capillary. The histological structure of the neoplasm is compact layers or concentric groups of capillary vessels, closely adjacent one to one. The wall of each vessel consists of a basement membrane and 1 or several layers of epithelial-like cells. The lumens of fused capillaries are filled with formed elements of blood. In some cases, groups of vessels form lobules separated by stroma.
Cavernous. It consists of multiple cavities of various shapes and sizes, which are lined with 1 layer of endothelial cells, similar in structure to the endothelium of blood vessels. In some cases, rupture of the septa occurs with the formation of papillae in the lumen of the caverns.
According to location, vascular hyperplasias are divided into:
- Simple, with a subcutaneous location throughout the body;
- Cavernous, localized under the skin;
- Combined, having a supra- and subcutaneous part;
- Mixed, including other tumors, for example, lymphangioma, originating from lymphoid tissue.
By origin:
- Congenital, appearing immediately after birth or in the first months of life;
- Acquired, occurring in adults. Acquired red moles can only be of a subcutaneous location, i.e. simple. Complex forms of the disease, discovered due to complications or by chance, are congenital and not diagnosed in childhood.
With the flow:
Simple, not presenting a risk of complications or dysfunction of organs; Difficult:
- near large vessels or vascular nodes;
- on or near vital organs and structures (eye, brain, ear);
- in places that are difficult to access (vertebrae).
Treatment of red moles
Most red moles do not require treatment and go away on their own. If a mole does not interfere, does not increase in size and does not bother its owner in any way, it does not have a negative effect on the human body and is completely harmless. Experts do not recommend removing red moles that appear on closed areas of the body. The situation is different with those moles that are localized, for example, on the face and spoil a person’s appearance. Rapid growth and change in color of a mole requires immediate contact with a specialist.
There are several ways to treat red moles. It should be noted right away that the cauterization method is not suitable for removing moles.
A mole is most often located in the deep layers of the skin; only its upper part is on the surface. If, after removing a mole, its roots remain in the skin, it may reappear in the same place. The optimal treatment method is prescribed by the doctor after examining the mole for the presence of benign cells. Most often, laser surgery is used to get rid of a red mole.
The most modern methods for removing red moles are light or infrared coagulation of blood vessels, sclerosis of the vascular bed and radiotherapy treatment. Flat moles can be treated faster than those that rise above the skin. During the removal procedure, a numbing cream may be used if necessary. Anesthesia is usually not required in most cases.
It should be remembered that the procedure for removing a mole is very unpleasant and requires some investment. After it is carried out, small reddish spots appear at the site of the removed moles. After some time they disappear completely. After removing a red mole, it is recommended to refrain from visiting a solarium and prolonged exposure to the sun for at least one month.
Spontaneous problem resolution
Red moles go away on their own if they are superficial or simple. This is possible in no more than 15% of cases. Most often, formations that are localized on closed parts of the body regress.
At first, the tumor becomes less bright and decreases in size. After six months, the mole becomes a pale pink spot located at skin level. In this case, the skin over it atrophies. After another 3-4 years, only a small depigmented area remains on the skin.
Sources:
- www.neo-med.biz/articles/krasnyie-rodinki-na-tele.html
- https://boleznikogi.com/ot-chego-poyavlyayutsya-krasnye-rodinki
- https://lechenie-simptomy.ru/krasnye-rodinki-na-tele
- https://udalenie.klem-clinic.ru/angioma
- https://www.ayzdorov.ru/lechenie_pigmentnie_pyatna_krasnie-_rodinki.php
Clinical picture
Simple angioma
This is a spot of varying sizes, predominantly red, rising above the skin. With simultaneous finger pressure on the edge of the tumor and healthy tissue, the angioma becomes pale and shrinks, and after the compression stops, it returns to its previous shape and color. In babies up to 3-4 months, peripheral growth of the vascular tumor is clearly visible. This can be verified by making an initial paper stencil of the tumor and applying it to the hemangioma after 15-20 days.
Cavernous angioma
This is a formation in the subcutaneous tissue with unchanged skin above it. It can be diffuse without clear boundaries or encapsulated. A bluish-colored formation is detected under the skin; in some cases, feeding vessels are visually visible. When pressing on the skin above the tumor, the formation decreases, and when the compression stops, it returns to its previous size.
The skin over the tumor may be warmer than the rest of the skin. No pulsation is detected above the formation. In some cases, upon palpation, the lobulation of the formation is noticeable. Cavernous hemangiomas located on the head, neck and near the ears are characterized by rapid growth with active germination into surrounding structures.
Combined angioma
This is a formation with a cutaneous and subcutaneous part; the subcutaneous part, as a rule, is larger.