Warts are one of the most common benign neoplasms. To date, it has been found that the cause of their appearance is the human papillomavirus. But other formations that resemble warts in appearance may also appear on the skin. These can be nevi, papillomas, condylomas, keratomas, fibrokeratomas, cutaneous horn, hemangiomas, fibromas. Some of these formations can become malignant, so it is necessary to detect their symptoms and identify them in a timely manner.
Nevus (mole)
Systemic nevus
Moles are the most common wart-like growths. They are benign accumulations of melanocytes in the skin. May be congenital or acquired. Moles actively appear in children, especially under the age of one year and during puberty. In adults, the causes of the appearance of nevi are: exposure to ultraviolet radiation, hormonal changes, chronic trauma to the skin area, skin diseases, friction against clothing, etc.
Heredity is a significant factor in the formation of moles. The frequency and even localization of the appearance of nevi is hereditary. Acquired nevi appear most often in women in the face and head.
Depending on their appearance, there are two types of nevi:
- systemic - looks like a large accumulation of dark-colored growths (pictured).
- single - clearly defined moles with a diameter of up to 1 centimeter.
Nevi in children under two years of age are treated medicinally with compresses with salicylic acid, preparations with vitamins A, E, D. In adults, surgical removal of moles is practiced. This is done if the mole causes physical discomfort or there are signs of growth or transition to a malignant process. Nevi are also removed for cosmetic purposes.
If moles are removed incorrectly, they may become malignant and become malignant.
Prevention measures
The main methods of prevention include maintaining a strong immune system and preventing HPV from entering the skin. In the latter case, it is enough to follow the rules of hygiene. That is why you need to use only personal hygiene items. All wounds and skin damage must be treated with an antiseptic, covered with an adhesive plaster or a bandage.
Vaccination can be used for prevention. The effectiveness of this prevention method is 70-100%. This vaccination is especially indicated for young girls who have not entered into sexual activity, since HPV in women can cause breast and cervical cancer.
Important! In 120 countries around the world, such vaccination is mandatory. But our country is not yet included in this list.
To protect against infection during sexual intercourse, you must use a condom. If you had sexual contact with a partner suffering from HPV, then after it it is necessary to treat the internal and external genitalia with an antiviral drug for external use.
To prevent malignant degeneration of any skin tumors, when they first appear, you should immediately contact a dermatologist for removal and appropriate treatment.
Papilloma
Papilloma
Benign neoplasm of the skin. The cause is the human papillomavirus, transmitted through contact and sexual contact. It differs from a wart in shape, size and color: papilloma has a leaf-shaped or lobular shape, size - 1-2 cm, color - from white to dark brown. The wart looks like a denser, homogeneous structure with a pronounced border. Papillomas most often appear on the neck, false vocal cords, as well as on the surface of the skin subject to increased sweating - the axillary and inguinal folds.
One of the symptoms of papilloma is itching. Constantly scratching it increases the risk of malignancy.
The appearance of multiple papillomas is called papillomatosis - a skin disease that indicates reduced immunity, against the background of which the human papillomavirus is actively developing. In this case, an urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary, who will prescribe general antiviral drugs. Treatment of single papillomas includes the use of local antiviral drugs, immunomodulators and surgical removal of the growth.
Routes of infection
The causative agent of the disease is HPV, which can enter the body in several ways:
- The process of obstetrics. If papillomas are observed on the butt, then there is reason to believe that the infection occurred during childbirth. The expectant mother was a carrier of the virus throughout her pregnancy. Regardless of whether the birth was natural or a cesarean section was performed, infection is possible in both cases.
- Household contact. Infection is possible both through the use of personal hygiene items by others and in places of high humidity. It must be emphasized that the virus thrives in a humid environment, so it can be picked up in a swimming pool, public bath, or sauna.
- Intimate relationships. Also, one of the ways of transmitting the virus is sexual intercourse. Penetration of infection through mucous surfaces is faster. If a partner has papillomas in the intimate area, infection occurs in 100% of cases.
One of the ways of transmitting HPV is through sexual intercourse!
It is also necessary to note the fact of self-infection. If an adult knows that he has an infection on the surface of his buttocks, but does not in any way interfere with its further functioning, then the virus may spread throughout the body. To do this, it is enough to spread the infection throughout the skin using a towel.
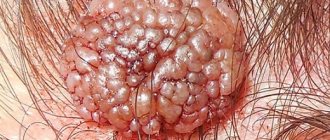
Condyloma
Condyloma
Soft papillary formations on a stalk that look like cauliflower. They occur most often in the perineal area, on the skin of the genitals. Somewhat less frequently, condylomas appear in the armpits, on the face, and in the oral cavity. The cause is infection with the human papillomavirus.
When treating condylomas, antiviral drugs and immunostimulants are used. Single condylomas detected at an early stage can be eliminated by cauterization with special preparations. Large condylomas must be removed. For this purpose, methods of cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, and laser surgery are used.
And finally
Papillomas and molluscum contagiosum are benign skin formations and are of infectious origin. Most often, they do not require intervention and the immune system copes with them on its own. But from an aesthetic point of view, especially when placed on the face, especially in girls and adolescents, they cause great problems in communication, embarrassment and shame.
A child with papillomas or molluscs cannot be limited in communication, they are not isolated from school or kindergarten, however, you need to know about observing basic hygiene measures - after all, these formations are contagious.
Keratoma
Keratoma
A benign formation that develops from the stratum corneum of the epidermis. It occurs most often in older people and is localized mainly on the skin of open areas of the body exposed to ultraviolet rays - face, neck, forearm, back of the hand.
When a keratome appears, it appears as a grayish or brownish spot, which then grows and protrudes above the skin in the form of a plaque up to 6 centimeters in diameter. As a result of increased keratinization of the epithelium, the keratome becomes covered with scales. This formation is characterized by a slow course and can disappear on its own or transform into an acrochordon - a cutaneous horn.
Keratomas prone to malignancy are treated with local administration of cytostatics and colhamin ointment. Keratoma is also treated surgically using methods of electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser and radio wave surgery.
How can you prevent childhood warts?
Proper hygiene is the first and most important factor in preventing warts, as is the case with many other dermatological conditions. If there are people or regular visitors in the house who are accidentally affected by warts, make sure they wash their hands before touching the child. Also, keep your child away from surfaces that the victim regularly touches. Avoid sharing towels. Warts are not medically harmful and the condition usually goes away within two years even if left untreated.
Acrochordon (cutaneous horn)
Acrochordon
At first they look like small tubercles of keratinized skin, ranging in color from white to dark brown. Their size is usually 1-4 mm. Then the acrochordon grows in length and width, and sometimes reaches 4 cm or more in diameter. Usually the skin horn itches, since dry horny scales irritate the skin receptors. There are often several acrochordons.
The cause of the appearance of cutaneous horn has not been established. Acrochordon appears against the background of diabetes, obesity, pregnancy, and at the onset of menopause. This indicates that the neoplasms are hormonally determined. Acrochordons often appear in old age in healthy people, which is considered by experts as a natural manifestation of skin aging.
Acrochordons can be removed with scissors, without anesthesia. A small skin horn can be easily eliminated using electrocoagulation and cryotherapy methods. Large lesions exceeding 2 cm in diameter should be excised.
Causes
For the development of any inflammatory process, there must be factors that have a beneficial effect on increasing the activity of viruses of various etiologies. HPV, in this case, is no exception. It is necessary to highlight several points that provoke a decrease in immunity and further activity of the pathological infection:
- hormonal disorders;
- long-term treatment with drugs from the antibiotic group;
- chemical exposure;
- loyalty to bad habits;
- psychological and emotional stress, including stressful situations;
- colds;
- allergic reactions of various forms of manifestation and localization;
- a risk group for diabetes mellitus, or a diagnosed disease of the endocrine system;
- functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including the course of inflammatory processes;
- chronic diseases of various body systems;
- period of future motherhood;
- decrease in the body's defenses.
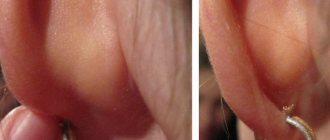
Acquired fibrokeratoma of the fingers
Acquired fibrokeratoma of the little finger
These hard, keratinized bumps most often form in the area of the interphalangeal joints of the hands and feet, but can appear anywhere on the skin of the hand or foot. In most cases, they have a mushroom shape and a ring at the base of dry, keratinized skin. Many experts believe that fibrokeratoma of the fingers occurs as a result of chronic trauma to the skin, which explains the frequent appearance of the tumor on the little toe of the foot, where there is constant friction with shoes. But the exact reason has not yet been established.
To treat fibrokeratoma, direct surgical excision is used, or a saucer-shaped depression is formed in the tumor bed with secondary healing. The use of cryotherapy and laser surgery has shown good results.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
For any unclear dermatological rashes in a child, parents should consult a doctor at least as a precaution.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- The child's warts began to hurt.
- If the color of the warts has changed or there are warts of several colors on the body.
- If you notice that warts have begun to actively spread and grow.
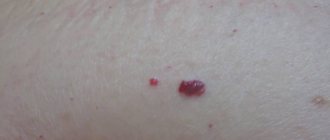
- If the wart is injured and it begins to bleed.
- When a wart creates inconvenience and causes great discomfort for the child.
Absolutely all warts are safe and do not cause harm to health. But some species, when neglected, turn into carcinogens. Self-medication is dangerous in cases where the growth identified as a wart is not actually one. Also, self-medication of warts may leave large and visible scars.
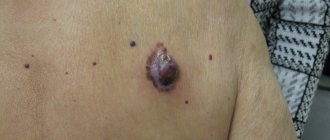
Hemangioma
Hemangioma
A benign tumor that develops from endothelial cells - the inner lining of the vascular wall. Hemangioma has the appearance of a reddish, purple or bluish spot, which slightly rises above the surface of the skin. The contours are irregular, and an expanded vascular network can be seen in its area. The main distinguishing features are the tendency to grow rapidly and lighten after pressing for a few seconds.
In most cases, this is a congenital tumor, the appearance of which is usually associated with a complicated or disrupted pregnancy. In 70% of children, hemangioma disappears on its own by the age of seven. In very rare cases, hemangioma develops in adults due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation and chronic skin trauma. Hemangioma is treated by removal. In this case, the method of laser surgery shows itself to be the most effective.
Methods for treating warts on the butt in children
There are two directions in the treatment of warts on the butt in children. In the first case, it is recommended not to take active actions, waiting for the growth to reduce on its own; in the second, a whole range of means is prescribed to remove the growths. Both treatment options - observation or active destruction - are complemented by the use of immunostimulating and antiviral drugs that improve the body's overall defenses. With the help of such means, the virus that causes warts on the butt in children is suppressed from the inside. Apologists of traditional medicine are also adopting an integrated approach, helping the body cope with the virus from the inside through nutritional correction, as well as using aggressive compounds for the external destruction of warts on a child’s bottom.
Medications for a wart on a child’s bottom
The photo shows medications for warts on a child’s bottom
Not all wart remedies, both for internal and external use, are suitable for treating children. Pharmacy medications should be selected based on the age and individual tolerance of the young patient. You must first consult your doctor.
To fight the virus from the inside, the following may be prescribed:
- Antiviral - Alpizarin, Normomed or Amizon. Before starting use, you must read the instructions and use a dosage appropriate for your child’s age category. The cost of tablets from this series is within 120 hryvnia (180 rubles).
- Immunostimulating - Imunorix, Panavir (for children over 12), Genferon. The safety of using the drug Genferon for children has not yet been studied, so use is permissible only after consulting a doctor. Immunostimulating agents cost from 100 hryvnia (180 rubles) to several hundred. So, Imunorix will cost 835 hryvnia in Ukraine, 1055 rubles in Russia for a therapeutic course (10 doses), but it has a general strengthening effect on the body.
For external use as gentle pharmaceutical agents, the following can be recommended:
- Solcoderm is used for children over 5 years old; the product must be applied to the wart on the child’s bottom several times a day. Education will go away within 2-3 months. The drug costs 700 hryvnia in Ukraine, and 942 rubles in Russia.
- Duofilm based on salicylic acid is used to remove formations in children from 2 to 12 under the supervision of adults; the product is applied once a day after a hot shower. To avoid adverse reactions, the drug should not be used during periods of exacerbation of viral infections. Duophilm can be purchased in Ukraine for 450 hryvnia, and in Russia for 800 rubles.
- Podophyllin is also recommended for use after hardware removal of warts on the buttocks in children. The product prevents relapses and promotes tissue healing. Analogs of the drug may be recommended, for example, Condilin or Verrukacid. At the same time, Verrukacid is not used to treat children under 7 years of age, and Condilin - under 12 years of age. The cost of such funds is on average 500-800 rubles (120-180 hryvnia).
Skin fibroma
Soft skin fibroma
A benign neoplasm consisting of mature elements of connective tissue. It has clear boundaries, the color is flesh or light pink. Often mushroom-shaped; the photo shows a pedunculated variety. Develops slowly.
There are two varieties:
- A hard skin fibroma looks like a lump - it is located on a wide base, dense to the touch, and inactive.
- A soft fibroma (pictured) looks like a small wrinkled sac on a leg. Women in adulthood are more susceptible to the appearance of soft fibroids.
Fibroids usually form on the skin of the neck, chest, armpits and groin areas. The cause of fibroma has not yet been fully elucidated, although a connection has been established with the aging process of the skin and endocrine pathology. Fibroids are treated surgically.
Molluscum contagiosum or infectious molluscum
This is a skin tumor of a viral nature, benign in nature.
Typically, viruses infect the cells of the upper layer of the skin - keratinocytes, as a result of which control over cell division is lost and a certain area of the skin grows. In addition, viruses block immune cells that control cell division, so molluscum is more likely to occur in those who have problems with the immune system. And since in preschool children the immune system still works imperfectly, therefore they are more often susceptible to this disease than others. This disease is purely human, so you cannot get sick from it through contact with animals (for example, domestic or street animals). She's contagious. Therefore, several children in a family, and even adults, can get sick, although this is rare, it does happen.
The main routes of transmission from a sick baby to a healthy one are through direct close contact. The second option for infection can be the use of common hygiene items, wearing clothes of a sick child, or his soft toys. Children with skin problems are more likely to get sick when there are areas of damage - abrasions, scratches, dermatitis - then it is easier for the virus to penetrate the thickness of the skin.
Based on the method of transmission, it is most often found in organized children's groups - kindergartens, boarding schools, camps. Another great place to pick up this virus is public baths or swimming pools - humid air, skin contact and a large number of people contribute to this.
Not everyone is equally susceptible to the virus - usually children from the group of frequently ill people, allergy sufferers, and digestive problems are more likely to suffer. The incubation period usually lasts from 2-3 weeks to two months, and there may be a primary lesion and further screenings from it.
How can you recognize him?
Rashes can appear on any part of the body - face, arms, neck, legs, shoulders, abdomen and even genitals - they cannot only appear on the palms and soles, which is why they differ significantly from papillomas. Therefore, if you find a mollusk in one of the children, the entire family and all parts of the body of each member must be thoroughly examined.
Usually one or more nodule-like elements appear in the thickness of the skin, they are flesh-colored or pink, sometimes described as “pearl-like” lumps. There is usually a “umbilicus-shaped” depression or depression in the center of these lumps. They do not come in large sizes, usually from 1 to 15 mm in diameter; if they merge, they can form quite large areas.
There are usually no other manifestations - no fever, no malaise, rarely babies can feel a slight itch, scratch them and inflammation occurs. Then the elements may turn red. A characteristic symptom that distinguishes molluscum from all skin infections and lesions is that when you press on it with tweezers, curd-like crumbs are released. They contain a lot of virus inside them. Therefore, you should not touch or crush it with your hands - you can spread the infection.
Usually they are not complicated - but if a child picks or combs them, microbes can join and a wound may appear. It only needs to be treated with antiseptics to prevent the development of suppuration.
Of course, in the case of a typical course and manifestation in several children, there is no doubt, but sometimes the mollusk is difficult to recognize. Therefore, let a dermatologist make an accurate diagnosis and treatment. In adults, molluscum may go away on its own, but because of its potential to be contagious, children are usually advised to remove the molluscum as soon as it is discovered.
After the doctor notes all the elements, their quantity and location, he will offer several methods to choose from. Typically, each nodule is either squeezed out or scraped out with a special instrument - a sharp Volkmann spoon. After this, the place where the mollusk was is treated with antiseptics (iodine, fucorcin or others) so that a crust forms.
After any of these effects, the crust is treated with antiseptics two or three times a day, but it is not allowed to be torn off, so as not to spread the mollusks still in it. The crust should fall off on its own. Sometimes it is recommended to apply a special gel around the wounds; it will prevent the elimination of new elements from the wound and will not allow the development of the mollusk to recur.
In addition to local treatment, for severe rashes, immunotherapy with Viferon or its analogues is prescribed.
During treatment, special attention must be paid to the child’s things - all linen, bedding and all the child’s clothes are washed at 90 degrees and carefully ironed, all his toys are thoroughly washed and washed. To prevent the development of infection, it would be good to protect the child from children in the kindergarten, notify the teacher so that the rest of the children in the group can be examined. There is no quarantine for this disease, but all children require treatment.
To avoid contracting this unpleasant disease, hygiene is required - both personal and home hygiene. It is worth providing the child with a separate towel, washcloth and soap, and regularly inspecting the baby’s body for rashes.
Bowen's disease
Bowen's disease
This is a tumor formation, which is an obligate precancerous condition. Without adequate and timely treatment, it can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Some authors consider Bowen's disease to be an initially malignant formation that does not grow into adjacent tissues and does not metastasize at the initial stage.
The cause of Bowen's disease is considered to be UV radiation, exposure to toxins, especially substances containing arsenic, and chronic inflammatory skin diseases. Occurs mainly in older people. Localized on the upper extremities and genitals.
A small red lump with jagged edges first appears on the skin. It then grows in size and turns into a scaly yellowish-red plaque with jagged edges. Dry scales often cause itching. Then the epidermis thickens and wart-like growths appear.
Bowen's disease is characterized by a very long course - months, years. The skin growth grows very slowly and turns into squamous cell carcinoma of the epidermis. Treatment depends on the location of the lesion and its size. Small lesions are eliminated conservatively: ointments with cytostatics and cryodestruction are used. In other cases, surgical removal and laser treatment are practiced.
Symptoms of pathological HPV activity
The appearance of papillomas on the butt does not always remain noticed. In cases where the pathology does not manifest itself in any way, there is no itching and no increase in the size of the growth, many adults are not even aware of the existence of the virus in their body.
The appearance of growths is often accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- itching;
- pain during defecation;
- burning sensation;
- bleeding;
- feeling of moisture in areas affected by papillomas.
For timely detection of the disease, you need to visit a gynecologist annually.