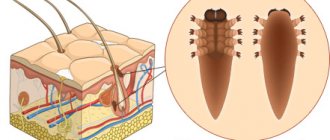
What kind of disease is this?
The external manifestations of Dühring's dermatitis (the disease has another name - dermatitis herpetiformis) are quite unpleasant, there is a feeling of danger of infection. However, a rash on a person’s body does not pose a threat to others. The exact cause of this autoimmune skin pathology is not known; the disease can occur at any age, but is most often observed in people 20-40 years old. Dermatosis is characterized by the formation of entire groups of blisters, similar to garlands and rings.
Dühring's pathology has a protracted chronic course. The blisters are similar to the symptoms of herpes.
| On the left - Dühring's dermatitis, on the right - herpes |
Clinical rash is characterized by external manifestations:
- erythematous scarlet spots with dilated vessels, rounded in shape and defined boundaries;
- bubbles - occur when elements are filled with liquid contents from capillaries; increasing in size they become very wide.
It is important to know! Patients with dermatitis herpetiformis have hypersensitivity to iodine. If potassium iodide is consumed or gets on the skin, the disease will worsen.
Dermatitis on the skin is defeated!
A natural product without any chemicals or danger to the skin. Just remember to apply twice a day….
>
Due to unbearable itching, a person scratches the pathological areas vigorously, as a result of which crusts form. Dühring's dermatitis is qualified by the appearance of vesicles up to 2 cm in size. At the time of infection, lumps of blood appear, and erosive tissue is noticeable upon dissection.
Symptoms
External manifestations of dermatitis are unpleasant in appearance, causing a feeling of danger and the possibility of infection. Rashes on the body do not pose a threat to others. Dühring's dermatitis is a skin disease that belongs to the group of autoimmune diseases. Its exact cause is not known; the process can begin at any age. More often the disease is detected in men between 20 and 40 years old. Dermatitis is characterized by the appearance of entire groups of bubbles and blisters, which can form:
- rings;
- Garlands;
- half rings
Dühring's disease is characterized by a chronic, protracted course, paroxysmal appearance of an itchy rash on the body and limbs. The blisters are similar to the symptoms of herpes, which is why its other name is dermatitis herpetiformis. Clinical rashes with Dühring's disease differ in appearance:
- Erythematous red spots with dilated capillaries, have a round shape, clear boundaries.
- Blisters - appear when elements are filled with liquid from vessels. As the size increases, individual spots merge into large lesions.
Severe itching provokes scratching of the areas and the appearance of crusts on top of the blisters. Herpetic dermatitis is characterized by the formation of vesicles. These are cavities above the surface of the skin, filled with liquid, reaching sizes up to 20 mm. When dermatitis becomes infected, lumps of blood appear, the contents thicken and become cloudy, and upon opening, erosive tissue is visible.
The main signs of the disease - rashes - burst when scratched, the liquid gets onto the healthy surface of the skin, forming new lesions. The following symptoms are observed with dermatitis:
- severe itching;
- soreness;
- gastrointestinal problems;
- fatty gray stool;
- the appearance of ulcers;
- tissue ulceration;
- crust formation.
Herpetic vesicular dermatitis spreads throughout the body, the typical location is on the elbows, in the flexion areas of the forearms, and on the face. The disease does not appear on the feet or palms. Consider the symptoms:
- nervousness;
- deterioration of health;
- the appearance of nagging pain in the joints;
- lethargy;
- allergic signs - runny nose, swollen tissues;
- weakness;
- changes in body temperature;
- worsening mood due to dietary restrictions;
- psychological problems;
- depressive state.
The exact origin of Dühring's disease is unknown to medicine. Experts believe that genetic predisposition is the likely cause of dermatitis. It is worth noting the factors causing Dühring’s disease:
- weakened immunity;
- dysfunction of absorption in the intestines;
- sensitivity to cereal protein – gluten;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Among the causes of dermatitis, high sensitivity to iodine preparations is considered. The development of the disease can be triggered by:
- stressful situations;
- physical overload;
- vaccination;
- hormonal abnormalities during menopause;
- poisoning of lymph cells, blood and secretions by toxins;
- allergies to foods or medications containing iodine;
- viruses for herpes;
- parasites in the gastrointestinal tract;
- ARVI;
- stomach ulcer;
- pregnancy.
After diagnosis, patients are examined for the presence of malignant neoplasms and gastrointestinal pathologies. Since the disease has a chronic course, dermatologists are faced with the following tasks:
- transfer dermatitis into a stage of long-term remission;
- relieve the patient from external manifestations so that he feels comfortable physically and psychologically;
- eliminate rashes so as not to provoke infection;
- show and tell methods of preventing Dühring's dermatosis.
To obtain the best effect in treating dermatitis, the patient is required to follow simple rules:
- do not take baths;
- exclude visiting the bathhouse;
- wash in the shower without using soap or a washcloth on the affected areas;
- Sleep duration should be at least 8 hours;
- take long walks;
- avoid stressful situations;
- do not overload physically;
- follow a diet;
- take vitamins, ascorbic acid.
Drug therapy for Dühring's dermatosis includes the use of drugs that solve various problems. Dermatologists prescribe medications:
- antihistamines - remove signs of allergies, eliminate itching - Suprastin, Claritin;
- sedatives - calming - Persen, natural preparations - Motherwort, Valerian;
- hormonal agents for severe forms - Prednisolone, Triamcinolone;
- for external use - lubricate the skin with Fukortsin liquid, a solution of brilliant green, salicylic acid, ointments.
The main effect in the treatment of Dühring's dermatitis is exerted by drugs of the sulfone group. The use of the drug Dapsone has a good effect. When assigning, take into account:
- admission 5 days;
- break - two days;
- carry out at least 5 cycles;
- dosage – 100 mg twice a day;
- after the symptoms disappear, a maintenance measure is 5 mg twice a week;
- contraindications – incompatibility with barbiturates, amidopyrine.
Ointments that are effective in the treatment of psoriasis and eczema help to quickly heal wounds and relieve unpleasant symptoms. The drugs have a disinfectant, anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and drying effect. Popular ointments for dermatitis:
- Dermatol;
- Zinc;
- Naftalanaya;
- corticosteroid – Celestoderm;
- antihistamine – Suprastin;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory – Bufexamac.
The disease can begin suddenly and last throughout life, alternating with a state of remission, during which the patient may experience virtually no symptoms. The disease can be triggered by changes in the endocrine system, often in women due to pregnancy and menopause. With a genetic predisposition to this type of dermatitis, the following conditions can increase the likelihood of the disease:
- chronic intoxication;
- excessive physical activity;
- emotional fatigue;
- excess iodine in the diet;
- the presence of malignant tumors.
The onset of dermatitis manifests itself in the form of slight itching and tingling in a certain area of the skin, after which pathological formations begin to develop within 12 hours. At the same time, they can look very different - at the same time you can see both a small rash and large vesicles or blisters.
Tense cavity formations often contain fluid mixed with blood. All these formations are accompanied by severe burning, itching and the desire to scratch the affected area. If the blisters are not damaged by scratching, on the 3-4th day they open on their own, leaving wounds and darkening of the skin after healing. If liquid gets on healthy skin, it leads to the formation of new elements and further spread of the disease.
With the further development of the pathological process, scaly elements, skin crusts and erosive processes develop. Typically, such skin lesions occur localized and symmetrically. Dermatitis often develops around the outer side of the elbow, knee, as well as on the buttocks, shoulder blades and face.
This type of disease is characterized by a chronic course. Doctors believe that one of the most likely causes of such dermatitis is impaired absorption. This condition develops from hypersensitivity to gluten. This protein is found in cereals - wheat, oats, rye, barley. The diet for Dühring's dermatitis should not contain gluten-containing products.
Prohibited for use:
- All dishes with flour (including soups, gravies and creams);
- Wheat oil;
- Chocolate with filling;
- Coffee substitutes of natural origin from barley, kvass, beer;
- Cereals;
- Legumes;
- Cabbage;
- Flour food products;
- Breaded dishes (cutlets, chops, schnitzel);
- Sausage.
The diet for Dühring's dermatitis should include:
- Baked goods made from corn, rice and soy flour;
- Porridge – buckwheat, rice, corn;
- Fish and meat in their pure form (boiled, steamed);
- Vegetable and butter;
- Homemade mayonnaise;
- Potatoes, onions, garlic, carrots, zucchini, beets;
- Milk (up to 0.5 liters per day);
- Dairy products;
- Honey;
- Compotes, jelly and jams;
- Fruits of all kinds;
- Natural coffee, herbs, spices, nuts, seeds, olives;
- Mineral water without iodine and bromine;
- Non-iodized salt.
Dermatosis often has a recurrent or chronic course with symptomatic manifestations in the form of painful sensitivity, unbearable itching and burning.
- At first, papules, vesicles, and blisters may simultaneously appear on the skin.
- Over time, secondary signs of a chronic condition begin to appear - areas of erosion, scales, pale yellow crusts on the body, mucous membrane of the lips, extensor parts of the arms and legs, and gluteal region.
- When one of the vesicles is opened, serous or hemorrhagic fluid flows out.
- Body temperature may be normal or significantly increased. This is especially true when an open wound gets infected.
A more severe form is bullous. The size of the bullae reaches on average about two centimeters. Detection of a cloudy shade of bullae indicates the addition of a secondary infection.
Before starting complex treatment (drug and non-drug), you need to make a final diagnosis. It should be based on laboratory and diagnostic studies. In addition to donating general blood and urine, a cytological examination of the secreted fluid from papules, pustules and others is carried out.
Diagnostic testing is carried out using an iodine test. By applying a small amount of iodine to the surface of the skin, new affected areas appear.
For the treatment of herpephoid dermatitis, the following groups of drugs are prescribed for internal and external use:
- drugs of the sulfonic group;
- GCS (glucocorticosteroids);
- antihistamines;
- topical corticosteroids;
- antiseptics for treating affected areas of the skin, especially after opening the lesions.
List of drugs:
- Gentamicin;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Betamethasone;
- Dexamethasone;
- Desloratadine;
- Loratadine;
- Clotrimazole;
- Methylprednisolone;
- Mometasone;
- Neomycin;
- Zinc oxide (ointment);
- Cetirizine;
- Chloropyramine;
- Sulfasalazine.
Depending on the severity of the disease, the doctor prescribes inpatient or outpatient treatment. Non-drug therapy includes diet and preventive measures. No surgical treatment is required.
Reasons for the development of the disease
There is no exact cause for the development of Dühring's dermatitis. Doctors mainly refer to genetic predisposition. Factors that can provoke pathology are:
- weak immune system;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- disruption of absorption in the intestine;
- inflammation of the digestive tract;
- sensitivity to gluten.
Among the causes of dermatitis herpetiformis are sensitivity to products containing iodine. The disease can be caused by:
- physical stress;
- hormonal disorders in women (menopause, pregnancy);
- ARVI;
- allergic reactions to medications, certain products that contain iodine;
- viral diseases with herpes;
- parasites in the intestines;
- malignant tumors;
- stress, depression;
- stomach ulcer;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- increased sensitivity to vaccination.
Attention! Despite these factors, many experts argue that Dühring's dermatitis is an autoimmune disease, that is, caused by a disorder of the immune system.
Hypoallergenic diet for atopic dermatitis
For atopic dermatitis, it is recommended to follow a special hypoallergenic diet. This diet is recommended for nursing mothers with a history of skin diseases. This factor puts the child’s health at risk: any allergy of the mother can provoke the same in the baby; read about atopic dermatitis in children in this article. A hypoallergenic diet involves the following dietary principles:
- Vegetables and meat are boiled rather than fried in oil with seasonings;
- Before cooking, cereals should be soaked for 30 minutes, then rinsed thoroughly with clean running water;
- Before eating raw vegetables and fruits, you need to peel them;
- Meat or fish broth must be cooked in several stages. Initially, the products are soaked in clean water for 1 hour, then the broth is boiled, drained and the next one is boiled (until transparent).
It has been proven that adults and children most often develop allergies to vegetables and fruits of rich scarlet colors. Therefore, tomatoes, strawberries, raspberries, and red currants should be excluded during the therapeutic diet.
When breastfeeding, avoid eggs, chocolate, citrus fruits, seafood, and sweets. It is not recommended to constantly consume the same foods, as a cumulative allergic reaction may develop. Before buying food in a supermarket, carefully read the ingredients - it should not contain dyes, preservatives, or emulsifiers.
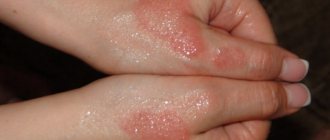
Symptoms
This type of dermatosis is characterized by a variety of rashes. Papules, blisters, spots (all at the same time) may appear on the skin.
| External manifestations may vary |
The typical symptoms of dermatitis are:
- spots are the first manifestations, have defined boundaries with a smooth surface, after which papules, blisters or blisters appear on their foci;
- papules - slight compactions with light red contours;
- blisters - burst after 3 days, then become crusty;
- bubbles – inside there is a clear (less often cloudy) liquid, ranging in size from 2-20 mm.
The rash can be everywhere, on the elbows, arms, legs, shoulders, and occasionally on the oral mucosa. The areas of damage are symmetrical, the epidermis may not change in appearance at all, but sometimes becomes red and swollen.
Pensioners and young people, do not ruin your skin with pharmaceutical chemicals! Dermatitis can be treated with a natural remedy called...
Dühring's dermatitis also has general symptoms: burning, intense itching, malaise, slight tingling on painful areas. It is also possible to increase body temperature, diarrhea, sleep disturbances, and changes in the function of the thyroid gland and other internal organs.
Dependence of nutrition on the type of disease
Previously, doctors did not yet fully understand the nature of all the processes leading to pathological changes in skin tissue, called Dühring's dermatosis. Many people often confuse Dühring's disease with herpes, since the rashes are very similar to each other, which led to the medical name of this disease - dermatitis herpetiformis. Today, the mechanism that is one of the main operating forces of this disorder in the body has been clarified.
It is known that many people have gluten intolerance, which manifests itself in the form of impaired absorption of cereal proteins. Gluten is not absorbed in the body due to a lack of enzymes on which the breakdown of this substance in the digestive organs depends. This phenomenon belongs to genetic diseases that are inherited. When one of the fractional components of this protein, gliadin, enters the intestines, the mucous areas of the digestive tract are damaged.
The body’s natural reaction to gliadin is the production of protective substances - antibodies, which bind to this protein and create complex formations associated with immunity. The movement of these formations along with the blood flow leads to the fact that they are concentrated in the upper layer of the skin, provoking inflammatory processes.
The basis of correct therapy is adherence to the principles of proper and balanced nutrition for dermatitis, in especially severe cases the introduction of a hypoallergenic diet, which should be on par with conservative treatment.
The type of pathology affects the diet for dermatitis. The main list of prohibited products remains unchanged. Allergens that cause one or another type of pathology are added to it.
Allergic
Allergic dermatitis develops if a person eats foods that the body cannot tolerate. Food allergens that cause dermatitis should be excluded from the patient’s menu.
Allergies are often triggered by orange-red fruits and berries, milk protein, peanuts, cocoa, bee products, etc. Fried, salty, fatty and spicy foods can provoke the disease.
Minimize the consumption of sweet and salty foods.
Seborrheic
The diet for this type of dermatitis includes:
- fermented milk products,
- vegetables, greens, berries, fruits,
- low fat meat,
- clean water up to 2 liters per day (liquid dissolves toxic compounds and removes them from the body).
If the disease is caused by stress, herbal teas with soothing herbs (mint, chamomile, lemon balm) are introduced into the diet.
It is prohibited to consume industrial sweets and juices, carbonated water, flour products, fast food, semi-finished products, alcohol, fried, spicy foods.
Dühring's disease
Dühring's dermatitis occurs in people with hypersensitivity to cereal proteins. Gluten is a protein found in oats, wheat, barley and rye. The following is removed from the patient’s diet:
- flour, products and dishes prepared with it (sauces, pasta and bakery products, kvass, beer, drinks containing barley),
- dishes from legumes and cereals, cabbage,
- ice cream, chocolate,
- flour and bread coating.
For Dühring's dermatitis, you are allowed to eat:
- corn, soybeans, rice, buckwheat,
- meat, fish, milk,
- fermented milk products,
- vegetables, fruits, herbs, berries.
Atopic
With atopic dermatitis, do not eat foods that cause allergies. Be sure to exclude common allergens:
- smoked and canned,
- bee products,
- food containing cocoa
- berries,
- citrus,
- spices,
- nuts.
The transition to a diet begins with fasting. For 1-2 days, patients are allowed to drink water and weak tea without sugar. After this, the diet is expanded: fermented milk products, milk, white meat and fish dishes are introduced.
In children
The diet of children with dermatitis should include neutral foods. But you should take care of a balanced diet. Products are selected taking into account the age of the children and individual developmental characteristics.
For infants up to 6 months of age, breast milk is sufficient. To prevent the baby from developing dermatitis, the mother must adhere to a diet.
The infant's diet begins to expand from 4-6 months. Hypoallergenic foods are introduced into the diet for children under one year of age. First, the baby is given vegetables and cereals. Then the menu is supplemented with homemade cottage cheese, kefir, fruit and meat purees. The baby will adapt to unfamiliar food without consequences if only 1 product is introduced for complementary feeding for 7-10 days.
The diet of children after a year with dermatitis is close to the diet of adults.
According to reviews from doctors and patients, dietary nutrition for dermatitis almost always has a positive effect on the condition of the skin. The diet suppresses the signs of a difficult-to-treat disease, restores the functioning of organs, and accelerates recovery.
The diet for any dermatitis has its own nuances, depending on the type of pathology, the degree of damage, and the stage. In one case, the dietary table has strict restrictions, in others it allows for relaxations in the quality of consumption of certain products. The list of what you can eat for dermatitis can expand during the course of successful relief from symptoms and vary based on the nature of the disease. Therapeutic diets for each type of dermatitis have their own characteristics.
Allergic
Since this type of dermatitis is a “response” of the skin to a specific food irritant or a combination of them, it is necessary to remove foods that cause an allergic reaction from the diet. In addition, limit your consumption of pickles and sweets.
What can you eat if you have allergic dermatitis:
- It is recommended to eat cereals (buckwheat, rice, corn).
- The diet includes pumpkin, zucchini, watermelon, and potatoes.
- Fermented milk products and lean meat will not cause aggravation.
A diet for facial dermatitis involves using exclusively fresh foods. Before cooking vegetables and fruits, they must be thoroughly soaked - this will reduce the risk of nitrates getting into the food. You should also be careful about the quality of the water you consume - purify it through filters that exclude harmful components, or use purchased drinking water.
Seborrheic
Nutrition for seborrheic type dermatitis requires excluding from the diet all food groups that negatively affect the functioning of the sebaceous glands and skin microflora. These include:
- alcoholic drinks;
- sweet soda;
- fried, spicy, overly salty and sweet foods;
- smoked meats and preservatives;
- baked goods;
- honey, jam.
The diet necessarily includes correction of the drinking ration. It is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of water per day, provided that it is fresh and does not contain harmful impurities. It is necessary to include fermented milk drinks, fresh herbs and vegetables, low-fat jellied meat, jelly, jelly, lean pork and other types of dietary meat in the treatment table.
A diet for dermatitis is a set of foods that does not burden the liver. If harmful components come with every portion of food, it may not cope at all.
If the occurrence of dermatitis is associated with disorders of the nervous system (stress, insomnia), then the diet can include the use of decoctions of chamomile, valerian, motherwort and other medicinal herbs.
Dühring's disease
Dühring's dermatitis has its own specific origin. As a rule, the pathology is associated with increased sensitivity of the body to gluten, contained in many cereals. The dietary table for this disease, as well as the general diet for dermatitis in adults and children, prohibits the consumption of gluten-containing products.
In case of Dühring's disease, it is prohibited to consume semolina, rye, wheat, oat and barley cereals, legumes such as beans, lentils, beans and peas, as well as dishes containing their derivatives:
- liquid dishes with flour or malt (gravies, soups, sauces);
- flour products, including pasta, cakes, and semi-finished products containing dough;
- breaded dishes;
- cereal-based drinks (beer, kvass, barley coffee);
- chocolate with cereal fillings and ice cream.
The list of acceptable products includes:
- dishes with added rice and corn;
- low-fat kefir, fermented baked milk, hard cheese, low-fat cottage cheese;
- milk (up to 0.5 l per day), butter;
- all fruits;
- fresh herbs;
- nuts;
- spicy seasonings;
- green vegetables;
- honey;
- lean varieties of meat and fish.
Atopic
The nature of this type of dermatitis has not yet been fully elucidated. Doctors associate the pathology with reduced immunity, exhaustion of the nervous system, liver problems, hereditary disorders or the presence of food allergies.
The disease is chronic and manifests itself in outbreaks, so a hypoallergenic diet for dermatitis is followed constantly, with relief during the period of remission.
A diet for atopic dermatitis is prescribed with a low calorie content. There is a certain list of foods that definitely need to be excluded from the diet. First of all, these are alcoholic drinks and products that contain ethyl alcohol. You should not eat smoked foods; you should not add too much salt or pepper to your food.
This diet excludes the consumption of all allergenic foods. Preservatives, smoked foods, alcohol, fried and fatty foods, processed foods, sausage, and gluten-containing foods are not recommended.
It is allowed to include lean boiled meat, melons, fermented milk products, potatoes and corn, berries, green fruits, and the addition of a small amount of whole milk and meat by-products into the diet.
Other types
Other types of the disease with characteristic skin rashes are also treated with dietary adjustments. Limiting dietary factors are regulated based on the individual characteristics of the body.
Forms and types
Dühring's dermatitis has several types and forms. The forms of pathology depend on the skin rash. The most common is:
- Papular - a variety characterized by the appearance of numerous nodules of small diameter with the absence of voids;
- Vesicular – this type is characterized by small bubbles similar to vesicles.
- Urticariform - qualified by the appearance of multiple blisters and detachment of the upper layer of the epithelium.
- Bullous - the largest number of blisters is noted, inside of which there is a clear liquid.
If, with Dühring's dermatitis, the rashes connect with each other and then turn into erosions, then one can definitely indicate an atypical form of the disease.
| Bullous and papular forms in the photograph |
Types of dermatitis:
- localized – symptoms appear only on a small area of the skin;
- eczematoid - in the pathological area there is a numerous rash of blisters, papules, which in turn turn into weeping erosions;
- vegetative – complicated villous-type areas are observed;
- trichophytoid - rashes with this aggravation have a wavy, scaly outline; the symptoms here resemble a fungal infection; therefore, doctors often recommend a full examination to determine the root cause of unfavorable symptoms;
- strophuloid - papules and blisters are localized on the body; nodules initially appear, and small blisters form above them;
- pemphigoid - Dühring's dermatitis is characterized by a rash of dense blisters of significant size, difficult to rupture.
| Localized and trichophytoid types of dermatitis |
There is another form of herpetiformis disease, the so-called senile dermatitis. It is formed as a result of age-related changes, at a time when metabolism goes astray, liver dysfunction and circulatory disorders occur. With this disease, rashes of different sizes are located throughout the body. Pathology in old age is very dangerous. Therefore, at the initial signs, you should visit a dermatologist.
Diet for skin diseases of the hands
Nutrition for skin lesions of the hands according to an individual scheme. Chocolate, cocoa, and fatty lard-based foods are not allowed. To make the menu more varied, add vegetable and fish soups, cereals, and low-fat dairy products.
With oral dermatitis, an allergic person should eat exclusively water-based cereals, low-fat broths, boiled vegetables, and baked fruits. It is recommended to drink herbal tea to cleanse the body. Only by following a strict diet is it possible to improve the patient’s well-being.
In case of acute hunger, doctors advise snacking on yogurt with live bacteria. Most skin problems occur due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive disorders. Active live bacteria improve the digestion of food, the absorption of nutrients in the stomach, and also help remove toxins from the intestines.
Danger and complications
To ensure that Dühring's dermatitis does not provoke any complications, a specialist monitors the treatment process and periodically sends for tests. In some situations, the pathology is associated with nausea and vomiting; in complex cases, inpatient therapy will be required.
It is important to know! If treatment is not carried out, the dermatosis becomes the most dangerous form for the patient and the likelihood of a secondary infection increases several times.
Acute periods of the disease alternate with remission and last for a couple of months. A person is tormented by itching, burning, and the skin is repelled by its appearance. Because of this, the patient worries, begins to communicate less with people, sleep is disturbed, and appetite decreases. The result is a psycho-emotional disorder, depression.
| Complications in the photograph |
Treatment of Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis
The doctor prescribing examinations, tests and treatment must be a qualified specialist in the field of dermatology.
The patient is advised to exclude cereals and iodine-containing products from the daily diet. Complex treatment includes the use of medications. Treatment in cycles of five to six days with short breaks is necessary with dapsone, DDS, sulfapyridine and other drugs of the sulfone group. In unsuccessful cases, therapy is replaced with corticosteroids.
The symptoms of the disease are treated separately: the patient is prescribed medications that reduce the sensation of itching, burning and tingling. This could be Claritin, Erius or other antihistamine medications.
To relieve the painful manifestations of Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, warm baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate are prescribed.
Diagnostics
Dühring's pathology is determined by a dermatologist who performs a visual examination, interviewing the patient, and performing certain tests.
The following will help diagnose the disease:
- blood analysis;
- histology;
- studying the contents of liquid from bubbles;
- biopsy;
- thyroid examination;
- skin analysis using immunofluorescent method.
The most accurate method for determining Dühring's dermatitis is considered to be the Jadassohn test (susceptibility to iodine is determined). The essence of the diagnosis is that a compress with an ointment containing potassium iodide is placed on the skin area. When, after 24 hours, a rash or redness is noticeable in that area, this indicates dermatitis herpetiformis.
You may also need to consult other doctors to determine gluten-associated enteropathy. Due to the possible association with malignant tumors, especially in old age, other organs are examined through mammography and ultrasound.
Pharmacies hid it!
Even “advanced” dermatitis can be cured at home. Just remember to apply twice a day….
>
Characteristic features of HD
An organism weakened by chronic diseases is easily susceptible to the effects of the herpes virus. The risk group includes people who have undergone complex surgical operations, suffer from AIDS, and carriers of a hereditary trait at the gene level.
The photo shows herpetic dermatitis on the lips in an adult patient:
Herpetic dermatitis on the lips in an adult patient
The herpes type of disease is a type of Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, it can manifest itself in various forms:
- Papular - the formation of papules on the skin.
- Bullous - similar to thermal burns with the appearance of blisters.
- Vesicular - the rash takes the form of vesicles.
- Urticariform - rashes like nettle marks.
- Paraoncological – for carcinogenic oncological manifestations.
- Eczematous, strophuloid, trichophytodes - the rarest form, belongs to the atypical group.
GD is divided into the following types:
- Congenital.
- Acquired.
The disease affects the skin of the following organs:
- Limbs.
- Facial area.
- Small of the back.
- Groin.
Sometimes it affects the mucous membrane, affecting the oral cavity, eyes, some internal organs, the nervous system, and genitals.
According to ICD-10, the disease is classified: / A00-B99 CLASS I Some infectious and parasitic diseases / B00-B09 Viral infections characterized by lesions of the skin and mucous membranes / B00 Infections caused by the herpes simplex virus.
The pathogenesis of HD lies in the ability of the herpes virus to penetrate the skin, where it rapidly multiplies and kills epithelial cells, forming foci of necrosis.
It is worth noting that the herpes virus is present in more than 90% of people. If the body has a strong protective force, the disease goes away in 7-10 days and does not manifest itself for many years. If HD appears in a person with weak immunity (HIV, other severe infectious diseases), the disease poses a serious danger.
The most important threatening feature of a skin disease is the ability of a viral infection to spread quickly. When the leaking infected fluid from the bursting vesicles hits the healthy epithelium, it affects it. In addition, if the skin barrier is broken, the virus enters directly into the blood and affects the nerve endings. Thus, it permanently settles in the body, introducing itself into the structure of the cell and taking root in it. As soon as changes occur in the functioning of organs and systems, immunity decreases and relapses occur.
Treatment methods
In accordance with the degree of complexity of Dühring's dermatitis, the specialist carries out therapy on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. Non-drug treatment involves dietary nutrition, traditional options for eliminating the disease, and preventive measures. No surgical therapy will be required.
Therapeutic recommendations
Clinical rules for eliminating dermatitis:
- The main part of treatment is adherence to a gluten-free diet, elimination of enteropathy, elimination of antibodies to immunoglobulin A.
- Required use:
- Sulfasalazine - carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor, since adverse effects are possible (proteinuria, allergy to the main component of the drug, increased presence of crystals in the urine); in addition, the use of the medication is often accompanied by dyspeptic disorders (vomiting, nausea, loss of appetite); if such symptoms occur, the drug should be replaced with an analogue; method of use of Sulfasalazine: daily dose is 1-2 g;
- Dapsone is an excellent safe analogue of the above, the dosage of the drug is 1 mg/kg per day; Therapy with anti-leprosy medication lasts up to 2 years as needed.
- Antihistamines (Loratadine, Zodak, Suprastin, Diazolin) - reduce itching, burning in dermatitis and the presence of negative manifestations of certain medications.
- Glucocorticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) - systemic drugs will significantly eliminate pathological itching and burning of the skin.
- Antiseptics (hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin) - used to treat the epidermis. Medicines consist of aniline dyes. In case of secondary infection, aerosols based on corticosteroids should be used.
- Antibiotics (Metronidazole, Clindovit) are necessary when pathogenic organisms penetrate open wounds.
- Antipyretics (Ibuprofen, Aspirin) – for increased body temperature.
- Antibacterial ointments, tablets (Enterol, Levofloxacin, Erythromycin) are required when admitted to affected areas of secondary infection.
- Vitamins (Vitrum, Neurovitan) - will help strengthen the immune system.
Attention! It is necessary to change antihistamines every 10 days, since addiction to the active ingredient occurs and the result weakens.
Diet
The main task of healthy nutrition in Dühring's pathology is to limit foods that contain gluten and iodine. Cereals (rye, wheat) should be excluded.
Below is a table of prohibited and permitted products for dermatitis:
| Prohibited Products | Authorized Products |
| Flour products, pasta | Fruits, vegetables, garlic, onions |
| Sea fish, shrimp | Nuts, honey |
| Sausage | Rice and buckwheat porridge |
| Smoked meats, marinades, seasonings | Kissels, compotes |
| Sweets, chocolate | Butter, sunflower oil |
| Beer, kvass, coffee drinks | Greens, olives |
| Sea kale | Homemade mayonnaise |
Dermatitis will disappear in a matter of days. Write down the prescription from Dr. Kochetkov...
People with Dühring's dermatitis are required to follow a gluten-free diet throughout their lives. This will help reduce the number of medications used and symptomatic manifestations.
| Manifestations of poor diet |
Traditional methods
A complement to drug therapy are traditional options for eliminating dermatitis. Recipes will help increase the speed of healing of scratches, wounds, and itching. It is important to make sure before use that the products will not cause allergies.
Effective folk methods:
- birch buds - you will need 1 glass, place in a saucepan, add 300 ml of liquid, keep on low heat for 15 minutes, cool, strain; Treat the affected areas with the resulting decoction 3-4 times a day; the product will safely remove inflammation, itching, and soothe the skin;
- St. John's wort oil – 30 g of plant (flowers, leaves) should be crushed, put in a container, add 200 ml of sunflower oil; leave for at least 2 weeks; then filter and smear the necessary areas three times a day;
- tea with lemon balm - 2 tsp. pour 200 ml of boiled water over the plants; consume warm 2 times a day; the drink has a general strengthening, anti-inflammatory effect;
- belladonna-based ointment – melt pork fat, finely chop the medicinal herb (ratio 2:1), mix; simmer the mixture in the oven, then strain; treat damaged areas every day;
- herbal tincture - you will need 1 tbsp. l. nettle, tansy, the same amount of yarrow, juniper, calendula; all components are poured into half a liter of vodka, the product is infused for 10 days in a dark place, filtered; wipe the rash daily;
- St. John's wort ointment - keep the plant juice in a water bath until it thickens, cool, combine with butter in a ratio of 1:4; The medicine helps heal wounds and erosions, kills pathogenic microorganisms, disinfects, and soothes the skin.
A competent specialist should choose a treatment regimen; self-medication can cause a secondary infection, as well as transformation of dermatitis into a more complex form.
Useful products for skin diseases
During an acute allergic reaction, it is necessary to exclude allergenic foods from the diet. A mandatory item should be products that promote the process of regeneration of damaged epidermal tissue. The diet should contain the following food items:
- Liquid porridge with water (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat, pearl barley, corn);
- Vegetables, boiled or steamed: zucchini, Brussels sprouts, carrots, chickpeas, green peas;
- Boiled chicken meat;
- Baked green apples;
- Low fat dairy products;
- Sea fish;
- Green or herbal tea without sugar;
- Freshly squeezed vegetable and fruit juices.
To cleanse the body and remove waste and toxins from it, it is necessary to adhere to a balanced water regime. Drink clean water at the rate of 30 ml per kg of body weight. If a person weighs 80 kg, then his water requirement per day is 2.4 liters.
It is necessary to limit salt intake to a minimum, as it retains fluid in the body and prevents its cleansing. Doctors usually recommend eliminating major unhealthy foods for 2 weeks, and then reintroducing them after you feel better. If a rash or redness of the skin occurs, you should completely avoid the allergen product.
Forecast
The development of Dühring's dermatitis is long, cyclical, with short-term remissions. But, in some patients, there is a complete weakening of symptoms and subsidence of the disease.
The treatment may result in a new rash, so the medications are reviewed. In many patients, dietary nutrition leads to a noticeable improvement in the condition, but this does not reduce the need for Dapsone.
| Treatment results |
Diet for allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis develops as a result of close contact with an allergen substance. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend excluding from the diet those foods that are most likely to provoke an unwanted skin reaction.
You need to remove honey, nuts, coffee and tea, cocoa, berries (viburnum, raspberries, currants, watermelon), and citrus fruits from the menu. During the period of food restriction, you need to adhere to a strict diet: do not eat fried, smoked, salty, sweet. For most followers of the allergic dermatitis diet, it will seem tasteless. But, spices and excess salt are also prohibited in the diet of people suffering from skin reactions.
Before each meal, try to prepare fresh food. Meat, fish, cereals, and vegetables must be soaked in water for more than an hour before cooking. This will reduce the concentration of nitrates and other chemical components in them.
Allergy sufferers are allowed to eat:
- Baked apples and pears;
- Zucchini, pumpkin, broccoli;
- Poultry meat;
- Kefir, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk;
- Olive and sunflower oils;
- Oatmeal, buckwheat, rice.
Use bottled water for cooking. In tap water, as a rule, the concentration of permissible chemicals (minerals) is not maintained, which leads to the occurrence of allergic dermatitis. For culinary purposes, buy clean water from the store.
Prevention
Dühring's dermatitis is a chronic pathology and complete cure is impossible. However, forgetting about the disease for a long time is quite acceptable. It is necessary to pay special attention to preventive actions:
- exclude medications containing iodine;
- maintain a gluten-free diet;
- avoid stress and emotional disturbances;
- eliminate fungal and viral infections in a timely manner;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- do not overcool or overheat;
- observe hygiene rules;
- ensure healthy sleep;
- Carry out an annual examination with a doctor.
Unfortunately, Dühring's dermatitis is mainly associated with complex relapses, which is dangerous for elderly patients. It is simply impossible to predict the course of pathology and the course of therapy. Only timely assistance, a competent approach, and the implementation of all recommendations will allow a person to achieve remission and return to normal life. Dermatitis is difficult to treat and therefore requires great patience and peace of mind.
Diet for seborrheic dermatitis
If you have seborrheic dermatitis, you should not eat:
- Alcoholic and caffeinated drinks;
- Fast food;
- Fried and smoked dishes;
- Food from packages (noodles, puree) with a high content of chemical components;
- Juices in packages with added sugar;
- Cakes, pastries, yeast bread.
During the diet, you need to limit your consumption of sweets based on refined sugar. Pay attention to chocolate, sweets, and cookies for diabetics. Do not consume fast carbohydrates in the form of honey or fruit jams. It is recommended to cook vegetables, meat, and fish in a double boiler or bake without seasoning in the oven.
If strict dietary restrictions do not help get rid of the symptoms of a skin disease, you must additionally take allergy tests. Thus, it will be possible to exclude the allergenic product.
In order to intensively remove toxins from the body that are formed under the influence of the inflammatory process of the skin, drink plenty of water - up to 3 liters per day.
Since one of the causes of seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis is stress, it is necessary to include teas based on lemon balm, valerian, chamomile, and mint in the diet. In complex treatment, herbal teas have a sedative effect on the nervous system.
Causes of herpetic dermatitis
The main etiological factor, as already mentioned, is infection with the herpes virus. However, not all infected people show symptoms of the disease. It is still unknown what exactly becomes the provoking factor in the development of herpetic dermatitis.
The main reasons that can cause manifestations of herpes dermatitis include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- infectious diseases (viral and bacterial);
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- helminthic infestations;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine or digestive system;
- immunodeficiency states.
In any case, the development of this disease should alert you and force you to consult a doctor.
How can you get infected with herpes dermatitis?
In addition to the fact that herpetic dermatitis belongs to a number of infectious diseases, it is also highly contagious (the ability to be transmitted from sick people to healthy people). Doctors say that approximately 90% of adults are carriers of the herpes virus, but not every carrier can become a source of infection. The virus can be transmitted to a healthy person from a carrier only if there are any microtraumas on the mucous membrane. Infection mainly occurs through contact with people who have manifestations of this infection (i.e. rashes on the skin or mucous membrane). The main routes of infection with herpes virus type 1 are:
- contact and household path. For example, when using shared towels, dishes, lipstick, etc.
- airborne route. In direct contact with the patient's saliva. For example, when kissing or touching the mucous membrane with skin on which there is a rash.
Genital herpes type 2 can be transmitted in the following ways:
- sexual tract. Most often, it is through sexual contact that infection with the herpes virus type 2 occurs. Even if the infection is in an inactive state, the risk of infection is high, because During sexual intercourse, microtraumas occur through which the virus penetrates.
- vertical route (infection of the fetus from the mother). If a woman does not know about the presence of infection, herpetic dermatitis can worsen during pregnancy, when the body's protective capabilities are reduced. In this case, there is a risk of intrauterine infection, as well as transmission of the virus to the child during childbirth.