Why does atheroma occur?
The appearance of a cyst is caused by blockage of the outlet duct of the sebaceous glands. As a result, the sebum produced by the gland does not come to the surface, but accumulates inside. The duct increases in size, and the body’s defense system, trying to stop this process, forms a cyst of connective tissue in the form of a cavity around the atypical formation.
Factors leading to blockage of the sebaceous glands:
- Injury to the epidermis - skin cells, after being damaged by a blunt object, clog the lumen of the sebaceous gland duct.
- Low level of personal hygiene - dust particles and other contaminants must be regularly removed from the surface of the skin so as not to clog the excretory ducts of the glands.
- Hormonal imbalance, the predominance of male hormones - testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone - leads to changes in the functioning of the sebaceous glands, increased secretion of sebum and its thickening.
- Postmenopause - during menopause, the concentration of estrogen in the female body sharply decreases, which increases the likelihood of changes in the composition of sebum and the formation of atheroma.
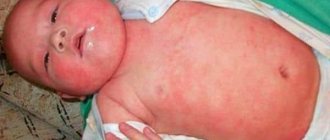
Although atheroma most often occurs in adults, the congenital form of this neoplasm is rarely diagnosed in children. The cyst forms in front of the ear and looks like a small ball up to 2 cm in diameter. The cause of atheroma in children is a small defect of the epidermis in the area of the auricle. In the future, such atheroma does not develop and does not affect the child’s health.
Types of neoplasms
The following types of atheroma are quickly diagnosed and well known to doctors:
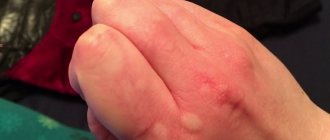
- Epidermoid. Congenital benign tumors, the cause of which can be considered a genetic predisposition in humans. The main places of localization are the groin area and the head.
- Retention follicular. They belong to the so-called secondary neoplasms and appear when the sebaceous duct is blocked. Sometimes they are classified as a complication after acne. Place of origin: upper torso.
In most cases, there are multiple benign neoplasms of adipose tissue, and one person can have up to 10 or more pieces. Isolated cases occur less frequently.
Symptoms of atheroma
Since the formation of atheroma is not accompanied by an inflammatory process, there are no symptoms such as weakness, fever, loss of appetite, hyperemia and changes in the surface layer of the skin. If the atheroma does not become inflamed, then no problems other than a cosmetic defect are recorded.
Location of the cyst:
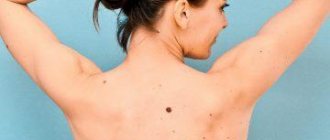
- Back - most often occurs on the skin between the shoulder blades, although another area of this part of the body is not excluded;
- Head – face, back of the head, area around the ears, chin;
- Crotch;
- Coccyx;
- Armpits;
- Popliteal fossae.
In those areas of the human body in which there are no sebaceous glands (palms, feet), atheromas never form.
Causes
To avoid the appearance of this skin disease, you need to know the causes of its occurrence and try to eliminate all possible risk factors.
Most often, atheroma occurs for the following reasons:
- changes in the functioning of the sebaceous glands;
- poor diet, eating large amounts of fatty and unhealthy foods;
- disruption of the body's metabolic processes;
- problems in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- structural features of the skin, namely incorrect location of the sebaceous glands;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- improper or insufficient skin care.
Risk factors
Considering all the reasons for the formation of a wen, the following group of people is identified who are at risk of developing atheroma:
- the formation of atheroma is not associated with age, but most often such bumps appear in people under the age of 35;
- disruption of the sebaceous glands can occur due to hormonal imbalance, so pregnant and lactating women are at risk;
- Skin clogging often occurs due to improper care and hygiene;
- The danger is posed by excessive sweating and damage to the integrity of the skin.
Differentiation of atheroma from similar pathologies
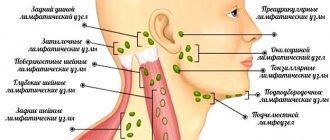
A sebaceous cyst may be similar in its symptoms to other subcutaneous formations - an enlarged lymph node, fibroma or lipoma. It is important to know their characteristic features in order to distinguish them from each other. Other formations are so rare that their symptoms are not important for diagnosis.
| Sign | Atheroma | Lipoma | Fibroma | Lymph node |
| Mobility of the skin layer over the formation | Inseparable from the skin, as it is formed in the thickness of its layer | They are located under the skin layer, so the skin is mobile | ||
| Appearance | Looks like a round formation rising above the skin | Often invisible without the use of special equipment or magnification | ||
| Density | Consistency is soft | The consistency is thick | ||
| Soreness | Usually painless, with suppuration there is pain on palpation | The formations are painless | Painful | |
The main signs make it possible to differentiate atheroma from similar pathologies.
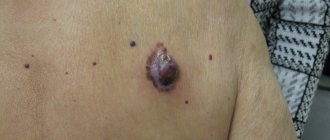
Inflammation of atheroma
When pathogenic microorganisms enter the cavity of the cyst, its tissue can become inflamed. The cause of inflammation is injury to the epidermis as a result of cuts, punctures of the skin, scraping of the top layer, attempts to squeeze out atheroma on the face, neck, or back of the head.
Signs of inflammation:
- Increase in size of atheroma by several centimeters in the shortest possible time;
- Hyperemia;
- Swelling;
- Pain on palpation of atheroma.
As a result of inflammation and melting of tissues, pus finds its way out, breaking through the skin. After applying a sterile dressing, you need to contact a surgeon to remove the remaining connective tissue of the capsule and sanitation of the wound.
If you do not consult a doctor and self-medicate, the remaining parts of the capsule will cause the re-formation of atheroma.
Drug therapy
In newborn children, removal of atheroma is unacceptable, since the operation cannot be performed using local anesthesia. Any movement contributes to damage to the cyst capsule. As a result, its contents can infect nearby tissues and lead to an abscess.
Therefore, after assessing the situation, the doctor prescribes drug therapy. It consists of taking antibiotics to stop the inflammatory process. Medicines are used by injection or orally, as well as topically. In the latter case, the following antibiotic ointments have proven themselves to be effective: Levomekol, Zinerit, Gentaxan.
Removal of atheroma for older children is also not always indicated. For example, with an active inflammatory process, surgical intervention can only worsen the situation. In this case, drug therapy with antibiotics is also prescribed. After the inflammation has resolved, the decision to undergo surgery can be made.
Surgical treatment of atheroma
The only effective way to treat atheroma is surgical removal, because drug therapy or traditional medicine recipes do not bring any significant results and can cause a relapse.
As soon as signs of inflammation appear around the formation, you should immediately go to the outpatient clinic or the emergency room of a surgical hospital. Uncomplicated atheroma is operated on as planned.
The main goal of surgery is the removal or destruction of the cyst and its contents. Methods of surgical treatment:
| Method | Contents of the method | Advantages |
| Classic method | An incision is made in the superficial layers of the skin, through which the cyst is removed without violating its integrity. A suture is placed on the wound, and then the threads are removed during dressing after healing |
|
| Argon plasma coagulation | Atheroma is destroyed using a beam of plasma at the end of a special scalpel; simultaneously with the destruction of tissue, the blood is stopped |
|
| Laser destruction | The laser knife destroys the cyst and its capsule |
the disadvantage of these methods is their low prevalence due to the high cost of equipment and its absence in public clinics |
| Electrocoagulation | An electric knife removes a cyst using high frequency current | |
| Radio wave knife | Atheroma tissues are burned using high-intensity radio waves |
All surgical methods require local anesthesia. The operation to remove atheroma rarely lasts more than 20 minutes.
Traditional medicine methods
When you detect the first signs of atheroma, you should immediately seek medical help, because traditional medicine can help relieve inflammation and get rid of pain, but not remove the root of the disease.
Anti-inflammatory drugs for oral administration
- A few coltsfoot leaves are poured into a glass of boiling water and simmered over low heat for 5-10 minutes. The resulting decoction is drunk half a glass once a day;
- Daily consumption of wheat germ juice will help improve the general condition of the body and relieve inflammation;
- 3 burdock roots must be crushed and poured with 150 milliliters of vodka. The resulting mixture is bottled, hermetically sealed and infused in a dark place for a month, while the container is constantly shaken. The prepared tincture is consumed twice a day, half an hour before meals.
Traditional medicine for external use
- lamb fat needs to be melted a little and rubbed into the resulting wen 5 times a day;
- atheroma can also be lubricated with freshly prepared aloe juice, the procedure is repeated 5-6 times a day;
- 2 tablespoons of crushed peony roots are poured into 500 ml of hot water and boiled for 2-3 minutes. Cool the broth and wipe the sore spot with it;
- 3 tablespoons of finely chopped wormwood are poured into 500 ml of boiling water and left for 30 minutes. The tincture is then filtered and used as a compress;
- Pour 1 tablespoon of primrose herb into a glass of boiling water and cook for about 5 minutes. Then the broth is cooled and filtered. Used as a bath additive.
Skin melanoma: treatment with folk remedies.
Details about herpes zoster: symptoms and treatment in adults.
Read all about the causes and treatment of myositis in this article.
Traditional medicine methods suitable for certain areas of localization:
- in order to get rid of atheroma on the head, it is necessary to wipe the neoplasm daily with a decoction of anti-inflammatory herbs such as chamomile, St. John's wort and calendula;
- A mixture of laundry soap and onions is also good for this area. To prepare it, 1 chopped, baked onion is mixed with a tablespoon of grated soap. Lubricate the wen with the prepared product 3 times a day;
- Egg film is well suited for the face, which must be carefully separated from the raw egg. It is applied to the atheroma and held until completely dry;
- For the earlobe, a compress prepared using a bandage, which is moistened in a mixture of 2 tablespoons of ammonia and 2 tablespoons of water, is well suited. The duration of the procedure is 5-7 minutes; after removing the lotion, the wen should be thoroughly rinsed with water.
We recommend reading: Signs of scabies and treatment with folk remedies
Treatment of atheroma with ichthyol ointment
To relieve inflammation in atheroma, you can use ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky ointment.
These two products are similar to each other in the method of influence and rules of application. The main difference lies in the composition of the drugs. Before use, squeeze a little ointment onto a gauze pad or cotton pad.
This product is secured to the affected area using an adhesive plaster.
Postoperative period
In the first days after removal of the capsule, it is important to carefully monitor the condition of the wound. At first, the surgeon performs daily procedures, changing the drainage device and antiseptic dressings. The total duration of the postoperative period is 10-14 days. It takes place on an outpatient basis. Occasionally, complicated forms of atheroma are treated in a surgical hospital.
After the formation of connective tissue between the edges of the wound, the sutures are removed. This manipulation takes no more than 3-5 minutes and is usually painless.
Dangerous signs of complications after surgery
- Addition of inflammation after removal of an uncomplicated form of the cyst, appearance of pus;
- An increase in temperature indicates tissue infection; normally, hyperthermia disappears within 2-3 days;
- Dehiscence of wound edges – discovered during dressing;
- Leakage of blood through the bandage - increased bleeding is diagnosed in hepatitis, hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, enlarged spleen, as well as in patients using anticoagulants (Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl, Heparin, Thromboass).
The appearance of any of the above signs is a reason to consult a doctor, who will assess the risk of complications and carry out therapeutic measures.
Reviews
Removing atheroma surgically is quite radical, but the most optimal method. Most patients who had the sebaceous cyst completely excised did not experience recurrences. However, due to the occurrence of scars after removal of atheroma, reviews are mixed. This method is not suitable for formations located on open areas of the body, for example, the face or neck.
Removal of atheroma surgically will be performed through an external incision, which inevitably entails the formation of a scar. But there are alternatives. If the formation is small in size, you can resort to removing the atheroma with a laser. Feedback on this procedure is positive. The operation goes quite quickly, and there are practically no scars left. Many note that the rehabilitation period also goes much faster.
Regardless of whether the atheroma is removed with a laser or surgically excised, all patients experience a complete recovery.
Answers to frequently asked questions
- Is there a risk of atheroma reappearing?
Yes, even a small number of surviving cells can give rise to the appearance of a new cyst.
- What does a postoperative scar look like? Is it possible to avoid it?
Minimal scars are formed after surgery using radio wave radiation. In second place is the argon plasma method. After these interventions, there may be no scars at all. Traditional surgery leaves noticeable scars.
- How to prevent atheroma?
There are no specific methods of prevention. It is important to control hormonal levels, maintain hygiene, and avoid skin injury.
- What is the difference between atheroma and lipoma?
Lipoma is located in the thickness of the fatty tissue, it is caused by excessive growth of connective tissue and is a benign tumor.
- Can the process become malignant?
No, such cases are excluded, this is not a precancerous disease.
- Can cyst destruction occur on its own?
No, this is impossible, atheroma cannot resolve, it remains unchanged for a long time.
- Is a surgeon required to operate on non-inflammatory atheroma?
Services under the compulsory medical insurance policy may not provide for the removal of non-inflammatory atheroma. The solution is to undergo surgery in a private clinic or wait for inflammation to develop, which does not guarantee the absence of a cosmetic defect after the intervention.
- What are the consequences of self-squeezing atheroma?
The cyst is usually located in areas of intense blood circulation, so there is a high risk of infection spreading to the brain through the blood vessels if bacteria gets into the wound. You cannot squeeze out the cyst - you need to seek qualified medical help.
Author of the article:
Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich |
Ph.D. surgeon, phlebologist Education: Moscow State Medical and Dental University (1996). In 2003, he received a diploma from the educational and scientific medical center for the administration of the President of the Russian Federation. Our authors