general description
Pemphigus (pemphigus) true (objective) (L10) is a dermatosis characterized by acantholysis with the formation of intraepidermal blisters.
Prevalence: 1.5% among all dermatoses. People aged 40–60 years old are most often affected.
There is a spread of rashes throughout the skin, progression of the process, often leading to death.
Predisposing factors:
- Immune disorders.
- Family predisposition (cases of similar diseases in close relatives).
Causes
The causative agent of pemphigus is the Coxsackie virus. The disease can be transmitted by airborne droplets or by contact with contaminated objects. Symptoms of the disease do not occur in all children.
The main condition for the development of pemphigus is considered to be weak immunity.
If the protective functions of the child’s body are not impaired, then contact with a carrier of the virus can do without negative consequences.
increase the risk of infection for a child:
- weakening of the immune system under the influence of uncontrolled use of potent medications;
- congenital autoimmune pathologies;
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal disorders in the body;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- negative impact of the environment on the child’s body;
- pathologies associated with the central nervous system;
- contact with common objects without observing safety measures.
How to treat herpes on a child’s body? Find out about this from our article.
Pemphigus symptoms
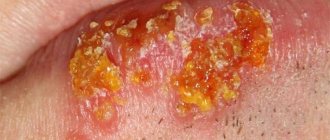
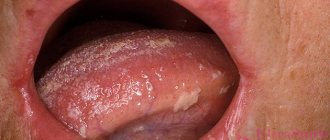
First, blisters appear on the mucous membrane, most often in the oral cavity (80%). In this case, hypersalivation with an unpleasant specific odor is noted (65%). Then blisters appear on the skin, rapidly increasing in size, with transparent contents, which then become cloudy (up to 100%). Some of the bubbles collapse and shrink into crusts; the rest rupture to form a wound surface. Affected areas may become infected (70%).
A physical examination of the skin reveals blisters in the mucous membranes of the oral, nasal cavities, and genital area; chronic painful erosions.
There are some specific symptoms (90%): “pear symptom” (by the shape of the blisters), Nikolsky’s symptom (with a slight touch, the blisters open with detachment of the epidermis), Asbo-Hansen’s symptom (when pressure is applied to the bubble, it increases in size).
Pemphigus
Pemphigus (true pemphigus) is a chronic disease of an autoimmune nature, which is characterized by the appearance of blisters on clinically healthy skin and mucous membranes. Features of the clinical course of pemphigus have allowed clinicians to identify the following forms of the disease: vulgar, erythematous, vegetative and foliate. Pemphigus is diagnosed by detecting acantholytic cells in the impression smear and histological identification of blisters located inside the epidermis. In the treatment of pemphigus, the main thing is a course of glucocorticosteroids; it is successfully combined with methods of extracorporeal hemocorrection: plasmaphoresis, hemosorption, cryoapheresis. Pemphigus - occurs in people of both sexes, most often over 40 years of age. Children get sick very rarely. The disease is severe and is manifested by the formation of blisters on non-inflamed skin and mucous membranes, which quickly spread throughout the entire skin. Pathological cells can be detected in fingerprint smears obtained from the bottom of erosions. Without adequate treatment, the disease leads to death. Based on symptoms and course, 4 forms of the disease are distinguished.
Pemphigus vulgaris - tense blisters the size of a pea, a hazelnut or larger, with transparent, gradually becoming cloudy contents, appear on apparently unchanged skin or mucous membranes. The blisters open, forming bright red erosions, or dry out, turning into a crust. Persistent pigmentation remains at the site of the rash. The general condition of the patients is serious, they suffer from insomnia, their temperature often rises, and their appetite worsens.
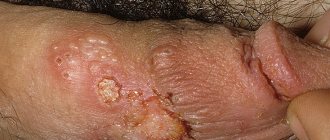
Pemphigus vegetans - quickly bursting blisters form in the oral cavity, on the lips, in the armpits, inguinal folds, and on the external genitalia. At the bottom of the erosions, easily bleeding growths (vegetations) up to 1-2 cm high appear. In the regression stage, the discharge shrinks into powerful loose crusts, which cause excruciating pain.
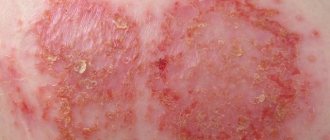
Pemphigus foliaceus is characterized by the sudden appearance of flaccid blisters in the form of grouped lesions on the face and body. The bubbles are easily destroyed, the exudate shrinks into thin lamellar crusts, similar to puff pastry. Very quickly the pathological process spreads to the entire skin. The mucous membranes are usually not affected.
Seborrheic, or erythematous pemphigus - begins with the formation of small blisters on the face, scalp, back, chest, and sometimes the oral mucosa, which quickly dry into crusts. The eroded surface underneath is exposed. The disease lasts a long time and in most cases is benign.
Treatment:
The main agents are corticosteroids and cytostatics. Therapy should be continued continuously indefinitely until the rash completely disappears. Antibiotics and sulfa drugs are prescribed in cases of secondary infection. Locally - general baths with low concentration potassium permanganate, wheat bran extract, oak bark decoction, antibacterial ointments or aqueous solutions of aniline dyes.
The affected mucous membrane of the oral cavity is irrigated with warm solutions of 0.25-0.5% novocaine, rivanol (1:1000), infusion of chamomile, eucalyptus. Patients with pemphigus are registered at the dispensary and receive medications for free during outpatient treatment. They need to avoid physical overload and nervous tension, and adhere to rest and sleep patterns. Changes in climatic conditions and treatment with mineral waters at resorts are not allowed.
A hypoallergenic diet and exclusion from the diet of roughage, canned food, simple carbohydrates, salty foods and other extractive substances are indicated for patients with any form of pemphigus. If the oral cavity is affected, then it is necessary to include puree soups and mucous porridges in the diet in order to prevent a complete refusal of food; protein-rich foods included in the diet accelerate the process of cell regeneration and epithelization of open erosions.
All patients with pemphigus should be monitored by a dermatologist; a gentle regimen, lack of physical activity and avoidance of sun exposure are recommended. Frequent changes of underwear and bed linen prevent secondary infections.
The administration of glucocorticosteroids immediately in high doses is indicated, since otherwise the therapeutic effect will not be achieved; after the acute manifestations of pemphigus are relieved, the dosage of hormonal drugs is gradually reduced to the minimum effective. In the treatment of pemphigus, methods of extracorporeal hemocorrection are used: hemosorption, cryoapheresis and membrane plasmapheresis.
As a local treatment for pemphigus, aniline dyes and non-aggressive antiseptic solutions are used.
The prognosis of pemphigus is always unfavorable, since in the absence of adequate treatment, the death of patients occurs quite quickly from additional complications. Long-term hormonal therapy in high doses increases the risk of side effects, but when you stop taking glucocorticosteroids, pemphigus begins to recur.
Diagnosis of pemphigus
The diagnosis is made based on the dermatological picture. Conducted:
- General clinical blood and urine tests (anemia, leukocytosis, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, hypoalbuminemia, proteinuria).
- Determination of total Ig G.
- Cytology for acantholytic cells in fingerprint smears in the area of the bottom of blisters and erosions.
- Histology of the biopsy specimen (intraepidermal location of blisters).
- Immunofluorescence examination (suprabasal fluorescence).
Differential diagnosis:
- Bullous pemphigoid.
- Dühring's disease.
- Chronic benign familial pemphigus.
- Lyell's syndrome.
Recommendations for caring for a sick child
If a child develops symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to call a doctor. Once a diagnosis is made, a certain type of care must be provided to the patient.
This care is as follows:
- The child is bathed once every few days, adding special herbal decoctions to the water;
- Eliminate fatty, salty, sour foods from the diet;
- It is necessary to change household items and personal towels daily;
- Home clothes should not be too tight and have a synthetic composition;
- Bed linen must be changed every three days;
- Every day, the room where there is a person suffering from viral pemphigus must be cleaned and ventilated;
- Isolate the patient from other family members for at least 7 days;
- Treat skin lesions in a timely manner;
- Make sure that no bubbles are scratched.
Proper parental care can much more quickly reduce the unpleasant symptoms of viral pemphigus in children and also prevent the development of complications.
Treatment of pemphigus
- Glucocorticoids.
- Antiseptics.
- Dieting.
- Elimination of insolation and physical overload.
- Clinical examination.
Treatment is prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis by a medical specialist.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
- Prednisolone (systemic GCS). Dosage regimen: it is recommended to start treatment with large doses, however, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the body, age, contraindications and the clinical picture of pemphigus. Impact daily doses of Prednisolone are 60–80 mg, and in case of damage to the mucous membranes - up to 100 mg. It is recommended to stop taking hormones or reduce their daily dose very carefully and gradually. Thus, during treatment, as obvious improvement occurs, the daily dose of the hormone is gradually reduced, approximately once every 4-5 days by 2.5-5 mg of prednisolone until the minimum maintenance effective dose of the hormone is reached, the introduction of which ensures remission of the disease .
- Azathioprine (an immunosuppressant from the antimetabolite group). Dosage regimen: set individually, taking into account the indications, severity of the disease, dosage of simultaneously prescribed drugs. Usually prescribed orally at 1.5-2 mg/kg/day in 2-4 divided doses. If necessary, the daily dose can be increased to 200-250 mg in 2-4 doses. The duration of the course of treatment is determined individually.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of viral pemphigus are used at the beginning of the formation of diseases. And they help to quickly reduce unpleasant symptoms and improve the child’s condition.
However, all methods may have hidden side effects, so you should consult your doctor before use.
The most commonly used methods are:
- Nettle juice – helps reduce inflammation and has an antiseptic effect. It is necessary to chop the leaves and stems of fresh nettle and add a glass of water, let it brew for an hour. Strain, moisten cotton wool in the treated liquid and apply to the locations of the bubbles;
- Baths with a series - helps reduce discomfort and has the property of healing damage to the epidermis. To prepare, you need to pour two tablespoons of dry herbs with two glasses of boiling water and let it brew for 20 minutes. Add to water while bathing. Used from birth, in a course of two days;
- Mint and calendula flowers have the property of strengthening the immune system. To prepare, you need to mix a teaspoon of mint herb and a teaspoon of calendula flowers and pour a glass of boiling water. Give your child a tablespoon twice a day for 7 days. Recommended for use from the age of 3 years;
- Olive oil – has beneficial qualities for restoring the skin, it is recommended to use a cotton pad, apply a small amount to damaged areas and leave until completely absorbed. Allowed for use from the age of 6 months. Duration of treatment is 10 days.
Recommendations
It is recommended to consult a dermatovenerologist, a cytological examination for acantholytic cells in imprint smears in the area of the bottom of blisters and erosions, and a histological examination of the skin.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Director of the Central Dermatovenerological Institute of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation Kubanova A.A. |
Diagnostics
In most cases, doctors are able to identify pemphigus in children by visual examination.
If an additional infection or specialists suspect a complication of the pathological process, then an additional examination is prescribed.
Children who have had pemphigus are recommended to be examined by a dermatologist. After recovery, children need to be regularly examined by this specialist.
procedures can be used :
- general and biochemical blood test;
- cytological examination of fluid from blisters;
- checking blood for the presence of specific antibodies;
- histological studies;
- comprehensive stool analysis;
- cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0 | 0 | 2 | 56 | 56 | 94 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 108 | 108 | 201 | 96 |
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of viral pemphigus, it is recommended to follow simple prevention methods:
- Children at any age should have their own personal hygiene equipment. This is especially true for toothbrushes, washcloths and towels. The towel must be changed every two days. Before this, iron the item at high temperature;
- You should maintain proper nutrition and exclude harmful foods. The diet should contain all the necessary vitamins and minerals to improve immunity;
- The children's room must be kept clean;
- Clothing must be clean and changed daily;
- Avoid contact with infected people;
- Maintain proper hygiene, especially after visiting public places;
- Treat all emerging diseases in a timely manner, do not self-medicate.
Following these simple preventive measures can reduce the likelihood of contracting viral pemphigus. However, parents should be aware that no one is protected from the risk of becoming infected with pemphigus.
Symptoms
| Occurrence (how often a symptom occurs in a given disease) | |
| Skin pain at the site of the lesion | 100% |
| Pain in the mouth when eating, talking, swallowing saliva | 90% |
| Bubbles in the mouth, throat | 90% |
| Wounds that do not heal for a long time after opening the blisters | 90% |
| Rash in the form of blisters on the external genitalia | 80% |
| Rashes on mucous membranes | 70% |
| Bad breath (halitosis) | 70% |
Complications
If viral pemphigus is not treated correctly, the following types of complications may occur:
- Formation of a chronic form of the disease;
- Infection of wounds with discharge of pus;
- Malfunctions of internal organs;
- Meningitis;
- Development of pneumonia;
- Major weight loss;
- Possibility of spots and scars after treatment of the disease.
Pemphigus can cover a child's entire body and cause other types of skin diseases that make the viral infection worse.
Types of pemphigus
Depending on whether acantholysis (destruction of intercellular connections) occurs in the skin, all pemphigus is divided into true (acantholytic) and non-acantholytic (pemphigoid). In both cases, blisters appear on the patient’s body, which are very similar to each other.
Currently, doctors distinguish the following forms:
- pemphigus vulgaris;
- pemphigus vegetans;
- Brazilian pemphigus is endemic and is found only in some peoples of Brazil;
- pemphigus foliaceus;
- erythematous pemphigus;
- paraneoplastic pemphigus – provoked by cancer;
- chronic congenital familial pemphigus (also known as Hailey-Hailey disease);
- Dühring's dermatosis herpetiformis;
- cicatricial pemphigoid;
- bullous pemphigoid.
Top
Treatment of severe forms of pemphigus
Acute forms of pemphigus are often treated with corticosteroid hormones.
Very often doctors prescribe drugs:
- prednisolone;
- polcortolon;
- metipred;
- dexamethasone.
Contraindications to the use of hormones are peptic ulcers of the stomach or duodenum. In cases where such indications are present, hormonal drugs are administered intramuscularly.
Long-term hormonal therapy can lead to various side effects:
- Symptomatic Itsenko-Cushing complex.
- Obesity.
- Diabetes.
- Erosive and ulcerative formations in the digestive tract.
- Hypertension.
- Thrombosis.
- Osteoporosis.
- Psychological effects: insomnia, psychosis, depression, euphoria.
- Attachment of various infections.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system.
There are many disadvantages of corticosteroid therapy:
- The presence of side effects is not a reason to discontinue therapy.
- Correction of treatment with the help of therapeutic measures is necessary.
- Discontinuation of corticosteroid treatment leads to relapse of the disease.
- Along with hormonal medications, you need to take antibiotics and antifungal medications.
During therapy you must adhere to the following dietary intake:
- complete exclusion of carbohydrates and fats from the diet;
- enrichment of food with proteins and vitamins;
- introduction of potassium chloride into the diet;
- taking cytostatics: methotrexate;
- azathioprine;
- cyclophosphamide.
To increase the effect of cortecosteroid drugs on the body, extracorporeal techniques can be used:
- Plasmaphoresis;
- Hemosorption;
- Hemodialysis.
Treatment at home
Hospitalization for the diagnosis of pemphigus is rarely carried out, only in critical situations. Patients are often treated at home. In this case, it is especially important to follow the instructions of your doctor.
However, during therapy at home, parents should adhere to certain recommendations:
- pay increased attention to the child’s hygiene procedures;
- change bed linen more often;
- do not allow the child to comb the blisters to avoid additional infection.
To relieve itching and irritation, follow a few rules:
- Anti-inflammatory creams or lotions can be applied to the affected areas.
- After the wounds have dried, it is recommended to use an emollient cream.
- Cool water reduces mouth soreness.
- It is necessary to ventilate the room periodically.
- Wet cleaning must be done daily.
Pemphigus vulgaris is
Utricularia or water bladder or bladderwort is one of the most diverse and bizarre genera of carnivorous plants. Found on every continent except Antarctica, these carnivorous plants capture prey using a clever bladder trap that sucks up tiny insects and nematodes. These insects make up the majority of their diet.
| Domain (Regio) | Eukaryotes _ |
| Kingdom (Regnum) | Plants (Plantae) |
| Type (Phylum) (division) | Flowering plants (Angiospermae) |
| Class (Сlassis) | Dicotyledons (Dicotyledones) |
| Squad (Ordo) (order) | Lamiales _ |
| Family _ | Bladderworts (Lentibulariaceae) |
| Genus _ | Pemphigus (Utricularia) |
| Species _ | Common bladderwort (Utricularia vulgaris) |