general characteristics
Excessive sweating is a subjective complaint: patients notice that they sweat more than other people.
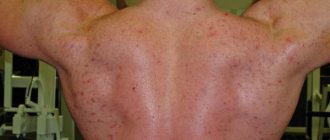
A person finds wet stains from sweat on clothes, not only in the armpits, but also on the chest or back. Sweating is combined with cold skin and an unpleasant, pungent odor that can be easily felt from a distance. Patients may note that a large amount of sweat appears only on certain parts of the body - for example, on the palms and soles of the face. Increased sweating is provoked by stress, minor physical activity, and food intake. The symptom also causes psychological disorders: the person begins to experience a feeling of shame, discomfort, and avoid contact with others. Great inconvenience is caused by excessive sweating of the palms, which interferes with professional activities and makes it difficult to meet people and shake hands. A short-term increase in sweat production in response to physical labor or emotional shock is considered normal, but persistent hyperhidrosis, which disrupts the quality of life, is an indication for contacting a specialist.
Prevention of hyperhidrosis
First of all, if you have a tendency to excessive sweating of the face, you should learn to control your emotional state and try to avoid stressful situations. If hyperhidrosis is observed on the scalp, it is necessary to choose hairstyles that do not lead to blood stagnation. It is advisable to abandon the ponytail and tight spikelet. The ideal option is loose hair. In the event that the problem becomes pronounced, it is worth making an appointment with a therapist as soon as possible.
Classification
The difficulty of identifying individual variants of excessive sweating is due to the great subjectivity in assessing symptoms. Depending on the frequency of occurrence, hyperhidrosis is classified into permanent, the severity of which does not depend on the time of year, seasonal, in which sweating increases in the hot months, and intermittent, characterized by periodic relapses. In clinical practice, the classification of symptoms by prevalence is important, according to which they distinguish:
- Limited (local) hyperhidrosis
. Characterized by increased secretion of sweat glands in certain areas of the skin. In accordance with this, the local form is divided into facial, palmar, plantar, axillary (axillary) hyperhidrosis. This variant is more often associated with dysfunction of the apocrine glands. - Generalized hyperhidrosis
. Increased sweating is observed over the entire surface of the skin. The development of this disorder is due to the increased work of all sweat glands, which is often associated with changes in hormonal levels, infectious diseases, and other systemic pathological disorders.
Various pathogenetic mechanisms determine the division of pathologically increased secretion of sweat into two forms: primary idiopathic, the causes of which have not been established, and secondary, caused by damage to different organ systems. Night sweats associated with chronic infectious processes or hormonal fluctuations are classified as a separate type. Due to a special development mechanism, doctors distinguish stress sweating (the so-called “cold sweat”), provoked by an increased concentration of catecholamines (adrenaline) in the blood. Taking into account the degree of social discomfort, there is:
- a mild form of sweating that does not limit the patient’s interaction with other people;
- moderate hyperhidrosis, in which daily activity is somewhat limited and discomfort occurs when shaking hands or close contact with people;
- a severe form, characterized by heavy sweating with a pungent odor, which forces the patient to avoid other people and provoke psychological disorders.
Why does sweat occur?
- The reasons for the appearance of perspiration throughout the body or in individual places in each of the listed cases are different. For example, hyperhidrosis of the extremities can occur as a result of an increase in the concentration of sweat glands or as a result of an incorrect reaction of the body to habitual stimuli - physical activity, emotions, heat. In such a situation, sweating can exceed normal by 10 times. Most often, this reaction of the body can be observed in a stressful situation and in a state of nervous tension.
- When considering the reasons for the appearance of perspiration on the face, we first need to mention food. Sweating often occurs when consuming a number of foods, such as hot tea, coffee, chocolate, alcohol, and spicy foods. Moreover, it is noticeable on the forehead and above the upper lip. You can notice it within a couple of minutes after eating such food.
- Perspiration on the face can be caused by more serious reasons - surgery on the salivary gland or its severe disease. In infants, this phenomenon occurs due to damage to the facial nerve during childbirth, when obstetric forceps are used.
- Neurological disorders that cause perspiration include neurosyphilis, stroke and Parkinson's disease.
Causes of sweating
Causes of cold sweat
Increased sweating is often accompanied by a sharp cold snap and pale skin. A similar reaction normally occurs during severe emotional shocks, but more often the appearance of cold sweat is caused by pathological conditions:
- Migraine
. - Severe pain syndrome
. - Viral infections
: mononucleosis, influenza. - Critical conditions
: hypoglycemia, acute cardiac or respiratory failure. - Autonomic regulation disorders
. - Intoxication
: alcohol abuse, formation of endogenous toxins in renal and liver failure.
Causes of general sweating
Excessive sweating over the entire skin is a normal reaction in hot climates, after intense physical activity. Persistent hyperhidrosis with no apparent cause is a sign of illness. Increased general sweating is caused by:
- Endocrine diseases
: thyrotoxicosis, menopause in women, pheochromocytoma, etc. - Infectious processes
: brucellosis, malaria, HIV infection. - Oncological pathology
: lymphogranulomatosis, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, neoplastic syndrome. - Poisoning
: consumption of poisonous mushrooms, ingestion of organophosphorus compounds. - Complications of pharmacotherapy
: long-term use of cholinomimetics, anticholinesterase drugs. - Rare causes
: Riley-Day syndrome, Cassirer's acroasphyxia, polyneuropathy.
Causes of sweating head
Severe sweating in the face and scalp, accompanied by hot flashes or, conversely, severe pallor and coldness, develops in the presence of painful disorders. Local sweating of the head is caused by:
- Nightmares, sleep disturbances
. - VSD
: increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system. - Neurological disorders
: Parkinson's disease, neurosyphilis, stroke. - Hypertensive crises
. - Damage to the nerve trunks
: chorda tympani syndrome, Lucy Frey auricotemporal syndrome. - Genetic diseases
: Beech, Jadasson-Lewandowski, Hamstorp-Wohlfahrt syndromes.
Causes of night sweats in women
Women are more susceptible to various pathological reactions of the autonomic nervous system and hormonal imbalances, so hyperhidrosis is more common in them. Excessive night sweats in women can be caused by the following diseases and conditions:
- Hormonal changes
: a few days before menstruation, in the first trimester of pregnancy, in the premenopausal period. - Neuropsychic pathology
: multiple sclerosis, psychosis, depressive states. - Systemic connective tissue diseases
: rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, rheumatism. - Complications of pharmacotherapy
: taking tranquilizers, antipsychotics, antihypertensive drugs.
Causes of night sweats in men
Normally, sweating increases at high temperatures in the bedroom when using synthetic bedding. Unreasonable release of large amounts of sweat, causing the pillow and sheets to get wet, indicates the possible presence of a pathological process. In men, night sweats are most often caused by conditions such as:
- Withdrawal syndrome:
with abuse of alcoholic beverages and narcotic substances. - Hormonal imbalances
: in adolescence, middle and old age due to decreased testosterone levels. - Endocrine diseases
: carcinoid syndrome, pheochromocytoma, damage to the hypothalamic-pituitary system. - Tuberculosis infection.
- Tumor
and: testicular cancer, prostate cancer. - Rare causes
: sarcoidosis, histiocytosis.
Reasons for decreased sweating
A decrease in the secretion of sweat glands (anhidrosis), which occurs against the background of normal health, is observed in older people due to natural age-related changes in the skin. Sweat production is noticeably reduced in the following conditions and diseases:
- Severe dehydration:
with limited water intake, repeated vomiting and diarrhea. - Skin lesions
: atrophic acrodermatitis, radiation dermatitis, scleroderma. - Hereditary pathologies
: Sjogren's disease, ectodermal dysplasia. - Complications of pharmacotherapy
: treatment with antiepileptic drugs, ganglio- and anticholinergic blockers.
What causes hyperhidrosis?
In general, a person needs sweat, as it allows for thermoregulation. For example, a person sweats in the heat, during increased physical activity, and so on. Evaporating moisture cools the body and allows it to maintain normal temperature.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the work of the sweat glands, which sends signals at the right moments and activates the glands. But if the operation of this system is disrupted for some reason, then sweat can be released at any time, regardless of the ambient temperature and the person’s condition.
What are the causes of hyperhidrosis? They can be very different:
- diseases of the thyroid gland, in particular hyperthyroidism;
- poor diet (eating excessively spicy or hot foods can lead to increased sweating);
- some malignant neoplasms, for example, Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, malaria, syphilis, brucellosis and some others;
- wearing very tight clothing made of dense, synthetic and breathable fabrics;
- diabetes;
- overweight or obesity;
- menopause in women;
- parkinsonism;
- some diseases of the cardiovascular system, such as tachycardia;
- cystic fibrosis;
- frequent stress, increased nervous tension, overexcitement;
- taking certain medications;
- consequences of a stroke (such a disease can lead to damage to the hypothalamus, as well as to disruptions in the functioning of the thermoregulation center located in the brain).
Hyperhidrosis can also develop independently, in which case heredity is the influencing factor in most cases.
Diagnostics
The primary diagnostic search for excessive sweating is carried out by a general practitioner or general practitioner. The main objective of the examination is to identify disturbances in the functioning of the body that provoked changes in the functioning of the sweat glands. For this purpose, special functional tests, laboratory tests and instrumental visualization methods are prescribed. The most valuable for diagnosis are:
- Quantitative and qualitative tests
. To determine the degree of excessive sweating, a gravimetric method is useful, which involves weighing a piece of filter paper after 1 minute of contact with the skin. To measure the area of hyperhidrosis, the Minor test is used. Verification of the primary form of increased sweating is carried out using the chromatographic method. - Laboratory research
. The levels of the main hormones are measured - corticosteroids, thyroxine, tropic substances of the pituitary gland. Women must be tested for estrogen and progesterone levels. To exclude diabetes mellitus, fasting glycemia is determined, and a glucose load test is prescribed according to indications. Blood tests look for signs of inflammatory and tumor processes. - Neurological examination
. The appearance of increased sweating is often associated with pathologies of the nervous system, so all patients are examined by a neurologist. In addition to physical examination and assessment of basic reflexes, EEG and ultrasonography of peripheral nerves are used. According to indications, CT and MRI of the brain are prescribed.
When organizing further examination, accompanying symptoms are taken into account: in case of signs of an infectious process, serological tests are performed; in autoimmune diseases, the levels of rheumatoid factor and other specific markers are measured. Some patients are recommended to undergo a psychiatric evaluation. To diagnose doubtful cases of excessive sweating, consult other specialists (dermatologist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist).
Antiperspirants reduce sweat production and neutralize unpleasant odors
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce the unpleasant odor of sweat and prevent irritation, it is necessary to take a hygienic shower at least 2 times a day, use underwear made from natural fabrics and loose clothing that does not rub the skin. In some cases, herbal sedatives are effective, which normalize the functioning of the nervous system and reduce psychological discomfort. If you experience excessive sweating, you should consult a specialist to find out the cause of hyperhidrosis and select the optimal treatment regimen.
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics for sweating are aimed both at relieving the underlying disease and at reducing subjective discomfort. Medicines are combined with physical therapy methods - reflexology, electrophoresis with solutions of anticholinergics. To eliminate psychological problems associated with increased sweat production, individual psychotherapy sessions are offered. To treat hyperhidrosis, medications such as:
- Sedatives
. Sedatives normalize the autonomic regulation of sweating and reduce the functional activity of apocrine sweat glands. For severe hyperhidrosis, tranquilizers are used. - Local agents
. Anticholinergics are often used. Medicines with tanning properties are effective - aluminum salts, plant extracts, which reduce sweat production and reduce skin irritation. - Hormonal drugs
. Used as replacement therapy for various endocrine disorders. In most cases, after correction of hormonal levels, excessive sweating completely disappears. - Antibacterial agents
. Antibiotics help prevent secondary bacterial skin lesions in areas of constant friction. Widely used for etiotropic treatment of infections accompanied by hyperhidrosis. - Botulinum toxin
. The drug is used for local sweating and is administered subcutaneously or intradermally. The product blocks the transmission of nerve impulses to the sweat glands, which helps reduce sweating.
Treatment: what to do if your face is sweating?
Sweating of the face and head causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient, so therapeutic measures are required to eliminate the problem. To treat hyperhidrosis, special face creams, solutions, and medications are used. It is also possible to use folk remedies that will help you quickly cope with mild facial sweating.
Help with medicines
Medications that are used strictly as prescribed by a doctor help reduce sweating. If one medicine for hyperhidrosis does not work, then another is prescribed. If there is no effect of drug treatment or in the later stages of hyperhidrosis, surgery is prescribed. It is possible to carry out therapy through Botox injections, but such procedures are not affordable for everyone. Doctors often prescribe the following medications to patients for excessive sweating:
- cream “Formidon” or “Formagel”;
- anticholinergic drugs;
- medications that reduce hyperhidrosis - Oxybutin, Benzotropin;
- medicines including belladonna - “Bellataminal”, “Belloid”, “Bellaspon”;
- drugs with a sedative effect - “Persen”.
Laser therapy is no less effective for hyperhidrosis, as there are no adverse reactions and the problem of sweating is painlessly eliminated. Doctors recommend that the patient undergo several hypnosis sessions, take yoga classes, and meditate. Physiotherapy procedures provide special results:
- electro- and iontophoresis;
- electrosleep;
- climate therapy;
- water procedures;
- electrotherapy.
A special deodorant is used that eliminates facial hyperhidrosis. Deodorants help only in the initial stages, when increased sweating occurs, then such products will not help.
How effective are folk remedies?
Herbal baths are recommended for the treatment of sweating.
Treatment with folk remedies for hyperhidrosis is used only after consultation with a doctor. One alternative therapy is powerless for severe sweating, so it is recommended to use it in conjunction with medications. Natural ingredients almost never cause side effects, are easy to use and accessible to every patient with hyperhidrosis. Facial hyperhidrosis is effectively treated with the following recipes:
- Herbal infusions for herbal baths. You can make an infusion from oak bark, chamomile inflorescences, string and thyme.
- Poison from medicinal herbs. For external use, prepare a decoction of mint, sage and oak bark. Take 1 tbsp of each component. l. and pour 500 ml of boiling water. After straining, add 100 g of vodka and wipe the problem areas twice a day.
- Birch leaf mask. To prepare, you need a small handful of leaves, which is poured with 250 ml of boiling water. After thoroughly squeezing, the leaves are applied to the affected area.
- Chicken protein mask. Add 20 g of starch and a couple of drops of lemon juice to thoroughly beaten raw protein. The finished mixture is applied to the skin for a quarter of an hour.
- Rubbing using cucumber. The vegetable is cut into thin slices and the affected area is wiped three times a day.