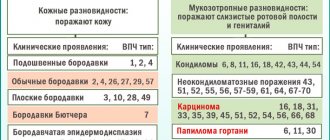
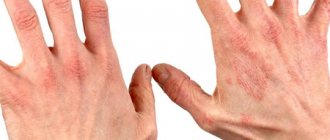
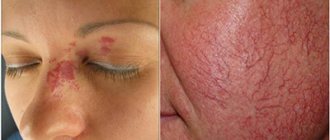
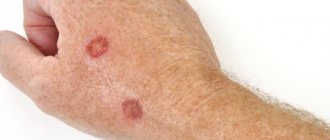
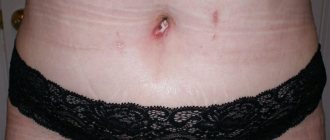
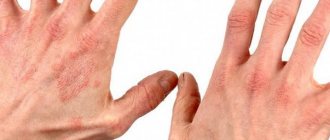
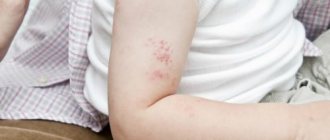
Vitiligo is quite easy to notice; the initial stage has a quite noticeable manifestation. On the skin, the initial stage of vitiligo (photo 2) appears as barely noticeable white spots, the size of which does not exceed 0.2-0.3 cm. Often, such minor symptoms of vitiligo are simply ignored.
Dermatological studies have shown that if a patient has had skin melanoma, the occurrence of vitiligo increases the chances of regression of this disease. Under favorable conditions for the pathology, the initial stage can develop, turning into other forms:
- stationary;
- progressive;
- repigmentation stage.
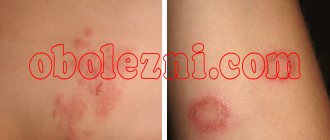
During the stationary stage, the white spots (photo 3) do not change, and new signs of vitiligo do not appear. With progression, there is a “reproduction” of spots, existing lesions increase in size. The rate of growth depends on the individual characteristics of the body; the symptoms of vitiligo may intensify over several weeks.
Vitiligo after treatment can go into the repigmentation stage. When exposed to chemical agents or taking medications, skin pigmentation disorders become less aggressive. If you ignore the pathology, complications may develop, which include:
- psoriasis;
- focal baldness;
- dermatitis;
- early gray hair;
- lichen planus;
- scleroderma.
In some cases, the cause of skin pigmentation disorders is pityriasis versicolor in a person , the symptoms of which are somewhat similar to vitiligo. This disease is an infectious pathology and usually affects adults.
Types of childhood vitiligo
Vitiligo has its own qualifications. Based on the nature of the spots, their color, and location, two large categories are distinguished: type A and type B.
Type A:
- vulgar leukoderma - spots are found on 2 or more parts of the body;
- acrofascial – depigmentation is localized only on the hands and feet;
- mixed - combines several subspecies, spots are scattered throughout the body, face, head.
Type B:
- focal - spots grow strictly on one side of the body;
- mucous membrane – vitiligo is localized exclusively on the mucous membranes, including the genitals;
- zosteriform - a large number of small spots appear in one area;
- segmental - accompanies lesions of the spinal and other large nerves.
Based on the number and location of spots, several subtypes of the disease are also distinguished.
Generalized
The spots cover more than 80% of the skin and mucous membranes. They can be of various shapes, sizes and shades, periodically fade, then appear in new places.
Localized
The disease develops strictly of one type in a specific area of the body, on the mucous membrane or on the head and face.
Symptoms of vitiligo in children
Typically, symptoms of the disease begin to appear in children aged 9-10 years. It has been found that girls suffer from it more often than boys. What this is connected with and why this happens, scientists cannot yet explain.
The clinical picture of the disease can be different in infants and older children; the severity of symptoms and the rate of development are influenced by the general condition of the child, the presence of chronic diseases, immunity, environment, and nutrition, among other things. The most important symptom of the disease is milky spots on the neck. At first they may be small in size, pinkish in color, and round in shape. Then the spots become milky white and take the form of blots.
As a rule, the spots are painless, but if a child spends a long time in the sun, is injured or comes into contact with aggressive chemicals, then the following symptoms may occur:
- dryness and flaking of spots;
- redness and irritation;
- compaction of stains;
- sometimes increased body temperature.
The spots may itch, hurt, and crack. If a child scratches them, the risk of wound infection and inflammation increases.
If leukoderma affects the scalp and body, then the hair in this area becomes discolored and turns gray. There is also a decrease in the skin's reaction to cold and heat in the affected areas.
Vitiligo does not affect the internal organs, so the child’s general condition is stable, he does not need quarantine or bed rest.
Causes
Scientists cannot currently pinpoint the exact causes of vitiligo. Despite this, a number of hypotheses have been identified that determine the factors that provoke depigmentation.
- Autoimmune disorders . With pathologies of antibody synthesis, the body’s protective cells begin to attack not foreign cells, but the body itself. This leads to disruption of melanin synthesis and the appearance of light spots on the skin.
- Endocrine disorders . If there is a malfunction of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland or gonads, the synthesis of pigment in the skin may change.
- Enzyme deficiency . Tyrosinase deficiency leads to a lack of melanin synthesis in the skin.
- Hereditary predisposition . Studies of hereditary factors show that patients with a family history of vitiligo are more likely to develop spots under the influence of triggers. But here we should focus on the impact of triggers - without a reaction to them, vitiligo may not appear. There are also cases where both parents were susceptible to pathology, but it never manifested itself in the child.
One of the triggers that provoke the occurrence of vitiligo is solar radiation - this explains the location of the spots - they are most often located on the face, legs or arms.
In addition to solar radiation, the following factors can become a catalyst for melanin disruption:
- constant mechanical impact, skin trauma;
- bacterial infections;
- hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- deficiency of micro- and macroelements;
- high levels of stress;
- chronic pathologies of internal organs;
- intoxication;
- helminth infestations.
Diagnosis of vitiligo in children
The manifestations of leukoderma are quite specific; an experienced dermatologist will never confuse it with lichen, psoriasis or dermatitis. Therefore, for diagnosis, an external examination of the child and a survey of parents is usually sufficient. Additionally, an ultraviolet lamp can be used, in the light of which subtle spots are visible on the skin.
In any case, the doctor will write out directions for general blood and urine tests, and may take a scraping for histological examination. Depending on the presence or suspicion of concomitant diseases, an additional consultation with specialized specialists - an endocrinologist, psychotherapist, or immunologist - may be prescribed.
Causes and symptoms
The causes of depigmentation are usually divided into congenital and acquired. They are related to the absence of a dye in a certain area of the dermis. Sometimes skin cells have no pigment at all. An example is albinism, which is congenital.
Acquired causes include:
- dysfunction of the endocrine glands;
- chronic diseases;
- autoimmune disorders;
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and ultraviolet radiation;
- concomitant dermatological diseases: psoriasis, leprosy, streptoderma;
- inflammatory processes;
- long-term corticosteroid therapy;
- iron deficiency (pregnancy, poor nutrition).
Sometimes depigmentation is observed after a burn or trauma with damage to the skin (post-traumatic).
We recommend reading
- Why the labia are dark: causes of darkened skin
- Causes of darkening of nipples during pregnancy
- Why pigment spots appear in the chest area and how to get rid of them
Stages of vitiligo in children
Leukoderma in childhood develops in the same stages as in adults.
1. Initial. The disease begins with the appearance of one small spot in the favorite places of localization: on the child’s face, palms, fingertips, elbow and knee bends, less often on the chest and back. For a long time, the spot may not increase in size and remain single, but there are cases when the disease progresses rapidly.
2. Progressive. We can talk about the progression stage if over the course of several weeks a large number of new spots appear on the skin, and the old ones have greatly increased in size.
3. Repigmentation stage. Repigmentation is said to occur if not a single new spot has appeared for three months. And those that have already been beaten do not increase in size, darken or even disappear completely.
Vitiligo can recur. Therefore, even if it was possible to completely get rid of the spots with the help of complex treatment or spontaneous recovery occurred, parents should understand that after some time the disease may well return again.
Is vitiligo transmitted from father to child?
The occurrence of vitiligo in a child if the father has the disease has a probability of up to 40%. There is a greater chance of inheritance if both parents suffer from pigmentation disorders.
It is important to know the overall picture of the father's genome. If recessive traits predominate (blue eyes, fair skin), the percentage will be minimal.
We recommend reading
- Pharmaceutical products based on duckweed for the treatment of vitiligo
- Causes of vitiligo in intimate places
- The effectiveness of using vitiskin hydrogel for vitiligo
A certain combination of genes in the DNA is responsible for vitiligo, however, it only causes a predisposition. A child may be a carrier of a mutagen, but this will not manifest itself outwardly at all, but it may make itself felt in subsequent generations.
It is possible that exposure to provoking factors will directly contribute to the activation of the disease, even if not in childhood, then in adulthood.
Causes of vitiligo in children
The origin of leukoderma has not been precisely established to date. It is known that this disease can be transmitted from parents to children. That is, there is a genetic predisposition to leukoderma. If close relatives of a child suffer from melanin deficiency, the baby is automatically placed at risk.
The pathological process can be triggered by one of the following factors:
- dysfunction of the immune system, when the body begins to perceive melanocytes as foreign cells and produce antigens to them;
- improper metabolism, deficiency of certain vitamins and microelements: vitamins A, E, group B, copper, zinc, iron;
- chronic diseases;
- acute infectious processes;
- therapy with certain medications, chemotherapy;
- low-quality cosmetic and hygiene products;
- chemical burns or intoxication of the body after inhaling fumes of harmful chemicals;
- problems with the organs of the endocrine system - dysfunction of the adrenal glands, thyroid or pancreas;
- helminthiasis;
- diseases of an autoimmune nature;
- any physical damage to internal organs, traumatic brain injury.
The occurrence of vitiligo in a child during the prepubertal period is often associated with unstable hormonal levels. The psychological factor also plays a role. Stress, emotional upheaval, and nervous tension also provoke the development of vitiligo in children and adolescents.
Is it dangerous
Vitiligo does not pose a threat to the life and health of the child. However, the disease begins due to problems in the functioning of various systems and organs. Therefore, it is better to examine the child in a clinic.
Vitiligo in children is not considered a dangerous disease, but its treatment will take a long time and will require an individual approach and compliance with all specialist prescriptions.
It is better to have less direct sunlight on the skin, otherwise the depigmented areas will be very pronounced and a burn is possible.
If an infant or teenager is diagnosed with vitiligo, you should pay attention to:
- thyroid function;
- what medications does the child take;
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system;
- skin problems.
It happens that vitiligo is diagnosed with progressive myopia and pneumonia.
If, in addition to vitiligo, the child is concerned about concomitant pathologies, the attending physician should be notified about this. Quite often, patients need psychological help. An external defect leads to isolation, depression, and difficulties in communication.
Treatment
Complex treatment can be carried out at home. Since vitiligo is not an infectious disease, the child can continue to attend preschool and school educational institutions. A doctor can recommend treatment in a hospital setting only if vitiligo is complicated by concomitant diseases or if surgery is planned.
Drug treatment
There are 4 main groups of medications used to help reduce the manifestations of leukoderma:
- Glucocorticoids - hydrocortisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone.
- Photosensitizing hormonal drugs – Melagenin, Beroxan, “lamadin”.
- Immunomodulatory agents - “Interferon”, “Arbidol”, “Likopid”.
- Antioxidants – “Glutargin”, “Actovegin”.
Be sure to select a multivitamin complex for the child.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods for treating vitiligo in children give good results in most cases. The following procedures may be prescribed:
- phototherapy - irradiation of the skin with a UV lamp, more detailed information about lamp treatment;
- photochemotherapy – drugs are additionally used to stimulate the skin’s sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation and the production of pigments;
- skin whitening - with this procedure, healthy areas of the skin are bleached using certain compounds to even out the overall tone; it gives good results for the generalized form of vitiligo.
What is the difficulty of treating a child - not all means and procedures are harmless to an unformed organism. Prescriptions are made strictly by the doctor and constantly monitor the condition of the little patient. It is important to use minimal dosages and durations of treatment courses to avoid complications and side effects.
Surgery
Surgical methods in pediatrics are usually not used for the following reasons:
- not all children tolerate anesthesia well;
- there is a high risk of rejection of transplanted tissues and suppuration;
- There is no 100% guarantee of healing from vitiligo even after surgery; the spots may reappear on other parts of the body.
Only in extreme cases is transplantation of healthy melanocytes, transplantation of skin sections, or injection of melanocytes into skin cells performed. The donor can be the child himself or another person.
What is the danger of vitiligo?
The violation itself does not pose any direct danger to the patient’s life. But it should be understood that it occurs as a result of the pathological course of processes in the body, which can already cause further deterioration of the condition. Therefore, if depigmented areas appear on the body, you should consult a doctor for a detailed examination. A timely identified violation will be quickly eliminated, and after the cause is eliminated, the vitiligo lesion will not spread. In such cases, it is even possible to restore normal melanin synthesis.
Traditional methods of treatment
Many parents prefer to treat their children with a variety of infusions and decoctions based on medicinal plants. It must be said right away: so far, not a single folk remedy has helped to completely cope with the symptoms of an unpleasant disease. Lotions, compresses, and applications based on homemade potions more often cause allergic reactions in children than provide a noticeable therapeutic effect. But infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants can be used to generally strengthen the child’s body and maintain immunity; the most effective of them are described in this article.
Forecast
Unlike most diseases, the prognosis for vitiligo does not always depend on the stage at which it was discovered and what treatment methods were used. Each case of the disease is unique. Some children benefit from one course of phototherapy and vitamins. Others do not heal even after many years of therapy with various means and methods. Modern medicine continues to search for an effective and safe cure for vitiligo. In the meantime, in extreme cases, you can always use numerous cosmetics and procedures to disguise skin defects.
Prevention
To avoid the development of vitiligo and prevent the appearance of new spots, it is recommended:
- adhere to the principles of proper nutrition,
- avoid stressful situations,
- support immunity,
- promptly treat helminthic infestations and other diseases.
It is difficult to prevent the development of vitiligo due to the lack of reliable information about the causes of the disease. Modern treatment methods make it possible to eliminate the external manifestations of pathology and normalize skin color. For vitiligo therapy to be effective, it is necessary to seek specialized help immediately after the appearance of white spots.