Keratosis - treatment
Keratosis is a pathological skin condition associated with excessive production of keratin.
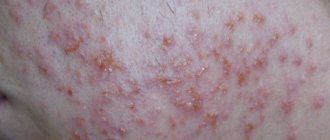
The disease manifests itself in the form of compactions with dry, rough scales, which, as the disease progresses, cause pain, cracks and bleeding appear, and as a result of infection - erosive phenomena. The etiology of keratosis has not yet been fully studied; scientists continue to work to identify the causes of the pathology. The main reason is considered to be prolonged exposure to external factors, as a result of which metabolic processes under the skin are disrupted, affecting the epidermis, dermis, blood vessels, sebaceous glands and melonocytes.
Factors contributing to the development of keratosis
There are many reasons that are considered the basis for disruption of the skin-fat balance and the appearance of keratosis. These include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- constant exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- influence of chemicals;
- weak immunity;
- infectious diseases associated with liver dysfunction:
- skin aging;
- endocrine disorders;
- menopause period;
- AIDS carriers;
- chemotherapy after tumor removal;
- poor hygiene;
- wearing uncomfortable clothes and shoes;
- weak nervous system, etc.
As a rule, the disease develops in people over 50 years of age, but in recent years cases have also been recorded in young people.
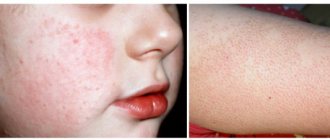
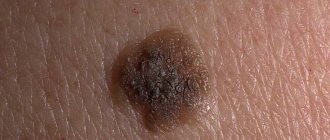
Clinical manifestations in the initial stages of keratosis may be invisible. These are small roughnesses and irregularities of brown or red color located on different parts of the body. As the pathological process develops, the affected areas peel off, itching appears, and the hairline is damaged.
Prediction and preventive measures of the disease
Keratosis of the skin develops gradually. Each type has its own clinical picture. In the cyanide form, as the tumor grows, the area of the skin affected by the pathology becomes dark and loose. At the second stage, cysts form in the tissues.
The skin becomes lumpy and begins to peel. When the keratoma is damaged, it begins to bleed and becomes painful. Sometimes an inflammatory process occurs.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pd4cxZNIMQk
In the initial stages of angiokeratoma, blue-black vascular nodules, the diameter of which is 2-5 mm, form on the patient’s skin. They are based on dermal cells. At the second stage, the nodules become rough and begin to peel off. At the last stage, the nodules begin to bleed and become inflamed. This form of disease also occurs in newborns.
The pathological process is localized in the area:
- scrotum;
- belly;
- hips;
- buttocks;
- armpits;
- oral cavity;
- vulva;
- stop;
- lips;
- cheeks;
- fingers.
Keratosis of the skin. Photos of adults show what neoplasms may look like.
The follicular form most often develops in women. It is characterized by the formation of flesh-colored keratinized plugs on the hair follicles. New growths are uneven. Their structure resembles flat, silvery scales. The size of the neoplasms is no more than 1.5 cm.
Most often localized in the area:
- faces;
- buttocks;
- neck;
- armpits.
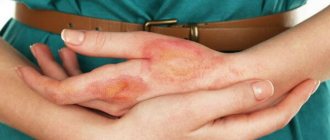
Keratosis of the skin (the photo in adults shows only external symptoms) begins in the cold season. In warm weather, the symptoms are erased. At a late stage of the disease, the nodules increase in size. The surface of the skin becomes rough. At the last stage, they may begin to bleed and hurt. The seborrheic appearance is characterized by slow development and chronic course.
A spot on the skin of a yellowish tint reaches a diameter of 3 cm. It has a dense morphology with scabs. At the second stage, the spot begins to increase in size and many layers form in it. The neoplasm becomes crusty. The thickness of the stain reaches 1.5 cm. On the last steel, the seal begins to turn black, crack and bleed.
The pathology is localized in the area:
- backs;
- breasts;
- faces;
- neck;
- scalp.
This type of pathology does not develop into an oncological form. In the actinic form, which often develops into a cancerous tumor, nerve rough spots appear in the first stage. At the last stage, they transform into keratinized scales of burgundy color.
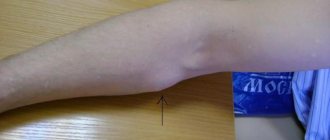
Keratomas are located singly. They grow very slowly, reaching 2 centimeters. This form can disappear on its own, and appear under mechanical stress or injury.
In the initial stages of solar keratosis, a large number of small spots appear that begin to peel off. They rise above the epidermis. At the last stage of the disease, the spots transform into plaques covered with hard scales.
This form of pathology is localized in the area:
- faces;
- backs;
- soles;
- legs;
- hands
This form of the disease is considered precancerous. It is triggered by radiation. The initial stage of cutaneous horn is characterized by the appearance of gray or brown spots on the skin. At the second stage of keratosis of the skin, the spots begin to become covered with keratinized scales.
Externally, in the photo of adults, they resemble a tubercle that rises greatly above the skin. Some neoplasms take the form of a flat, silvery plaque. At the last stage, keratomas begin to peel off and bleed.
- lips;
- nose;
- century;
- forehead;
- mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- ears;
- scalp.
This form can turn into an oncological form.
The prognosis of the disease depends on when treatment is started. Following certain recommendations from a dermatologist will help avoid relapses.
Preventive measures include:
- use of moisturizers;
- proper nutrition, which provides the skin with all the necessary “building” components;
- limited exposure to sunlight - this will reduce the effect of harmful ultraviolet radiation on the skin;
- use of sunscreens when exposed to solar radiation - ointments, creams with a high SPF content;
- use of selected protection for skin surfaces when working with chemicals.
Children with detected keratosis pilaris should not stay in the sun for a long time to prevent the appearance of skin rashes.
Schoolchildren and teenagers need to be explained the harm of scratching the skin and squeezing out “pimples”, which affect the appearance of inflammation.
Diagnosis of hyperkeratosis is based on physical examination and medical history. The examination is carried out by a dermatologist. He clarifies the presence of somatic pathologies, hereditary predisposition to hyperkeratosis, possible use of hormonal drugs, dietary features and lifestyle.
In doubtful cases, a general blood test (determination of hypovitaminosis) and histological examination of tissues may be needed. The main diagnostic criterion is the nature of the formations on the skin.
In cases where hyperkeratosis is a symptom of internal pathologies, additional examination and etiotropic treatment are prescribed.
Classification of keratosis
Depending on the etiology, congenital and acquired keratosis are distinguished. In the first case, there is a hereditary factor, in the second – endogenous and exogenous factors. Depending on the location, a distinction is made between diffuse keratosis (large areas of the body are affected) and local (single areas are affected).
Depending on the clinical manifestations, keratosis is distinguished:
- follicular;
- warty;
- diffuse;
- hyperkeratosis of the feet;
- lenticular;
- disseminated;
- seborrheic;
- polymorphic.
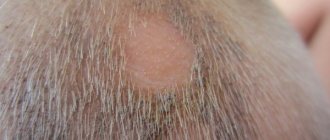
Keratosis follicularis
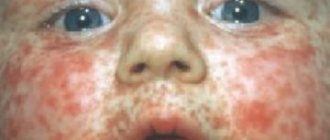
The follicular form is most often observed in the area of the knees, hips (on the outside), elbows and buttocks. As a result of the pathological process at the mouth, the follicles are filled with epidermal scales (dead cells that have separated from the upper layer of the skin), aseptic inflammation develops, which manifests itself in the form of bright red tubercles (goose bumps). Follicular keratosis is most often observed in the abdomen, shoulders, neck, and armpits, and usually develops in the cold season. In summer, signs of the disease disappear.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of actinic keratosis have a characteristic morphology. An experienced doctor can make the correct diagnosis during examination.
To exclude the presence of cancer, a histological examination of the skin section is prescribed.
On microscopic examination, actinic keratosis is characterized by the presence of so-called atypical cells. Such cells may be larger, with a changed shape, or a different morphology of the cell nuclei.
In keratosis, such cells are found only in the epidermis. If atypical cells cross the basement membrane, which is the border between the epidermis and the dermis, then we are talking about the beginning of a cancerous process.
Seborrheic keratosis
This form of keratosis manifests itself as formations in the form of plaques or nodes with a warty surface. The plaques are covered with a keratinized substance of brown or black color. This form is also called senile, as it is observed in people over 50 years of age. Plaques are localized in the face, neck and chest. They do not occur on the soles and palms. In most cases, the disease becomes chronic with exacerbations and remissions. Seborrheic keratosis formations never develop into a malignant tumor, but sometimes the tumor can masquerade as keratosis. Therefore, an important condition for diagnosis is a biopsy.
Symptoms
Actinic keratoses most often present as a white, scaly plaque of variable thickness with redness around it. The skin located close to the damage is characterized by noticeable pigment changes.
AK symptoms:
- in some cases, a hard, warty surface;
- dry skin and scattered telangiectasia;
- lesions are usually asymptomatic, but can itch, bleed, and cause a burning sensation;
- dry lips.
Actinic keratosis is classified according to its clinical manifestations; I degree (slightly visible and slightly palpable), II degree (slightly visible, palpable), III degree (clearly visible and hyperkeratotic).
Treatment of keratosis
Treatment of keratosis is prescribed by a dermatologist. This is a long process that includes complex measures. Drug therapy is required to stop the growth of keratotic formations and alleviate the patient’s condition. But oral medications cannot completely cure the disease, so local therapy is also used (the use of various ointments, creams and applications containing urea).
Among the medications used are Ureatop, Ureaderm, Keratosan and Akerat. Efudex cream, Diclofenac Gel, Imiquimod and Fluorouracil are effective as topical preparations. For keratosis of the scalp, special medicated shampoos are used.
Ritenoids are also prescribed internally, which slow down the growth of keratomas. And to improve immunity, vitamins B, A and C are prescribed. For better results, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out.
Prevention
UV promotes the development of actinic keratoses by causing mutations in epidermal keratinocytes, which leads to proliferation of atypical cells. Therefore, preventive measures should be aimed at limiting exposure to solar radiation.
Recommended:
- Avoid exposure to the sun during midday hours, when UV radiation is strongest;
- sunscreens that block UVA and UVB radiation as often as possible
- use all possible methods of protection: wear hats, long-sleeved shirts, long skirts or trousers.
Recent studies that have proven the involvement of human papillomavirus in the development of actinic keratoses indicate that HPV prevention is also necessary to prevent UV-induced mutations and oncogenic transformations.
Treatment of keratosis with folk remedies
People know many remedies that alleviate the condition of a patient with keratosis. But they have only a symptomatic effect, so they can be used in combination with other therapeutic agents and only after consultation with a specialist.
The patient's condition is greatly alleviated by grated raw potatoes, which are applied to the sore spot and covered with clean gauze and polyethylene on top. Leave for 40 minutes and rinse with warm water.
Calendula, which is included in the content of many ointments, has a good keratolytic effect. It softens rough areas well and has a calming effect. Dandelion juice and chamomile decoction are effective.
Birch tar, which is sold in all pharmacies, is effective in treating keratosis. It contains more than 10 thousand useful substances that have an anti-inflammatory and healing effect. The only downside is the unpleasant smell.
Conservative therapy
The goal of drug treatment is to reduce the number of keratoses before using radical removal methods. Therapeutic agents alleviate the course of keratosis, reduce symptoms, but do not cure it completely.
To soften keratonic areas, applications of drugs with different urea contents (12-30%) are used:
- Ureaderm;
- Ureatop;
- Keratosan;
- Akerat.
Preparations for the therapeutic treatment of keratoses:
- Efudex cream;
- Fluorouracil;
- Imiquimod (Aldara);
- Diclofenac gel 3%.
Special shampoos have been developed for keratosis of the scalp. Aggressive detergents are not suitable for it.
Retinoids are prescribed for oral administration, helping to slow down the growth of formations, vitamins A, B, C. Additionally, courses of physical therapy are carried out.
How to quickly get rid of stye on the eye? We have the answer!
Find instructions for using Skinoren for acne at this address.
After clicking on the link, you can read an interesting article about preventing measles in children.
Radical treatment methods
In some cases, conservative treatment methods do not give the desired result, and the formations are removed. Radical methods are more often used for actinic keratosis, when there is a risk of plaques transforming into a malignant tumor.
Cryodestruction methods are used - freezing formations with liquid nitrogen, as well as radio wave removal, during which plaques are excised. Radical methods include electrocoagulation; the essence of the method is to cauterize problem areas with high-frequency electric current. Laser destruction is used to target the affected area.
Causes
The main cause of the formation of actinic keratoses is ultraviolet radiation. Research shows that even one episode of painful sunburn in a person during childhood increases the risk of actinic keratoses in adulthood.
On this topic
- Keratosis
Best Treatments for Keratosis
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 28, 2020
UV-B radiation (wavelength 290-320) adversely affects the DNA of keratinocytes. Causes the formation of thymidine dimer in DNA and RNA, which leads to significant cellular mutations. A major role in the formation of AKs is played by the tumor suppressor gene p53, located on chromosome 17p132, which stops the cell cycle when DNA or RNA is damaged.
Thus, dysregulation of the p53 pathway leads to uncontrolled proliferation of dysplastic keratinocytes, thereby acting as a source of neoplastic growth and the development of actinic keratoses, as well as possible carcinogenesis. Ultraviolet light absorbed by the skin enhances the production of arachidonic acid, its metabolites, and other pro-inflammatory cytokines.
UV-A radiation (wavelength 320-400 nm) penetrates deeper into the skin than UV-B and causes oxidative damage to nucleic acids, membrane lipids and cell proteins through the production of reactive oxygen species, which interrupt natural cellular and intercellular signaling pathways , causing altered proliferation.
Diet for keratosis
Nutritional adjustments are also necessary for patients with keratoses. It is worth including in your diet fruits (peaches, plums, strawberries, lemon, etc.) and vegetables (cauliflower, spinach, carrots), which contain large amounts of vitamins C and A. It is necessary to exclude spicy and fatty foods from the diet, as well as allergy-causing products.
The prognosis of keratosis depends on the complexity of the form. It is important to consult a dermatologist in a timely manner. You should not self-medicate; an illiterate approach can only aggravate the situation.
Possible complications
The main complications of keratosis include:
- development of microbial eczema;
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- degeneration of growths into a cancerous tumor;
- tooth loss.
Keratosis of the skin is fraught with serious complications, and the photo of adults shows that this pathology is a serious skin disease that requires treatment by a dermatologist and excludes self-medication.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky