Kinds
Science distinguishes between two types of disease. If a person becomes infected from an animal, then the disease is called microsporia, but if a person infected a person, then trichophytosis. Scientists have identified more than 20 types of the causative agent of lichen, which are divided into pathogenic groups (zoophilic, geophilic, atropophilic). Depending on the symptoms that characterize the disease, doctors distinguish several types of it:
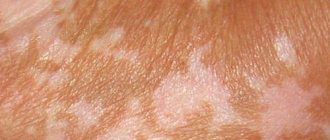
- Surface type. The spots appear on open areas of the skin and go away without complications. If the patient receives treatment, the disease disappears within 3-7 days.
- Erythematous-edematous type. Swollen, red, scaly spots appear on a person’s skin, which itch and cause discomfort. The disease is more often diagnosed in children and young women.
- Deep type. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate deep into the skin, forming spots on the legs covered with keratinized scales.
What is lichen
Feline ringworm is the general name for skin diseases. It is characterized by the presence of a small rash in the form of separate frequent nodules. The animal’s nails may also suffer and hair may fall out. Ringworm can appear in a variety of ways - infection, virus, food allergies, weakened immunity and other factors. Dogs, ferrets, and other pets can suffer from this problem.
Infection occurs through contact with an infected individual or through household items. These can be stray or wild animals, small rodents. There are cases when a cat is a carrier of lichen, but does not suffer from it.
Cat lichen is treated quite quickly and easily. Especially if you managed to see him in time. Full recovery occurs in the third week, but full recovery may take up to 6 months, depending on the severity of the disease.
The incubation period for lichen ranges from 3 days to a month. At this time, the cat is already sick, but she does not have any external symptoms.
Causes and routes of infection
Feline ringworm is considered contagious, has an infectious nature, and is caused by pathogenic microorganisms. In medicine it is called dermatophytosis, dermatophytosis or dermatomycosis.
You can become infected with lichen not only through contact with stray animals. A pathogenic microorganism can be brought home by a pet if it is walked with, or by the person himself on the soles of his shoes.
The fungus that causes lichen in humans is resistant to disinfectants and can live at home for two years. Children from three to fourteen years of age, pregnant and lactating women, and people with weak immunity are most often infected with lichen.
Transmission from animal to human
Most often, a person becomes infected with the disease after contact with a sick street animal (cat). In this case, the spores of the pathogenic microorganism that cause dermatophytosis are transferred to the pet owner and other pets living in the house.
A person can also catch lichen from a seemingly healthy domestic cat that has no symptoms of the disease. In this case, the animal is a carrier of the fungus, but does not get sick itself, since it has good immunity.
Person-to-person transmission
The disease can easily be contracted from a person who suffers from dermatophytosis. To prevent this from happening, the patient must be isolated from healthy family members and provided with personal bedding and hygiene products.
Pathogen
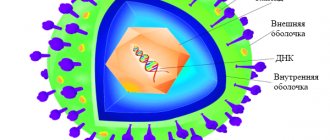
The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Microsporum canis. The structure of the pathogenic microorganism is similar to mold spores. Once on the skin of a person, cat or dog, after 4-6 hours the fungus grows into the upper layers of the dermis.
Its threads penetrate deeper and deeper into the body over time, receiving nutrition from neighboring tissues. Not only the skin is affected, but also the hair follicles and the hair itself. After a week, microorganisms begin to multiply.
Prevention measures
To prevent your cat from getting shingles, you need to take some precautions. Firstly, you should not touch unfamiliar animals on the street, because feline lichen is easily transmitted to humans. And if you have already pet the animal, you need to immediately wash your hands. Secondly, it is not recommended to neglect daily inspection of your pet for lesions. Thirdly, it is worth periodically disinfecting personal belongings, especially those with which the animal often comes into contact. Fourthly, in the autumn-spring period you need to take vitamin complexes to prevent weakening of the immune system. Fifthly, if signs of lichen are detected on the body of family members or animals, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Pets give people many positive emotions, but we should not forget about the dangers they can bring with their fur. Although lichen is not a fatal disease, it can significantly worsen the life of a cat owner and his family. Therefore, it is very important to quickly detect the disease and begin treatment.
Symptoms
Symptoms of lichen vary depending on where the elements of its manifestation are localized (on the skin or scalp). Also, the signs of microsporia depend on how deep the pathogen has entered the body.
Incubation period
The incubation period is the period of time between the moment of transmission of the fungus from a cat to a person until the manifestation of clinical symptoms of the disease.
For some people, the incubation period lasts only one week. During this period, the pathogenic microorganism has time to grow and begin to multiply. It grows so quickly that it causes inflammatory processes on the skin or scalp.
In other cases, the incubation period takes up to three weeks. If a person has a strong immune system, then the disease is expressed by weak clinical manifestations, or they are completely absent.
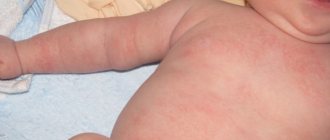
Typical signs
Typical signs of lichen in humans are as follows:
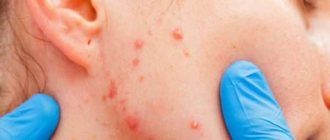
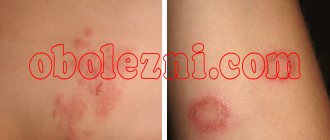
- Scaly spots with clear boundaries appear on the skin. Gradually, the neoplasms increase in size, thickenings of skin with nodules and crusts appear at the edges.
- If dermatomycosis is localized on the scalp, then round spots form in this area, and the hairs in these places break off almost at the roots. The dermis turns red, peels off, a blistering rash appears on it, and yellow crusts appear.
In addition to the above symptoms, a person may experience itching. Rashes should not be scratched, otherwise fungal spores will spread to healthy areas of the skin.
Atypical manifestations
Atypical forms of the disease are observed in people with systemic diseases. Also, atypical manifestations of lichen develop while taking certain types of medications. They can be recognized by the following signs:
- The infiltrative form is characterized by the fact that many areas with broken hairs appear on the head, which have a red tint and rise above the rest of the dermis.
- The exudative form of the disease is characterized by the fact that the neoplasms look swollen and fluid oozes from them. When they dry, they turn into a crust.
- The purulent form manifests itself in extensive inflammation of the areas of the skin where nodes appear. When pressed, pus oozes out of them.
- The seborrheic form is characterized by thinning of the hair on the head and the appearance of flaking. Foci of inflammation may be absent.
- The trichophytoid form of the disease is diagnosed by the appearance of small spots on the head on which the skin peels. The rashes have no clear boundaries, there is no inflammation.
Transmission of the disease from a cat
Treatment of lichen in humans from cats should be carried out immediately, immediately after its signs are detected and identified. The disease usually affects the hair and skin. Fungal and viral infections can present with a variety of symptoms and lead to a wide variety of consequences.
The causative agents of this infection can live for a very long time in soil, wood and even on the bedding of a pet. At first, the spores exist on their own, and subsequently infect an animal or person. The spores land on the hair and are very quickly absorbed by the skin, where they multiply at incredible speed. Soon after this, you may notice white, red or pink spots on your pet's body. Hair will fall out at the site of the lesion, and the skin around it will begin to actively peel off. Of course, such a disease significantly spoils the appearance of your furry. But this is not the main problem. When an infected animal comes into contact with a person, there is a huge risk of transmitting the disease. This is especially true for children and people with very weak immune systems.
Is cat lichen dangerous for humans?
Incorrect and untimely treatment of the disease can lead to complications, including death.
Frequent consequences of lichen are:
- blindness;
- development of tumors, including malignant ones;
- baldness;
- viral pneumonia;
- neuralgia;
- hearing impairment;
- meningitis.
Treatment of complications after microsporia is a labor-intensive and long process, so disease prevention measures should be observed and its therapy should be started on time. Contact your doctor and do not self-medicate.
Diagnostics
In addition to a visual examination, the doctor prescribes additional methods for diagnosing dermatophytosis:
- Bacteriological research. For examination, skin and hair samples are taken from the affected areas. They are studied using a microscope.
- Use of Wood's lamp. The device emits ultraviolet light, and the affected hairs glow green when used. Using the method, you can detect lichen in the early stages if only one hair is affected.
- Culture method. It is used after the examinations described above in order to determine the type of fungus and prescribe the correct treatment. Human biomaterial is placed in a nutrient medium, then the growth of pathogen colonies is observed.
How to treat feline ringworm in humans?
Modern medications allow you to get rid of the disease quite quickly, although they do not protect against its relapses and the development of a chronic form.
Taking medications
Local treatment of the disease involves the use of ointments:
- Clotrimazole;
- Ketoconazole;
- Triderm;
- Lamisil;
- Bifonazole.
The patient is also prescribed medications for oral administration (antibacterial tablets, medications containing iodine, immunomodulators, antihistamines and antiallergic drugs):
- Mycozoral;
- Claritin;
- Griseofulvin;
- Fluconazole;
- Amiksin;
- Iodinol.
The use of special shampoos (Nizoral, Sulsena) is often added to the main treatment for lichen localized on the scalp, as they contain antifungal components.
Folk remedies
Remedies made according to folk recipes should be used with caution in the treatment of microsporia after permission from the treating specialist. The most commonly used are the following:
- Propolis. Propolis tincture from the pharmacy is lubricated daily on the affected skin areas. Gradually the disease recedes.
- Tincture of calendula. Rub the product over the skin rashes at least five times a day until the spots disappear completely.
- Vinegar. Microsporia stains are smeared with apple cider vinegar several times a day. The pathogenic microorganisms that cause lichen gradually die.
- Iodine solution. The product is diluted with water in proportions 1:1. The resulting composition is used to treat the affected areas on the head or other skin.
Diet
During the treatment period, it is important to follow a diet that consists of proper nutrition. You should avoid alcoholic beverages, fast food, pickled vegetables, canned food, spicy and fried foods, and sweets.
Cat treatment
The cat is treated by a veterinarian. Therapy is complex and includes the use of the following medications:
- Vaccines (Microderm, Vakderm F). They are used at the initial stage of the disease and are administered according to the standard regimen.
- Local processing. Skin lesions are treated with antifungal drugs (Miconazole, Sanoderm), chlorhexidine or iodine solution. The wool from the treated area is pre-cut and burned.
- Tablets (Terbinafine, Itraconazole). Used if preparations for external treatment are ineffective. Medications have side effects, so they are rarely given to pregnant cats.
Therapy with folk remedies
To achieve a positive result, basic drug therapy can be combined with traditional methods of treatment.
Here are the most basic effective folk remedies:
- Iodine-vodka solution, diluted 1:1. This solution can be used to treat and treat affected areas of the skin, both on the body and on the scalp;
- It is worth taking 50 grams of peeled garlic, chop it thoroughly, pour it into a 250 ml glass jar and pour in 100 ml of medical alcohol. After the product has been infused for 24 hours, it can be used to rub the affected areas of the skin. This should be done 5-6 times a day and no less than 7-10 days. It all depends on the general condition of the skin.
After a course of treatment, a sample is taken from a person in the form of a scraping to determine the level of effectiveness of the treatment. If no bacteria were found, therapy is stopped, but a repeat analysis is performed after three months. If three tests have shown the absence of feline lichen, it can be considered cured.
Prevention of feline lichen in humans
To protect yourself from the development of microsporia, doctors recommend taking the following preventive measures:
- Vaccinate domestic cats.
- Examine the skin of your pet, adults and children living in the house.
- Regularly carry out wet cleaning using disinfectants.
- If your pet has spots on the skin, bald patches, or hair loss, contact a veterinary clinic immediately.
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene, wash your hands after going outside or contacting animals.
- Try to avoid contact with street cats and dogs.
Treatment at home
When figuring out how to treat lichen in a cat, and how long the infection is treated, you need to take into account the type and form of the disease.
After the diagnosis is made, restorative therapy begins, during which the affected skin is treated with antifungal ointments. The pet is prescribed the correct diet for the duration of treatment and is isolated from other animals or people. The animal is also regularly checked for symptoms of other diseases.
If lichen develops into a complex form, it is necessary to use not only local treatment methods, but also oral medications. If the pet has thick and long fur, it is cut off. But when performing this procedure, it is important to exercise extreme caution to prevent the infection from spreading throughout the body. Before this, the instrument is thoroughly sterilized.
Feline lichen in a child
The disease is often diagnosed in children aged 3 to 8 years. A child can pick up a fungus in a sandbox or by interacting with an outdoor cat.
If you see rashes and spots on your child’s skin, you should visit a dermatologist. Recovery will come faster if the baby does not have contact with a sick animal.
During the treatment period, the child’s skin should not be subjected to water procedures (except for a shower) or washed with washcloths. There should be no sources of allergens in the patient’s room, that is, soft toys, carpets. You need to wet clean the room every day.
Features of the disease in cats
Features of the disease in cats
Among pets, young individuals with long hair are most often susceptible to developing lichen. The causative agent of the disease is a fungal infection. It gets on the cat's fur and can lie dormant there until favorable conditions arise. A history of skin or other diseases increases the risk of developing lichen in cats. The main reasons for the development of the disease in kittens:
- eating disorders;
- low animal immunity;
- malignant formations;
- treating your pet with immunosuppressive drugs.
It is very simple to determine the presence of a disease in a cat: rounded bald patches appear on the fur, the skin looks inflamed, and the animal is constantly itching.
There are several forms of feline lichen: ringworm, pink, red, weeping, pityriasis versicolor. Of these, several species can be transmitted to humans, but the ringworm is the most dangerous.
Feline ringworm during pregnancy and lactation
Treatment of microsporia in pregnant women should be started as soon as possible. This will avoid consequences for the unborn child. Therapy during pregnancy consists of treating the skin with iodine solution or salicylic ointment; washing hair with special shampoos is allowed. Taking antibacterial drugs is highly undesirable.
To avoid contracting shingles, a pregnant woman needs to regularly wash her hands, take vitamins and eat healthy foods to strengthen the body's defenses.