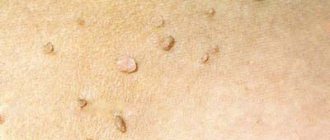
Papillomas are benign formations that grow on the skin or on the genitals (the inner labia minora of the vagina in women) and look like small nipples. The size of the growth can be about 1-2 centimeters.
Most often, the virus affects the mouth, nose, throat, vocal cords, bladder, and genitals in men and women.
- Review of medications for papillomas
Causes of growths on the genitals
Papilloma is a warty, benign formation that develops from epithelial cells. Its appearance is associated with the development of papillomatosis, i.e., an infectious disease caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
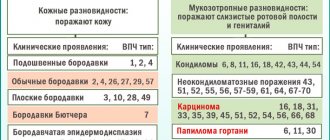
Depending on the strain of the virus, its oncogenicity is high and low, which represents the main danger of the pathology.
The disease affects people of both sexes almost equally, with the intimate area being one of the most vulnerable places. In men, papillomas are found on the penis and on the skin of the scrotum.
For women, localization is typical on the labia minora and majora, in the vaginal cavity, on the surface of the cervix. Representatives of both sexes often suffer from the appearance of anal formations.
Infection most often occurs through sexual contact with an infected partner, and even using a condom does not always help.
The virus is present in almost all biological fluids, which creates the risk of transmitting HPV through contact, when wearing someone else's underwear, in a bathhouse or swimming pool. A child can become infected in the womb or during childbirth.
Important! HPV, having penetrated the human body, remains so forever, and so far there is no means to destroy it. Only its manifestations in the form of papilloma are removed.
The immune system in a normal state is able to effectively resist the virus, driving it into a latent state for a long time. Activation of HPV, leading to the growth of papilloma, occurs when favorable conditions appear. The following provoking factors can be identified:
- deterioration of immune defense, immunodeficiency;
- intoxication of the body;
- hormonal imbalance;
- prolonged and frequent physical overload;
- stress and nervous overload;
- poor environment, harmful emissions in production;
- uncontrolled use of certain drugs (cytostatics, immunosuppressants, antibiotics).
In women, the risk of papilloma increases significantly during pregnancy. In addition, they can occur when taking oral contraceptives, vaginal rings and spirals.
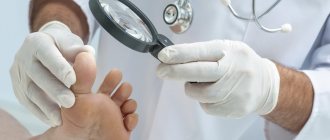
Diagnostics
To get help, just contact a gynecologist, then the doctor will refer you to other specialists for examination. The doctor will examine the affected areas using a microscope (colposcopy), and then tell you how to get rid of papillomas on the labia. Sometimes the following procedures are prescribed:
- treating warts with a special solution that will whiten the sore spots;
- collection of biological material for histology and cytology, they determine the type of HPV and also help identify cancer cells;
- collection of secretions from the genital tract, necessary to confirm or refute sexually transmitted pathologies.
Be sure to write out a referral for PCR to determine the DNA of papilloma and select the most suitable drug. Most often, a woman needs to undergo microflora smears to rule out STDs. According to statistics, 90% of patients with papillomas suffer from sexually transmitted diseases. Sometimes a specialist advises consulting with an endocrinologist and taking the necessary tests for hormones.
As for the timing of receiving survey results, they will be ready either immediately or in a few days. After colposcopy, the gynecologist can immediately make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. After treating the mucous membranes with the solution, you must wait about fifteen minutes for the product to take effect. Cytological examination lasts from one to three days, however, in emergency cases, testing is carried out using the express method. Histology will be ready in 3–5 days.
Currently, many pharmacies offer rapid tests for home testing. The results are not always accurate (more than 80% of patients respond negatively to the products), so they cannot be completely trusted. Only laboratory testing can detect the disease even at an early stage.
Which doctor should I contact?
It is not difficult to identify the presence of papilloma in an intimate place due to their characteristic appearance. In women, the primary diagnosis is made by a gynecologist during a routine examination or targeted treatment. A man should consult a dermatologist.
When developing a treatment regimen, specialists such as an immunologist and an infectious disease specialist are usually involved. A consultation with a surgeon will be required to prescribe surgical treatment. Important! You should not self-medicate.
This can lead to dangerous complications. All medical procedures, including the use of herbal medicine, should be agreed with a doctor.
How to get rid of tumors using the hardware method?
Treatment of papilloma is based on their removal or destruction. The following hardware methods of influence are recognized as one of the most effective:
- Cryogenic destruction . It is achieved by quick and deep freezing of the affected area using liquid nitrogen. The technology has been used for a long time and is well developed. This method can only be used on the external parts of the organs (penis, labia). It is impossible to remove formations on the vaginal mucosa or cervix. Tissue restoration occurs within 12–15 days.
- Radio wave surgery . A directed radio frequency wave becomes a kind of thin scalpel (“radio knife”), which is capable of influencing tissue with great precision. The most famous source of such radiation is the Surgitron generator. The radioknife excises only the formation without affecting healthy tissue. The impact site heals within a few days, with no side effects detected.
- Electrical coagulation . Electrical destruction of papilloma is ensured by burning them out by exposure to high frequency current (“electronic knife”). After such exposure, all excised vessels are glued together, which stops bleeding. After the operation, only a small scar remains, which resolves over time. This method is considered safe and can even be prescribed to pregnant women.
- Laser surgery . This is one of the most modern and effective ways to remove papilloma. A laser beam is capable of destroying the formation of any germination depth and any location. Postoperative scarring does not occur, and the tissues heal very quickly. The only drawback is that the necessary equipment is available only in specialized clinics.
How does laser removal of tumors in intimate places work?
- The papilloma is anesthetized through infiltration anesthesia, i.e. an anesthetic injection is given.
- The area is treated with an antiseptic solution.
- Next, they begin to directly remove the papilloma in an intimate place. To do this, it is treated along the entire perimeter with laser radiation. The neoplasm tissues evaporate layer by layer, and a dry crust remains in their place.
- After the procedure, the patient can go home immediately.
- Surgical exposure . Traditional excision of the formation with a scalpel is the most traumatic and requires a longer recovery period. Scars remain at the site of exposure for a long time.
The choice of surgical treatment method depends on the advanced stage of the disease, the size of the formation and its location. When operating on the cervix or cervical canal, there should be no scars that could disrupt female reproductive functions.
The technology is selected by the doctor based on the results of diagnostic examinations, oncogenicity and the capabilities of the medical institution.
Removal of papillomas in intimate places
Papillomas that are localized in intimate areas must be removed. Even if they do not cause discomfort, do not violate the quality of life, or interfere with the performance of natural life processes. This is due to the potential danger of the transformation of the form of these neoplasms from benign to malignant.
How to remove papillomas, is it necessary, how painful is it during the procedure, is it worth doing this at all - a highly specialized specialist (urologist, gynecologist, proctologist) can tell you about all this. The features of papillomas removal will largely depend on where they are located, what type they are and how old they are. There are many ways to remove tumors of this type, so patients have the opportunity to choose one method or another if they have the appropriate doctor’s recommendation:
- Laser technology. In this case, special laser equipment is used, which, under the supervision of a specialist, forms a thin laser beam that acts directly on the papilloma and burns it to the base. Immediate death of all cells of the neoplasm occurs as a result of laser cauterization, due to which it disappears on its own after a few days. You can find out how the laser therapy procedure will take place and what its advantages are with a specialist during a consultation or in this article.
- Cryodestruction (treatment with liquid nitrogen). The tumor is completely frozen, as a result of which the papilloma cells begin to gradually die, and within a week the growth disappears on its own. Excellent technology that allows you to prevent the occurrence of new growth in the treated area in the future. The method is not used if papillomas are localized in the mucous membrane area (the use of liquid nitrogen to freeze mucous membrane tissue is prohibited).
- Radio wave technology. A relatively new method, which is characterized by high efficiency and speed of the procedure. It is especially suitable if the papillomas are localized in different intimate places - there are practically no restrictions on the use of the technology (this is the main way the method differs from laser and cryodestruction).
- Surgical surgical treatment. This approach is always used in cases where there is a certain risk that a benign papilloma may develop into a malignant neoplasm. The procedure is traditional, after it small scars or scars will remain on the skin, but the likelihood that the oncological process will be stopped is quite high.
Questions and answers
Is it painful to remove formations in the intimate area?
No, it doesn’t hurt, since the removal takes place under infiltration anesthesia and the patient does not feel anything at all.
How long does it take to remove formations in the intimate area?
Depending on the type of formation and their quantity. For example, 5-10 kandillomas on the mucous membrane of the intimate area are removed in 3-4 minutes, taking into account the administration of anesthesia.
Is it possible not to remove formations in the intimate area?
No, they need to be removed, since formations in the intimate zone tend to grow in quantity and size.
Types of acne on the genitals
There are primary elements that appear on unchanged skin or mucous membranes and secondary elements that develop from primary rashes.
Most acne on the labia is primary.
They are divided into cavity-free and cavity-bearing.
Primary rash:
- Spot. They are vascular formations of an inflammatory nature no more than one centimeter in diameter - roseola, up to 5 cm - erythema. For example: syphilitic roseola, erythema - with dermatitis. Secondary spots – pigment spot, scales.
- A blister is an element that rises above the surface of the skin. Elements form quickly and disappear just as quickly. Blisters can form due to toxicoderma, insect bites, and urticaria. Formed itchy pimples are often pink or whitish in the center, in some cases accompanied by a burning sensation.
- Papules are elements that rise above the skin and do not have a cavity. They can vary in size, depth of lesion, inflamed or non-inflamed. The formation can transform into pigment spots, scales, cracks, and fissures. Sometimes papules merge to form plaques.
- The tubercle is a cavityless element of a dense structure, up to 1 cm in size. Instead of it, scar tissue is subsequently formed. In some cases, it may leave crusts, scales, growths, and ulcers. In case of syphilis, leprosy, leishmaniasis, skin tuberculosis, the element is located at a sufficient depth of the skin or mucous membrane.
- Knot. This is a cavity-free formation rising above the skin, ranging in size from 1 to 10 cm in diameter. The formation forms inside the skin. An inflamed internal pimple (syphilitic gumma) on the mucous membrane of the labia can appear during the tertiary stage of syphilis. A non-inflamed pimple-pimple inside the labia is formed as a result of deposition of metabolic products or, as a result, degeneration into lymphoma.
- Vesicle. It is a single or multi-chamber bubble, up to 5 mm in size, equipped with a tire. With genital herpes, watery rashes have serous content. Pimples can also be bloody. After opening the elements, weeping erosions remain, in place of which pigment spots subsequently form. After some time they disappear.
- Bulla, bubble. Unlike blisters, a bulla is a huge pimple. After the elements resolve, scars, age spots, crusts, scales, and erosions sometimes form.
- Pustules or pustules. Such formations are equipped with a cavity containing pus. They can be follicular - formed in the hair follicle and develop when infected with staphylococcus, appearing on the genitals as yellow elements, as well as non-follicular - provoked by streptococcal infection. After opening, a purulent pimple leaves ulcers, scars, spots, and crusts.
- Painful pimple. Soreness is typical for subcutaneous elements.
Types of secondary formations:
- scales. They are a loose stratum corneum of cells in the form of a plate;
- crusts - the contents of pimples after drying;
- cracks - their occurrence is associated with a violation of the elasticity of the skin;
- abrasion - occurs as a result of mechanical trauma to the surface layer of the skin;
- erosion – remains after opening of the cavity elements;
- ulcer – is a deep skin defect;
- scar or scar - formed during skin regeneration with the formation of connective tissue;
- hypo- and hyperpigmentation – lightening or staining of the damaged area of the skin;
- vegetation - the process of growth of a skin area at the site of localization of the inflamed element;
- lichenification - compaction, dryness, thickening, discoloration, deepening of the skin pattern.
Medical removal
Papillomas in the intimate area can be removed using medications. They have different mechanisms of action, but all are aimed at reducing the activity of the virus and destroying the formation. The following drugs are most effective:
- Kondilin . It is based on podophyllotoxin, a plant alkoid. This active substance blocks the transport of intracellular nucleotides, which leads to necrosis of the affected epithelial cells and destruction of the papilloma. The drug is available in the form of a 0.5% alcohol solution. They treat the formation for 4 days (2 times a day), and the daily dose is no more than 0.5 ml. The real result appears after 2 days of treatment.
- Solcoderm . The basis of the product is 70% nitric acid. In addition, the composition includes oxalic, acetic and lactic acid, copper nitrate. By treating papilloma, its acid burning is achieved (devitalization and mummification of tissue). The scab formation disappears within 5–10 days. The drug is used once, and the treated area should not exceed 4 sq. cm. Re-use is allowed after 8–10 days. When treating papilloma, extreme care must be taken, applying the composition pointwise, without cauterizing healthy tissue.
- Fluorouracil . This drug is a potent agent used in the fight against malignant tumors. Ointment with 5% fluorouracil is recommended for removing papilloma. This active substance inhibits cell division by blocking DNA synthesis. For papillomatosis, the ointment is used daily for 7 days.
- Imiquimod . When treating papilloma, a 5% cream is used. It is an effective immunomodulator. The drug does not directly affect HPV, but by helping to induce interferon and cytokines, it helps the body fight the infection. The course of treatment is 4 months, during which the cream is applied once every 2 days.
In addition to the most common medications listed, the doctor may prescribe Papilite. Imitation of cryogenic destruction is provided by such means as Cryopharma, Wartner.
A decrease in viral activity is achieved by subcutaneous injection of Allokin-Alpha. A positive result is observed with long-term use of oxolinic ointment.
Papilloma in the intestines: symptoms of the disease
Have you been fighting PAPILLOMAS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of papillomas by taking every day...
Read more "
In most cases, papillomas develop on human skin. They appear on the hands, neck, face, and grow in the genital area. However, in some cases, the development of the disease can occur inside the human body, including growths found in the rectum. Such papillomatosis is difficult to diagnose, but at the same time it poses a very real threat to human health.
Neoplasms in the intestines and their danger
All papillomas are of a viral nature - epithelial growths are provoked by the human papillomavirus. This distinguishes them from other neoplasms that occur on the skin and mucous membranes.
Papillomatosis of the rectum is manifested by growths of different types. The most common among them are:
- Flat.
- Pointed.
- Growths on the leg.
80% of cases of papillomatosis are diagnosed near the anus; elongated formations can even fall out. The disease manifests itself as single growths and groups of papillomas.
Neoplasms caused by HPV are considered benign. However, there are types of papillomavirus that provoke the degeneration of tissue into malignant ones. Unfortunately, it is in the intestines that oncogenic types are more common - 16, 18, 35, 45, 51. Therefore, the disease requires mandatory treatment.
Causes of papillomatosis
The main cause of the development of rectal papillomatosis is a virus - only infected people face this problem. However, not all carriers of the infection manifest it as a disease, especially with formations in the intestines. In almost 90% of people, HPV is successfully controlled by immune cells.
Doctors include the following factors that provoke the disease:
- General deterioration of immunity due to poor nutrition and bad habits.
- Frequent acute respiratory infections, prolonged illnesses, long-term (more than 2 months) treatment.
- Diseases associated with the immune system - immunodeficiencies, autoimmune diseases.
In addition, the condition of the intestinal mucosa also plays an important role. Microtraumas, an inflammatory process affecting the rectum, make it easier for the virus to become active in these areas. According to statistics, every third patient with diagnosed papillomatosis had inflammatory processes before the onset of the disease.
Papillomas occur in people suffering from irritable bowel syndrome, dysbiosis, severe poisoning or bacterial intestinal infections. The patient’s diet is also important - an abundance of fatty and protein foods (meat, lard, smoked meats), alcohol, spicy and fried foods provoke irritation of the rectal mucosa.
Doctors note that the localization of papillomas near the anus and the entrance to the large intestine is associated with sexual transmission of infection. Unconventional sex with an infected sexual partner provokes the growth of tumors in this area. Papillomas in the intestines are diagnosed in patients with viral lesions of the intimate area, groin, labia and penis.
Symptoms of papillomatosis
All forms of papillomatosis are characterized by a latent course of the disease - the growths do not hurt, do not itch, or cause other discomfort. Papillomas on the body are most often discovered by chance; even small tumors on the skin may not be noticed by the patient for several years. Therefore, papillomatosis on internal organs may not be diagnosed for a long time, grow and even degenerate into malignant neoplasms. Proctologists note that many patients seek help already at the stage of cancer, with a disease that has been progressing unnoticed by the patient for 10-15 years.
If papilloma in the intestines manifests symptoms, then a person notices the following signs of the disease:
A folk recipe will get rid of papillomas. Take the simplest...
This is what our grandmothers did. The warts will go away in 10 days. Just take...
- Constipation, stool disorders.
- Feeling of discomfort, foreign body in the anal area.
- Pain after defecation.
- Excess moisture near the anus.
- Rectal bleeding (occurs after defecation).
- Blood in stool. Sometimes it can be detected by a change in the color of the stool - it becomes darker, scarlet inclusions may be observed. But it is not always possible to detect blood visually; tests are performed to confirm the symptom.
Bleeding and blood in the stool may indicate damage to the papilloma or be a symptom of a complication of papillomatosis - rectal cancer.
Despite the fact that the listed signs are also characteristic of other proctological diseases, in particular hemorrhoids, they cannot be ignored. Doctors have confirmed that papillomatosis can go away without treatment - after the body’s immune defense becomes better, the tumors disappear. But this applies to growths that appear on the skin, small in size and not prone to growth. If papillomas are found in the rectum, treatment must be completed.
Diagnosis of the disease and examination of the intestines
The gold standard for diagnosing any neoplasm in the large intestine is colonoscopy. The examination is carried out using a special flexible tube with a video camera at the end, which is inserted through the anus. The doctor sees the mucous membranes on the monitor (the image is enlarged), so he can easily notice any changes on the surface of the rectum.
To clarify the results of colonoscopy, if necessary, the patient is recommended to undergo additional diagnostics:
- Ultrasound.
- X-ray.
- CT and MRI.
- Stool analysis (hidden blood is detected).
- Blood test for tumor markers.
Colonoscopy is a screening examination, which means that all people need to undergo it, regardless of the presence or absence of symptoms of the disease. Diagnostics is recommended primarily for people over 50 years of age. You need to undergo it every 5 years if the previous examination did not reveal any pathologies of the mucous membrane. If, during the examination, polyps or papillomas were found, the person is immediately prescribed treatment. After recovery, he must undergo preventive examinations annually to prevent recurrence of the disease.
Traditional methods
Herbal folk remedies can help in the fight against pathology. The greatest effect is achieved by combining herbal medicine with antiviral medications. Folk remedies based on the following medicinal plants are especially popular:
- Celandine . The burning ability of the juice of this plant is used in such a pharmaceutical product as the drug SuperClandestine. Self-squeezed, concentrated juice should be used carefully, avoiding burns to adjacent tissues. Its application is ensured pointwise.
- Kalanchoe . When treating external formations, a plant leaf or a swab soaked in its juice is applied to the affected area. Internal papillomas are lubricated with juice. The treatment is long-term – it may take 1.5–2 months before real results are obtained.
- Aloe . This plant is used similarly to Kalanchoe.
You can supplement drug therapy by taking the following folk remedies:
- Melissa infusion . It is prepared by infusing plant leaves in boiling water, with plant materials and water taken in equal proportions. During the day, drink 3 tablespoons of infusion.
- Sage infusion . The herb (1 tablespoon) is infused in boiling water (500 ml). Drink 1 tablespoon every 3-4 hours.
- St. John's wort decoction . It is prepared at the rate of 10 g of raw material per 200 ml of water. Drink 100 ml before each meal.
- Plantain infusion . The proportions are similar to the previous product. Use 4–5 times a day, 1 tablespoon.
Garlic, which has cauterizing properties, is widely used in folk medicine. With long-term treatment, castor oil shows good results.
You can treat the affected areas with fir oil or tea tree oil.
You can cauterize the formations with ammonia and hydrogen peroxide, but they must be used with great caution.
Consequences of the disease
Some people are overcome by doubt whether it is necessary to treat papillomas at all. After all, they do not hurt, and in intimate places they are invisible. This must be answered clearly and unambiguously - they need to be treated to avoid serious consequences.
Firstly, the presence of papilloma on the genitals is fraught with mechanical damage when putting on underwear, sexual contact, etc.
Small, bleeding wounds appear, which become a favorable environment for various infections. Secondly, the virus in its active state is highly contagious. During sex, the likelihood of infection is very high, which means you should not put your partner at risk.
The most dangerous phenomenon is a tendency to malignancy. Of course, not all HPV strains are oncogenic, but the possibility of transformation of a benign tumor into oncology exists.
In men, this phenomenon is practically undetectable, but in women, it is quite possible to provoke vaginal or cervical cancer. A sick woman poses a huge danger to her child.
Symptomatic manifestations
The incubation period of a viral infection with HPV ranges from several weeks to several years. Everything is determined by the strength of the immune system. Anogenital warts occur most often in the groin and perineum.
In women, genital papillomas occur on the labia, vagina, clitoris, cervix, external opening of the urethra and even on the hymen, perineum, their color is flesh-colored or light brown, on the labia they are covered with a stratum corneum.
In men - on any part of the penis: head, frenulum, shaft, scrotum, foreskin. There are usually no symptoms. When papillomas grow in these places, women often experience constant sensations of moisture in the intimate area (due to humidity, a persistent foul odor appears), an increase in vaginal discharge, itching, and general discomfort - but these are indirect signs that may not exist.
Cervical condylomas have no symptoms and are detected only during examination by a gynecologist. They can be determined by treating the area with 5% vinegar. After or during sex, you may experience some spotting. In men, papillomas on the shaft of the penis and scrotum are also covered with a stratum corneum and are called keratotic. When immunity decreases, the rashes merge into plaques.
Some types of HPV in men can cause Bowen's disease, which is manifested by the appearance of a red, velvety plaque on the penis. This pathology is more common on the scalp. First, a dark spot with jagged edges appears, then it transforms into a scaly plaque with raised edges. May be single or multiple. It is dangerous due to its degeneration into squamous cell carcinoma.
Bowenoid papulosis is caused by HPV types 16, 18, . It is considered a precancerous skin condition. The head of the penis is covered with plaques of different colors: pink, yellowish and white, most often red. They are smooth and doughy in consistency. Unpleasant sensations from papillomas in an intimate place can be expressed in itching, burning and pain.
Prevention
It is much easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. HPV is not excreted from the human body, and therefore it is very important to avoid infection. First of all, casual sex and a large number of sexual partners should be avoided.
If the virus does get inside, then it is necessary to take all measures to increase immunity and eliminate provoking factors.
A healthy lifestyle will help with this - giving up bad habits, optimal nutrition, combining activity with proper rest.
Diseases, especially those related to the genitourinary system, must be treated promptly and adequately. Taking vitamin complexes will help strengthen the immune system.