Nowadays you can meet many people with dark warts on the face or hands - keratomas. It looks unpleasant and ugly. But many people forget that this is a disease that needs to be treated and cannot be neglected.
What is a keratoma? A keratoma is a benign formation on the human skin. It looks like a large convex mole of light yellow color.
Unlike actinic keratosis , with which it should not be confused, seborrheic keratosis does not develop into a malignant pathology.
The tumor can be multiple or single. If left untreated, it can become malignant or develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
There are several types of this education. The most common types of keratomas found in people are senile (senile) and seborrheic keratomas.
- Senile (senile) keratoma appears after 30 years. Most often, senile keratomas appear on the face, neck, on the back of the arms, and much less often on the chest, abdomen, back, forearms and legs.
They look like moles of white or gray-yellow color. They increase in size gradually, and sometimes inflammation may begin. These are one of the most benign skin formations.
- Seborrheic keratoma of the skin is the most dangerous of all. Seborrheic keratoma is localized on the scalp, arms, legs, neck and face, most often on the nose.
In most cases, this type of keratoma is multiple. At first it appears as a brown or yellow speck, then it quickly grows, becomes rough, darkens, and noticeable cracks appear. Quite often, its appearance and growth is accompanied by pain, itching and bleeding.
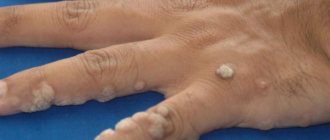
There are also types of keratomas called senile (senile) warts (also sometimes called age-related keratomas), and seborrheic warts.
The first appears after 50 years and exclusively in the eye area. It looks like a flat or slightly protruding formation with clear contours. Color - from gray-yellow to brown .
Papules can be of different sizes, depending on the subject and depending on the area affected by the keratosis: in general, there are spots with a diameter of 1 millimeter to 1 centimeter, but there have been cases where the papules were even larger.
Malignancy occurs extremely rarely. A wart grows very slowly and usually only interferes with its appearance. Seborrheic wart is another name for seborrheic keratoma.
The first appears after 50 years and exclusively in the eye area. It looks like a flat or slightly protruding formation with clear contours.
Color - from gray-yellow to brown. Malignancy occurs extremely rarely. A wart grows very slowly and usually only interferes with its appearance. Seborrheic wart is another name for seborrheic keratoma.
About seborrheic keratosis of the skin
Seborrheic keratosis is a disease that causes the appearance of special tumors on the skin. Considering that the disease most often develops in people much older than 40 years of age, these formations are called senile warts (another term is seborrheic keratomas)
Keratoses are a group of skin diseases, the common symptom of which is excessive thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. One of the common types of keratosis is seborrheic keratosis, which develops after 30 years, but is especially common among people 40 years of age or older, and therefore it also received such names as senile keratosis, senile keratosis, senile warts. Tumors do not disappear on their own. Over the years they change their color, shape and outline. The disease can last and progress for decades.
- ICD 10 code: L82.
Causes
Keratomas are benign skin formations that can be in the form of single or multiple elements and in rare cases degenerate into cancer. The causes of seborrheic keratosis have not been fully established.
Assumptions about viral etiology and the negative effects of solar radiation on the skin as a provoking factor have not found convincing evidence. Theories about the predisposition to the disease of people with oily seborrhea, about the occurrence of the disease in people whose diet contains insufficient amounts of vitamins, vegetable oils and excess animal fat are also unreliable.
Doctors suggest that the following factors may contribute to the appearance of seborrheic keratoses:
- age-related changes in skin structure (after 50 years);
- genetic predisposition (the chance of growths appearing in blood relatives is much higher);
- frequent microdamage to the skin surface (for example, chafing, peeling, calluses, tight clothing); regular and prolonged exposure to sunlight;
- exposure to chemicals (acids, alkalis, detergents, deodorants, fresheners, toilet water, work in a chemical laboratory, factories);
- chronic diseases of the endocrine system; immunodeficiency;
- poor monotonous diet, lack of vitamins and minerals;
- taking hormonal medications, including contraceptives;
- pregnancy period.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of keratosis in old age, it is necessary to adhere to preventive rules from youth:
- Sunbathe properly using a cream with a good level of ultraviolet protection. Go to the beach no earlier than ten in the morning or later than four in the evening.
- Avoid vitamin deficiency by eating vitamin-rich vegetables and fruits, and take vitamin complexes in winter.
- Eat properly. Animal fats contribute to the development of keratoses and increase cholesterol.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, which will help boost immunity and regulate metabolic processes.
- Protect yourself from stressful situations.
- Get enough time to sleep.
If even light and small spots appear on the surface of the skin, it is necessary to see a dermatologist, since untreated disease is a prerequisite for the development of cancer.
Classification
The choice of treatment tactics for seborrheic keratosis is directly dictated by the stage of progression of the disease. Thus, the following stages of occurrence are distinguished, slowly replacing each other:
| spot | this is the initial degree, in which, apart from yellowish-brown spots, no other clinical manifestations are observed. Often, treatment of the disease at this stage is not carried out, since the disease does not cause discomfort to the patient. In the vast majority of cases, the first spots begin to form between the ages of fifty and sixty. |
| papular form | the affected area of the skin begins to change color, and a nodule or papule rises above its surface. Neoplasms may differ in volume and number |
| keratotic form | formation of a senile wart or keratoma is observed. If you accidentally damage the tumor, slight bleeding will begin. |
| keratinization | in this case, the formation of a cutaneous horn occurs. Most often, it is at this stage of the course that patients seek qualified help from a dermatologist. |
Etiology
Previously, it was believed that the disease was one of the symptoms of the human papillomavirus or occurred due to prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. However, after lengthy clinical studies, specialists in the field of dermatology decided that such theories are not relevant to seborrheic keratosis, in particular because the pathology in the vast majority of cases is diagnosed in people over forty years of age.
Nevertheless, the following are considered to be predisposing sources:
- repeated mechanical damage to the skin;
- chemical influence of aerosols;
- the occurrence of chronic diseases of the endocrine system in humans;
- a wide range of autoimmune processes;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications, in particular hormonal substances containing estrogen.
It is generally accepted that genetic predisposition plays an important role in the development of this disease. Diagnosing this type of seborrhea in one of your close relatives increases the risk of developing a similar pathology in descendants by approximately 40%.
Symptoms of seborrheic keratosis + photos
The main symptoms of seborrheic keratosis are single or multiple elements, localized mainly on the back and front surface of the chest, less often on the scalp, neck, face, dorsum of the hand, back of the forearm, and in the area of the external genitalia. Very rarely, keratomas appear on the palms and plantar surfaces of the feet. Tumors often have a round or oval shape with a diameter of 2 mm to 6 cm, clear boundaries and rise above the surface of the skin, often accompanied by itching.
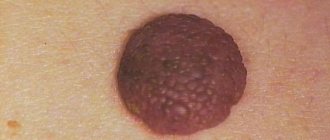
The color of the new growths can be pink, yellow, dark cherry, dark brown, black. The surface structure is often similar to many small flaky warts, covered with a thin, easily removable crust that bleeds with minor mechanical damage. Over time, black dotted inclusions appear in it, it gradually thickens, reaching 1-2 cm, and becomes covered with a network of cracks.
Although the entire formation has a soft consistency, the crust becomes denser, the edges acquire irregular, sometimes jagged outlines. Sometimes the keratomas become pointed or convex in the form of a 1 mm dome with a smooth surface and with black or whitish grains of keratin.
It is also worth noting the signs that require you to seek medical help from a dermatologist. These include:
- severe discomfort caused by papules or nodules - while the neoplasms begin to interfere with normal daily activities;
- severe bleeding;
- attachment of the inflammatory process;
- significant growth - the volume of spots or nodes changes upward every day, which is noticeable even to the naked eye;
- localization of the formation in a visible place, which causes not only physical, but also emotional discomfort;
- multiple keratomas, the number of which is constantly increasing; attachment of pain.