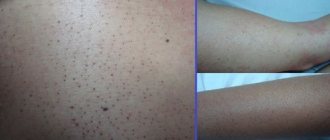
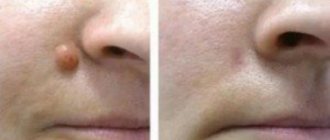
Signs of fulminant acne
Multiple conglobate acne is a problem that most often occurs between the ages of 20 and 40 years, but can occur at an older age or be a continuation of juvenile acne. Both sexes are susceptible to the disease, but men are more often affected. This form of acne is in most cases combined with seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis.
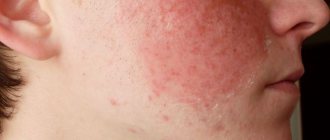
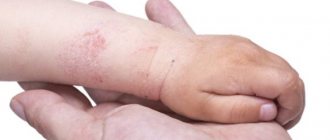
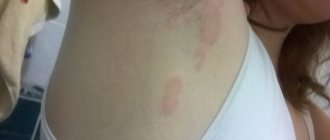
The predominant location of conglobate acne is the back and neck; the skin of the face can also be affected. Less commonly, nodes appear on the chest and abdomen. Acne does not form only on the soles of the feet and palms.
Conglobate elements are either comedones grouped in a specific area or cystic nodular formations. This property of uniting into groups, piling up on each other, gave it another name - piled up.
Acne conglobata is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the presence of an inflammatory process;
- constant and intense pain;
- feeling of skin tightness;
- large sizes (from 2 to 10 mm);
- inactivity of the skin in the affected areas;
- globular acne protrudes noticeably above the surface;
- the skin is uneven, dense, purple-blue in color.
At the first stage of occurrence, a dense subcutaneous node is formed. As it develops, an accumulation of infiltrate (pus) occurs inside the element. The pimple rises above the surface, it opens and the thick, creamy contents come out. The pain decreases and the healing process begins, which ends with the formation of a scar. The scarring process occurs because in the cavity left by the acne, adipose tissue and collagen fibers are destroyed and their place is taken by harder connective tissue. Scars can form either superficial or deep. Initially they are red in color, but gradually become whitish. Very often they resemble bridges, as they tend to move from one area of the skin to another. With a disease that has become chronic, one area may have infiltrated elements, opened acne and scarring changes. The peculiarity of scars after conglobate acne is that they cannot be completely corrected. Attempting to correct the defect with surgery may result in even more scarring of the skin.
How to get rid of acne on your face at home
Tip 1 How to get rid of closed comedones Tip 2 How to remove comedones Tip 3 How to get rid of comedones at home
How to get rid of acne on the face? This is a question that 9 out of 10 people have asked and are asking in their lives. Acne is reported in 85% of adolescents and 20% of adults. They appear on the face, back and chest. Half of all women experience acne on their faces regularly. Acne appears in a person up to the age of 50.
Acne is located on the skin of the face, chest and back - in areas where the largest number of sebaceous glands are located. The disease can be mild (open comedones), moderate in severity (closed comedones and papules), and severe (pustules).
Acne is a serious disease. Only a doctor knows how to get rid of acne on the face, back and chest. However, you can do a lot yourself at home.
Conducting a clinical and laboratory examination of the patient, finding out the causes of acne and identifying risk factors is the responsibility of the doctor before starting treatment.
Treating acne on the face, chest and back is not an easy task. As soon as acne appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will help you understand the causes of the disease. Perhaps, along with external therapy, the doctor will recommend general therapy, hyposensitizing, detoxification and vitamin therapy. A mandatory component of complex treatment is a balanced and rational diet.
- Sexually transmitted infections, polycystic ovary syndrome, gastritis, which is caused by Heliobacter, are often combined with early forms of acne.
- Uterine fibroids, mastopathy, pelvic inflammatory diseases, recurrent candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis and other diseases caused by hormonal dysfunction are often combined with late forms of acne.
Drug treatment for acne must be adequate and consistent.
External therapy is prescribed for mild to moderate acne. It is intended to use creams, gels, ointments and lotions containing substances that:
- prevent the formation of comedones or destroy them,
- reduce sebum production,
- prevent the development of inflammation.
General therapy is prescribed when local therapy is ineffective and severe acne and involves the use of:
- antibiotics,
- synthetic derivatives of vitamin A (isotretinoin),
- specific immunotherapy drugs,
- antiandrogens.
Limiting the intake of easily digestible carbohydrates, the amount of animal fats, extractives and table salt are the basic principles of dietary nutrition in the treatment of acne.
Causes
It is difficult to single out one cause of conglobate acne. Most often, its appearance is associated with the following factors:
- Frequent stressful situations and nervous tension, of course, are not the root cause of acne, but have a powerful effect on the level of hormones in the body;
- hormonal imbalance (excessive production or activity of male sex hormones, dysfunction of the ovaries) affects both the size of the sebaceous glands and the amount of sebum they produce and its composition; diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, pancreatitis, dysbiosis);
- weak immunity due to which the body is unable to overcome pathogenic microflora that has penetrated the sebaceous ducts;
- any infectious diseases that weaken the immune system;
- genetic predisposition in men (the influence of an additional Y chromosome is noted);
- long-term use of hormonal and anti-tuberculosis medications.
Conglobate elements are formed where the sebaceous glands are located and their primary cause is hypersecretion of sebum and hyperkeratosis. The sebaceous secretion does not have time to reach the surface, where it performs protective functions and prevents drying of the skin, but thickens and clogs the ducts. An airless environment is formed, which is optimal for the life of acne bacteria that live on the surface of the human skin. The result of the invasion of bacteria and their proliferation is the onset of an inflammatory process, which affects not only the epidermis, but also the deep dermal layers.
Principles for diagnosing acne acne
Fulminant forms of acne have a characteristic appearance, which allows a quick diagnosis. One inflamed element is enough for a dermatologist to identify a severe form of acne.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor must find out the cause of the disease and possible risk factors.
The following studies are prescribed:
- blood chemistry;
- checking hormonal levels in women if there are external signs of excessive androgen activity;
- bacterial culture to determine the resistance of microflora to antibiotics.
The presence of concomitant diseases is also determined, so the opinion of other specialists may be needed.
Treatment tactics
When diagnosing conglobate acne, treatment depends on the severity and duration of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies, age and gender, and also takes into account the psycho-emotional state of the patient.
In any case, an integrated approach is taken when choosing treatment tactics: taking local and systemic antibiotics (mandatory), physical and dietary therapy, preventive measures and treatment of scar changes. People with acne accumulations should prepare for a lengthy treatment that can take months or even years.
Antibacterial drugs
Globular acne requires the use of systemic antibiotics. These are drugs such as Vilprafen, Erythromycin, Doxycycline, Minocycline, Tetracycline. Taking antibiotics is long-term – 2-4 months and occurs in cycles. As a rule, treatment begins with the maximum calculated dose, which is gradually reduced after a certain time interval. Erythromycin is rarely prescribed due to the fact that bacteria very quickly develop resistance to it and the drug loses its effectiveness. Tetracycline is also not a drug of choice as it has many side effects on the body.
In parallel with antibiotics, antimycotic drugs are prescribed to normalize the balance of intestinal flora.
If there is no effect from taking antibiotics, the drug Rokkautan is prescribed. The dose is strictly calculated by the doctor and depends on the patient’s body weight. The drug has many contraindications and side effects. It should not be used by women during pregnancy and lactation. Also, a month before the start of treatment, on time and a month after the end of therapy, it is necessary to take contraception, since Rokkautan can affect the embryo during a possible pregnancy.
Oral contraceptives
If fulminant acne in women is associated with hormonal changes in the body, then the excess of androgens is corrected with hormonal drugs, in particular oral contraceptives. Products based on drospirenone, cyproterone acetate and dienogest have proven themselves best. These substances reduce the production of male sex hormones and interrupt the connection between androgens and their receptors located at the exit sites of the sebaceous gland ducts. In medical practice, therapy is carried out using drugs such as Diane 35, Diecyclen. Therefore, for successful treatment, women may have to visit not only a dermatologist, but also a gynecologist and endocrinologist.
Topicals
Local remedies are also actively used in the treatment of conglobate acne. First of all, these are drugs based on the following substances:
- Azelaic acid has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties. Products based on it are used primarily for the treatment of hormonal acne. The acid combines well with other medications without reducing their effectiveness.
- Benzoyl peroxide is active against acne-causing bacteria. Its use is possible only under the supervision of a doctor, since in each specific case it is necessary to calculate the exact dosage of the drug.
- Retinol and retinoid-like compounds are used primarily in men. They reduce the level of secretion of the sebaceous glands, normalize the process of keratinization, and dissolve existing sebaceous plugs.
Local antibiotics, although they do not eliminate the causes of acne, can regulate the number of pathogenic bacteria. They rarely provoke skin reactions in the form of irritation, burning and itching, but bacteria may become resistant to the active substances of the medications. The most commonly prescribed are Clindamycin, Zenerit, Fucidin, and Erythromycin ointment. Fulminant acne cannot be treated with topical antibiotics alone. With excessive sebum secretion, it becomes simply impossible to create the necessary concentration of the medicinal substance in the ducts of the sebaceous glands. Therefore, they are used as an adjunct to oral antibiotics.
Other drugs and methods
Since the treatment of conglobate acne involves the use of systemic antibiotics, drugs are also prescribed that reduce their negative impact on the body - these are antifungal agents to prevent candidiasis, hepaprotectors to reduce the load on the liver and probiotics to prevent dysbiosis. During hormonal therapy, injections of vitamins A and E are also recommended.
It is also possible to open the spherical elements in an outpatient setting, during which the pus is removed and the cavity is treated with an antibacterial solution.
For the speedy maturation of the abscess and then healing, ichthyol and Vishnevsky ointment are used in the form of applications.
Diet therapy
Diet therapy plays a significant role in complex treatment. People suffering from severe acne should minimize or completely avoid eating fatty, spicy, fried foods, and reduce carbohydrate intake.
Epidemiology
Acne conglobata is not very common. In general, this type of acne is more common in men than women. There have been numerous reports of athletes with this type of acne published over the past 30 years, and it is thought to be primarily related to the use of anabolic steroids. Outside the United States, little is known about conglobate eels. The condition is usually seen in young people and very rarely in children or the elderly. Onset usually occurs in the second and third decades of life. It is not known whether the disease is more common in any particular race.
Removing the effects of acne
Unfortunately, the appearance of scars with conglobate acne cannot be avoided even with timely treatment. Today, there are many methods that allow you to lift sunken areas and polish protruding scar elements to the same level as the skin. Dermabrasion, acid peels, laser resurfacing are just a few methods that allow you to correct skin defects.
What do conglobate acne look like: photo and description
Not only that, conglobate acne is multiple, these pimples will also turn into very large skin-colored comedones. These lumps can also turn into cysts, which will release pus if accidentally touched.
When pus gets on the skin, it causes even more rashes to appear. For this reason, the largest number of acne occurs on the back.
As acne conglobata accumulates on your skin, you may develop large, rough scars. They are classified as thin (atrophic) or thick (hypertrophic).