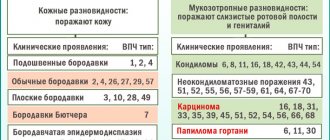
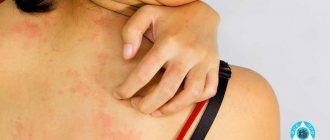
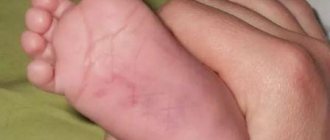
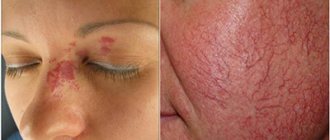
The epidermis serves as a kind of barrier that protects internal tissues. He may be susceptible to various diseases. Skin defects can be associated with exposure to both external and internal factors.
Since the skin serves as protection for the entire body, one of the important preventive tasks is to protect it from the occurrence of pathologies.
It is skin diseases on the hands that are the most common cases of dermatological problems, since this part of the body is almost impossible to protect from provoking factors.
Causes of dermatitis
Skin diseases on the hands can occur for many reasons. The following main factors provoking the development of dermatitis are identified:
- Biological - allergenic vegetables and fruits, some plants (euphorbia, nettle, etc.); exposure to viruses, fungi and other harmful microorganisms.
- Physical - solar radiation, friction and pressure of clothing, thermal effects.
- Chemical – household chemicals, paints and varnishes, acids, industrial chemicals, cosmetics, perfumes.
Also, skin diseases on the hands often appear as a result of dysfunction of internal organs, which are responsible for metabolism and removal of various toxins from the body (kidneys, liver, lymphatic system, etc.). Sometimes inflammation is associated with stress, nervousness, and depression, which provoke hormonal imbalances.
In most cases, dermatitis develops for internal reasons, as well as due to the entry of certain allergens into the body.
Complications
An unpleasant fungus that affects the epidermis on the fingers of the lower or upper extremities, in the absence of timely treatment or the wrong approach to treatment, can cause a number of complications:
- Small islands of rash merge with each other, forming large foci of inflammation .
- Pimples often burst , releasing purulent matter and leaving wet marks.
- The cracks increase in size.
- Due to severe itching, a person scratches the skin almost until blood appears.
- The pain intensifies so much that the person cannot normally stand on his entire foot and pick up various objects.
- The infection affects the nail plates and also spreads to the epidermis of other parts of the body.
- The fungus penetrates deep inside, affecting the tissues of internal organs.
How to identify skin diseases
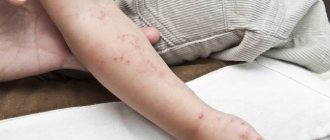
Depending on the cause of inflammation, its external manifestations may differ slightly. In acute forms of dermatitis, intense redness, severe burning, itching and pain are observed. These are typical symptoms that describe skin diseases on the hands. Bubbles, erosions and swelling appear in complex inflammation and can have varying degrees of severity. For example, when damaged by a chemical agent, blisters filled with liquid form, which gradually burst, and in their place weeping erosions remain. After drying, dry crusts form on the affected area.
In the chronic form of dermatitis, swelling of the skin can persist for a long time. The top layer of skin thickens noticeably, the hand turns blue, and its surface becomes dry and flaky. If left untreated, the disease threatens atrophy of the epidermis.
If dermatitis on the hands is caused by mechanical damage, then traces of abrasion remain on the affected areas. Sometimes swelling and blisters filled with serous fluid occur.
Skin diseases on the palms of the hands can take the form of calluses. With further exposure to the irritating factor, yellow-brown plaques form. This part of the skin is more sensitive.
Skin diseases on the fingers very often occur after prolonged exposure to the cold and are expressed in itching, burning and bluish-red swelling.
Symptoms of erysipelas
Erysipelas is one of the ailments that occurs on both the upper and lower extremities. Erysipelas of the skin of the legs is more common than the hands, face or other parts of the body.
Signs of inflammation vary depending on the form of the disease:
- The mild form has muted manifestations. The patient feels weak and has an elevated body temperature.
- Moderate form. It has more acute symptoms and a longer duration.
- Severe form. The acute course is complemented by a violation of the mental state.
- Recurrent. In case of unfinished primary treatment, as well as in a weakened body, inflammation may appear in the same place.
Important. To avoid complications, you must carefully follow all doctor's instructions.
Lack of treatment threatens complications from the cardiovascular system and kidneys
Types of skin diseases of the hands
Depending on the cause of development, all skin ailments of the upper extremities are divided into the following groups:
- Contact dermatitis. They are caused by the direct influence of an irritating factor on the skin and are divided into simple (temperature, radiation, chemical burns and mechanical damage) and allergic, which manifest themselves when the body is prone to rashes, as well as when the functions of the immune system are impaired. The main difference between contact dermatitis is the limited influence of the irritant and the rapid recovery of the affected skin after the provoking factor is eliminated.
- Toxidermy. This type of disease occurs as a result of the penetration of a harmful substance into the body, which is manifested by a skin rash. This group of diseases includes neurodermatitis, atopic and dry dermatitis. Their main feature is that the irritant enters the body through airborne droplets and through food.
- Secondary dermatitis is a skin disease that occurs as a result of other ailments of the body, hormonal disorders, etc. Some of them affect the nail plates and the tissues closest to them.
Fungal dermatitis
The most common contact dermatitis is fungal diseases on the fingers. You can become infected with them almost anywhere: in public transport, in the gym, in the swimming pool, sauna, etc. Women are most susceptible to the disease during manicures.
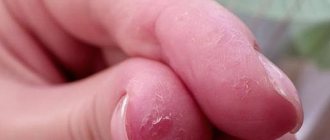
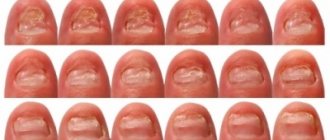
Fungal diseases on the hands develop gradually. The nail plate is affected first. Nails acquire a yellowish tint, become brittle and look unkempt. Then the disease affects the folds between the fingers. Fungus on the skin appears as characteristic spots that may become wet or peel. The affected areas may vary in size and range in color from pale pink to blue. Sometimes the folds of the skin dry out and crack.
Most often, this type of dermatitis affects people with weak immunity, diabetes mellitus and endocrine system disorders.
Often, under the influence of physical factors, non-fungal diseases of the fingernails develop. Thus, with frequent hand injuries, onycholysis can develop, in which the nails turn white and separate from the nail bed. This group of diseases also includes grooves, hangnails, and splitting of nails.
Fungus on the fingers: photos, symptoms and treatment with ointments and folk remedies
Fungus on the fingers is a serious disease. It affects both the skin and nail plates of humans. It is easy to catch a fungus, since spores of pathogenic microorganisms are present almost everywhere. They peel off along with the scales of the epidermis and end up on household items, etc.
If there are wounds or tiny cracks on the hands of a healthy person, then fungal spores penetrate through them and begin to multiply. Other factors also contribute to the development of fungal infections, the main one being disruption of the immune system.
Fungus between the fingers is often detected in patients who suffer from mycosis of the feet. When handling limbs without gloves, they become self-infected.
Let's look at what causes the development of fungus on the fingers of the upper extremities, and how does infection occur? We will also find out the symptoms of the disease and treatment features.
Causes of fungus on fingers
The mechanism of the onset and progression of the disease is simple - spores of a certain type of microorganism fall on human skin and penetrate into the deeper layers of the epidermis. There they begin to develop and multiply, which eventually manifests itself in symptoms of the skin and nails.
So, the immediate cause is the activity of the fungus. Contact of fungi with human skin does not always lead to disease, because the state of the human immune system plays a significant role. If it is weakened, then the likelihood of illness is high.
Among the factors that provoke the development of fungal infection are:
- Hyperhidrosis.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Long-term use of antibacterial agents.
- Skin injury, open wounds.
- Frequent stress, neuroses.
- Pregnancy.
The occurrence of fungus occurs due to the influence of one factor or a combination.
How does infection occur?
Most often, the infectious disease develops as a result of self-infection - when treating the feet, the patient transfers the fungus to his hands. In medical practice there is such a thing as “two feet and one hand syndrome.” This means that with mycosis of the feet one hand is affected. A right-hander has the right, a left-hander has the left.
Relatively rarely, a fungus appears as a primary disease. This is facilitated by skin injuries and touching household objects that have fungal spores. Often all members of the same family get sick. Fungus is a contagious disease, and if there is no prevention of infection of other household members, everyone suffers.
Important addition: What does fingernail fungus look like: symptoms and treatment
The risk group includes people whose professional activities involve constant contact with water, chemical solutions, and alkali.
Infection occurs when:
- Handshake.
- Visiting a bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, etc. places with high humidity.
- Contact with objects in medical institutions, public transport and other crowded places.
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to constantly wash your hands after visiting public places.
Symptoms of a fungal infection on the fingers
Mycosis is an infectious pathology, and we will consider in detail what it will look like and how to recognize it. At the initial stage, the skin of the fingers is affected. If treatment is not started at this stage, the disease begins to progress and affects the nail or nails.
Symptoms include excessive peeling and dry skin. Many patients experience itching. It tends to intensify after water procedures. Against the background of damage to the nail plates, characteristic signs also appear.
filamentous fungus
Sporotrichosis is an infectious skin disease caused by a filamentous fungal microorganism. The risk group includes gardeners, rural workers, and flower growers. Fungi penetrate through microcracks in the skin, scratches; when inhaling air.
Filamentous fungus is also contagious. It is transmitted not only from sick people to healthy people, but also from sick animals.
Patients complain of the following symptoms:
- Nails lose their natural shine and become cloudy - this happens because entire colonies of microorganisms multiply in the plates.
- Their color changes - dark gray, white, yellow, brown.
- There are microcracks on the fingers that do not heal well.
- The nail plates become brittle, crack, peel, and crumble.
- Partial peeling of the plate is revealed.
The thumb and index fingers are most often affected, less often the little finger.
Candida lesion
Saprophytes (yeast fungi) belonging to the Candida family are always present on the human body. This is the norm; they appear to be opportunistic microflora.
In the presence of certain disorders and malfunctions in the body, their numbers increase exponentially, and they become pathogenic pathogens. That is, they provoke the disease.
The most common causes of candidiasis of the nails include:
- Deficiency of minerals and vitamins in the body.
- Violation of metabolic processes.
- Excessive consumption of sugary foods.
- Long-term use of antibiotics.
- Close contact with rotten fruit.
Women who work in high humidity conditions, for example, as a cleaner, cook, dishwasher, laundress, are at risk.
Description of symptoms:
- Red edematous lesions with papules are observed.
- Both the nail fold and the nail itself are affected.
- In the center of the nail there is a shiny erosion covered with a whitish coating.
In most clinical pictures, inflammation does not progress and does not spread to the lateral surface of the fingers.
Yeast form of mycosis
A fungal pathology that affects the nail plates, fingers, palms, and interdigital space. It develops regardless of age - in middle-aged men and women, young children, adolescents, and the elderly.
Signs of infection:
- Severe peeling in the interdigital space.
- Suppuration of the nail.
- Severe itching.
- Increased dryness of the skin of the hands.
- Hyperemia on the fingers.
- Papules form between the fingers.
Yeast infection can easily be confused with psoriasis or eczema, so differential diagnosis is carried out.
How to cure fungus on hands?
The doctor will tell you how to treat fungus on your fingers. The treatment regimen is determined by the specific type of pathogen and the degree of infection. In the early stages, mild forms are treated with local medications - cream, ointment, gel. In severe cases, taking tablets and capsules is required.
Application of ointments
The use of external agents is a mandatory part of the therapeutic course. The form of the drug is prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s preferences and capabilities. This can be antifungal nail polish, cream, gel, solution, etc. Therapy occurs at home.
It is necessary to get rid of the fungus competently, that is, first determine the type of pathogen and act on it. Only those medications are prescribed to which the detected fungus in the patient is sensitive.
Effective inexpensive ointments for fungus:
- Candida for nail fungus in the form of an ointment. Clotrimazole is a component with biological activity. Use 2 times a day. Duration of treatment – from 4 months.
- Nizoral (cream). The main component is ketoconazole. Use once a day, treatment varies from 2 to 4 months.
- Exoderil is a more modern drug; once a day is enough, and the entire therapeutic course lasts 4 weeks.
Contraindications to the use of most antifungal drugs are pregnancy, hypersensitivity to the composition, and liver/kidney dysfunction.
Systemic therapy
Systemic exposure is recommended in severe cases, as well as when the use of external agents does not help.
Names of medications often prescribed for fungus:
- Fluconazole. Tablets are taken once a day. The treatment course is 14-28 days. Do not take during pregnancy or lactation; use is prohibited in children under six years of age.
- Itraconazole The course is determined individually, depending on the dosage. The higher it is, the shorter the course of therapy. Do not use during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- Ketoconazole. Take 1-2 tablets per day. The course of treatment is determined individually.
Systemic treatment is always combined with external agents. Only with the help of complex influence can one count on a favorable prognosis.
Diagnosis of skin diseases
If you suspect the presence of skin diseases, you should definitely consult a dermatologist or allergist. During the examination, you may also need to consult a neurologist, endocrinologist and gastroenterologist.
Common skin diseases on the hands are diagnosed based on an external examination of the patient and a survey about the possible causes of the disease. If allergic manifestations are suspected, the allergen must be identified. In this case, special skin tests, general and biochemical blood tests, stool tests are carried out, and the performance of the endocrine and immune systems is also determined.
To determine more complex types of dermatitis, additional diagnostic methods can be used: microscopic examination of tissues taken for analysis or bacteriological culture of skin scrapings.
Scabies
Scabies is a skin disease that is caused by the active activity of the scabies mite. There are several types of scabies: typical, nodular, complicated, and so on. The main symptom is the appearance of a red, often watery rash on the skin (mainly between the fingers and on the sides of the palms). Usually accompanied by severe itching, which intensifies during sleep (the period when the mite is especially active). Scabies can also be distinguished by the nature of the localization of the rash: pimples on the skin are usually located in pairs.
Infection occurs through direct contact with the patient’s skin and personal belongings. The disease often does not manifest itself in the first days after infection, because the incubation period is 7-10 days.
To prevent complications such as a purulent infection (which can develop from scratching the rash), it is necessary to use soothing agents and control the itching.
The disease is diagnosed by visual examination by a dermatologist and examination of the mite and scraping. Scabies is treated externally with special preparations, along with which the doctor can individually prescribe general treatment with immunomodulators and sedatives. It is recommended to thoroughly wash and iron things that the patient comes into contact with.
Treatment of dermatitis
The method of dealing with skin diseases of the hands depends on the cause of their occurrence. For contact, atopic and neurodermatitis, systemic therapy is prescribed, which includes the use of antihistamines, sedatives and vitamins A, B and E. In the case of infectious dermatitis, antibacterial and antifungal treatment is used.
Physiotherapy procedures are often used in combination with drug therapy: laser treatment and sanatorium-resort treatment.
There are some skin diseases on the hands that can only be treated with ointments. As a rule, these are uncomplicated dermatitis with minor symptoms.
In addition to basic treatment, you need to follow recommendations that are important for all types of dermatitis. So, it follows:
- Eliminate exposure to the irritating factor.
- Provide care with nourishing and restorative products.
- Limit water treatments.
- Carry out parallel treatment of other diseases that affect the skin.
- Stick to a diet: during treatment you need to exclude salty, fried, spicy foods, sweets and baked goods, as well as foods that cause allergies (citrus fruits, honey, fruits, mushrooms, etc.).
Prevention of skin diseases
To prevent dermatitis, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid contact with allergens.
- Do not be nervous.
- Take care of dry skin.
- Avoid hand sanitizers.
- Use hypoallergenic powders and rinse clothes thoroughly after washing.
Following these simple rules is not difficult at all. They will help not only prevent unpleasant skin diseases on the hands, but will also help preserve their youth and health for a long time.
www.syl.ru
Since the human skin protects the body from external influences, it performs many functions and is subject to many influences. Dermatological diseases are the most common. The skin can be affected by both mild ailments and more serious ones that require professional treatment. Skin diseases on the hands require timely diagnosis and treatment. How do hand ailments manifest themselves?
The epidermis serves as a kind of barrier that protects internal tissues. He may be susceptible to various diseases. Skin defects can be associated with exposure to both external and internal factors.
Since the skin serves as protection for the entire body, one of the important preventive tasks is to protect it from the occurrence of pathologies.
It is skin diseases on the hands that are the most common cases of dermatological problems, since this part of the body is almost impossible to protect from provoking factors.
Types of skin rashes
The rash that appears on the body comes in various forms. For example, the patient may find:
- small rash;
- bubbles;
- papules (pustules);
- blisters;
- plaques.
Important. Identifying symptoms early increases the effectiveness of treatment.
Knowing the cause of the skin disease on the arms and legs, you can prevent it from becoming chronic and other complications.
Unlike internal diseases, skin ailments have unaesthetic external manifestations, which causes not only unpleasant sensations, but also emotional suffering.
Diagnosis of illnesses
Based on the patient’s complaints, symptoms, location of sores and examination, a preliminary diagnosis is established. Further examination confirms a certain disease of the skin of the hands or refutes it.
To determine the nature of some pathologies, skin scrapings are taken with a special glass or the blunt end of a scalpel. Some research methods include palpation of the skin.
Laboratory diagnostics includes a complex of various tests. To identify the pathogen, a general blood test, urine test, and biochemical blood test are prescribed. To determine the presence of helminthic infestation, a stool test is prescribed.
Types of skin diseases
The most common hand skin diseases:
- Dermatitis. Redness accompanied by swelling, itching and peeling.
- Scabies. Itchy, paired pimples and profuse redness.
- Mycoses (fungal pathologies). Reproduction of fungal microorganisms in the layers of the dermis.
- Eczema. There is compaction, itching and peeling of the integument.
- Acne. There is no itching, but it causes discomfort. It is a consequence of dysfunction of internal organs.
- Hives. The blisters merge to form a large spot. When they burst, they cause discomfort and pain.
- Scleroderma. It is expressed by tense skin, changes in the shape of nails and fingers.
- Psoriasis. Has several varieties.
- Toxicoderma (toxic-allergic dermatitis). It is characterized by a rash of various types (spots, nodes, blisters, ulcers) and a protruding vascular network as a result of toxic damage to blood vessels and tissues.
The location of the skin rash is one of the criteria for diagnosing the disease, but not the main one
Symptoms of rashes
Depending on the lesions of the skin, the symptoms appear brightly or covertly. There are several groups of manifestations:
- skin color changes from natural to red or pale;
- sensation of pain, itching, burning;
- the normal condition of the skin is replaced by excessive dryness, tightness - these manifestations are typical for the palms or feet;
- formation of skin elements (tubercles, rash).
Any formations can be triggered by various diseases or allergic reactions.
Important. It is very difficult to independently diagnose skin diseases on the hands. Although it is possible to establish the correct diagnosis, experts recommend immediately contacting a medical facility to determine an accurate diagnosis and begin proper treatment.
Fungal diseases and their consequences
One of the vulnerable places of the human body is the nails. Pathogenic microorganisms, affecting the upper extremities, also affect the nails, changing their natural shape, and the skin around them itches and turns red. The nail plates also reflect various problems in the functioning of organs. Symptoms of mycosis include thickening or brittleness of the nails and a change in their shade. Because nails peel and crumble, they do not grow back. Even after healing, the skin continues to peel for a long time.
Mycosis provokes the appearance of erysipelas, and also delays the treatment process for the latter
A person who sweats excessively, does not observe good hygiene, or has reduced protective functions is more likely, in addition to mycosis on the hands, to become a victim of a disease of the toenails or the skin around the nail plates.
Remember. Treatment of fungus takes a long time, the effectiveness of therapy depends on the correctly identified type of microorganism.
Fungus on the upper extremities is much less common than on the lower extremities. The disease may begin to develop in the legs and then move to the arms.
Symptoms of erysipelas
Erysipelas is one of the ailments that occurs on both the upper and lower extremities. Erysipelas of the skin of the legs is more common than the hands, face or other parts of the body.
Signs of inflammation vary depending on the form of the disease:
- The mild form has muted manifestations. The patient feels weak and has an elevated body temperature.
- Moderate form. It has more acute symptoms and a longer duration.
- Severe form. The acute course is complemented by a violation of the mental state.
- Recurrent. In case of unfinished primary treatment, as well as in a weakened body, inflammation may appear in the same place.
Important. To avoid complications, you must carefully follow all doctor's instructions.
Lack of treatment threatens complications from the cardiovascular system and kidneys
External causes of hand skin diseases
The wide distribution of skin diseases of the hands in humans is explained by the fact that, in addition to the protective function, the covering of the upper extremities performs a receptive function. When coming into contact with surrounding objects, it is difficult not to become infected.
Exogenous (external) factors affecting the epidermis:
- contact with a chemical (alkali, acid, paint);
- irradiation (x-ray, ultraviolet);
- contact with pathogenic microbes (anthrax, leprosy);
- sudden temperature changes (hypothermia, frostbite, burns);
- parasitic effects (fleas, mosquitoes, bedbugs).
Adverse external influences irritate the epidermis, causing the appearance of pigment spots, burning, and itching. Careless handling of dangerous objects may result in personal injury. And with age, the regeneration of epidermal cells is disrupted.
Important. The patient can independently diagnose the disease, but in case of an erroneous diagnosis, the situation will be aggravated by incorrect treatment. If primary symptoms are detected, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist.
Even the smallest members of the population suffer from skin defects. Allergic dermatitis is especially common. A skin reaction to an allergen manifests itself in the form of inflammation, peeling, rashes, and spots. The skin becomes dry and itchy.
Many dermatological diseases are caused by dysfunction of internal organs.
The main symptoms indicating damage to the skin include:
- irritation, burning;
- skin redness;
- rash;
- painful sensations.
Internal causes of skin diseases
Endogenous (internal) causes often influence changes in the epidermal layer. The following can lead to an inflammatory process of the dermis localized on the hands:
- hormonal changes (most often in adolescence);
- nervous tension;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disorders;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
The individual characteristics of the body, previous diseases, a tendency to allergic manifestations, and heredity are of great importance.
Each skin type needs special care; any wounds should be immediately disinfected
Preventive actions
To avoid allergic reactions and infectious diseases, you must adhere to certain rules. There are only two main methods of prevention:
- The most important point is hygiene . Since hands are exposed to constant contact with external factors, it is important to carefully monitor their cleanliness. A large number of microorganisms are concentrated on the dermis. Sweat secretions and dirt accumulated in the skin folds lead to inflammatory processes.
- Skin care. This includes cleansing of dead layers of the dermis, moisturizing and nutrition with the help of pharmaceutical and cosmetic preparations.
To prevent skin diseases of the lower extremities, it is also necessary to follow certain rules. Shoes must be of high quality and well ventilated. There should be no debris or dust inside. The skin of your feet should always be dry. After taking water procedures, you should wipe the skin between your fingers especially carefully. If sweating is increased, you need to take special medicinal baths. All hygiene items must be strictly individual.
All skin diseases are conventionally divided into contagious and non-contagious. Prevention is hygienic in nature. By following the rules of hygiene, you can protect yourself as much as possible from various types of skin diseases.
zkozha.ru
Skin diseases on the hands are a fairly common pathology. Occurs everywhere in all age groups. Pathologies have a variety of origins. The clinical presentation of skin diseases also varies widely.
Some diseases are contagious, that is, they can be transmitted from person to person. Each pathology requires diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Skin diseases are treated not only with local, but also with systemic means.
Symptoms of rashes
Depending on the lesions of the skin, the symptoms appear brightly or covertly. There are several groups of manifestations:
- skin color changes from natural to red or pale;
- sensation of pain, itching, burning;
- the normal condition of the skin is replaced by excessive dryness, tightness - these manifestations are typical for the palms or feet;
- formation of skin elements (tubercles, rash).
Any formations can be triggered by various diseases or allergic reactions.
Important. It is very difficult to independently diagnose skin diseases on the hands. Although it is possible to establish the correct diagnosis, experts recommend immediately contacting a medical facility to determine an accurate diagnosis and begin proper treatment.