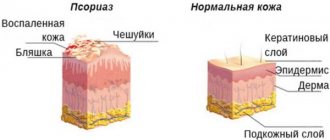
Types of growths
Skin growths are divided into three main groups - benign, malignant and precancerous. And each group has its own subspecies.
Benign
Such neoplasms on the skin do not pose a direct threat to their carrier unless they are subjected to various types of mechanical influence.
Atheroma
A skin tumor that forms as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands. Externally, the growth resembles a small dense bump, with a clearly defined contour. This cone feels very elastic and mobile to the touch. When palpated, it does not cause pain or other discomfort. The lump can fester and even burst. When a rupture occurs, a purulent-sebaceous fluid is released from the growth. During the period of inflammation, the temperature rises and the atheroma can hurt. The growth forms in places where there is a large accumulation of sebaceous glands - on the scalp, neck, back, and groin area.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a vascular tumor neoplasm, it can be:
- Capillary - a growth on the surface of the skin that can reach large sizes. Color from red to bluish. Often grows to the sides.
- Tricky - limited subcutaneous nodular growth. The skin in the area of a cavernous hemangioma usually turns red. Such tumors often appear in newborns in the neck and head area.
Lymphangioma
A tumor that develops on the walls of the vessels of the lymphatic system. The tumor is characterized by very slow growth. An inflated skin tumor grows in the area of the lymph nodes; it is painless. The neoplasm can be cystic, consisting of several isolated or combined cysts. The disease mainly affects children, but can also develop in adults. This disease usually occurs in the fetus during intrauterine development. The disease is not dangerous, but tends to grow instantly under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors. In this case, immediate surgical excision is required.
Lipoma or wen
A neoplasm that develops under the skin from fatty tissue cells. Externally, the wen looks like atheroma. The subcutaneous lump is completely painless. It feels like a hard and moving ball when palpated. Lipoma can develop on any part of the body where there is subcutaneous fat. The growth can be single or multiple. One wen can grow in size from a large pea to a medium-sized apple. The tumor brings aesthetic discomfort to its owner.
Papillomas and warts
Growths on the skin that form from epithelial tissue. Such growths can be spherical (in the form of a papilla), horny (thread-like) or flat. The neoplasms are small and painless. They can develop on any part of the body. The color of the growths can be flesh-colored, brown, red and even black. The appearance of warts signals the presence of HPV (human papillomavirus) in the body.
Nevi and moles
These are congenital or acquired flat neoplasms in the form of one or several spots. Such growths are a small or large accumulation of cells overflowing with the natural coloring pigment - melanin. New growths can vary in color (from beige to dark brown), texture, shape and size. Such growths do not pose any particular harm to health.
Fibroma
A growth that forms from an accumulation of connective tissue. Externally, fibroma resembles a wart on a thin stalk. The growth looks like a cluster of small spherical skin nodes. The surface of the fibroma can be smooth or loose. The color of the growth varies from flesh-pink to dark brown. Fibroma grows very slowly and does not cause discomfort (except for mechanical inconvenience caused by clothing or its location). If there is no effect on the fibroid, it is safe.
Neurofibroma
A skin neoplasm that forms from nerve cells. Most often it develops due to stress and nervous overexcitation. Often the growth is located in the area of subcutaneous fat and under the skin itself. Externally, the neoplasm is a dense tubercle, with a pigmented outer ball of skin. The growths quickly grow over the skin and are very rarely isolated. Most often it affects the back, neck, elbows and knees.
Malignant
This category of skin tumors often appears through the degeneration of a benign growth into a malignant one. Such growths require immediate identification and disposal.
Melanoma
A neoplasm that occurs as a result of incorrect removal of a mole (nevus) or its degeneration into a malignant form. Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. The disease is very aggressive and quickly spreads throughout the skin. Such a tumor very soon metastasizes throughout the body, to internal organs and even to the brain.
Basalioma
Squamous cell skin cancer, which is formed from cells of the basal layer of the epidermis, in the form of flat, single purulent wounds. Small nodular tumor wounds quickly progress and develop into mushroom-shaped ulcerative growths. Most often, wounds appear on the face, affecting the cheeks, wings of the nose, the area behind the ears and ears, and the lower eyelid. This type of cancer does not metastasize to internal organs and does not spread much throughout the skin.
Kaposi's sarcoma
A malignant neoplasm on the skin in the form of extensive dark spots (from the color of boiled blood clots to black), which merge into large affected areas. The disease is diagnosed in most cases in HIV-infected people late in the course of the disease. Locations affected by sarcoma: hands, legs and feet. This disease is a consequence of serious problems with internal organs, it cannot be cured, you can only relieve the severe symptoms with a little medication.
Liposarcoma
A tumor that occurs due to damage to adipose tissue. This is a large subcutaneous round growth (single node) that can grow up to 20 centimeters. The growth itself is uneven, with irregular outlines. When palpated, it may be hard and elastic. This growth often occurs in people over 50 years of age and mainly in men. Liposarcoma occurs through the degeneration of a lipoma or atheroma into a malignant tumor. The growth grows very slowly and does not spread metastases to internal organs.
Fibrosarcoma
A neoplasm developing in connective soft tissues. Most often, the growth affects the skin of the lower extremities.
Fibrosarcoma can be located externally or subcutaneously. The cutaneous protrudes above the skin; such a growth has clearly visible boundaries and a dark blue or brown tint.
Subcutaneous fibrosarcoma is located deep under the skin and is hardly noticeable. We see only a small venous tubercle.
Precancerous
Despite the scary names of the category, most of these neoplasms, if quickly identified, can be removed and cured without serious harm to health.
Lump under the skin below the elbow, above the elbow, causes
Sometimes patients complain that they have a lump under the skin below the elbow or above the elbow and are interested in the reasons for such skin lumps.
Formations such as balls, compactions, bumps are a common phenomenon that almost every person encounters.
Most cases do not pose a serious threat to human health, but only cause cosmetic discomfort, and some cases require your attention and treatment.
Causes
Lumps and lumps can appear in various parts of our body, including the elbow areas. Sometimes formations grow extremely slowly, and we do not notice them for a long time until they reach tangible sizes. This is how benign skin formations and soft tissue compactions develop.
If lumps or lumps in the elbow area cause pain or discomfort, most often this is a consequence of infectious diseases. The patient may have an increase in general or local body temperature.
Redness of the skin over the lumps may also be observed. The patient may experience general malaise and a feeling of weakness. If treatment is started in a timely manner, such symptoms will pass quickly enough.
Less common are malignant tumors that the patient can identify independently. It is important to recognize these diseases at an initial level and consult a specialist as early as possible.
The most common disease that causes the formation of lumps, tumors under the skin in the elbow area, may be hygroma. This disease is a formation in the form of a ball of a motionless nature.
Hygroma, as a rule, does not cause severe pain, the only thing is that if it is located, for example, on the palm, it can cause discomfort during daily work.
Hygroma is, in fact, accumulated fluid in the area of fibers and tendons and, with random mechanical influence, can disappear on its own.
In diseases associated with joints (arthritis, arthrosis), hard, inactive compactions of small sizes can often appear under the skin. These nodules appear specifically in the elbow joints, they are also called rheumatoid nodes.
After suffering from colds, inflammation of the lymph nodes most often occurs. Lymph nodes can be located in groups in areas such as the neck, lower jaw, armpits, just in the bends of the elbows and knees, groin and other parts of our body.
Lymph nodes are necessary for our immune system to filter interstitial fluid from infectious and foreign impurities, as well as tumor cells. With enlarged lymph nodes - lymphadenopathy - elbow bumps can become very painful when pressed.
If the patient promptly treats the underlying ailment (sore throat, otitis, burn), this will lead to a reduction in the size of the nodes. If the lymph nodes turn red and become sharply painful when pressed, it is possible that pus has accumulated there, in which case it is necessary to urgently seek advice from a surgeon.
Do not delay visiting a doctor, as in the early stages the problem can be solved with antibiotic therapy.
If you feel a dense formation under the skin in the form of a lump, and the skin above it does not fold, there is a possibility that the node is damaged by a malignant tumor. In this case, you also need to consult an experienced oncologist.
Malignant lumps are less common compared to other diseases, but it is necessary to know the symptoms of such formations in order to recognize them in time. The lump or nodule will gradually grow. On the one hand, it does not hurt or itch. The skin can be either normal color or acquire a darker shade, becoming covered with a crust.
Treatment
Malignant formations must be recognized by the following signs:
unclear tumor boundaries;
enlargement of nearby lymph nodes;
fairly rapid growth in education;
immobility of the formation and connection with the surface of the skin;
possible areas of bleeding and ulcer-like formations on the surface of the cone.
At the slightest suspicion of such symptoms, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible for diagnosis and timely treatment.
We advise you not to self-medicate, but to find a good specialist dermatologist, surgeon and oncologist at the first signs and suspicions. You can also turn to a therapist for help in the first case; he will be able to correctly diagnose your formations in the elbow area and write out the right referral to specialists.
Source: https://zdravskin.info/shishka-pod-kozhey-nizhe-loktya-vyishe-loktya-prichinyi.html
Types of growths on the skin
All neoplasms developing from skin cells are classified into:
1. Benign, not posing a serious threat, but capable of causing physical and mental discomfort if extensively localized or located on areas of the body not covered by clothing.
2. Malignant, which is essentially a cancerous tumor. These growths quickly grow, affect the deep layers of the dermis and spread metastases throughout the body.
3. Borderline, potentially capable of transforming into a malignant form.
| Laser tumor removal | Prices, rub. |
| Laser removal of papillomas, warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 300 — 600 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. II. difficulties | 600 — 1200 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. III. difficulties | 1200 — 2400 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - IV category. difficulties | 2 400 — 5 000 |
| CO2 Laser callus removal (per unit) | 1000 — 3600 |
| Removal of atheroma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. I. difficulties | 6550 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Category II. difficulties | 8250 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. III. difficulties | 12 350 |
Make an appointment
Let's look at the features of these skin growths in more detail.
It is formed during blockage of the sebaceous gland and has the appearance of a compacted “ball” rising above the skin, which does not cause discomfort. Atheromas can form on any part of the body, including in the genital area; the neoplasm can be either single or multiple. In case of suppuration and inflammation, atheroma can be removed by surgical excision or laser.
If the functioning of the ducts of the sebaceous glands is seriously impaired, then without special treatment of the underlying problem, they will be re-clogged and, as a result, atheromas will appear again and again, usually in the same place.
A vascular neoplasm that can be localized in both the upper and deep layers of the skin, as well as internal organs, and affect the vascular network. It has a burgundy or bluish-black tint and can reach large sizes. Treatment involves laser removal of hemangiomas, sclerotherapy or surgery.
Hemangiomas most often occur on the body, but can sometimes develop on the scalp, face, neck, upper and lower extremities. The neoplasm itself is not dangerous, but it is very easy to injure. Injuries to hemangiomas are accompanied by heavy bleeding.
This type of tumor develops on the vessels of the lymphatic system and is characterized by slow growth. The disease occurs during intrauterine development of the fetus. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, the tumor, as a rule, increases significantly in size, which becomes an indication for its surgical removal.
Lymphangioma primarily affects children and is easily diagnosed during the first year of a child’s life. The tumor itself is not dangerous, but its tendency to spontaneous and almost instantaneous growth can harm the child’s internal organs and even threaten his life.
A lipoma or wen is a benign tumor that develops under the skin from adipose tissue cells. The neoplasm can occur on almost any part of the body where, one way or another, subcutaneous fat is present. The neoplasm is felt under the skin as a small movable compaction; the tumor is absolutely painless.
Lipomas can be single or multiple. The tumor is prone to growth. And, despite its benign quality, it causes aesthetic and, often, physical discomfort to the patient. That is why it is advisable to remove lipomas using modern methods. You can learn more about lipomas in the article “Lipoma or wen: what is it?”
5. Papillomas and warts
Warts and papillomas are benign neoplasms that develop from epithelial tissue. They have a similar viral origin, but different places of formation and development. The cause of the appearance of papillomas and warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is very common in the world.
New growths are usually painless. Externally, they are small (up to several millimeters) horny outgrowths on the skin. The appearance of warts and papillomas most likely signals a weakened immune system, and the combination of antiviral therapy with correction of the immune system leads to complete elimination of tumors. Today, the most effective treatment method is laser coagulation; learn more about the removal of papillomas and the removal of warts using this method.
6. Nevi and moles
Nevi and moles are formed from melanocytes - cells containing the main coloring pigment of the body. As a rule, most of these tumors are not dangerous to health. However, their size and location can create some discomfort, especially if they are located on the face or open parts of the body.
7. Fibroma Fibroma is a benign neoplasm that develops from connective tissue cells. The tumor has the appearance of spherical nodules protruding above the skin with a smooth or warty surface. The color of fibroids can be bluish-black, gray, or brown. More detailed information on fibroids can be obtained in the article “Skin fibroids. Description, symptoms, consequences. Laser removal."
Symptoms and location of the cyst
Most often, hygroma is localized on the right hand. This is due to the fact that most people are right-handed, so the main load falls on their working hand. Hygroma on the left hand occurs in musicians and left-handers.
Visually, it is a small ball rising above the surface of the skin. The color of the skin over the swelling remains unchanged. The capsule contains jelly-like joint fluid.
A cyst can form and grow gradually, or it can appear suddenly and disappear spontaneously.
The hygroma itself does not hurt, but as it grows, it compresses the nerve endings and causes unpleasant symptoms - pain, burning, squeezing sensations in the hand.
On the back of the hand
The back of the hand in the area of the wrist joint is a favorite place for localization of hygroma. In the initial stages, the disease does not bother its owner in any way and causes only aesthetic discomfort. As it grows, it begins to cause pain when bending and straightening the hand, making it impossible to perform professional activities, work at the computer, and in severe cases, even perform everyday functions.
In advanced cases, when damaged and infected, the hygroma can fester. In this case, the skin around the tumor becomes red, the local temperature above the swelling increases, swelling, pain and stiffness of movement increase.
On the palm
Hygroma on the palm occurs extremely rarely, but in almost every case it is accompanied by unpleasant, painful symptoms. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, even small cysts quickly lead to compression of nerve endings and tendons, causing discomfort and dysfunction of the hand.
These types of hygromas usually appear after injuries and operations on the hand.
On fingers
Several types of hygromas can occur in the finger area. One of them, a mucosal cyst, occurs against the background of arthrosis of the joints in older people. It is usually localized in the area of the interphalangeal joints and makes itself felt during exacerbation of the underlying disease and activation of osteophytes.
Another option is tendon hygroma. Its capsule, filled with synovial fluid, is formed from tendon fibers. This tumor causes pain and discomfort and significantly limits hand movements.
What are neoplasms?
Unusual growth of skin cells is commonly called neoplasms. Experts cite exposure to ultraviolet rays as the main cause of the appearance of tumors. The second cause of skin damage is carcinogenic substances. Any new formation that appears on the skin must be monitored and promptly consult a doctor - an oncologist. He will carry out all the necessary diagnostic procedures. And he will recommend what further actions you will need to take.
Benign skin tumors
A characteristic feature of benign formations is their slow growth. These neoplasms do not infect adjacent skin cells. The formations are single and do not have additional lesions (metastasis). Benign neoplasms do not cause harm to the human body, but nevertheless they sometimes tend to degenerate into malignant ones.
Types of benign neoplasia:
- Papilloma . Benign warty growth of skin tissue. The surface of the papilloma is hairless, but nevertheless fleecy. It tends to increase in size, but this takes a long period of time. The color of the neoplasm ranges from brown to gray. The shape of papillomas is most often round, but can be absolutely any.
- Seborrheic wart . Another name for this neoplasm is senile papilloma. It looks like a clearly visible warty element. It has a color from brown to black. It appears most often in older people, hence the second name. The places where they form are most often the head, under the hair, or areas of the skin that are hidden under clothing. Seborrheic warts are formed when the placement of skin cells in the basal layer is disrupted.
- Keratoacanthoma is a cancer of the skin of the face and hands, but it is benign. A dense formation is formed on the dermis, the central part of which is the horny mass. After the formation grows to three millimeters, it disintegrates on its own, but a small scar forms. This neoplasm is not capable of degenerating into cancer. In any case, such rebirths have not yet been encountered. The site of appearance of keratoacanthoma is most often a nevus. From the name it is clear that the formations consist of pigment cells of the epidermis. Pigmented nevi are dark in color due to the high content of melanocytes. There is no specific place for their appearance, since neoplasms occur in completely unexpected and different places. Some of the nevi that appear can turn into cancer. Most often, pigmented nevi that form on the soles of the feet, palms, and genitals degenerate.
- Dermatofibroma . Newly formed tumor on the connective tissues of the skin. Visually it looks like a single or multiple nodular pigmented growth.
- Lipoma . Formed in the fatty layer of the skin. The affected epidermal tissue appears soft and nodular. It can grow to a maximum size of ten centimeters. Mostly a single tumor is formed, but cases of multiple neoplasias have been observed that form on unprotected areas of the skin. Formed after insect bites and various minor injuries. The nodules are rich in color and do not develop into larger formations in the future.
- Angioma . A neoplasm that forms on the inner walls of blood vessels and the lymphatic system. It looks like spots on the skin that disappear when pressed. Angioma is quite difficult to diagnose in the initial stages, due to its location and appearance (visually the tumor follows the structure of the vessel). Neoplasia forms both on the surface of the skin and on internal organs.
- An angioma, having formed in a vessel, disrupts its functioning and, naturally, is dangerous to a person’s general health. The resulting angioma on the face is a pink to bluish spot. The surface of neoplasia is varied (i.e., it can be both smooth and lumpy). According to the place of formation of angiomas, they are divided into:
- venous-cavernous
- mixed
- arteriovenous
Itchy bumps on hands – Arthrologist’s Office
Do you have terrible bumps on the sides of your fingers? Worried about how serious and dangerous it is? These may be bumps, blisters or swellings that appear small, bumpy or very raised.
They may indicate long-term skin diseases, disorders, or other immune problems.
This article will help you guess the causes based on their signs and symptoms, and also tell you about possible treatment methods.
Scabies
Scabies rash
Scabies is caused by an infestation of microscopic mites. They burrow into the human skin where they live and lay eggs. This is a highly contagious disease. Ticks can be transmitted from an infected person to another through direct skin contact, sharing bedding and towels.
Symptoms of scabies
- severe itching;
- small itchy red bumps;
- sometimes blisters appear if the itching becomes intense;
- Once the blisters appear, scabs (dry crusts) may appear.
Bone spurs and rheumatoid nodules
Rheumatoid nodules
If you suffer from arthritis, then there is a chance of getting inflammation around your joints due to bone friction. Your body will react by causing small, unsightly calloused and hard bumps. These are known as bone spurs.
Although they are not dangerous, they can be a source of discomfort. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis may develop red-pink, painless nodules or bumps.
chills
chills
This refers to an abnormal skin reaction to cold that results in small, itchy, red and painful bumps. These little bumps sometimes turn purple. If they cause the skin to burn, blisters usually form.
Risk factors include lupus, smoking and certain conditions that affect blood vessels. This condition can be corrected after diagnosis. Home remedies for chills include keeping your hands and feet warm and applying lanolin cream. Natural antiseptics are used to prevent infections.
Animal or insect bites
Insect bites also cause a rash on the skin, but the nature of the formation will depend on whose bite it is. For example, mosquitoes leave round, swollen, itchy or irritating bumps immediately after the bite.
The swelling may get worse depending on how your body reacts to the bite. For example, redness or inflamed bumps do not always occur after mosquito bites. But scratching and touching or pressing can increase swelling or increase pain.
In other circumstances, such as those associated with a bee sting, a severe allergic reaction may occur, resulting in swelling over a larger surface area. Some people may also experience hives, dizziness, swelling, etc.
Other common small critters that can cause bumpy swelling on the hands or fingers include midges, spiders, ants, wasps, caterpillars and mites.
Small or tiny bumps
The bumps that form on the fingers are often small or tiny, especially when the skin lesion is just beginning to show symptoms.
However, they may vary slightly in terms of color and appearance. As you can see from the photos above, they can be red, transparent or purple.
Depending on what causes them, they can also be hard, soft, or blistering.
Conditions such as dyshidrotic eczema, reactions to medications (immunosuppressants), chills, and specific small animal bites can cause small bumps on the fingers.
Itchy bumps on fingers
The rashes that become blisters on the fingers can be unbearably itchy. Here are their main reasons:
Scabies . If this condition occurs in children, the itchy rash can be harmful, given that young children cannot tolerate itching, especially at night.
Dyshidrotic eczema . Doctors need to do skin tests to find out what actually causes this condition. The itching and blistering may persist for up to several months before subsiding.
Other causes of itchy bumps on fingers are insect bites.
Formations that do not itch or hurt
Skin bumps (especially around joints) without signs or symptoms, such as itching or pain, and that do not go away completely on their own should be taken seriously. These painless bumps, whether small or very noticeable, should be seen by a doctor.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention
While some types of finger bumps will go away on their own within a short time, others must be diagnosed and investigated for proper treatment.
In addition to a routine examination by a doctor, many different tests and tests may be ordered, especially when symptoms are similar between different diseases. Diagnosis may include skin patch tests (checks for an allergic reaction), a biopsy or a blood test.
Treatment of dyshidrotic eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema has no reliable treatment, but it can be controlled with good skin care (moisturizing, cleansing) and avoiding factors such as moisture and irritants. Regardless, people need to learn and understand the types of eczema they are susceptible to in order to tailor treatment and manage the condition more effectively.
Other measures that may help:
- Using a humidifier in cold or very hot weather;
- maintaining proper care of fingernails and toenails;
- avoiding contact with tissues that irritate the skin;
- Controlling activities that may increase sweating.
Corticosteroid ointments for itchy bumps
Patients are advised to consult a physician before purchasing or using corticosteroid ointments and creams to avoid side effects or reactions.
Prescription ointments are preferred over over-the-counter treatments. However, your doctor should perform skin tests to prescribe the correct forms of medication.
Remedies for rashes from insect bites
Some insect bites, such as mosquito bites, usually go away on their own, although home remedies such as aloe gel (the pulp and juice of the plant) can help. However, if you do not know what is causing the bumps and blisters on your fingers, seek proper medical help or treatment.
Home Remedies
Appropriate home remedies are very helpful in eliminating symptoms and preventing further complications if the cause is benign and does not necessarily require seeking help.
Cold compress
A cold compress can be helpful for pain relief, especially if the lesions look like small blisters from a minor burn, skin injury, or poison ivy.
- Place ice in a plastic bag or heating pad. Wrap it in a towel or other cloth and apply it to the affected area for a few minutes. Repeat several times or every time you start to feel pain or burning in your skin.
- If the bumps are caused by a skin rash, you can use a clean washcloth. Dip it in ice water and place it on the rash for a few minutes.
Note: To relieve itching due to an insect bite, apply a cold compress as soon as possible when swelling begins.
WARNING : Never place ice cubes directly on blisters or open wounds on the skin.
Baking soda and coconut oil
You need baking soda (not baking powder) and some clean water. This method helps reduce itching and inflammation associated with the rash.
Procedure
- Add 1 part baking soda to three parts water and mix well.
- Apply the mixture to the affected area.
- Leave it on for a few minutes before rinsing off.
- Do this once a day for several days.
Alternatively
- Add a few drops of coconut oil for baking.
- Apply and leave for a few minutes and rinse thoroughly.
Note: Leaving baking soda on your skin for too long will cause further irritation.
Ground oatmeal
Colloidal oatmeal is an effective remedy for treating and improving skin. Officially included in the US Pharmacopoeia
Oatmeal is a well-known natural remedy for its anti-inflammatory and soothing properties, making it great for treating irritated and inflamed skin. Particularly effective for rashes caused by poison ivy, eczema, sunburn or allergies.
The easiest way to use this remedy for rashes is to wash the affected area with a paste of water and oatmeal.
Additionally, it can be combined with other natural products such as honey and milk powder to improve rash treatment.
Aloe vera juice
Among other healing properties, aloe extracts are excellent at reducing skin inflammation caused by rashes. It may also help reduce redness.
- Buy aloe vera extract/juice for skin or take fresh pulp from the plant.
- Apply this to the back of your hands, including your fingers.
- Leave for 20 minutes.
- Rinse with cold water (preferably boiled).
- Repeat the procedure at least three times a day.
Crushed aloe leaves have additional medicinal properties. They are used in traditional methods of treating psoriasis, eczema, skin dermatitis, as well as various types of allergic reactions on the skin.
Olive and castor oils
Olive oil enhances healing with its strong moisturizing properties and vitamin E. If desired, choose extra virgin olive oil (labeled extra virgin olive oil or virgen extra) or drugstore castor oil for skin rashes if you have minor itching.
You can mix the oil with honey or turmeric powder and apply it three times a day or as needed.
Apple vinegar
The acetic acid in apple cider vinegar is great for fighting infections. Use diluted vinegar if your skin becomes itchy. For best results, use raw, organic vinegar. The easiest way to use is to soak a cotton swab in apple cider vinegar and place it on the affected area.
More complex application method:
- Mix 2 tablespoons of olive oil with 1/4 cup of apple cider vinegar.
- Clean and gently dry the affected area of skin.
- Dip a small cotton ball into this solution.
- Apply it to the bumps or rash and leave for a few minutes.
- Repeat this periodically until you feel a change.
Apply a gentle antiseptic solution to prevent germs from multiplying.
Remedies for blisters on fingers
These remedies can relieve pain that is accompanied by blistering.
Aloe vera
Extract the aloe vera pulp and apply it on the blisters. You can cover the bandage with the bandage, but do not tighten it.
Cold water
If the blisters do not burst, apply a cold, wet cloth or washcloth to them to relieve the pain.
Tea tree oil
Once the pain has completely subsided, apply tea tree oil to prevent bacteria and germs from entering the affected area.
Make sure you keep the blistered area clean and dry at all times. Avoid scratching or piercing them. Without proper care or treatment for your skin problem, symptoms are likely to get worse.
Source: //kabartro.ru/cheshutsya-shishki-na-rukah.html
Malignant neoplasms
Malignant tumors that appear on human skin behave very aggressively. This manifests itself in an accelerated increase in the size of formations, the formation of additional lesions, and infection of adjacent dermal tissues.
The most common types of malignant tumors:
- Squamous cell carcinoma . This formation on human skin looks like a dense keratinized layer of the epidermis, which then degenerates into an ulcer that does not heal. Squamous cell carcinoma destroys the skin tissue adjacent to the ulcers and secondary foci of the disease form. Actinic keratosis can be a precursor to squamous cell carcinoma. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays and chemicals creates excellent conditions for this cancer. Like other types of malignant neoplasia, squamous cell carcinoma attacks neighboring skin cells, infecting them.
- Melanoma . The fastest growing malignant neoplasm, which consists of lumpy papules. Sometimes, under bad conditions, they degenerate from moles. This is why you should closely monitor any changes in nevi on your skin. Pay close attention to moles that are located on the head under the hair or in the perineum. These are the areas where nevi are most often injured. As in other cases of low-quality tumors, try to spend less time in the sun.
- Basal cell carcinoma . The most common type of cancer. It got its name due to damage to the basal layer of the skin. Features that characterize basal cell carcinoma are no metastatic foci, penetration into neighboring skin cells, parasitic growth. The formation is a papule with blood flow from its center. Basalioma is a subtype of squamous cell carcinoma. The site of tumor formation is in areas of the skin that are usually under clothing.
- Fibrosarcoma . A malignant cancerous neoplasm forms in the connective layers of the epidermis. Education can be both external and internal. The external formation rises slightly above the rest of the skin and is brown with a blue tint. Conventionally, fibrosarcoma is divided into:
- Poorly differentiated. It is fraught with dangerous consequences in the future.
- Differentiated. The size gradually increases; additional tumor foci do not form.
- Liposarcoma . The tumor consists of fat cells that have degenerated into malignant cancer cells. Formations reach significant sizes. Neoplasia grows slowly. The shape resembles a circle. Liposarcoma mostly affects older people. Sometimes metastases form.
- Angiosarcoma. A benign angioma tumor degenerates into a malignant angiosarcoma. This type of cancer is considered the most dangerous, as it often ends in death. Tumors appear in people with weak immune systems. Externally, this oncological disease looks like purple spots on which formations appear united with each other, transforming into ulcers in the future.
Cause of compaction
There is no clear answer to why a lump appears after a mosquito bite. Experts say that this is a peculiar reaction of the body.
It is believed that bumps from mosquito bites in a child appear as a result of an “unsuccessful puncture.” Similar to how lumps remain on the human body after an injection. The needle enters the vessel, it is damaged, and blood is found at the puncture site. The next day a lump appears there, which does not disappear for a long time. May be present for six months.
If the bump after a mosquito bite is accompanied by severe itching and redness, it is said that there is an allergic reaction. The mosquito injects an anticoagulant under the skin that thins the blood. The substance facilitates the feeding process, but causes an allergic reaction. The result is swelling and redness, itching, and a lump may form.
A standard situation is when a lump appears on a child’s head from a mosquito bite. When first aid is provided, the swelling goes away, the redness disappears, the skin calms down, and is completely restored after a few days. The child stops scratching the sore spot half an hour after treating the epidermis.
Important!
If a large lump from a mosquito causes discomfort to the child, it hurts, itches very much, and in addition there is a deterioration in general health, it is necessary to give the child an antihistamine and treat the lump with antiallergic ointment.
Borderline or precancerous skin conditions
Borderline or precancerous skin conditions are neoplasias that are in the stage of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Types of precancerous neoplasms:
- Bowen's disease . The disease is characterized by inflammation of skin cells and accelerated division of dermal cells, which subsequently leads to the development of squamous cell carcinoma. The lesion will most likely be on the skin of the temples, forehead, genitals or hands. Visually, the neoplasm looks like a rough pink to brown spot with slightly protruding edges. The tumor grows in size up to five centimeters. The human body can heal itself from this disease. But nevertheless, if the disease is left to chance, then in a few years you will become the owner of another more dangerous disease. You can determine the transition from Bowen's disease to one of the forms of cancer yourself, as it is quite simple. If ulcers appear on the surface of the neoplasia, degeneration into cancer has occurred.
- Actinic keratosis . This neoplasm appears most often in people aged forty-five years and older, but cases have been observed in young people with fair skin. It appears in skin that has been irradiated by solar radiation. The main danger from actinic keratosis is the progression to a more complex disease - squamous cell carcinoma. A sure sign of keratosis is rashes on those parts of the body and face that are not protected by clothing and hats. The formation looks like a round red plaque with a rough surface. Rashes occur in the following forms:
- warty
- hypertrophic
- erythematous
- horny
- pigmented
Diagnosis of neoplasms
As soon as you discover a new skin formation on your body or face or a change in a mole, you need to contact an oncologist. A qualified specialist in appearance is able to determine an approximate diagnosis. And with the help of a biopsy, the goodness or malignancy of the neoplasm is determined. Therefore, do not try to diagnose a skin lesion on your own, but immediately contact a specialist.
Treatment and removal methods
Only an oncologist has the right to choose the method of treatment for a new growth on your skin. He will make a choice based on a biopsy of your tumor, as well as the type, rate of growth, location and extent of the tumor.
Basic treatment and removal methods:
- Surgery . Removal of tumors is the most common treatment method. The tumor is excised completely, together with the surrounding healthy skin tissue and lymph nodes.
- Radiation exposure . Used for small formations. The disadvantage of this method is that the surrounding uninfected skin cells are destroyed.
- Cryogen . This removal method uses liquid nitrogen.
- Chemotherapy . Used when surgery is no longer possible. Chemotherapy is usually combined with radiation.
Your oncologist will determine which treatment method is right for you. They are all good in their own way.