How not to miss the appearance of head lice?
Pediculosis of the scalp occurs as a result of infection with a head louse, and it is very difficult to detect it on the hair, because its size is up to 5 mm in length.
Lice infection occurs only from person to person and through personal hygiene items: combs, hats. In an environment without a host, a head louse can live no more than 2 days.
It is almost impossible to determine the moment of lice infestation. The fact is that the obvious symptoms of lice: severe, almost constant itching, nits on the hair appear about a few weeks from the moment of infection.
A mature individual feeds approximately once a day (1 bite), the female lays no more than 14 eggs daily, and larvae from eggs (nits), which also feed on blood, are formed no earlier than a week later. Accordingly, at least 7 days pass from the moment the parasite gets on the hair until obvious signs appear. Find out more about how long and how lice live here.
It is very difficult to suspect the appearance of lice on the head, both in children and adults.
Typically, children do not complain of an itchy scalp until severe scratching occurs until they bleed, which begins to tingle the next time they wash their hair. Adults begin to suspect lice when the itching begins to be periodic.
What are black dots in the head?
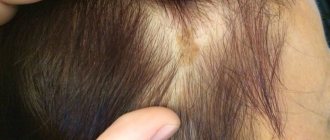
The concern of parents caused by the discovery of black spots on the child’s head is completely justified, because such a symptom may indicate the presence of diseases with serious consequences.
In order to identify the probable cause, it is necessary to know a number of characteristics of the pathological signs of the scalp.
There may be several reasons for the development of black dot formations on the scalp of a child; their etiology, diagnosis and treatment differ significantly.
Important: It is strictly forbidden to try to squeeze out or puncture dark spots. This can cause infection, the transition of a non-malignant tumor to a malignant one, and other transformations that pose a threat to the health of the baby.
Open comedones
With closed comedones, white dotted formations appear, and with open comedones, the black color is due to oxidative processes in the presence of atmospheric oxygen entering there. They are clots of secretion from the sebaceous glands at the base of the hair follicles and form into small cysts from impurities and sebum.
Open comedones are the most common cause of such spots.
- Clogged skin pores. In infants, the pore opening has a minimal size, much smaller than in an adult, which makes the risk of blockage more likely to occur than in other age categories.
- Insufficient facial hygiene. Prevention is done by thoroughly washing and wiping your face with special products.
- Genetic predisposition. If parents have this problem, then their child will most likely have open comedones on the scalp.
- Consequence of taking medications. When such drugs are discontinued, the problem disappears after a few days without the use of additional therapy.
- Diseases of the liver, gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system.
To carry out a diagnosis, you need to contact a pediatrician, who will conduct an examination and give referrals to specialists or prescribe treatment independently.
- Prescriptions of drugs for topical use based on salicylic acid.
- The use of keratolytics to soften the contents of a clogged pore and facilitate the release of the secretion of the inflamed gland to the surface of the dermis.
- Avoid frequent contact of the scalp and hands, especially in public places (transport, supermarkets, etc.).
- Maintain hygiene, carry out water treatments, wash your hair using special shampoos.
- After steaming the head, perform mechanical combing to prevent clogging of the pores with sebaceous secretions.
Trichophytosis
The causative agents of this pathology are mycoses (fungi).
Due to damage by mycotic elements, growth stops, fragility increases and hair breaks at the base of the scalp. The broken areas look like dark dotted formations. They are usually localized in the occipital and temporal regions.
- The hair shaft breaks off at the point where it exits the scalp.
- It is difficult to diagnose because the onset of the disease is not pronounced: single fractures are difficult to detect. Bald spots become noticeable only after a significant aggravation and spread of the disease to lesions with a diameter of 1 - 2 cm. By this point, from one to three months have passed, the mycoses have shifted to the middle and deep subcutaneous layers.
- In some cases, mycoses of a trichodermal nature, in the absence of correct treatment, spread to the keratin layer of the nail plates of the hands and feet and become systemic.
- In connection with the visualized foci of dark dots, the disease acquired the name “black dot trichophytosis”.
- The causative agents of a number of trichophytosis are anthropophilic fungi, specific parasites of the skin and the internal cavity of human hair.
- Another category of pathogens are zooanthropophilic fungi. These mycoses are transmitted to humans through contact with animals. They surround the hair follicle and cause inflammation.
- In boys, self-healing may occur in the first year of life.
- In girls, in the absence of targeted treatment, it becomes chronic and causes severe hair thinning, and in severe cases, complete baldness.
- Infection through tactile contact with sick animals (cows, horses, mice, stray cats and dogs).
- During communication with people who are carriers of “black dot trichophytosis”.
- Use of personal hygiene items for sick people. The fungus colonizes and the hyphae gradually grow into the skin structures.
- Acute hypovitaminosis of vitamin A reduces immunity to fungal diseases.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine system (multiple dysfunctions of the endocrine glands).
- Based on the classic manifestations, the dermatologist classifies the symptoms and gives directions for all the necessary tests.
- If necessary, the diagnosis of a newborn is agreed upon by a mycologist and an infectious disease specialist.
- A scraping is taken for microscopic examination for the presence of mycorrhiza. The mother can get acquainted with the results of the analysis in half an hour - an hour.
- In some cases, differential diagnosis is carried out with cultural identification of the pathogen. To obtain results, you need to wait a few days (4 - 7), during which, during a bacterial analysis on a nutrient medium, the spores obtained from scraping the newborn’s head will germinate. This type of analysis allows you to determine the sensitivity of the fungus to various types of drugs.
Source: //womaninred.ru/chernye-tochki-v-golove-chto-jeto/
The first signs of lice on the head
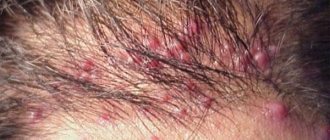
The first signs of head louse pediculosis are the appearance of moderate itching on the scalp, which is a consequence of parasite bites, and slight redness in the affected areas.
Itching occurs mainly in the back of the head at the base of the neck, above the ears. It intensifies at night and is especially pronounced after shampooing, when the hair is still damp.
Children become restless, inattentive, and when examining the scalp, scratching and scabbed skin lesions can be detected.
- Carefully inspect your scalp for lice bites, which appear as red or pinkish vesicles. Most often they can be found in the area above the ears and in the back of the head.
Take a magnifying glass and carefully examine the skin. At the base of the hair you can find the parasites themselves, which look like gray poppy grains.
Next, inspect your hair for lice eggs (nits). Nits are small white specks (3 - 5 mm) that look like dandruff. They cling to the hair. If you find a white speck on the hair that is not brushed off, but is tightly attached to it, then this is a nit.
If you find nits, take a fine-toothed comb or a special comb and a white sheet of printer paper.
Tilt your head slightly forward and run the comb through your hair several times. Flakes or grains resembling dandruff should fall onto the sheet, which look slightly grayish against the background of the paper. Try crushing the grain by holding it between your nails.
If during the crushing process you hear a cracking sound (click), then this grain is a nit, and the presence of lice on the head is beyond doubt.
A frequent companion to pediculosis is lymphadenitis (enlarged lymph nodes that are painful when touched) of the neck and occipital region. The skin in areas of scratching is prone to suppuration, tangling of hair, and the formation of tangles.
Parasites in human hair on the head: how to get rid of the disease
The term “parasites” refers to a whole group of various parasitic microorganisms - lice, mites, protozoa, bacteria and other individuals.
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
Read more "
They feed on soft tissues and useful substances, are capable of multiplying and intensively dividing in the human body, as a result of which a number of negative symptoms arise.
Lice are small insects that land on the scalp and can multiply in the hair. Most often, lice are found in children who go to kindergarten, school, or other public places with large crowds of people.
When the scalp becomes infected with such parasites, a parasitic disease called pediculosis develops. It is observed in patients until the person is completely free of lice.
Apart from humans, head lice are not able to parasitize other organisms. This feature is the high level of adaptability of lice to live and reproduce on the human scalp.
No one is immune from the appearance of lice; they can appear at lightning speed on a person’s scalp, so it is important to detect their presence in time in order to undergo appropriate treatment.
Appearance of lice
Parasites have a faded, whitish, and sometimes grayish color. They have three pairs of legs. They are easy to notice visually on the scalp, but lice are very agile and are able to quickly move from one place on the head to another.
Nits are the specific membranes in which lice eggs are located. They consist of a sticky substance, so they are quite difficult to separate from the hair. Any nit contains only one egg. As a rule, they are attached to individual hairs.
If a person has lice, the first thing you might notice is the nits. They are small oblong white balls that stand out especially against a dark background - dark hair.
When there are a huge number of lice on the hair, even after careful hygiene procedures, in particular, washing the scalp, it seems that small white grains have been scattered on the hair.
Features of the appearance of nits:
- The size of the nit is approximately one millimeter.
- Outwardly, it looks like a round and oblong ball.
- When examined under a microscope, you can notice the adhesive component in the shell.
It is worth noting that nits have a “small cap”, which, when the egg matures and turns into an adult, easily opens and releases parasites into the hair.
Causes and symptoms
Since parasites appear in places with poor sanitary and hygienic conditions, the main reason for their appearance is failure to comply with basic hygiene rules. Lice can be transmitted through underwear or bedding, through hats and other personal items.
An interesting fact, but lice can exist freely in open bodies of water, and even in a swimming pool where sanitary and hygienic requirements are not met. Swimming in them can cause you to become infected with lice.
In a number of situations, parasites can “hide” in the folds of clothing, where they lay their eggs; it is almost impossible to detect them. However, they crawl onto human skin to feed; in this case, areas of the skin such as the armpits, groin area, and back are affected, that is, in those places where clothing fits most closely to the human body.
Lice can also appear under the following conditions:
- Long journeys, trips when it is not possible to fully comply with hygiene rules.
- Seasonal work with large crowds of people.
- In children's institutions where children closely communicate and make contact.
- In other places where there are large crowds of people (sanatorium, hospital).
It is in such places that you should follow all the rules of hygiene and do not forget about preventive measures, which will avoid infection, thereby eliminating subsequent treatment.
As practice shows, the appearance of lice is quite difficult to notice. In some cases, parasites can manifest themselves immediately after a couple of days from the moment of infection; in other situations, they can remain on a person’s head for a couple of weeks, and there will be no signs of their presence.
As a rule, lice especially affect the back of the head and temples of a person's head. The following signs may be observed in this area:
You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of regular...
Parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach...
- Severe itching sensations, as a result of which a person scratches the scalp, sometimes until blood appears.
- The affected parts of the head can fester, resulting in the formation of ulcers, boils and other pathological phenomena.
- With a prolonged course of the disease, the scalp becomes denser and pigment spots appear.
In good lighting, you can visually observe nits on human hair that are attached to them. Usually they are located as close as possible to the root structure of the hairline.
Demodex: causes and symptoms
Demodex is a mite that can live and parasitize on the human scalp, in the sebaceous glands and glands of the cartilage of the eyelids. The parasite is small in size, not exceeding two tenths of a millimeter.
The main symptom of the presence of the parasite is redness of the edges of the eyelids, with painful sensations present, the eyelids are constantly irritated and itchy. This condition intensifies at night, and it is very difficult to endure; sometimes there is discharge from the eyes - it can be mucus or a foam-like liquid.
Demodex in women can lead to a white coating on the eyelashes or their complete loss. In addition, patients complain of constant lacrimation, redness of the eyeballs, and a feeling of “garbage” in the eyes.
Demodex can appear in any person, for example, due to the abuse of cosmetics that contain hormones, or when the skin is damaged, as a result of which an infection gets into the wound.
If there is a high number of demodex mites in humans, the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Acne and pink spots appear on the skin of the face.
- Itching in the hair.
- The skin of the face becomes lumpy and uneven.
- Individual symptoms - excessive expansion of pores on the nose, forehead, cheeks.
If the hair follicles are infected and treatment is not carried out, then over time the hair begins to fall out, and the person slowly but surely goes bald. It is worth noting that demodex, due to the release of a special substance, can provoke a malfunction in human metabolism.
There are two types of mites - one lives in the hair, and the second parasitizes the sebaceous glands. If the patient's eyes are affected, a microscopic examination of the eyelashes is performed. When there are lesions on the skin of the face characteristic of this parasite, a scraping is taken from the affected area.
Treatment of such a problem is difficult, and its duration can be up to six months. Treatment of the disease is aimed at the following goals:
- Increase the body's defenses, strengthen the human immune system.
- Eliminate parasitic microorganisms.
During therapy, antihistamines are prescribed to get rid of allergies. These can be a variety of ointments, gels or tablets. Treatment for mites on the face includes the following medications:
- Demalan (ointment) promotes increased tissue regeneration and is applied to the affected areas of the skin.
- Prenacid reduces the manifestations of an allergic reaction.
If a purulent manifestation of blepharitis has developed, the doctor recommends antibacterial medications. The most proven ones are Colbiotsin and Eubetal.
It is worth noting that you cannot get rid of such a mite on your own, and alternative medicine will not give the required effect, although there are options for treating demodex on the face at home, but they must be supported by traditional medicine.
Only the attending physician will draw up an adequate treatment regimen and help get rid of the problem.
Treatment and prevention of lice
Treatment of lice consists of choosing specific medications that act on the parasites, as a result of which their vital functions are inhibited and they die.
Despite the fact that the pharmacological market provides a huge selection of drugs, they will not help get rid of nits. The best way to get rid of them is a fine comb.
To get the desired result, the lice destruction procedure must be carried out several times. After each hair treatment, it is imperative to comb it with a fine comb to remove dead parasites.
The pharmacy sells many products that help get rid of parasites. But it is worth remembering that such drugs contain quite dangerous substances. In this regard, they are used carefully, adhering to the official instructions for use.
Treatment of pediculosis is carried out with the following medications:
- An effective product, Nittifor, is available as a cream or solution.
- Medifox comes in two types - gel or emulsion.
- Pedex - gel or lotion.
Treatment of the disease can be carried out at home, without consulting a doctor. However, there are situations when self-medication is strictly prohibited:
- Young child up to 2 years old.
- There is a history of allergic reactions and bronchial asthma.
- If nits are found on eyelashes or eyebrows.
After getting rid of lice, you need to reconsider your lifestyle, as well as your personal hygiene rules. Basic preventive measures for pediculosis:
- Wash your hair regularly, using only high-quality washing products.
- Regular change of underwear and bed linen.
- Constant hair care and combing.
- Limit contact with people who have parasites.
- Do not give your items for personal use.
In any case, the main recommendation to help prevent parasitic diseases is to follow basic hygiene rules, as well as be attentive to your health. These measures will help prevent infection and maintain human health. A specialist will tell you how to get rid of lice in your hair in the video in this article.
- Parasites in the human head: symptoms and treatment
- Parasites on human facial skin: acne and rashes
- Fascioliasis: treatment and symptoms of the disease in humans
What to do if detected?
What to do if lice appear on your head? You can get rid of lice at home by combining chemical and mechanical methods.
Anti-lice products mainly contain the active ingredient permethrin, which is a strong poison for insects.
Along with applying chemicals to the scalp, it is necessary to comb out nits from the hair using a fine-toothed comb or a special comb.
The effect after treatment occurs the very next day. To eliminate residual itching and relieve inflammation from the scalp, you can rinse your head with decoctions of medicinal anti-inflammatory herbs: string, chamomile, calendula.
What products are not recommended to be used?
The best measure to prevent acne in infants is to comply with basic hygiene measures, as well as the diet of mother and baby. If the baby is bottle-fed, the selected formula should suit the body as closely as possible without causing any cause for concern.
For the treatment of rashes it is not recommended to use:
- Oils and ointments with a fatty consistency;
- Alcohol solutions;
- Hormonal drugs;
- Adsorbents or lactic acid bacteria;
- Antihistamines;
- Antibiotics;
- Creams and gels intended for the treatment of adults.
Useful video:
Despite the fact that in most cases the appearance of red dots is absolutely harmless, the problem cannot be ignored. Treatment measures also depend on exactly how the red dots appear, so pediatricians strongly advise parents not to self-medicate!
Useful video
Pediculosis: truth and myths - all the details in this video:
[youtube.player]
Black lice are one of the varieties of blood-sucking ectoparasites, the appearance of which is caused by the infection of a healthy person by an infected one. Depending on the species of parasites and the specifics of their localization, several types of parasitic diseases are distinguished - pediculosis, phthiriasis.
To remove black lice, it is permissible to use chemicals or safer folk remedies. How to promptly detect infection with pediculosis and phthiriasis, get rid of parasites, and prevent their appearance - we will consider further.
Are there black lice and nits?
The color of skin parasites that feed on the blood of animals and humans can vary from light brown, yellowish to black. It turns out that black lice exist and belong to the species that parasitize the human scalp. They are large in size - up to two millimeters, and lack the ability to jump.
For comparison, the so-called pubic lice are minimal in size and light in color. The most common symptom of lice pubis is the appearance of severe itching and red spots in the groin area. Unlike head lice, pubic lice can only be picked up through sexual intercourse or when trying on someone else's underwear.
Are there black nits?
Since an adult insect differs from larvae and eggs in having the ability to move quickly, it is difficult to visually detect the appearance of parasites. A characteristic external sign of lice infection is the appearance of black dots and nits on the hair, while the former are waste products of insects.
There are no black nits, since the color of parasite eggs can vary from white to gray, dark shades are excluded.
Pubic louse
The pubic louse differs from the head louse in its smaller size and body shape, reminiscent of a crab. Another name for it is flat. It lives on the genitals, armpits, beard, and rarely on eyebrows and eyelashes. That is, on the hairy parts of the body, except the head. The greatest chance of becoming infected with this type of lice is in people who are promiscuous. But the risk of infection in public places, such as a dormitory, bathhouse, toilet, swimming pool, is also high.
First signs
This type of disease is never asymptomatic, so it is quite easy to recognize it by the following signs:
- severe itching, burning in the affected area, the symptom intensifies with an increase in the number of parasites;
- dark small dots on underwear are waste products of insects;
- blue spots in the area of bites;
- when checking, it is easy to see individuals and their larvae on the hair;
- If lice parasitize in the chest area, you can find crumbs similar to dandruff.
In advanced cases, eczema, blisters, and wounds form.
Clinical manifestations in children
In children, phthiriasis manifests itself in the form of conjunctivitis, myopia, chalazion, and blepharitis. Such diseases are caused by lice located on the eyebrows and eyelashes. In these places, parasites are more common in young children due to poor personal hygiene of the infected adult, namely, through a towel or bed linen.
Consequences of pubic mites
Lice are carriers of infections. Therefore, it is recommended to be tested for syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia and other sexually transmitted diseases.
Treatment
For quick and better results, you need to remove hair from the affected areas before treatment. Or rinse your hair with a solution of vinegar and water. This manipulation is carried out to dissolve the adhesive substance, with the help of which lice and larvae are firmly attached to the hair and skin.
After this, use special shampoos, ointments, sprays or anti-inflammatory medications prescribed by your doctor at least twice. The products have contraindications, so you should contact a professional or at least read the instructions for use. The sexual partner must also undergo treatment; the risk of infection is high.
It is necessary to disinfect the environment: wash everything that can be done at high temperature, or better yet, boil it in a soda solution, then carefully iron it on both sides. Those things that cannot be wetted should be sealed in bags and left for two weeks to naturally destroy parasites. It is good to vacuum the carpets, wash the floor, and do wet cleaning.
Reasons for appearance
The appearance of black lice and nits on hair is the result of an infection that can occur due to a number of factors.
Where do black lice come from and how can you get infected with them:
- Visiting various public places, for example, a swimming pool or bathhouse, traveling on public transport.
- Upon contact with a person infected with black lice or the belongings of an infected person.
- When exercising in gyms on fleecy surfaces.
- During sleep, for example, in a hotel, camp, sanatorium, kindergarten or other government institution.
- Infection with pubic lice occurs after sexual contact or wearing or trying on someone else's new underwear.
Black lice infestation can only result from contact between infected people. Transmission of parasites from animals to humans is excluded.
Important! Ectoparasites that live on animals can only live on a specific host. In the absence of the required amount of food, they can attack humans, but their constant parasitism on the skin or hair is excluded.
How can a healthy, prosperous child become infected?
First of all, it is worth clarifying that children become infected directly from a sick person, but also through things. So, in what situations can a child “shelter” an uninvited guest unnoticed?
- Direct contact of heads - when children hug, play with each other, for example, enthusiastically bowing their heads in the sandbox or over a board game. The longer the hair and the more freely it flutters, the easier it is for the parasite to crawl.
- Transfer through personal belongings. There is a high probability of catching the parasite if a child “out of friendship” exchanges clothes with an infected baby - these can be hats, scarves, as well as hair clips and combs.
- Sleeping in the same bed is a factor in the spread of parasites to brothers and sisters, and also, sadly, to mothers.
- A child has a small but definite chance of becoming infected, even if he does not attend kindergarten or is home-schooled. Head restraints in public transport seats are also a likely source of the disease.
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
So, as we have seen, it costs nothing for a small child to become infected. And for this parasite, it doesn’t matter at all whose head it runs on - the child of wealthy parents or whose income leaves much to be desired.
Signs of presence
A black louse in the head provokes a number of unpleasant symptoms.
The main signs indicating a lice infection are:
- Severe itching of the scalp. With a large number of black lice, discomfort increases, scratching on the skin, wounds, and inflammation appear.
- The excrement of parasites, which are often mistaken for black nits. They can be described as small black dots.
- Directly, lice eggs or nits, which are white or gray in color, are attached to the hair shaft through thick mucus.
Black lice are carriers of a number of dangerous diseases of infectious etiology, helminthiasis. Infection with parasites can cause the development of hepatitis, tuberculosis, intestinal infections, ascariasis, and a number of other unpleasant, dangerous diseases. To prevent dangerous consequences, it is necessary to treat pediculosis immediately after the first signs of invasion appear.
Methods of disposal
The modern market offers a wide range of different means, through the use of which you can remove lice and black nits. To remove a small number of parasites, it is enough to use anti-pediculosis shampoos and home remedies.
In case of severe infestation, the use of toxic pharmaceutical drugs is required, which have a detrimental effect on adult parasites, larvae, and eggs.
It is necessary to use the chosen remedy until the parasitic disease is completely eliminated.
In severe forms of parasitic infestation, getting rid of lice can only be done by using pharmaceutical products that contain toxic substances. Such drugs should be used with extreme caution, since violation of the instructions may cause poisoning.
The most popular pharmaceutical drugs are:
- Hellebore water. To destroy black lice, you need to thoroughly treat the hair strands and skin with liquid, and then put on a plastic cap.
- A simple and cheap remedy is boric and sulfur ointments. They have a detrimental effect on lice, but do not destroy nits. To get rid of parasites, regular use of the selected product is required for at least two weeks.
- Medifox. An emulsion that is highly effective against adult parasites, but does not have a negative effect on parasite eggs. It is necessary to treat hair and skin until the parasites are completely destroyed.
- Pedilin. A highly toxic shampoo that can be used to kill eggs and adult parasites. Contains insecticidal agents that are harmful to lice. To obtain the desired effect, you need to apply a small amount of the drug, lather thoroughly, leave for some time, and rinse.
Before choosing an effective remedy against black lice, it is recommended to consult with a specialist, since toxic anti-lice drugs have a wide range of contraindications.
Most anti-lice medications contain toxic substances that can be dangerous for children and pregnant women. When parasites appear in people of the above categories, it is recommended to use the simplest but most effective method: generously apply any vegetable oil to the scalp and hair, then put on a polyethylene cap.
This remedy helps get rid of adult parasites, but does not have a harmful effect on their eggs.
Accordingly, to remove insects, it is necessary to repeat the procedure periodically for at least two weeks.
You can get rid of black lice at home by using simple folk remedies. Their use is completely safe, but has a low level of effectiveness. To destroy lice, repeated use of the selected product is required.
The most popular alternative medicine recipes:
- Tea tree oil mask. To prepare the product, you need to mix the specified oil, high-quality medical alcohol, and water in equal proportions. Apply the product to your head, put on a polyethylene cap, and leave for one and a half to two hours. After completing the procedure, rinse your hair thoroughly with shampoo.
- Pomegranate juice . Boil two glasses of freshly squeezed juice for three minutes, after adding several mint branches to the liquid. Apply the resulting home remedy to your hair and leave for two hours.
- Cranberry mask. Mash a couple of handfuls of berries thoroughly, apply to your hair, and put on a polyethylene cap. After a couple of hours, wash off using any shampoo. Fresh cranberry juice contains natural acids that destroy the sticky mucus that glues nits to the hair.
After using any folk remedy, you must comb your hair using a sparse comb. Carrying out this procedure will help remove adult black lice and nits. To make combing easier, you can apply a small amount of geranium essential oil to the comb. After each combing, it is important to treat the comb with soapy water and boiling water.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will get + to karma
[youtube.player]
Lice are quite an unpleasant problem that no one wants to deal with. But not many people know that infection with these parasites is considered a real disease called pediculosis. And if it is not detected in time, then such an illness can lead to serious consequences and complications in the form of advanced dermatitis or pyoderma. In addition, lice are the causative agents of many infections. Therefore, the sooner they are identified, the fewer difficulties a person will have to face.
However, it is difficult to immediately notice such parasites. The symptoms indicating their appearance can be so unnoticeable and insignificant that a person does not even realize that they are infected. And in order not to worsen the situation, you need to learn to identify these parasites in the early stages, especially if they have started on a child’s head.
Features of lice and ways to detect them
Lice are tiny insects characterized by their translucent body and small size. They do not have wings and cannot jump, but they move nimbly and quickly on their six legs. An adult lives about 5 weeks. The female is capable of laying up to 20 eggs (nits) daily, after a week they form larvae that can cause as much discomfort as a large individual.
These insects hide near the hair roots and can be difficult to detect due to their appearance. Difficulties arise if a person’s hair has a similar shade to the body of the lice. But if you conduct a thorough examination of the scalp, then the presence of these parasites can be detected. To do this, it is better to use a comb with wide teeth so that it is convenient for her to move apart the hair strands. However, if the infection has only recently occurred and we are talking about one or two insects, then it is difficult to immediately recognize their presence, since they know how to hide among the strands.
Typically, lice are located either on the skin itself or on the hair shaft, but closer to the base of the bulb. There may be red dots on the surface of the head, indicating a bite from these insects. And upon careful examination, you can find nits that look like small white larvae. However, usually their obvious manifestation becomes noticeable already at the last stage of infection. But there are other signs indicating the presence of these insects.
Early symptoms of lice
- Itching. The child scratches his head intensively, at night and during the day. An astonished parent, having examined and found nothing suspicious (no white or black dots), may attribute the phenomenon to an allergy - but antihistamines have no effect.
- A rash, red spots on the scalp can also make a parent think about an allergy. Especially if the child is a girl and the parents use different care products - for example, a new brand of shampoo or means to make hair easier to comb.
Many children have red spots on their heads that appear at the time of birth, when passing through the birth canal. These “angel kisses” are usually located on the forehead and just on the back of the head. But, as a rule, after the first year of life they turn pale. In the case of lice, spots appear not only directly on the back of the head, but also closer to the ears; they are bright red.
- Scratching may also be visible at the sites of parasite bites (yes, these insects are not shy and bite children, so extermination measures must be the most stringent)
- The presence of the mentioned eggs is nits. It is worth considering that nits will not remain “harmless” spots on the hair for long, and after about a week, new parasites will form from them, eager to feast on the baby’s blood.
What to do?
If your child gets itchy and it has nothing to do with a new shampoo, dandruff (which also requires treatment, but in a different way) or an allergy, run to the doctor, especially if the child is 2-3 years old. Of course, modern means make it possible to get rid of parasites relatively painlessly, and they are recommended for use by children from two and a half years of age. But complete control of the cure is possible only under the supervision of specialists.
Fortunately, this is the 21st century and there is no need to shave off the luxurious hair of children. As well as pouring kerosene, more modern products based on permethrin have appeared in the arsenal of mothers. Short hair can be treated with cream, while long hair can be treated with an aerosol.
However, all other “old-fashioned methods” of controlling the spread of parasites remain in force:
- The child must be isolated from visiting child care institutions for the duration of treatment,
- All bedding (both children's and adults) must be washed in a washing machine at 90 degrees or boiled. The same applies to hats and scarves.
- Clean linen must be ironed with steam on both sides (this is when this measure is really necessary!)
- Carefully examine the hair of other family members (including fathers and mothers), as well as pets.
- If parasites are detected, all victims must be “treated” at once!
Symptoms of infection
You need to pay attention to itching and suspect that you have lice if this sensation bothers you at night and does not go away after thoroughly washing your hair. As for children, the alarm should be sounded when the child constantly scratches his head, combs his hair with a brush for a long time, regularly straightens and touches it. If these parasites appear in very young children who cannot report any discomfort, then you can find out about this by their changed behavior. They become moody and may cry constantly and for no reason.
On dark hair, when there are a lot of lice and their intensive reproduction occurs, you can see white larvae. These are nits that look like light dots. They are located at different distances from the root of the hair shaft and on dark hair a person can easily detect them. And even when the nit matures and leaves its larva, its white and dry shell can remain on the hair for some time.
Complications of advanced pediculosis
When the stage of infection by these parasites has already advanced, the patient may experience symptoms indicating advanced stage of lice. This:
- nervous disorders that develop due to constantly present itching;
- groundless and regular irritability;
- the appearance of ulcers at the bite sites due to their re-infection;
- pyoderma (skin lesions with changes in pigmentation and leaving scars);
- deterioration in sleep quality.
A person also begins to see crawling insects everywhere and feel them on his skin, even if they are not visible during a normal cursory examination. Some people may have a reaction to lice bites, resulting in a severe allergy. And at such a moment the temperature may rise and the lymph nodes may enlarge.
After recovery...
Measures to prevent re-infection are similar to measures of primary prevention and largely involve explaining the rules of behavior:
- The child must be taught that he should not exchange clothes (hats, scarves, snoods) even with close friends - just like using other people’s combs.
- Also, you should not use someone else’s towel (this measure is intended to protect not only from lice).
- Girls should be taught to braid their hair and have moderately tight ponytails when attending kindergarten.
- Of course, parents should carefully comb their baby’s or toddler’s hair every day, and periodically inspect it to eliminate the notorious white (eggs) and black (lice) “dots.” Especially if the child is of kindergarten age and cannot yet fully comb his hair and do his own hair.
In the matter of prevention, regular hygiene procedures come to the fore: regularly wash your hair, get a haircut, change clothes and bed linen. And then, with a high degree of probability, the unpleasant illness will pass you by. Well, if not, and according to the indicated signs you find uninvited guests, you should not faint, and, moreover, beat yourself in the chest and shout “Shame!” No one is immune from infection, just like from respiratory infections.
Itching with pediculosis
Head lice often cause significant itching on a person's scalp. This itching does not occur as a result of lice bites, but is an allergic reaction to these parasites.
However, not everyone is allergic to head lice, so you or your child may not even realize that you have head lice.
Even if a person is allergic to lice, itching may not occur immediately. Sometimes itching occurs three months after infection.
In some cases, a rash may appear on the back of the neck as the body reacts to lice droppings.
Lipomas
A better known name is wen. Occurs due to the proliferation of adipose tissue. It acquires a dark color when an inflammatory process occurs. Without inflammation, it does not pose a health hazard, does not develop into malignant tumors and does not cause pain.
If the lipoma surrounds the hair follicle of a child with brown or black hair, it will turn black.
Reasons for appearance:
- Hormonal disbalance
- Imbalance in the composition of breast milk or infant formula
- Endocrine system dysfunction
- Diseases of the kidneys and excretory system
Diagnostics:
- When examined by a trichologist or dermatologist, most often a visual examination is sufficient to determine the type of lipoma of the scalp.
- In rare cases, MRI, tomography, and ultrasound examination are performed.
Treatment methods:
The choice of method is dictated by the age of the baby and the degree of complexity of the case.
- Laser method: absolutely painless, does not require the use of anesthetics. After the procedure, rapid healing occurs, and the risk of postoperative complications is minimized.
- Aspiration: a puncture is made with a needle and the contents of the lipoma are extracted through a hollow canal using evacuated vacuum.
- Conservative treatment: a drug is injected into the cavity of the lipoma to promote the assimilation (resorption) of the formation cells.
- Surgical removal. Surgeons avoid using this treatment for up to 5 years, but in some cases surgery is inevitable. The choice of anesthesia (local or general) is determined by the characteristics of the child’s body and health indicators.
Life cycle of head lice
The female head louse lays eggs (nits) by sticking them to the hair (often close to the root), where they are kept warm by the scalp. The eggs are very small and therefore very difficult to see.
After 7 to 10 days, the lice begin to hatch, and the empty egg shells remain glued in place. Nits are white in color and due to constant hair growth, they become more noticeable over time.
Head lice bite through the scalp and feed on blood. From birth, it takes approximately 10 days before the young individual reaches maturity. It is usually the adults who crawl from head to head, and the female head louse can begin laying eggs nine days after she hatched. Therefore, to break the vicious cycle and stop their spread, they must be removed within nine days of hatching.
Head louse - photo
How to detect lice
It is quite difficult to detect lice on a child’s head simply by examining it - scratching makes it possible to more easily detect these parasites.
Searching for lice using a comb can be carried out on dry or damp hair, but combing wet hair makes it possible to more accurately determine the presence or absence of lice on a person’s head, since lice remain motionless when wet.
To find lice, you need to use a special fine-tooth comb, which you can buy at your local pharmacy. The comb has a tooth spacing of 0.2-0.3 mm, which makes it possible to comb out even the smallest lice.
A nit comb is not suitable for finding lice because the teeth are too close together. Lice can become trapped between the teeth and go undetected.
To detect lice on a wet head, you need to follow these steps:
- Wash your hair using regular shampoo and apply plenty of hair conditioner. Use a wide-tooth comb to straighten and detangle hair.
- Once the comb has started to comb the hair freely, begin using the comb to detect lice. Make sure that the spaces between the teeth of the comb reach the roots of the hair, lightly touching the scalp.
- Run the comb down to the ends of the hair each time, then check the comb for lice.
- Remove lice from your comb using a tissue or by rinsing it under the tap.
- Methodically comb the entire head area.
- Rinse the conditioner and repeat the procedure for combing wet hair.
To detect lice on a dry head, you need to follow these steps:
- Use a regular comb to straighten and detangle your hair.
- Once the comb moves freely through the hair, begin using the comb to locate lice. Comb your hair from the scalp to the ends of the hair, brushing absolutely every section of the hair three or four times before moving on to the next step.
- Inspect the comb for lice after each combing and remove any caught between the teeth.
- Continue combing your hair section by section until you have combed your entire head.
If you find a live louse in your hair, it means there is an infection and the person suffers from lice.
Combing lice out of the head is necessary not only to diagnose head lice, but also to treat this parasitic disease.
If you find lice in your child's hair, you need to check the rest of your family and alert close friends.
There is no need to keep your children away from school. Most likely, this parasitic disease has been going on for several weeks, so refusing to visit this establishment is unlikely to affect the spread of lice.
A simple itchy scalp doesn't necessarily mean you have lice. The diagnosis can only be confirmed if a live louse is found in your hair.
The itching may continue for days or weeks, even after all lice have been successfully removed from the scalp. In some cases, itching does not begin until several months after infection.
Treatment of pediculosis
Complete removal of head lice is a rather labor-intensive task due to the fact that it takes a lot of time, requires regularity and strict implementation of procedures, and the risk of re-infection is very high.
In the past, traditional insecticides have been used to treat lice infestations, but head louse often develop resistance to these drugs. In this regard, this type of treatment has been almost completely replaced by silicone and oil-based products, which have a physical rather than chemical effect on lice.
Once a head louse has been identified on the scalp, you can treat head lice at home by combing wet hair with a special comb or using a lice killing lotion or spray (see below).
However, neither method will protect against reinfestation if head-to-head contact occurs with someone with head lice throughout the treatment period.
By systematically combing head lice out of wet hair using a special fine-tooth comb, you can get rid of this parasitic disease.
The teeth of the comb should be located at a distance of 0.2-0.3 mm from each other. If you use a nit comb, lice caught in the nit comb may be torn apart or trapped between the teeth and you may not notice them because the teeth are 0.19mm apart.
You can buy a special lice comb at your local pharmacy or you can order one online.
Lotions or sprays should not be used when brushing wet. However, for this lice removal method to be effective, wet combing must be done regularly and thoroughly. Here are the step-by-step steps you need to take:
- Wash your hair using regular shampoo, followed by a generous amount of hair conditioner. Then, without rinsing out the conditioner, comb your hair with a wide-tooth comb to straighten and detangle it.
- Once the comb can move freely through your hair, you need to start using the comb to remove lice. Combing should be done starting from the roots of the hair, lightly touching the scalp, and ending with the ends.
- After each time you run a comb through your hair, you should check it for lice.
- Remove lice every time you see them on the comb using a cloth or a stream of water.
- Comb methodically every inch of hair until the entire surface of the head has been combed.
- Rinse the conditioner and repeat the combing procedure.
- Repeat this procedure on the 3rd, 6th, 9th, 12th and 15th days - this will make it possible to eliminate young lice without giving them the opportunity to reach maturity.
The duration of lice removal by combing depends primarily on the length of your child’s hair and its type. For example, short, straight hair can be quickly combed through with a lice comb within a few minutes. Longer, curly hair requires more time, patience and work.
Combing head lice while wet makes it possible to treat lice
Using a lotion or spray is an alternative treatment for head lice. However, in order to benefit from this type of treatment, they must be used correctly. Your doctor will be able to recommend a special lice lotion or spray and tell you how to use it correctly.
Lice spray for pediculosis
The lotion or spray should only be used when you detect a live (moving) head louse in your hair. Cream rinses and shampoos against lice are not effective and are therefore not recommended.
Make sure you have enough lotion or spray to treat everyone in your family. When applying these products to the scalp and hair (along the entire length), use so much of it that they completely cover the localization sites of these parasites.
When applying, follow the instructions that come with the lice lotion or spray. Depending on the product you use, the length of time you will need to leave the lice treatment on your head can vary from 10 minutes to 8 hours. It is recommended to repeat the treatment seven days after the first treatment. Some products also come with a comb to remove dead lice and nits.
Some lice treatments may be able to kill lice eggs as well as lice, although this is not certain. 3-5 days after treatment, check the head for hatched lice, and check the head again 10-12 days after that.
To kill these parasites, at least two head lice lotion treatments are necessary during the incubation period because lotions do not always kill their eggs (nits).
If lice appear after all head treatments have been carried out, seek advice from your school nurse, health visitor, pharmacist or doctor.
Before using any medicine, always read the instructions on the package, especially when it comes to the following groups of people:
- infants (under six months of age)
- pregnant women
- people with asthma or allergies
If you are still unsure about how to properly use a lice treatment, consult your healthcare professional before using the product.
Pregnant women are advised to use either wet combing or 4% demethicone lotion, which is licensed for use during pregnancy and lactation.
Healthy head lice can be accidentally transferred from the head to clothing, bedding, or soft toys. Their lifespan is about three weeks, and when they fall off their heads they die and cannot reproduce, so there is no need to treat things with hot steam or water.
Check the brushes and combs that are used during lice treatment and removal. If a louse does not drink human blood within 1-2 days, it dies.
Be aware that when vigorously brushing dry hair, you may inadvertently brush head lice off your scalp or hair. If the parasite lands on another person, it tries to climb onto his head.
Head louse
Depending on the location, there are head lice, body lice (underwear lice), and pubic lice. The most common type of louse is the head louse. Everyone has encountered this problem at least once in their life. Those with long hair, that is, female representatives, are more prone to the appearance of parasites.
First signs of infection
You can suspect an infection only after 7 days, when a person already has a lot of females and larvae on his head.
Characteristic signs of lice:
- itching from bites, especially in the occipital and temporal region, intensifies after washing, as well as at night;
- white dots that stick tightly to the hair;
- black spots on the scalp;
- bite marks, especially visible behind the ears and on the back of the neck;
- upon examination, especially if the infection occurred a long time ago, the individuals themselves are clearly visible;
- tangles, that is, hair sticking together due to infrequent washing.
Clinical manifestations in children
Children have several other symptoms: severe head scratching, restlessness, and moodiness. Lymph nodes may become inflamed.
Transmission routes
You can only become infected through household contact. The chance increases if hair touches during a hug or team games. And also when using other people's combs, elastic bands, hats, clothes.
The risk of becoming infected through water is not great, but in a pool where the water is rarely changed and the rules are not followed, you can easily become infected not only with lice, but also with many other diseases.
How does the disease manifest itself in an advanced stage?
The longer lice parasitize a person, the more of them there become. Therefore, all symptoms are more pronounced. The wounds become larger and pustules form.
Complications of pediculosis
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the individuals will multiply quickly and will take a very long time to remove. There will also be a risk of re-infection from persons who received the larvae. Complications of head lice include:
- scratch infection;
- nervous system disorders due to poor sleep;
- pyoderma;
- dark spots;
- rarely - infection with typhus, Volyn fever.
Treatment
First of all, you need to thoroughly examine the entire head, using a magnifying glass if necessary. The insect's body reaches a size of up to 4 millimeters, the color is transparent brown or red after eating. There are 3 paws on each side, no wings. The nits are white, up to 0.8 millimeters in size, and are securely attached to the hair.
If you manage to detect them, you should immediately begin treatment. Boys can simply be cut short, then inspected and remove any larvae if any remain. Girls and women will have to suffer, especially with long hair.
There are many “grandmother’s” methods of treatment, because lice appeared along with humans. But today you can simply buy a special pediculicide at the pharmacy. There are a lot of them, from the most expensive to the cheapest. They act equally effectively, but the more expensive ones are safer for the hair structure. After the first application, larvae often remain, which is why repeated use will be required.
For the treatment of young children, it is better to consult a pediatrician, because not all drugs are suitable. Use is also contraindicated for pregnant women. It is better for them to use traditional methods.
Then, for greater efficiency, you need to comb your hair with a sparsely spaced comb or an electric comb specially made for this problem. The method can be used without the use of drugs, but in combination they will give quick results.
When contacting a doctor, the period for re-examination of the patient after detection and treatment is 14 days.
Prevention
You should know and inform children about the following rules:
- avoid contact with potentially infected people (people without a fixed place of residence, arriving in places of detention, barracks);
- do not use other people’s things, especially those in contact with your head;
- folk methods say that tea tree essential oil repels lice, and also has a positive effect on the roots and structure of the hair;
- girls to braid their hair;
- monitor the condition, examine the head once a month.
All these methods will significantly reduce the risk of lice, but will not provide a 100% guarantee.