Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
7 years experience
Make an appointment
Follicular hyperkeratosis is a skin pathology that consists of the formation of nodules of keratinized epidermis at the mouths of hair follicles. The skin on the affected areas becomes dry and rough, covered with numerous reddish nodules that resemble goose bumps. Most often the disease affects the elbows and knees, gluteal areas, and outer thighs. It does not cause a deterioration in well-being, although it does cause some discomfort due to the feeling of dry skin and dissatisfaction with one’s appearance.
Types and classification
There are the following categories of disease:
- papular – associated with the formation of papules;
- vegetative;
- atrophying – can lead to atrophy of the epidermis.
Follicular dermatitis manifests itself in several forms:
- Warty. It occurs due to a genetic abnormality and is caused by inadequate production of keratin. It can be either congenital or acquired. The sore has an external resemblance to a wart. The growths tend to crack and are covered with a dense crust on top.
- Lenticular - characterized by the formation of large papules of a yellow or brown hue.
- Seborrheic. Affects the scalp and face. The rash consists of small spots with a greasy film on top. Formations tend to grow.
- Diffuse. It appears in large pathological spots and can cover parts of the body entirely.
Follicular dermatitis can be:
- primary, i.e. not related to internal pathologies;
- secondary – is a concomitant symptom of internal somatic diseases.
Pityriasis pilaris
It is an inflammation of the hair follicles. It is characterized by rashes covered with a hard crust on top, located on the inside of the knees, in the armpits. May be accompanied by itching.
Persistent lenticular hyperkeratosis of Vlegel
Associated with the formation of red and brown pimples on the hands. If you remove the superficial crust, a depression in the middle of the sore becomes noticeable.
Devergie's disease
The rash is yellow in color, the sores have the shape of a cone with tires. They can merge with each other, forming a single horny covering.
Superciliary ulerythema
Hyperkeratotic formations appear first in the superciliary region symmetrically to one another, then lesions appear on the forehead and cheeks. As the rash develops, it turns into scars, then keratinized crusts appear.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Before you begin to treat the disease, you need to find out why it appeared , and only then take any action.
In some cases, the disease goes away on its own , however, sometimes the child still requires adequate therapy.
You should not self-medicate, since children's skin is very sensitive to the effects of many medications that can cause serious irritation. Therefore, only a doctor should prescribe therapy.
Reasons for appearance
There are internal and external causes of follicular dermatitis. The first include:
- ichthyosis is a pathology in which small horny growths form on the skin, similar in appearance to fish scales;
- seborrhea - disruption of the activity of the sebaceous glands, accompanied by blockage of the ducts that remove secretions to the outside;
- lichen - a dermatological disease manifested in a small blistering rash;
- fungal infections, HIV;
- psoriasis;
- genetic abnormalities associated with excess or insufficient
- production of keratin;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- flat feet;
- diabetes mellitus (occurs when there is an increased level of glucose in the blood);
- overweight and obesity;
- hypovitaminosis (excess vitamin A);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (dysbacteriosis);
- erythroderma - pathological peeling of the epidermis;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances due to taking drugs that stimulate or inhibit the production of hormones;
- improper metabolism;
- neuropsychic overstrain, stress.
- Secondary causes of hyperkeratosis are:
- incorrect care: use of inappropriate cleansers for a specific skin type, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- lack of microelements in the body that affect the health of the epidermis;
- wearing excessively narrow, tight-fitting clothes made of dense materials that do not allow air to pass through;
- overweight and obesity.
Lack of vitamins
The disease is caused by a deficiency of vitamins A and D, which play an important role in the formation and normal functioning of the epidermis.
Hormonal agents
In girls, the initiators of hyperkeratosis are hormonal contraceptive drugs that activate the processes of keratin formation in cells. Disturbances in the structure of the skin also result from taking medications that are prescribed to women during menopause.
Poor nutrition
The problem may arise due to the patient's unbalanced diet. Patients with follicular hyperkeratosis are prescribed a special diet.
Psycho-emotional disorders
Stressful situations and instability of a person’s mental state provoke the development of the disease and aggravate the severity of its course.
Acquired keratosis pilaris
Keratosis pilaris usually develops as a result of:
- metabolic and endocrine disorders, especially with hypothyroidism and diabetes;
- poor nutrition with food products low in vitamins “A”, “E”, “C” and group “B”;
- tertiary syphilis, HIV infection, verrucous tuberculosis of the skin, fungal diseases of the legs (feet);
- autoimmune pathology of connective tissue (discoid lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, etc.) and allergic diseases;
- excessive exposure to X-rays and other types of radiation, as well as constant physical exposure to areas of the skin or contact with harmful chemicals, etc.
Acquired hyperkeratosis occurs in the form of single or multiple elements, which can be complicated by acne, and when a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection is attached - by an inflammatory process, and occur in the form of ostiofolliculitis and superficial follicullites, furunculosis, sycosis, etc.
Watch a video about gluten intolerance and keratosis pilaris on the hands:
How to get rid of acquired keratosis pilaris
Symptomatic forms of keratosis pilaris can be easily cured by eliminating the underlying cause or adequately correcting chronic diseases that provoked the development of keratosis, and using anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antihistamine therapy, specific immunotherapy and immunocorrectors, as well as lotions and creams with anti-inflammatory, peeling, enzyme, and vitamin components.
Treatment
It is necessary to treat not only the external signs of dermatitis, but also the diseases that led to its appearance. In order to get rid of the disease, they resort to drug therapy and the use of unconventional methods.
In order for the treatment of keratosis pilaris to be effective, the patient is prescribed physical therapy, strict adherence to a diet, and the elimination of external provoking factors, if any.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have a problem with hyperkeratosis, you should consult a dermatologist. Additionally, you may need to consult an endocrinologist or infectious disease specialist.
Drug treatment
Includes the use of ointments and gels for external application. They soften, moisturize the skin, and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Vitamin complexes and preparations based on fish oil are widely used for internal use.
For follicular hyperkeratosis the following are prescribed:
- castor oil;
- glycerol;
- "Decamine ointment";
- "Lachydrine";
- "Uroderm";
- "Davonex";
- "Tazarotene";
- "Elidel";
- "Protopic".
- The last two medications are immunomodulators and are prescribed for severe forms and complications of the disease.
Do not apply scrubs to the affected surface or rub it with a hard brush or pumice stone: there is a risk of damaging the top layer and causing infection. The skin should be cleansed using gentle cleansers.
In a child, treatment of manifestations of keratosis pilaris is carried out using:
- salicylic ointment;
- medications that contain urea;
- water-soluble petroleum jelly.
- Often childhood hyperkeratosis disappears on its own as the baby gets older.
Traditional medicine methods
To treat follicular hyperkeratosis, it is recommended to use folk remedies. In order for their use at home to be safe and bring tangible benefits, they should be used only with the permission of a doctor and under his direct supervision.
Propolis
Cover the areas affected by the rash with a thin layer of the product, apply a film on top, and wrap it with a bandage. Wear the bandage for several days.
Beet
Before use, the vegetable is thoroughly washed and the skin is removed. Then it is crushed into a paste, and the resulting mass is applied to the lesions. After three hours, wash off the compress and apply moisturizing cream to the affected areas.
Potato
The grated potato mass is applied to a cloth (gauze or bandage) and applied to the affected area. The compress is removed after 1-2 hours, the skin is washed and lubricated with cream.
Yeast
The dough is prepared with milk. After the yeast swells, add flour and make a flat cake. It is bandaged to the sprinkled areas and kept in place for several hours.
Aloe
Cut a leaf of the plant, pour boiling water over it, keep it in hot water until the liquid cools. Then the aloe is placed in the freezer, after three days it is taken out, cut into thin strips, which are then applied to the sore skin. Leave the compress on all night, remove it the next morning, and smear the painful papules with salicylic alcohol and Vaseline. Repeat the procedure until the rash disappears.
Prevention
There is no way to effectively prevent keratosis pilaris, but it is quite possible to prevent its exacerbations. To do this you should:
- in the cold season, lubricate the child’s skin with a rich cream every day;
- stick to a diet with sufficient fat and vitamins, take a course of multivitamins in spring and autumn;
- buy clothes for your child only from natural fabrics;
- avoid contact with allergens (food dyes, animal hair);
- Use mild detergents when bathing your baby.
In order for the disease to proceed favorably and not cause discomfort to the child, you just need to follow simple rules and treat exacerbations in a timely manner.
Complications and prognosis
Complications caused by follicular hyperkeratosis have not yet been identified in adults. The disease manifests itself as an unpleasant cosmetic defect, does not pose a threat to life and health, but can signal the presence of internal dysfunctions and pathologies.
Ignoring the signs of follicular hyperkeratosis in a child can provoke the development of an inflammatory process, which will lead to the spread of sores throughout the body (if the disease does not go away after puberty).
With properly selected therapy, the acquired anomaly can be easily eliminated. The congenital form is incurable.
Diagnostic methods
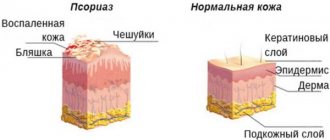
Follicular hyperkeratosis, as a rule, does not require special diagnostic studies. For an experienced dermatologist, the results of an external examination and a survey of the patient are usually sufficient to determine the nature of the disease. In adolescents, keratinization nodules can sometimes be confused with acne, but upon closer examination, dry and rough skin is revealed, in contrast to the soft texture inherent in acne. In some cases, there may be a need for differential diagnosis if the manifestations of follicular hyperkeratosis are similar to:
- ringworm;
- pityriasis versicolor;
- Darier's disease;
- follicular psoriasis;
- lenticular keratosis.
In these cases, a histological examination of the nodules is performed to study the nature of the skin formations and determine the cause of their occurrence.