Fungal infections, or simply fungi, are relatively common in children. They are caused by certain pathogens that affect the mucous membranes, the outer covering of the body and the nail plate. Fungal infections are also called mycoses. Young children have an imperfect immune system, and since their skin is thin and delicate, the body cannot resist infections.
There are:
- Yeast (Candida albicans, which causes thrush);
- Dermatophytes (shingles, which mainly causes a severe itchy, scaly rash);
- Mold (aspergillosis, causes respiratory problems);
Why can a child develop fungus?
Fungal skin infections can appear for completely different reasons. The pathogen is found almost everywhere, as it is highly resistant to many aggressive factors. They are not afraid of either high or low temperatures.
The pathology can be epidemiological in nature, affecting a large group of children. The location can be either a school or preschool institutions. Both humans and animals can carry the fungus. The place of infection can also be a beach, swimming pool, entertainment and games room, or hairdresser.
Fungal diseases occur in children much more often than in adults. This is due, firstly, to the fact that the barrier function of the skin is not yet fully formed, especially in infants. In this way, pathogens can penetrate the skin more easily. Secondly, the immune system is not yet working properly, and pathogens have to be fought quite hard.
If a skin fungus occurs in a child, one of two types is mainly considered - yeast fungi or dermatophytes (filamentous).
There are several causes of fungal diseases affecting the body:
- Acute and chronic forms of infectious diseases.
- Heredity.
- A disease of autoimmune origin.
- Excess or deficiency of minerals and vitamins in the body.
- Parasitic basis of infection.
Pathology can be provoked by the following factors:
- Contact with a carrier of the fungus.
- Touching a sick animal.
- Use of carrier objects.
- Increased sweating of the hands and feet.
The disease affects children at any age. In obstetrics, there are cases when a child is infected with a fungus already in the womb. The main breeding areas are nails, hair, scalp and groin area.
Causes
There are many causes of mycosis in children; a baby can be infected with it from birth. But infection could occur when the fungus is transmitted through the mother's mammary gland, passing through the birth canal, or due to a fungus that the child could pick up over time. Fungi multiply most actively on smooth skin and its derivatives (nails, hair). Signs of mycosis can be found in the armpits and in the area of the child’s inguinal folds. Causes of mycosis in children:
- congenital disease;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- unfavorable environmental factors, such as increased levels of radiation, polluted air;
- a diet that includes a large amount of sweet and salty foods;
- long-term therapy with drugs that have side effects.
Infection with mycosis often occurs in premature infants. Associated with taking a significant amount of antibiotics prescribed to premature babies. Pets often carry fungus, which, due to close contact, spreads to the baby’s smooth skin.
How are mycoses classified?
Infection of a child's skin occurs very quickly. There are about 35 types of fungi, which mainly affect the feet, nails and hair. Fungal spores penetrate the epithelium and subcutaneous layer.
The localization of the lesion is divided into four groups:
- Systemic – damage to internal organs and tissues (cryptococcosis, blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, coccidioidosis).
- Subcutaneous mycosis (subcutaneous form) - fungi settle on the subcutaneous tissue, skin, fascia and bones (sporotrichosis, chromomycosis, maduromycosis).
- Dermatomycosis (epidermycosis) is a lesion of the epidermis, hair and nails.
- Superficial – disease of the stratum corneum of the epidermis and hair (lichen nigricans, trichosporosis, keratomycosis, piedraiasis).
Mycoses can be classified according to various criteria.
Dermatophytes
They are filamentous fungi that infect only the skin and appendages, such as nails or hair. The medical form is divided into subgroups:
- athlete's foot,
- microsporia,
- trichophyton.
They cause only superficial mycoses, so they never affect the inside of the body. Dermatophytes, accordingly, lead only to diseases of the skin, legs or nails, or hair.
Yeast
Yeast can affect the skin and mucous membranes. With systemic mycoses, the internal organs of the child become infected. This can lead to severe sepsis. Children with weakened immune defenses are especially likely to suffer from yeast infections. They can lead to local mycosis, which mainly occurs on the skin and mucous membranes; fungal infection of hair and nails occurs less frequently.
However, systemic mycosis can also be caused by yeast. It then causes disease in the internal organs. Often yeast fungi lead to candidiasis (especially in the mouth and throat), thrush and vaginal fungus.
moldy mushroom
May also cause cutaneous, mucous and systemic mycoses. Mold is a filamentous fungus. Well-known mold genera are, for example, Aspergillus and mucor. Mold usually only affects children who have weakened immune systems.
However, they usually cause diseases of internal organs. For example, aspergillosis leads to a fungal infection of the lungs. Much less often, mold is the cause of superficial mycoses that occur on the skin, mucous membranes or hair.
This classification of the causative agents of fungal infection is important in order to be able to establish the appropriate treatment method after diagnosis. Different genera of fungi differ in terms of their infectiousness, as well as where they appear in the child’s body. In addition, there are differences in the course of fungal infections caused by different pathogens.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Symptoms of mycosis in children, the degree of their severity depends on the cause and form of the disease.
Instructions for using Keto Plus shampoo and cheap analogues
If the scalp is affected:
- crusts of a grayish, yellowish tint appear on the skin, which can be easily removed. Over time, crusts appear again;
- feeling of “lumpy” scalp;
- the area of the scalp infected with the fungus has the shape of a circle, the hair of the area becomes brittle (breaks at a distance of 2-5 mm from the skin). The skin and hair around the affected area show no signs of disease;
- The child complains of itching and burning in the area affected by the fungus. If a child cannot speak, he begins to scratch the irritating areas of the skin and allows him to wash his hair for a long time (even if he did not like it before).
If areas of smooth skin are affected:
- the skin is covered with spots that do not have clear edges;
- ring-shaped spots that have raised edges and a clear center;
- over time, small spots merge into one, having a large area of distribution, moving to previously healthy areas of the skin;
- bubbles appear on the skin containing a clear, light yellow liquid, which, due to their thin wall, burst easily;
- Dry crusts appear along the periphery of the spots, which separate when exposed to moisture;
- In the area of the affected areas, the child feels itching and burning.
As you can see, the symptoms in children can be different; their form of mycosis determines them.
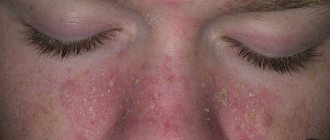
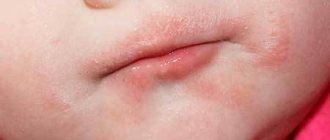
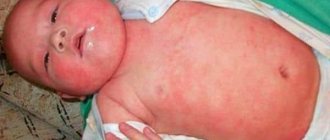
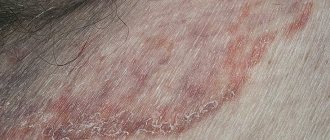
In the photo you can see what infectious lesions in the head area and smooth skin look like.
Manifestations of fungus in children
There are superficial and systemic mycoses. Mycosis of the mucous membranes is quite rare in the mouth of children with a healthy immune system. However, mycoses of the genital organs are much more common. Mycoses of the mucous membrane are usually caused by the pathogen Candida albicans. But mycoses that form on the mucous membranes of the digestive tract usually indicate a weak immune system, so the causative agents are weak parasites.
In so-called systemic mycoses, fungal pathogens usually enter the bloodstream through the lungs and can then affect internal organs. Systemic mycoses are usually difficult to treat.
Symptoms vary depending on the type and manifestation of systemic fungal disease. The first visible signs appear at the site of entry of the pathogen, for example, with a skin infection around an injury.
In many cases, the wound becomes infected, which can also be painful. However, sometimes the infection does not make itself felt at all. The fact that the fungus spreads through the blood and lymphatic tracts is often not perceived by the child at all.
If individual internal organs are affected, then corresponding dysfunctions occur: in the lungs this is shortness of breath; in case of blood poisoning, high temperature, chills and cardiovascular disorders occur.
In addition, large-scale distribution of lichens on the skin indicates a systemic fungal infection. If you notice such signs, you should definitely consult your doctor.
Important! Systemic mycoses are very serious infectious diseases that, if left untreated, can lead to disastrous consequences. They can also be a warning sign for other diseases because they indicate a significantly weakened immune system.
Symptoms
Children who are sick with fungus cannot always complain about the symptoms of illness that bother them. Therefore, parents should regularly examine the child for unnatural changes and, if necessary, seek the help of their doctor.
Signs of infection by pathogenic microflora of different species differ from each other. The manifestation of the fungus directly depends on its location and type.
| View | Features |
| On foot | The fungus is usually localized on the toes and feet. Small wounds appear in these places, which gradually turn into ulcers. The skin at the site of the lesion constantly itches and turns red. The child also has difficulty walking, as this process causes him pain. |
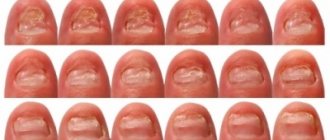
| On the nails | The nail plate begins to acquire a gray, then black color. It itself noticeably thickens and peels off. The appearance of inflammation of the skin that is located next to the infected area cannot be ruled out. |
| Ringworm | The fungus is active on the scalp and hair. They begin to fall out little by little or break off greatly. The skin in the affected area turns red and peels. The child is also bothered by itching. When scratching infected areas, wounds are formed into which pathogenic bacteria can penetrate. In this case, high temperature will also join the general symptoms. |
| Pityriasis versicolor | Most often, this type of fungus is noticed on the skin of the back. It is recognized by characteristic yellowish or white spots that may peel off. There is usually no itching. |
| Candidiasis | Yeast most often affects the intimate area or oral cavity of a child. A white coating with a cheesy consistency appears in the affected areas. If you erase it, small wounds and ulcers will appear on the mucous membrane. Sometimes with this form of fungal infection in children, the body temperature rises to 37.5. |
Based on the symptoms of the pathological process, you can first recognize the type of fungal infection from which the baby is suffering.
Symptoms vary depending on the type of fungus and location
Localization of fungal diseases (mycoses)
Skin fungi
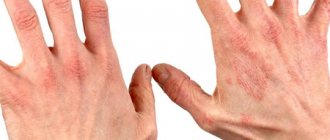
Skin fungi (especially the Trichophyton genus) cause oozing inflammation in areas of the body that have little contact with light and air. They occur mainly between the toes and in the armpits and groin area. Scaly, reddened areas may form, which are accompanied by more or less severe itching.
Yeasts
Yeasts (especially Candida) colonize the moist mucous membranes of the digestive and genital tracts, namely the mouth, throat, gastrointestinal tract, and vaginal mucosa.
When the digestive tract is infected with yeast (candidiasis), especially intestinal fungi, children may experience digestive disorders with diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and bloating.
Most often, transmission of candida occurs from mother to child during childbirth. The fungus can also be transmitted through breastfeeding.
In the oral cavity, the infection is called thrush and appears as a whitish coating on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and tongue. Often children complain of a burning sensation in certain parts of the body.
Vaginal fungus in a child
It makes itself felt by burning and itching, redness, swelling, a whitish coating of the mucous membranes and discomfort when urinating (stranguria). It is quite rare in children. Affected children may be children in the first weeks of life whose mother transmitted candida to them at birth.
In the body of infants, there are still female sex hormones of the mother - estrogens, which inhibit the regenerative ability of the mucous membranes, which, in turn, contributes to fungal infections.
Even just before puberty, girls are more likely to develop yeast infections because their bodies begin producing estrogen. Conditions favorable for fungal infections prevail, for example, after taking antibiotics, frequent visits to the pool, increased sweating and/or weak immune system protection. All this can lead to fungus.
With vaginal fungus, the intimate area is characterized by redness and swelling. It is important to always contact a dermatologist if you suspect vaginal fungus in a child for examination. If it is truly a fungal infection, it is treated with an antimycotic.
Mold fungus
Mold spores (especially of the Aspergillus genus) are usually inhaled into the lungs. In this case, aspergilloma, a form of aspergillosis, can occur in existing lung cavities. Often there are no symptoms at first, but cough and shortness of breath may occur later.
In children with severe immunodeficiency, aspergillus pneumonia may occur, with fever and cough without sputum, and resembles bacterial pneumonia. But mold also colonizes the central nervous system and the entire digestive tract, which is why it can sometimes be found in stool samples when tested.
The heart, liver, skin, thyroid and (rarely) spleen can also be affected by aspergillosis.
Symptoms
Mycoses provoke the appearance of many unpleasant sensations that negatively affect the health and well-being of the child. It all starts with redness of the skin, an increasing burning sensation, and constant itching. With candidiasis, unpleasant sensations in the throat cannot be ruled out.
The epidermis cracks, peels off over time, and blisters form on the skin. When the skin is traumatized, gray or red spots appear; they can be of different sizes, itch and burn.
In young children, thrush is also diagnosed; when the disease occurs, a white coating appears in the infected area. Due to constant discomfort, the child scratches the affected areas of the body, damaging the skin, causing bleeding.
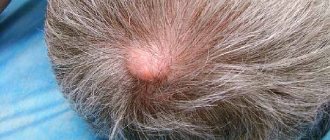
The most common mycosis is ringworm, which affects the scalp. When the disease occurs, lesions form on the scalp:
- round shape;
- with smooth edges.
The lesion is covered with small gray-white scales. Reddish plaques form on the skin and may peel off. There is a roll of bubbles and crusts around. Trichophytosis can manifest itself as loss of color, disruption of the natural growth and structure of hair. At the skin level, the hair constantly breaks off, and small bald spots appear between the peelings. The development of suppuration cannot be ruled out.
Mycoses can make themselves felt by small pinkish, brownish or coffee-colored flaky spots. The shape of the lesions is irregular, they actively grow along the periphery, but suppuration and characteristic itching are not observed.
With scab, thick, dry crusts of yellow or brown color form on the head, their edges are raised, pressed towards the center. The hair underneath is constantly deteriorating, gradually:
- dry out;
- break;
- fall out.
As the disease worsens, baldness and scar atrophy may develop.
Mycoses in children are manifested by damage to the hands and feet, dry skin, and the appearance of pink-red plaques. Just like in adults, the spaces between the toes and the soles of the feet are affected.
The lesion causes thickening of the skin and spreads to the nail plates.
Diagnosis of fungi in children
Because the symptoms caused by a fungal infection vary and may be due to another condition, the diagnosis of a fungal infection is not made based on complaints alone. If mycosis is suspected and confirmed by further diagnostic procedures (eg, dark-field microscopy), additional laboratory testing is usually required.
Samples of skin, nails, hair or stool are examined for the presence of fungi and their genus is determined. After this, appropriate targeted therapy can be carried out.
Mycosis in most cases is diagnosed by the attending physician using a sample taken from the affected tissue. From this sample, the pathogen is subsequently cultured (grown) in order to unambiguously identify it.
Since this method can be quite lengthy, treatment of the infection often begins in parallel. The doctor decides which therapy to use based on his experience. In addition, microscopic examination of the infected tissue sample may be performed.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of fungal infection is carried out under a Wood's lamp
If, during an examination, a pediatrician diagnoses a fungus of any kind in a child, then most likely he will write a referral to a mycologist. You can diagnose nail fungus in a child or mycosis of any other part of the body using the following methods:
- initial examination of the infected surface under a Wood's lamp;
- taking a piece of affected tissue for microscopic examination;
- sowing the scraping onto a nutrient medium. This method allows you to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to certain types of drugs;
If there is a suspicion of the development of mycosis, the doctor must carry out a differential diagnosis in order to exclude the development of psoriasis, dermatitis, vitiligo and other diseases, the signs of which are very similar to a fungus.
Therapy of mycoses
If there are other children in the house, first of all they are isolated from the sick child. It is important to disinfect the entire room and available items. Parents should ensure that their child follows good hygiene rules.
To avoid contracting the pathogen from the very beginning or to prevent the spread of the fungus in the body, you need to know the transmission routes through which a fungal infection usually spreads. The greatest importance for the prevention of fungal infection is given to the following measures:
- preventing infection by pathogens that cause fungal disease;
- sustainable strengthening of the protective immune system;
- body hygiene;
- choosing the right clothes.
Antifungals can be divided into two different classes, topical and systemic. Topicals fight fungal infection pathogens through external use. Systemic antifungals, on the contrary, are taken orally.
Prognosis and prevention
Most fungal skin diseases in children have a persistent course and require long-term systemic therapy, however, if the specialist’s recommendations are strictly followed, they have a favorable prognosis. Untreated mycotic pathologies become chronic with exacerbations and remissions and can continue into adulthood. Principles for preventing fungus in children:
- clothing in contact with the skin must be clean, not restrict movement, and made from natural fabrics;
- personal hygiene items – strictly individual and regularly disinfected;
- Shoes must be comfortable and always remain dry.
Today, the pharmacological market offers a wide selection of disinfectants and antifungal drugs. Their reasonable use, approved by pediatricians and dermatologists, will cure a child of fungus on the legs and other parts of the body in a short time and prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Oral medications for fungus in a child
Severe fungal disease and associated infection are treated with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. Drugs such as Griseofulvin or Terbinafine are recommended.
Diflucan also works great against fungal infections. It is the safest and most effective among antimycotic agents. The forms of administration are varied - it is produced in suspension, solution for intravenous administration and gelatin-based capsule.
To eliminate severe itching, Cetrin, Suprastin, Zyrtec, Loratadine are used. If the case is advanced, the doctor decides to prescribe corticosteroids - drugs that contain steroid hormones.
Their effect is lightning fast, they are taken in short courses, from 5 to 7 days, but they have numerous side effects and contraindications. It is possible to prescribe immunostimulants and multivitamin complexes.
Causes and forms of the disease
Young children often suffer from fungal diseases, which is associated with the immaturity of the immune system. The infection enters the body through microdamages on the legs, causing allergic reactions, peeling, the formation of spots, papules (cavity-free nodules), and blisters. Fungus on the feet of children occurs due to a decrease in the body's defenses and a violation of the barrier function of the skin. Factors that provoke its development include:
- violation of personal hygiene;
- vitamin deficiency;
- wearing tight shoes;
- foot hyperhidrosis;
- endocrine disorders;
- vascular diseases;
- flat feet;
- wearing socks made of synthetic fabrics;
- changes in the chemical composition of sweat;
- overweight.
Also, the causes of fungus include immunodeficiency states caused by exacerbations of chronic diseases and hypovitaminosis. The infection is transmitted through household contact, so the risk of mycosis increases with frequent visits to swimming pools, baths, and locker rooms at sports complexes.
In childhood, the following forms of fungus are most often diagnosed:
- Interdigital mycosis. Lesions form in the spaces between the toes on the feet, causing burning and peeling of the skin. If left untreated, cracks and blisters filled with pus appear. When walking, injuries to the legs cause severe discomfort and pain.
- Vesicular mycosis. The fungus primarily affects the feet and areas between the toes. Its development is evidenced by numerous bubbles forming on the sole. Gradually they increase in size and burst, leaving wet ulcers. Open wounds increase the risk of secondary infections, which is why ulcers often appear on the legs.
- Athlete's foot. A rare form of mycosis manifests itself in the form of a scaly “mark” covering the entire foot. In addition to the skin, nails are often affected by the fungus, which leads to their thickening and splitting. The skin is completely covered with keratinized yellow-brown scales, which is why the foot resembles a bird's beak.
- Erased form. The disease occurs in a latent form for a long time, affecting only the interdigital spaces. Over time, the skin becomes covered with a rash and swells, and the nail plates become deformed.
Children often ignore the primary manifestations of fungus (peeling, burning), which complicates its timely diagnosis. Delayed treatment of mycoses entails serious complications in the form of allergic reactions, dermatitis and purulent inflammation.
Local treatment of fungal infections
Erosion on the child’s body is treated daily with antiseptic solutions. This may be boric acid, furatsilin or potassium permanganate. Particular attention is paid to the areas between the fingers. Different types of lichen are treated with ointments, these include tar, zinc, salicylic acid, naphthalene, the drugs Miconazole and Clotrimazole.
Attention! The antifungal agent that the doctor prescribed after identifying the causative agent of the fungal infection must be taken in accordance with the instructions. In particular, it must be used for a specified period of time. This is the only way to ensure that the infection completely disappears.
If an antifungal is stopped prematurely, there is a risk that the remaining pathogen still in the affected area of the body will multiply again and cause a relapse of the disease.
Topical antifungals are intended for topical external use only. Antifungal agents, available in the form of ointments, creams or lotions, are applied to the affected areas of the body as prescribed by the doctor.
This superficial therapy is common for fungal infections of the skin as well as the mucous membranes. The most commonly used topical antifungals for topical use include:
- Narrow spectrum antifungals are Tolnaftate and Nystatin, which have been shown to be very effective against yeast fungi.
- Broad-spectrum antifungals, which include azoles such as Clotrimazole, Bifonazole. These also include Econazole, Miconazole and Ketoconazole. In addition, doctors prescribe Amorolfine and Terbinafine as broad-spectrum fungicidal antimycotics.
If your doctor has prescribed a topical antifungal, you usually don't have to worry about serious side effects. For topical medications, side effects are limited to skin reactions, such as skin irritation.
Unlike topical treatment, antifungal drugs are taken orally. Systemic antifungals must be taken by the patient either orally in tablet form or intravenously.
If long-term treatment with local antifungal agents has not shown any effect, the child is prescribed systemic antifungal drugs.
Treatment
Treatment of mycosis in a child takes place in several stages.
- If smooth skin (feet, head, nails, etc.) is affected without inflammation of the scalp, it is recommended to treat the infection areas with a two percent iodine solution every morning. Iodine disinfects and promotes healing;
- In the evening, you should apply an ointment that will moisturize the infected area and relieve itching during sleep. Most often, such ointments contain the following components: nystatin, miconazole and amphotericin A;
- Creams, suspensions, and gels also help with mycosis of smooth skin. They are used as Mikozolon, Mikoseptin, or Mifungar cream. But before using them, you should consult your doctor.
You can read in detail the instructions for a particular drug on the Internet, presented in the form of a photo, or posted on medical portals.
- Recommended reading: foot fungus in children
If there is an infection on smooth skin and hairy surfaces, the doctor will prescribe antifungal antibiotics, such as Griseofulvin.
The daily intake for a child is calculated based on the formula 22 mg per 1 kg of child weight. The medicine is taken together with vegetable oil after or during meals. Subsequently, the removal of the keratinized layer of the epidermis or the infected scalp is carried out using the “sealing” method. The affected area is covered with adhesive tape for about two to three days, which causes increased aggravation but makes it easier to remove the hairs.
Infection of the foot with mycosis in a child requires special treatment. After all, if you do not start timely therapy, then the nail plate may also suffer. One of the most popular remedies in this case is Lamisil. It has a disinfecting effect, moisturizes the feet, and also strengthens the nail plate. But it is only indicated for children over 12 years of age. For babies, you can use Pimafucin cream or Mikospor solution.
Treatment of mycosis of the throat and tonsils is carried out with antifungal agents. Including fluconazole, nystatin or levorin. If treatment for the tonsils and throat is not started in time, the infection may spread further, causing unwanted complications.
An important stage on which the treatment is based is the disinfection of the young patient’s bedding and clothing.
To do this, you need to boil things in a one percent soda solution with added soap for 15-20 minutes. For one liter of water, take 10 grams of soap and 10 grams of soda. The fabric surface of upholstered furniture and outerwear should be ironed or steamed several times.
The effectiveness of smooth skin treatment is tested using a fluorescent lamp. It helps determine the presence of fungus and track progress after starting drug therapy. A patient is considered healthy if there is no luminescent glow on a smooth area of skin.
Treatment of fungus in a child with folk remedies
Alternative medicine will complement treatment with the necessary enzymes if the child has a mild form of fungus. But be sure to consult a dermatologist and your doctor before using folk remedies.
- Garlic and salt compress. Grate the garlic clove and add 0.45 tsp to it. coarse salt. Everything is mixed and a gauze compress is made, which is attached to the wounds. You can also wipe the affected skin with garlic juice 3-4 times a day.
- Spruce tincture. 300 g of cones and needles are poured with 100 g of vodka or medical alcohol. Place the infusion in a dark and cool place for 14 days. The wounds are lubricated 2-3 times a day until the fungal infection goes away completely.
- Activated carbon and lard. Lard (100 g) is melted over a fire, coal (5 tablets) is added to it. Apply 30 minutes before bedtime, not in a thick layer.
- Some essential oils have antifungal and antibacterial properties. These include tea tree oil, which is applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day, 1 drop, until complete healing. Not recommended for children under 3 years of age.
- You can prepare a healing mixture from 10 ml of tea tree, 7 ml of real lavender, 3 ml of thyme with thymol and 30 ml of macadamia vegetable oil. Apply with massage movements to the affected area 2-3 times a day for at least 2 weeks.
- Coconut vegetable oil is a natural antifungal agent. It can be used alone or in combination with tea tree essential oil (one drop each), applied locally several times a day.
- Grapefruit seed extract also has antifungal and antibacterial effects. Take for 6 months.
- Baking soda: Dissolve a few tablespoons in a bowl of hot water. Use when affected by mycosis of the feet.
- Apple cider vinegar is also effective in fighting fungi. It has a strong cleansing effect. Dilute 3 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water and wipe the affected area with a cotton swab. Leave to act for 20 minutes and then rinse. Apply 3-4 times a day.
- To prepare a medicinal infusion, you need to mix sage, oak bark, chamomile and St. John's wort - 30 grams each. Everything is poured with 250 ml of boiling water and left for 1 hour. The infusion can be used within 1 hour. They clean wounds with it.
- To prevent detoxification of the body, take 30 g of yarrow, calendula officinalis, burdock, artichoke and rosemary. Place 4 tablespoons of the mixture in a liter of cold water. Bring to a boil for 3 minutes, then turn off the heat, cover and let simmer for 15 minutes. Drink 20 minutes after meals, 3 times a day. Do a three-week course of treatment, alternating with a week break.
In older children, the focus is on gut health, which is supported with enzymes (Festal, Mezim, Creon), yogurt and high-fiber plant foods. It is recommended to combine dishes with bitter substances such as wormwood or ginger. In addition, a cup of horsetail tea three times a day is recommended.
If you suspect a fungal infection in a child, you should consult a dermatologist to determine the type of mycosis and begin treatment.
Prevention
Fungus can be prevented by following the following rules:
- Wear only your own shoes in public places (sauna, bathhouse) and at home.
- Boots should be true to size and made from quality materials.
- After a walk, treat your child’s shoes with alcohol, dry and air them.
- Prevent viral diseases. This is facilitated by fortified nutrition, hardening, and exercises in the morning.
- Monitor the temperature of your feet, avoid excessive sweating, change socks when they get wet.
- When bathing, use antibacterial soap.
- After trimming a child's nails, treat scissors and clippers with alcohol.
- Pay attention to diseases in a timely manner and treat them.
Fungus is an unpleasant disease that is difficult to cure. If all prescribed measures are followed, the problem will be resolved faster, and the baby will return to a full life.