Dermatitis: what is this disease?
Dermatitis in newborns (infantile eczema) is a set of processes of inflammatory and allergic origin that occur against the background of sensitization (hypersensitivity) of the child’s body to all kinds of irritating substances that surround it. The impact of these agents (physical, biological or chemical) on the child’s body leads to a typical manifestation of dermatitis - a rash. Elements of the rash can be localized on different parts of the body: on the baby’s neck, on the face, on the stomach or limbs. As a rule, dermatitis is first detected in infants and children under one year old. The first cases of dermatitis detected in preschool age are very rare.
How to recognize atopic dermatitis?
There is an opinion that the disease is transmitted by bottle-fed children, but this is a myth, since the percentage of dermatitis in breastfed babies is rapidly growing. Timely diagnosis will allow you to easily get rid of the first manifestations of the disease.
The main signs may be:
- Redness, itching, peeling: neck, cheeks, back, elbows and knees, buttocks
- Dry skin
- Getting wet
- Peeling of the scalp and face
- Nodular rash
- Local change in cover color
- Thin, sensitive skin, prone to cracks and damage.
A newborn will not be able to tell his parents about inconvenience or pain, so you need to pay attention to the baby’s behavior. In particular, on his mood, sleep and appetite. But many attribute the presence of these symptoms to diathesis.
Why may dermatitis appear in an infant?
The sensitivity of infants to various environmental factors is determined, first of all, by the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the skin and immune system. In the first year of life, the skin does not perform protective and thermoregulatory functions well enough, and the immune system synthesizes antibodies in insufficient quantities (especially class A immunoglobulins, which protect the mucous membranes and skin).
The combination of the above features leads to the fact that at an early age, children quite often develop various types of dermatitis. People are accustomed to calling any dermatitis “diathesis”, but this is a mistaken opinion. Diathesis is not even a disease, but just a type of constitution that leads to certain developmental characteristics and includes the concept of a child’s predisposition to certain diseases.
It should be remembered that diseases of an allergic nature are not inherited, however, some features of the immune system can be passed on from parents to the child, which cause increased sensitivity to allergens. There are a number of factors that play a significant role in the occurrence of different types of dermatitis. These include:
- chemical agents (household chemicals, powders, body lotions, antiseptics used to treat skin);
- mechanical irritants (clothing made of rough, synthetic fabrics);
- physical factors (ultraviolet radiation, temperature disturbances, high or low humidity);
- biological agents (pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms that live on the skin, fungi, especially the genus Candida, Mallasezia furfur, plant pollen, fluff, dust, pet hair).
Pediatricians tend to believe that an increased risk of dermatitis exists in infants suffering from frequent viral and bacterial infections, pathologies of the digestive system, and immunodeficiency conditions. There is a high risk of developing this disease in premature babies, as well as infants who suffer from rickets, are overweight, and have anemia.
Traditional methods of treatment
You can also achieve the disappearance of an allergic reaction with the help of medicinal herbs. This option is used if a person cannot take hormonal medications or antibiotics.
Decoctions and baths will help cope with allergic dermatitis. Birch tar has a positive effect on the skin. This component has a number of advantages:
- Makes the skin softer and quickly eliminates dead cells.
- Elimination of harmful microbes.
- Eliminates redness and irritation.
- Removing subcutaneous water that causes swelling.
- Relieving itching.
- Kills parasites.
Traditional healers recommend using tar in its pure form. This option retains the maximum number of positive characteristics. To apply the composition, it is advisable to use a special brush. You can rub in the tar using light and gentle hand movements. The technique is considered correct if the surface is not rubbed too much. Otherwise, the risk of developing irritation and discomfort increases.
The healing properties of chamomile will help get rid of dermatitis
The product continues its effect for the next six hours. The course of treatment involves repeating the procedure twice a day. The duration is at least fourteen days.
Applying the cream to the skin can only be done if the baby has been previously bathed. At the first stage of treatment, an allergy test should be performed. To do this, apply a small amount of cream to the crook of your elbow. The composition can be used no longer than a certain period of time. There will be no positive effect on wet areas.
Newborn dermatitis: types, main symptoms
Dermatitis is a group of inflammatory skin diseases that includes many nosological units (various diseases, each of which differs in causes, course and treatment methods). The following types of disease are most often recorded in newborns: diaper dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis and toxic dermatitis. Each of the above forms has its own characteristics, which will be discussed in detail below.
Diaper dermatitis
This type of dermatitis, as a rule, occurs due to improper care of the child’s skin, for example, if the baby’s diapers are rarely changed or regular hygiene procedures are neglected. This is a fairly common problem, especially often diaper dermatitis occurs in girls aged 7-12 months.
Skin lesions are often observed precisely in those areas of the skin that are most in contact with diapers and diapers. This disease is accompanied by hyperemia (redness) and maceration (wetting) of the skin in the buttocks, genitals, perineum, lower abdomen, and inner thighs.
If treatment for diaper dermatitis is not started at the hyperemia stage, then a more severe lesion develops, which is accompanied by the formation of vesicles (bubbles) and papules (nodules). After this stage, an even more severe lesion develops: erosions and ulcers form, which can merge, then they become covered with crusts and peel off. Severe diaper dermatitis affects not only the skin, but also the general condition of the child: the baby becomes capricious and restless, may sleep poorly and refuse to eat.
Seborrheic dermatitis
The causative agent of this disease is considered to be one of the representatives of the opportunistic flora, namely the fungus Mallasezia furfur. Normally, it lives on human skin, but in conditions of decreased immunity it can become pathogenic, causing seborrheic dermatitis.
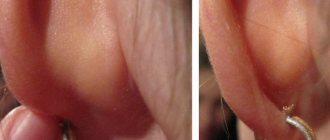
This disease usually appears in the first months of life and disappears without a trace by one year, and sometimes by 3 years. Gray scales - gneiss - appear on the scalp of the child, then they merge to form a sebaceous crust. Gneiss can also be on the skin of the forehead, on the eyebrows, behind the auricle. Seborrheic dermatitis often does not bother the child and does not affect his condition. It is important to note that under no circumstances should you try to remove the scales; in this case, there may be a risk of infection.
Is seborrhea contagious? You can read here.
Contact dermatitis
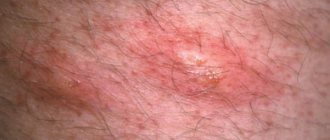
The difference between this form of the disease is that a skin rash appears exactly in the place where the damaging factor was affected. The affected area is always clearly limited and almost never spreads to other parts of the body. The skin at the site of contact with the allergen becomes hyperemic, and symptoms such as burning and itching are pronounced. Later, blisters appear filled with a clear serous fluid, then they open, forming ulcers that eventually become covered with crusts.
Contact dermatitis goes away on its own if the irritant is identified in time and contact with it is limited. If this is not done, the disease will become chronic, which is more severe and causes a number of complications.
Atopic dermatitis
This form of the disease is one of the most complex in its course; it has many consequences and complications, albeit long-term. Atopic dermatitis usually occurs after 6 months, when complementary foods are introduced. It is food products that most often provoke the development of symptoms of the disease.
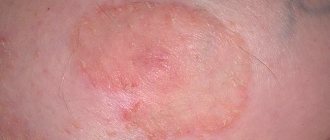
The clinical picture of atopic dermatitis consists of hyperemia of symmetrical areas of the skin with the appearance of either peeling and dryness, or blisters and weeping elements. Most often, the rash occurs on the face (especially on the cheeks); sometimes lesions are observed on the trunk and limbs.
The danger of this dermatitis is that there is a high probability of developing the so-called “atopic march” - a sequence of allergic diseases that are difficult to treat. These include atopic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis and bronchial asthma.
Toxic dermatitis
This disease develops when the allergen enters the child’s body through the mucous membrane of the respiratory or digestive system. It can develop gradually, making it difficult to diagnose. Typical manifestations of dermatitis are observed on the skin: redness, dryness and peeling; in severe cases, vesicles form and, as a result, ulcers. The main task of the doctor in this case is to recognize the allergen and isolate the child from it. More information here.
Dependence of the appearance of symptoms on the nature of the pathology
If the child has been in contact with one or another irritant and this has caused a rash, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. This is especially true in cases where the main “culprits” of the pathology are plants. In medicine, such dermatitis is called phytoderma. It most often appears in the form of a small rash, prone to slight changes in the boundaries. The skin becomes inflamed, and the spots that appear quickly acquire distinct boundaries.
Contact with any irritant can lead to acute contact dermatitis. But the nature of its course depends on both external and internal factors. Its further transformation into subacute and chronic forms can lead to the appearance of new symptoms that are unpleasant for the child:
Acute form of pathology
A small or large pink or red rash appears. It is swollen and has clear boundaries. Sometimes these are vesicles containing liquid inside. Combing them leads to the leakage of this component and the formation of dry crusts.
Subacute form
It is characterized by the appearance of dry, scaly plaques. Less commonly, the formation of hard, pointed blisters is observed.
Chronic dermatitis. The main symptom is lichenification.
The appearance of signs of allergic contact dermatitis also has its own characteristics. Most often, the first symptoms are a common or papular rash.
But the appearance of peeling occurs later than in cases of ordinary dermatitis. The disease also depends on the presence of other allergic pathologies in the child (conjunctivitis, rhinitis, bronchial asthma, etc.). This course of dermatitis may have additional symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness;
- headache.
Dermatitis causes severe discomfort in the child
Diagnosis of dermatitis
Diagnosis of this disease is carried out by dermatologists, immunologists and allergists. In addition to examining the child and talking with the mother, blood tests are also prescribed (complete blood count, immunoglobulin E test, biochemical blood test). Sometimes scratch tests, prick tests, and patch tests are used to determine the allergen. Also, in severe cases, dermatoscopy and consultation with other specialists are recommended (in order to exclude possible concomitant pathologies). In general, diagnosing dermatitis in an infant is not difficult for an experienced doctor.
Treatment of dermatitis in infants: basic principles
Today, an integrated approach is used to treat the disease in childhood, which includes the following measures: avoiding contact with the allergen, as well as pharmacotherapy.
To treat dermatitis in an infant, drugs from the following pharmacological groups are most often used:
- antihistamines. Up to the age of one year you can take Fenistil, Tavegil, Fenkoral. Fenistil is considered the safest drug - it can be taken starting from 1 month (for convenience, it is available in drops), and also in the form of a gel - Fenistil-gel;.
- enterosorbents. Drugs from this group are used to quickly remove toxins and their breakdown products from the body, thereby reducing the intensity of inflammation and allergic reactions. In infants, Polysorb and Smecta are used;
- glucocorticoids. In severe cases, drugs from this group are prescribed, but they have a lot of side effects, so they should be used only under the supervision of a doctor. They use drugs containing Prednisolone and Hydrocortisone, but do this only for absolute indications;
- emollients. Used to soften and eliminate dry skin. Panthenol and Bepanten are the most popular - they can be used from the first months of a child’s life. anti-inflammatory creams and ointments. They relieve the symptoms of the disease, reduce the intensity of inflammation, and have a healing effect. Methyluracil and Arnica are recommended for children under one year of age.
Non-drug treatment is also recommended, for example, physiotherapeutic procedures are highly effective: UV irradiation, magnetic therapy, hyperbaric oxygenation, and reflexology.
For seborrheic dermatitis, specialized skin care products are prescribed that restore normal skin microflora and improve metabolic processes in the epidermis. Shampoos and gels with tar and ketoconazole are used.
Irritants and allergens
Contact dermatitis in a child has 2 main forms - simple and allergic. Simple pathology develops without the participation of allergens. Most often, inflammatory processes occur due to contact with obligate irritants. These are objects and substances, contact with which causes a rash in all people, regardless of their age. Obligate irritants such as paints, acids, alkalis and oils are rarely the main cause of pathology in infants under one year of age. After all, caring parents try to remove everything unnecessary and dangerous to the most remote and inaccessible corners of the home for their “child.” But a factor such as friction is the most common cause of dermatitis. Poor quality clothing, the presence of rough seams on the inside, carpets and rugs - all this can harm the health of the child. The influence of physical factors, which include high or low air temperature, solar energy, etc., cannot be excluded.
Allergic contact dermatitis in children most often occurs due to the influence of irritants, which are called facultative. They are understood as factors, substances or objects, skin contact with which causes an allergic reaction. They are determined by genetic predisposition or the immune system of the patient himself. The immune system of babies is unstable to various irritants, and if they have a predisposition to such a reaction, then the risk of developing rashes on the body will always be high.
Clothes for babies should be soft and without thick seams
Disease prognosis
The prognosis for most types of dermatitis (contact, seborrheic, diaper, toxic) is favorable. If you go to a medical facility in a timely manner, signs of dermatitis do not appear in adulthood, and the child grows and develops absolutely normally. But if therapy is not started on time, the risk of complications is high.
Atopic dermatitis, as mentioned above, is one of the most dangerous forms of the disease. To treat this disease, it will not be enough to avoid contact with the allergen and use topical medications; it is often necessary to constantly monitor nutrition, follow a hypoallergenic diet, and also see a doctor in order to avoid the appearance of the “atopic march.” But even atopic dermatitis can be cured, you just need to start therapy on time and follow all the doctor’s instructions.
Localization
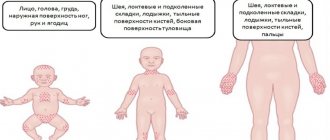
Allergic dermatitis is accompanied by severe itching. Red spots appear on the cheeks, legs, and arms. If the allergen reaction is strong, the abdominal and back areas are affected. Weeping ulcers may form on the affected area of the skin.
Let's look at the typical location of the disease:
- On the face: diathesis is accompanied by cough, nasal congestion and lacrimation. Rashes on the skin of the face are often provoked by fruits, vegetables, flavors and dyes. Symptoms of an allergic reaction appear fairly quickly - within 30 minutes.
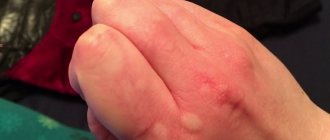
- On the hands: this is a common location for diathesis. With direct contact with an allergen (household chemicals, cosmetics), redness appears on the back of the child’s hands. The skin becomes dry and tight. Itching and peeling occur. Often, allergies on the hands appear after an insect bite. Severe itching forces the child to constantly scratch the affected area. This significantly aggravates the condition. An example photo of allergic dermatitis in a baby is below.
- Allergic dermatitis may appear on the hands after eating sweets, coffee, cocoa and some medications. Even a change in weather affects a child's health. Wind and frost cause redness, swelling and severe itching on the hands. Therefore, it is necessary to use a special cream for the baby’s hands and wear warm gloves in cold, frosty weather.
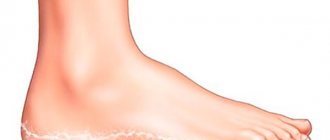
- On the legs, allergic dermatitis in children (photo below) is localized in the main affected areas - the thighs, calves, legs and knees.
- Often allergies appear on the feet. Pimples of various shapes and pustules form. In this case, the inflamed areas of the skin swell.
- Allergic dermatitis on the bottom of a child manifests itself in the diaper form of the disease. A common reason is failure to comply with hygiene rules.
- Allergic dermatitis on the head of a child is clinically manifested in the form of flaky crusts.
The latter type of dermatitis usually manifests itself in the seborrheic form, which we will discuss in more detail below.
Complications of dermatitis in newborns
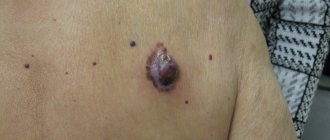
Parents of a child should always remember that damaged skin is an entry point for infection. And since the child’s immune system is not sufficiently developed, it will be difficult for the body to cope with a secondary infection on its own. A serious complication that can arise as a result of infection is Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis - its causative agent is most often pyogenic cocci. In this case, large blisters (over 5 mm) appear on the child’s skin, which then rupture, leaving bleeding ulcers. In this case, the child is in serious condition, and if there is extensive skin damage, the baby requires medical care and treatment in the intensive care unit.
Sometimes it is possible for the disease to become chronic (for example, with seborrheic, atopic, contact form). In order to avoid the consequences of the disease, it is necessary to consult a specialist in time, and also to determine the provoking factor that caused this condition.
Prevention of dermatitis in infants
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat, so experts recommend following a number of preventive measures that will help avoid the appearance of dermatitis in infants. These include:
- compliance with hygiene rules. It is necessary to change the baby's diapers often and bathe the baby regularly.
- Avoid diaper rash and hypothermia. To minimize the risk of dermatitis due to exposure to physical factors, you need to carefully monitor the temperature and humidity levels in the room where the child is. When walking, you also need to pay attention to whether the child is comfortable in his clothes.
- give preference to diapers and clothes made of soft fabrics. It is also desirable that these fabrics be natural - this is necessary in order to avoid excessive mechanical stress on the child’s delicate skin.
- carry out wet cleaning more often. This is necessary in order to prevent the accumulation of dust, because... this leads to the development of allergic reactions, including dermatitis. It is also recommended to ventilate the room more often.
- introduce complementary foods correctly. When introducing complementary foods, gradualness and caution are important. In no case should you immediately give your child a puree of several fruits or vegetables - you must first give the ingredients of the puree separately (give each one for several days and monitor the child’s condition and his skin).
Remember that only a specialist should diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment. Self-medication can lead not only to a deterioration in the child’s general condition, but also to a number of complications, some of which are quite dangerous.
Read more about the causes of dermatitis
There are many reasons why dermatitis may occur in a baby. These include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- viral and infectious diseases in the mother during pregnancy and lactation or in the baby in the first months of life;
- taking medications by the mother during pregnancy or breastfeeding, as well as their use in the child after birth;
- complicated pregnancy or childbirth;
- inadequate care of the infant;
- improper nutrition of the mother during breastfeeding;
- artificial feeding of the baby;
- early introduction of complementary foods and incorrect choice of products for it;
- intestinal dysfunctions in a baby, etc.
Often, dermatitis in newborns develops due to improperly selected diapers, infrequent changing of diapers, or the use of inappropriate detergents (soap, shower gel, washing powder for washing children's clothes, etc.).
The mother's nutrition during breastfeeding is important for the health of the baby's skin, since most substances penetrate into the milk. Thus, the baby can receive a certain amount of allergens during feeding, which will provoke allergic dermatitis in the baby. In the second half of life, children begin to be introduced to complementary foods. And here, too, you need to carefully consider the choice of products.
Hereditary predisposition always creates the preconditions for the development in children of the same diseases that their parents have. This is especially true for the tendency to allergies. In such cases, increased discernment is required when choosing baby cosmetics, diapers, detergents, and products for first feeding.
However, despite all precautions, up to 90% of all parents encounter childhood dermatitis of various etiologies.