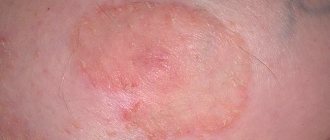
How is atopic dermatitis treated?
Treatment will depend on the symptoms, age and general health of the child, and how severe the disease is. There is no cure for atopic dermatitis, and the goal of treatment is to reduce itching and inflammation, moisturize the skin, and prevent infection.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis includes:
- Stay away from irritants as recommended by your doctor.
- Regular bathing in warm water or washing your face as recommended by your doctor.
- Trim your child's nails regularly and cover the affected areas with clothing or bandages to prevent scratching, which can cause skin irritation and infection.
- Use moisturizers recommended by your doctor.
The doctor may also prescribe medications, which can be taken separately or together. The following are most commonly used to treat atopic dermatitis:
- Corticosteroid cream or ointment. Cream or ointment is applied to the skin - helps reduce itching and swelling.
- Antibiotic. Drops or tablets can be taken orally to treat the infection.
- Antihistamines. Drops or pills can be taken before bed to reduce itching and improve sleep.
- Calcineurin inhibitor cream or ointment. Cream or ointment will reduce itching and swelling.
- Phototherapy (light therapy). Light therapy can be done in a hospital or at home.
- Immunomodulatory medicine. Take oral pills or tablets that affect the immune system. This method is used when other treatments do not work. The medicine has side effects, the child will have to undergo regular blood tests to check for them.
Local treatment
- Anti-inflammatory ointments and creams: “Tsindol”, “Ketotifen”, “Triderm”. The products relieve inflammation and are used for 10-14 days. Participate in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
- Hormonal ointments are used for long-term illness. There is no need to worry about the side effects of such drugs. The composition contains a small amount of corticosteroids, which cannot change the systemic blood flow. "Elocom", "Advantan" and other ointment preparations are approved by the Council of Pediatrics.
- Antihistamines to reduce itching: Suprastin, Fenistil. Many remedies are prescribed from the age of two.
- Calcium Gluconate tablets for itching.
- Cell membrane stimulants, for example, Ketotifen. The effects of the tablets are similar to antihistamines.
- Products for maintaining immunity: “Polysorb”, “Enterosgel”.
- Chatterbox. The suspension is prescribed by a doctor and is done in front of you upon arrival at the state office. pharmacy. You need to smear it 2 times a day, in the morning and in the evening at least an hour before swimming, so that it is absorbed, there is no need to rinse off.
Treatment
Drugs that help fight allergic dermatitis
Despite the existence of a large number of folk remedies, only a doctor can tell how to treat allergic dermatitis in a child so that his condition improves. Therapy under the constant supervision of a doctor is what can really help, and not the dubious advice of friends, neighbors and grandmothers.
Medicines
Depending on the age of the child and the nature of the skin lesions, the doctor may prescribe the following drug treatment for allergic dermatitis.
- Antihistamines: Peritol, Tavegil, Suprastin, Loratidin, Diazolin, Zyrtec, Finistil, Claritin, Clemastine.
- Antibiotics are recommended for bacterial infections of the skin.
- An antibacterial ointment for allergic dermatitis for children may be prescribed: Erythromycin, Lincomycin, Gentamicin.
- Membrane stabilizing agents: Ketotifen, Cetrizine, Loratadine.
- Vitamins.
- Some emollient cream against allergic dermatitis may be recommended as local preparations: for example, Advantan, Panthenol, Bepanten.
- Glucocorticosteroids: Dermovate, Hydrocortisone, Elokom.
- Medicinal skin moisturizers: Lipikar, Topicrem, Atoderm, Trixera.
- For weeping and purulent formations, wound healing drugs are prescribed: Actovegin, Methyluracil ointment, Solcoseryl.
- Sorbents for removing toxins from the body that cause allergic dermatitis: Activated carbon, Enterosgel, Latcofiltrum.
In addition to medications, the doctor may prescribe various auxiliary procedures.
Procedures
Since the treatment of allergic dermatitis in infants is a difficult task due to such a young age, when most medications are contraindicated, the doctor can prescribe therapeutic procedures for babies.
- Laser.
- Ultraphonophoresis.
- Quartz.
- Alternating magnetic field.
- EHF (electromagnetic radiation).
The main goal of such procedures is to relieve the exacerbation of allergic dermatitis and eliminate external symptoms. Sometimes a doctor may allow treatment at home with folk remedies if they are not contraindicated for the child.
Folk remedies
For allergic dermatitis, treatment with folk remedies is possible, subject to certain rules. Firstly, it should not be carried out as the main one, but only as an auxiliary one. Secondly, a clear doctor’s permission must be obtained for this. And thirdly, you first need to find out whether the child has any contraindications for such specific therapy.
- Tampons with aloe juice, fresh pumpkin or raw potatoes.
- Ointment made from St. John's wort juice (1 tablespoon) and butter (4 tablespoons).
- Ointment made from milk, glycerin and rice starch (1 teaspoon each).
- A mixture of linseed oil (100 g) with chamomile flowers (1 tablespoon).
- Dandelion infusion for oral administration.
- A paste of camphor (1 teaspoon) and sandalwood powder (2 teaspoons).
All these folk remedies for allergic dermatitis cannot guarantee 100% results. And curing a child completely is not within their competence. Relieve external signs of the disease, improve skin condition, reduce pain and itching - these are their main functions. We need to keep this in mind. Proper care of a sick baby and his skin will bring much more benefit.
On the role of heredity. According to studies, allergic dermatitis develops in 80% of children if both parents are sick with the same disease, in 60% if either the father or mother suffers, while the other parent is diagnosed with an allergic pathology of the respiratory tract, in 55% if someone is sick. then one.
Diet
When the first signs of skin lesions appear in a baby, a nursing mother should review her diet and include only hypoallergenic foods. A diet developed for a mother with atopic dermatitis in an infant should be based on the complete exclusion of the following foods:
- whole milk and egg whites;
- chocolate and cocoa derivatives;
- chicken, pork;
- coffee;
- honey;
- citrus fruits, red berries, fruits;
- fish dishes;
- mushrooms;
- sauces, spices, marinades;
- legumes;
- flour products, sweets;
- canned food in jars and packages.
The diet of a nursing mother with atopic dermatitis of a breastfeeding infant should be light, fresh, and free of dyes and preservatives. Pediatricians recommend the following products for the weekly menu of the mother of the child:
- steamed/boiled meat (lean beef, veal, rabbit);
- baked/boiled zucchini, potatoes;
- light soups based on cereals;
- dairy-free cereals;
- dry biscuits, drying;
- weakly brewed tea;
- dairy products;
- baked apples.
With caution, while observing the baby's reactions, you can introduce bananas (whole and pureed), watermelon, and cottage cheese casseroles. If the baby is bottle-fed, it is necessary to choose formulas based on goat and soy milk, but only after consultation with a pediatrician.
Living with atopic dermatitis
There is no cure for atopic dermatitis. But usually the skin condition improves and the dermatitis goes away on its own as your child gets older. There may be cases when a child has mild or no symptoms of the disease, but at some point the child’s condition worsens. This is called a flash. To prevent outbreaks, make sure your child:
- Avoids triggers. Common triggers include irritants (such as wool, soaps, or chemicals), allergens if diagnosed by your healthcare provider, and stress.
- Does not scratch the skin. Try to prevent your child from scratching. This can cause skin deterioration and infection.
- Always has short nails. in a timely manner so that they are short and he cannot scratch himself.
- Takes warm baths or showers (not hot). After the procedure, apply moisturizer to damp skin.
- Uses moisturizers. Apply creams or ointments immediately after bathing.
- Wears soft clothes. Do not dress your child in wool or other rough fabric.
- Does not receive smallpox vaccine. This is not a common vaccine, but people with atopic dermatitis should not receive the smallpox vaccine.
Talk to your doctor about other ways to improve your child's skin.
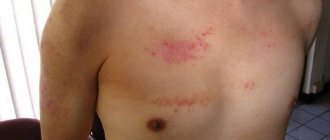
What is allergic dermatitis in children
Skin rashes that appear after eating new food or coming into contact with certain objects are the simplest definition of allergic dermatitis in a child. Unlike atopic dermatitis, this type of dermatitis goes away after the allergen is eliminated, although in a chronic course the symptoms may persist for some time. Despite the fact that the disease mainly consists of only temporary irritation of the skin, it requires mandatory treatment. Lack of therapy can lead to complications.
What is?
Diet for atopic dermatitis in children is an important component of recovery. A special nutrition system has been developed especially for children, which includes protection against all kinds of allergens in products. You should remove from your diet:
- seafood and ocean fish;
- chocolate;
- candies;
- sparkling water.
The baby's diet should consist of the following ingredients:
- meat: lean chicken, veal, rabbit;
- dairy products: cottage cheese, low-fat sour cream;
- all cereals and porridges;
- vegetables that are exclusively green in color;
- apples and pears from domestic producers;
- water and apple-based compotes; during the period of remission you can drink berry fruit drinks;
- synthetic complexes of vitamins and minerals important for growth and development.
Is swimming allowed?
To prevent your baby's skin from becoming dry during atopic dermatitis, it is worth moisturizing it regularly. This can be done by bathing. In addition, you can bathe even during the acute phase of the disease. The baby should not take a bath. The best solution is a shower.
It is best to use the shower daily, and after taking it, use creams that promote even more optimal hydration. For small children, not only are water treatments allowed, in addition to them you can use decoctions of celandine, wormwood and string, but only separately.
If you are worried about dermatitis on your child’s head, you should use medicated shampoos that have a neutral pH and do not cause allergic reactions.
How inflammation occurs
The mechanism of the occurrence of a delayed allergic reaction is quite difficult to explain, and it has not yet been fully studied. But based on the data available today, we can safely say that inflammation “organizes” the immune system itself. This behavior is quite understandable: allergen molecules are very small in size, and when such a substance first enters the body, vigilant and vigilant immune cells-lymphocytes are simply not able to “notice” that outsiders have entered.
Microscopic allergens, meanwhile, bind to certain proteins, as well as viruses and bacteria, and as a result noticeably “grow” and acquire substantial dimensions. The immune cells finally notice this, the “allergen + protein” structure is destroyed, but the uninvited guest is remembered for a long time. The next time a child comes into contact with the same allergen, lymphocytes, without wasting time, begin to “shoot sparrows from a cannon,” and the baby’s skin becomes covered with what results from such a fight - an inflammatory rash.
How to organize a routine for a child?
A daily routine is an important component for a child suffering from atopic dermatitis. The daily routine should include daytime sleep, for which you should allocate about 4 hours. During the rest period, the nervous and immune system is restored, the child feels cheerful and energized.
The duration of night sleep is from 8 to 9 hours, for children under one year old - 12 hours. During sleep, children's levels of histamine, a component that causes severe itching, decrease. During an exacerbation of the disease, physical activity and play decrease. The baby is uncomfortable, so he is capricious. It is better to minimize the number of games during this period; the child should get good sleep and rest.
Stages of dermatitis
When assessing the condition of a patient suffering from allergies, a doctor first tries to determine the stage of the disease. Based on the conclusions made, the issue of choosing treatment tactics is decided. There are 4 stages of allergic dermatitis:
- The initial stage is accompanied by hyperemia, swelling of the skin, and peeling. If you start treating diathesis in children in time, you can soon forget about all the unpleasant symptoms forever. At the same time, improper treatment or its absence leads to the development of the next stage.
- The expressed stage of the disease occurs in chronic and acute forms. Rashes lead to the formation of crusts and scales at the site of inflammation.
- The remission stage leads to a decrease or disappearance of all unpleasant allergy symptoms. This period can last for weeks and sometimes years.
- At the stage of clinical recovery, all manifestations of atopic dermatitis completely disappear for several years.
Possibilities of recovery in the sanatorium
The chronic form of diseases is the most insidious because of the inability to live fully. For children whose disease is difficult, different methods of ultrasound, magnet and light therapy should be used. It is more reliable to treat atopic dermatitis in a health center; the child will be prescribed several procedures at once, lasting from 1 to 2 weeks.
Therapy at the sanatorium has a positive effect on health, the number of exacerbations is significantly reduced. Children undergoing rehabilitation at sea feel much better, living a full life. It is best for children with atopic dermatitis to stay in sanatoriums near the sea for a period of 2 to 3 weeks.
Varieties
In medical practice, dermatitis is classified depending on the age of the sick child.
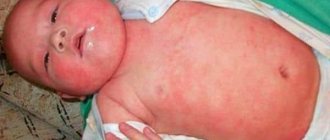
- In newborns, the pathological syndrome occurs after childbirth and accompanies the patient until he reaches 36 months of age. The rash occurs on the face, lower and upper extremities. It is possible for dermatitis to spread over the surface of the body, more often occurring against the background of a change in diet or teething.
- The pediatric variety includes a group of patients from 3 to 12 years old. The pathological syndrome affects the face and neck, rashes are possible in the elbows and knees. The affected areas swell and small cracks appear. After scratching the rash, a crust appears.
- Adolescence, from 12 to 18 years. A characteristic feature is the appearance of a rash all over the body. It is impossible to determine the exact localization of the pathological syndrome. Rashes appear and disappear on their own.
The development of a chronic form is possible. For several decades, the disease has been in remission, and sometimes suddenly makes itself felt.
Preventive measures
Disease prevention begins with the goal of preventing the acute phase of the disease. If your baby suffers from atopic dermatitis, try:
- follow a diet;
- use hypoallergenic components;
- use anti-allergenic agents during flowering and pollination;
- strengthen the immune system by piercing and active games on the street;
- take care of your baby’s skin: apply cream, moisturize it, wear only natural clothes;
- breastfeed as often as possible;
- Clean toys in warm water.
Key points about atopic dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis is a long-term (chronic) skin disease that is most common in infants and children, but also occurs in adults.
- A child with allergies or family members with allergies or atopic dermatitis are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis.
- Itching, dryness and redness of the nasolabial triangle are common symptoms.
- The goals of treatment are to reduce itching and inflammation of the skin, increase moisture, and prevent infection.
- Avoiding triggers is important during treatment.
- Atopic dermatitis usually goes away as the child gets older.
Diagnostics
Prescribing effective treatment requires timely diagnosis of the disease, clarifying its form and identifying the etiological factor. To quickly make a correct diagnosis, you should consult a dermatologist or allergist.
It is usually enough for a doctor to conduct a survey of parents to collect a complete history of the disease and the child’s life, detailing the existing risk factors for the development of allergic dermatitis. To confirm the diagnosis and differentiate it from other pathologies, additional research methods may be required:
- general, biochemical blood test;
- stool examination for dysbacteriosis, scatological examination;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys, pelvis;
- conducting allergy tests;
- study of immune status.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most out of your healthcare visit:
- Before your visit, write down the questions you want answered.
- When you visit, write down the names of new medications, treatments, or tests, and any new instructions the doctor gives you for your child.
- If your child has a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose of the visit.
- Find out how you can contact your doctor after hours. This is important if your child gets sick and you have questions or need advice.