Causes of painful swelling
A tumor in the ear also raises suspicions of various infectious and inflammatory processes - otitis media. Some forms of otitis may also be described as aging lumps in the ears. For example, with bullous otitis media, bubbles filled with bloody contents – bullae – appear in the tympanic cavity. After the bullae burst, blood is released from the auditory opening. However, this form of otitis is not accompanied by severe pain.
If it is not possible to see a doctor for a professional diagnosis, but it is necessary to take measures to prevent the development of the disease, you can focus on some symptoms characteristic of various diseases.
- Acute infectious otitis media. Accompanied by a sudden sharp pain, which is described by the sick word “shooting”. Body temperature becomes higher than 37.5C. A yellow-white or transparent secretion is released from the ear canal. However, with different forms of otitis, variations in symptoms occur:
- mild itchy pain sometimes indicates that the cause of the disease is a fungal infection,
- an unpleasant smell of secretion - that the cause of infection was staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria,
- long-term development of processes and a gradual increase in symptoms with a feeling of water flowing in the ear is characteristic of allergic otitis.
- Furunculosis and folliculitis. The place where inflammation occurs is the canal and the concha. Usually a boil is detected by pressing on the lower wall of the shell or tragus - such a lump in the ear hurts when pressed. However, a more reliable diagnosis is made if it is possible to see the characteristic canonical elevation of the boil. To examine it, they usually pull back the lobe, which with furunculosis is also accompanied by pain.
- Wen. At the time of formation, the wen looks like a pimple with redness and tension of the shiny skin above it. When it becomes inflamed, a local increase in temperature is recorded, and with the development of the disease, symptoms of general intoxication are noted.
- Ear plug. In this case, there is deterioration in hearing, congestion in one ear, and pulling pain.
- Foreign bodies that create a feeling of an inflamed formation in the patient can be detected by visual inspection using a mirror.
- Lymphadenitis. When the regional parotid lymph nodes become enlarged, pressure may occur. This condition is accompanied by deterioration in health, headache and weakness.
- The manifestation of caries and other dental problems is also often accompanied by unpleasant sensations and itching in the ear canal.
- Laryngitis and sore throat are often accompanied by ear pain, which is usually accompanied by a cough and burning sensation in the throat.
- Perichondritis and mastoiditis. In these diseases, either the auricle is affected in areas where cartilage tissue is present (perichondritis) or the mastoid process behind the concha, related to the temporal bone (mastoiditis). With the development of mastoiditis, severe ear pain can also be recorded, but in this case its localization shifts to the deep sections (compared to furunculosis), and the course of the disease is accompanied by deterioration of hearing. With intra-ear inflammation, these two diseases are usually easily excluded during self-diagnosis immediately when specific external signs are detected.
Neuritis and neuralgia can also manifest themselves as various reactions in the ear. If the patient himself or the ENT doctor does not find any pathology, and the pain appears as if “out of nowhere,” then the following causes of a neuralgic nature are possible:
- pain in the anterior part of the surface of the auditory canal indicates dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint,
- compression of the greater occipital nerve causes pain in the concha,
- pain in the eardrum is provoked by diseases of the internal organs (usually the stomach) - in this case, the eardrum is innervated by the vagus nerve.
Below are the most common causes of a painful lump or tumor.
Tumors of the external ear
Benign epithelial neoplasms of the outer ear include squamous cell papilloma and ceruminoma. Malignant neoplasms are represented by the following tumors:
- Squamous cell carcinoma;
- Basal cell carcinoma;
- Adenocarcinoma from ceruminoma;
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Oncologists detect the following soft tissue tumors in the ear and jaw area:
- Hemangioma;
- Neurofibroma;
- Neurilemmoma (schwannoma).
Fibrosarcoma or rhabdomyosarcoma can develop in and around the ear. Papillomas most often occur on the skin of the auricle. If the neoplasms are located in the external auditory canal, they often fill its lumen, resembling polyps that come from the middle ear. Ceruminoma of the external auditory canal is a very rare and long-growing tumor arising from the sebaceous (sulfur) glands.
Ceruminoma is usually observed in people over 20 years of age. With this type of ear cancer, the symptoms are as follows:
- Ear congestion;
- Hearing loss;
- Pain and discharge from the ear.
In the initial stage, the tumor is located on the wall of the external auditory canal. The tumor is pink. As it grows, it fills the ear canal and looks like a polyp. Radiologically, good pneumatization of the mastoid process is determined. Gradually, the tumor spreads to the middle ear and its walls, destroying them. These changes are determined on radiographs.
Mixed tumors of the external auditory canal are secondary. They most often originate from the parotid gland and penetrate the external auditory canal.
Nevi (benign pigmented tumors of the auricle and external auditory canal) do not differ in clinical course from nevi that are located on other areas of the skin. Soft tissue tumors (fibroma, hemangioma) arise from fibrous, fatty, muscle, vascular and other tissues.
Fibroma is most often located on the earlobe, at the sites of puncture with a needle for wearing earrings. Dimensions vary from 5 mm to 4 cm. Less commonly, the tumor is localized at the ascending branch of the helix of the auricle and at the entrance to the external auditory canal.
Hemangiomas develop in all parts of the ear. Capillary and cavernous forms of vascular tumors are more often observed. The first ones very often disappear in childhood. Cavernous hemangiomas are located in the thickness of the auricle. They occur in the form of individual or multiple neoplasms. They have a soft consistency and a bluish tint. Hemangiomas of the auricle can affect its edge and other parts. They often spread towards the external auditory canal, closing its lumen, and bleed when injured.
Furunculosis
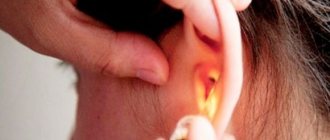
The occurrence of a boil is considered the most common reason for visiting a doctor with a painful lump in the ear. In the external auditory canal, the process first manifests itself in the form of itching, after which a sensation of tissue tension and soreness consistently arises. Pressing the tragus, pulling the lobe, yawning and chewing increase the pain response. Upon visual examination, you can notice swollen skin of the ear canal and sometimes a boil cone with a purulent head.
When diagnosing, you should pay attention to the lymph nodes that are located near the source of inflammation - they will most likely be enlarged and react painfully to palpation.
Types of papillomas
Papillomas can vary in color, size and location of appearance
Neoplasms can appear anywhere, both on human skin and internal organs.
There are special places for papillomas to be located - on the folds of the body, on the neck, eyelids, ears, armpits, chin, nasolabial folds and genital area. Due to growths on exposed parts of the body, a feeling of discomfort appears, and sometimes unpleasant changes in a person’s appearance.
The forms of neoplasms can be varied - these are pedunculated papillae, flat, round, rough, warty.
They can be light or dark brown in color.
Warts-papillomas on the ear do not grow to large sizes, but can narrow the ear canal and significantly reduce hearing.
Ear papilloma reveals itself when cleaning the ears, interfering with the hygiene procedure. Unpleasant discomfort, pain, burning, itching occurs.
Wen (lipoma)
It often takes a long time before the lump is discovered. Lipoma is painless, at first has a soft consistency and grows slowly. However, if the wen is damaged, pain may also occur.
The growth of a tumor can also lead to the same consequences if the formation is localized near the nerves. Then, with its increase, the lipoma begins to put pressure on the nerve processes. This condition can also be perceived by the patient as if something is swollen in the ear and hurts.
Forecast and preventive measures
It is difficult to immediately predict the further course of the cancer process. If it is detected in the early stages and adequate treatment is applied to it, the prognosis will be quite favorable.
Statistics show that with I-II degrees of damage, the survival rate reaches more than 74%. If the formation has grown into any organ, skull or lymph nodes, or has metastasized throughout the body, then the survival rate does not exceed 5%.
Scientists have found that in a third of patients, death from cancer occurs due to low quality of life. To prevent the development of the disease and avoid health problems, it is recommended:
- • observe the work and rest schedule;
- • monitor the quality and duration of sleep;
- • lead a healthy lifestyle;
- • eat enough fresh vegetables and fruits - the role of antioxidants they contain cannot be overestimated;
- • pay attention to physical activity;
- • limit or completely eliminate psycho-emotional stress.
Although these recommendations are simple, they help support the immune system and protect against troubles.
Sulfur plug
Usually a person does not experience any unpleasant sensations until the wax plug increases in size so much that it blocks the ear canal. The increase occurs gradually, but the manifestation, as a rule, is sudden. This happens mainly after water gets into the ear canal, which leads to a sharp increase in the volume of the plug and blocking of the ear canal. The result is congestion, noise, hearing loss, and often autophony (the sound of one’s own voice).
Since the cerumen plug hardens as it grows, the patient may subjectively perceive it as a dense formation or “bump.” If the plug begins to put pressure on the eardrum, headaches, dizziness, and nausea occur reflexively. And after this, inflammation (myringitis) and otitis media may develop, which causes pain directly inside the ear.
First signs
The dynamics of ear cancer do not differ significantly from those of other cancers.
In the early stages, it is asymptomatic, without characteristic external changes. At the very beginning, a small spot or bump, similar to a wart, appears on the ear (on the skin of the cartilaginous part or earlobe). These are the first visible harbingers of trouble, initial manifestations that often go unnoticed. Over time, they transform into a small lump or ulcer. As a rule, it does not hurt and is not expressed by burning, itching or other sensations.
Late complaints of the patient include:
- • weakness;
- • increased body temperature;
- • increased heart rate and breathing;
- • sweating;
- • pain syndrome;
- • hearing impairment;
- • mucopurulent discharge (appears in ulcerative form or when a tumor disintegrates).
Despite the fact that ear cancer develops unnoticed for a long time, when obvious signs appear, the speed of its progression increases, and the pathology quickly progresses.
Any dermatological manifestation has its own signs, the appearance of which indicates the presence of a specific health problem. Papilloma of the auricle also has a number of main symptoms, the appearance of which is a reason to consult a doctor:
- the growth of skin formations, as a rule, is accompanied by a feeling of itching and burning in the affected areas;
- as the size of the formation increases, the presence of a foreign body in the ears begins to be felt;
- deterioration of hearing qualities;
- when the papilloma is located near the middle part of the ears, a feeling of nausea and impaired orientation in space are noted;
- if a tumor grows into the eardrum, the process is accompanied by slight bleeding and suppuration of the inflamed area;
- as soon as the growth blocks the lumen in the auricle, all discharge stops.
The growth may also be located outside the hearing organ. Papillomas are often diagnosed on the earlobe, as well as near it.
The clinical picture of oncology depends on its type and degree of malignancy. Any unusual formation may be cancerous. An experienced oncologist can determine the type of formation during a routine examination.
The localization of education also matters. Middle and external ear cancer is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Ear pain radiating to the jaw or head;
- Headaches with dizziness;
- Burning pain in the ear;
- Hearing loss, feeling of congestion;
- Itchy manifestations;
- Mucopurulent discharge from the ear;
- Putrid odor from the ear;
- The appearance of bleeding, polyps or ulcerations;
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
At the beginning of the oncological process, the pain syndrome is periodic, but with the further development of cancer it acquires a constant, paroxysmal value.
If the tumor is located in the tympanic cavity, then the patient is worried about signs like:
- Pain syndrome;
- Progressive hearing loss;
- Extraneous noise.
What is HPV
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a disease that infects 70% of the world's people. Adults are infected with papillomavirus most often through sexual intercourse or through close contact with a carrier. Most people become infected in childhood: through household means or through intrauterine infection from the mother. Viral infection also enters the body through wounds, scratches, and mucous membranes upon contact with a patient with HPV.
Once in the body, the pathogen lives there and does not manifest itself until favorable conditions arise for this - a decrease in immunity.
The main factors influencing the suppression of the natural defenses of the human body are:
- stress, frequent emotional experiences,
- lack of sleep, fasting or unbalanced diet,
- chronic diseases,
- long-term use of medications,
- frequent colds,
- immunodeficiency,
- decreased immunity due to a person’s age (young children, elderly people),
- hormonal changes (adolescence, pregnancy),
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, allergies, problems in the nervous system in children.
Features of localization and diagnostics
The papillomavirus is activated when the body is weakened. Penetration of the infectious agent occurs through microcracks, wounds and cuts. Papilloma on the delicate skin of the earlobe is a consequence of piercing under the earring. Upon contact with an infected source, HPV infection occurs.
Papillomas on the shells of the ear and in the ear canals have several types. Vulgar, thread-like and flat growths are common. Diagnosis of formations is carried out by a dermatologist or otolaryngologist. The specialist will identify the type of virus and the degree of concentration in the blood.
PCR diagnostics allows you to determine the chronic or acute status of the disease. After analyzing the information, the doctor will be able to select the optimal therapy.
An additional study included a biopsy of papilloma biomaterial from the ear. Histological examination allows you to accurately determine the condition of cells and tissues. If the tumors are small, patients are prescribed an MRI. An alternative option is radiography and probing. Doctors use an otoscope during examination.
In what cases does papilloma form on the ear?
If the virus enters an organism with reduced immunity, it immediately begins to manifest itself. The main symptoms are growths on different parts of the body. The localization of neoplasms can vary significantly and depends, first of all, on the characteristics of the immune system and the presence of concomitant diseases. The growths often form in areas of constant irritation (for example, in areas of contact with clothing), that is, where small scratches and abrasions appear on the skin. But they can also appear on other parts of the body, including the ears.
Papilloma in the ear in adults can appear after going to the pool, piercing the earlobe, or due to touching the hand on which HPV is located. In newborns, ear papilloma manifests itself as a result of HPV infection from the mother: during childbirth or while still in the womb. The immunity of infants is very weak, so the virus successfully attacks the body, signaling this with papillomas.
In adolescents, growths in the ear occur during a period of hormonal changes in the body.
Papillomas in newborns
Papilloma on the ears of a newborn is a separate topic for discussion. Infection of a newborn is possible in two ways:
- Intrauterine or congenital. The diagnosis is made if the expectant mother was a carrier of HPV, and the child was born with papilloma on the ear. During the initial examination, a growth is found on the skin of a newborn.
The disease is also congenital if infection occurs during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal of the sick mother. In this case, the formation appears some time after birth. The discovery of a large number of papillomas in the genital organs of a pregnant woman is a reason for a cesarean section.
- Acquired. This occurs due to the lack of the child’s own immunity in the first year of life. The skin is easily injured, which is a favorable condition for the virus to enter the child’s body.
Due to the lack of its own immunity, the baby can catch HPV
Doctors have not come to a common conclusion regarding children born with papilloma. Some believe that it is enough to keep the babies under control, which will allow surgical treatment at the first sign of a complication.
Another part of doctors believe that if a child was born with a pathology, then immediate intervention is required to remove the growth. This will avoid further injury and, consequently, the spread of papillomas throughout the body.
In any case, parents are required to provide proper care for the child, harden him, and improve the child’s immunity in every possible way.
Since we are talking about complications, we need to emphasize those signs that should alert parents and may become a reason for surgical intervention:
- the wart has changed its original color;
- papilloma growth has intensified;
- painful sensations appeared.
In any case, if papillomas are found on the ears of a newborn, then such patients should be under constant supervision of specialists.
Types of growths in the ears
Auricular papilloma occurs in the area of the external auditory canal or in the auricle itself in the form of a wart. Such growths grow very slowly, cause discomfort, and are sometimes accompanied by pain, itching, and tingling. The danger of a neoplasm is its possible injury. Scratching papillomas can lead to additional infection and spread of the virus throughout the body. In addition, if the wart is not removed and the virus is not treated, the growth can transform into a malignant cancerous tumor.
What complications can there be from growths near the ear?
If papilloma near the ear is not treated in time, it can lead to dangerous consequences. Firstly, if the formation is not removed, the risk of damage increases significantly. Parents of young children especially often face this problem. Usually kids try to get rid of growths that bother them on their own. They scratch them, pick them off, or even tear them off. Such situations lead to serious problems. For example, a variety of infections can get into the resulting wound. HPV can also spread throughout the body, causing widespread papillomatosis.
Often warts become inflamed, bleed, and pus is released from them. This process can lead to the formation of an ulcer that does not heal for a long time, grows and brings physical and psychological pain.
Warts, if they are located in the ear area, easily spread inward. This can cause the ear canal to become blocked and cause hearing loss.
The most dangerous outcome of a warty growth is the degeneration of damaged cells into malignant ones. In order to notice a serious problem in time, you should consult a doctor immediately after the first symptoms of HPV appear. During the examination, the growth will undergo histological examination, which will make it possible to identify oncology in a person in the early stages.
Diagnostics
If a wart appears on the ear, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. The doctor will determine the type of HPV, the state of the person’s immune system, the degree of activity of the virus, and the presence of cancer cells . Taking into account all these factors, treatment is prescribed and the need to remove warts is determined.
The following research methods are used:
- visual inspection,
- PCR diagnostics,
- biopsy,
- histology,
- colposcopy.
Treatment methods
When diagnosing skin pathologies in adults, it is possible to use a whole range of treatment procedures. The same cannot be said about small patients. When a papilloma is detected on a child’s ear, therapeutic measures should be as gentle as possible. During the examination, the doctor determines the stage of the disease and the development of further risks.
During the examination, the doctor determines the stage of development of papilloma and assesses the risks
The main treatment is aimed at stopping the process of reproduction of formations, strengthening the immune system, and preventing further division of pathological cells. In cases of advanced disease, surgical treatment is suggested. It should be noted that there are several types of treatment for skin surface neoplasms:
- Conservative treatment. Used only for single papillomas. Treatment is aimed at the use of medications to enhance immunity, antiviral agents, vitamin complexes, and ointments for external use.
- Electrocoagulation. This implies the impact of alternating or direct current on the papilloma near the ear. Local anesthesia may be required. At the end of the procedure, scars often remain at the site of the manipulation. Healing occurs within 14 days. This method allows you to control the depth of impact.
- Cryodestruction involves the use of chemicals. In this case, liquid nitrogen is used, which is applied as an applicator to the affected area. The papilloma darkens and completely disappears approximately 2 weeks after application of the product. Does not require anesthesia, painless, no bleeding. There are no scars left after the operation.
- Cauterization. It involves exposing the affected area to a mixture of organic and inorganic acids. Under their influence, tissue death occurs. A crust forms at the cauterization site. Here it is important to hold out until it disappears on its own. If you do this forcibly, then a scar will remain at the site of the papilloma in the ear. Features a long healing period.
- Laser removal. One of the painless methods of treating papilloma in the ear. The healing period is up to 1 month. The disadvantage of the procedure is that a scar remains. Although, it does not cause such discomfort as a pathological neoplasm.
- Radiosurgery using a radioknife. It involves irradiating the growth using ions in sufficiently large quantities. Using a radio knife, the formation is cut off and sent for histology. Based on the results of the analysis, malignancy of the formation can be confirmed or excluded. The skin around the papilloma is not injured. Healing is quite fast. A scar does not form at the cut site.
After any medical procedure, it is important to follow the recommendations for a week:
- Avoid washing your hair and ears;
- give up hats for a while;
- limit sun exposure for both adult patients and children.
Not all therapy methods can be used to treat pathology in a child. The doctor will determine the treatment regimen individually.
Unconventional methods of treatment
Treatment in adults
Since HPV is not completely curable, therapy for the disease is aimed at suppressing the virus and transitioning it from an acute to a latent form. This is achieved by taking antiviral drugs and drugs that stimulate the immune system.
Sometimes after treatment, when the body’s defenses are restored, warts disappear on their own. If this does not happen, and the growths cause physical or psychological discomfort, it is recommended to remove them. Neoplasms can also be removed during treatment to prevent possible degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
If warts hurt, change color or shape, grow rapidly, block the ear canal, or undergo any other changes, their removal is essential. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor to examine the pathology. You can remove papillomas using:
- surgical intervention,
- hardware methods: laser or radio wave removal, cryodestruction, electric cauterization,
- topical agents: ointments, gels, creams, aerosols,
- folk methods (it is recommended to make compresses and lotions at home).
Keloids on the ears - treatment
Keloids are difficult to treat. However, you can try the following:
- softening the skin with creams or oils
- applying silicone or polyurethane patches to reduce scars
- use of silicone gel
- application of pressure bandages
In some cases, surgical removal may be required. However, this procedure may result in the development of an even larger keloid scar as the surgery creates a new wound.
Dermatologists may use the following treatments:
Corticosteroid injections
The injection results in a reduction of 50-80% of keloids. Corticosteroid injections are performed once every 3-4 weeks. After the first injection, the patient may notice that the keloid becomes softer.
Surgery
A dermatologist can remove the keloid. However, almost 100% of keloids recur after surgery. After removal, doctors administer a corticosteroid or use cryotherapy to reduce the chance of the keloid returning.
Laser treatment
A laser can be used to reduce the size and discoloration of the keloid.
Cryotherapy
This procedure, which works best on small keloids, can reduce the size and hardness of the keloid. The dermatologist freezes the keloid from the inside. The cryotherapy process is effective for newly formed keloids.
Ligature
A dermatologist may recommend using surgical thread to gradually remove the keloid if it is possible to tie it with thread.
The surgical thread needs to be replaced every 2-3 weeks.
Treatment in children
Children are prescribed therapy aimed at suppressing the virus and preventing its further development. The treatment is more gentle; the selection of medications should be done by a doctor. He will prescribe mild antiviral drugs. Immunostimulants are prescribed to children very carefully, based on the child’s age, general condition of the body and the composition of the medicine. As a rule, doctors prescribe safe homeopathic remedies, herbal remedies or interferons . In addition to drug therapy, parents are recommended to independently increase the child’s immunity:
- take walks in the fresh air more often,
- harden,
- breastfeed a newborn,
- eliminate allergens,
- if necessary, carry out treatment to improve the functioning of the child’s gastrointestinal tract.
Neoplasms in children, as a rule, are not recommended to be removed before the age of 14. The exception is when the growth:
- changed color
- began to grow quickly
- changed form
- blocked the ear canal
- accompanied by pain or brings severe discomfort.
In other cases, you just need to observe the papilloma on the child’s ear and consult a doctor at the slightest sign of changes. Some dermatologists suggest that parents remove the papilloma immediately after detection in order to avoid the dangers it poses. There is no consensus among doctors regarding the removal of papillomas in young children. Therefore, parents must approach this issue responsibly and make the decision themselves.
You can prevent the recurrence of warts by taking good care of your health and maintaining your immune system. A healthy lifestyle, diet and rest, calmness, hygiene, treatment of chronic diseases will protect the body from awakening the human papillomavirus and the appearance of warts on the body.
Source
The phenomenon in which a lump forms in the ear can act as a normal process or indicate a large-scale pathology in the body. Numerous phenomena can visually have a similar appearance. For example, general and local inflammation, tumors of benign and malignant nature. All doubts can be put to rest only by an ENT specialist who has interviewed the patient, studied the test results and sorted out the situation.
ethnoscience
Together with traditional methods of therapy, it is possible to use traditional methods of treatment. You must first consult with a specialist. Of the most popular, it should be noted:
- A five-day course of treatment with lotions with 3% hydrogen peroxide. Make sure that the solution does not get inside the ear.
- Apply celandine juice to the affected area.
- An infusion of walnut leaves can be used to wipe the papilloma area.
- Make a compress using warm egg shells. It must first be crushed and sprinkled on the site of formation.
- Compresses with freshly squeezed cabbage juice.
- A healthy lifestyle, which includes a balanced diet, physical activity, rest and walking, and adequate sleep.
Of course, if a child has a papilloma with which he is born or an acquired form of the disease, then all manipulations require preliminary discussion with the attending physician. Avoid self-medication, especially in children who are born with papillomas in the ear. This is especially important, as it can threaten the spread of tumors throughout the body.
Causal factors of the phenomenon
A tumor in the ear, which is accompanied by pain and has a bright red color, can act as a sign that a boil has formed. It is a purulent inflammatory process in the area of the hair follicle or sebaceous gland. As a result of this phenomenon, a necrotic core is formed, surrounded by purulent contents.
The causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus, which begins to become active when a favorable environment is created for it.
A lump on the ear can manifest itself due to a number of causative factors that are worth paying attention to:
- neglect of the simplest requirements and hygiene standards;
- traumatic phenomena in the area of the hair follicle or skin;
- frequent illness with purulent otitis media;
- hormonal surges;
- metabolic problems;
- progression of viruses and colds;
- excessive overheating or hypothermia;
- reduced immune system defense.
Thus, an ear tumor can arise as a result of simple phenomena that require only minor correction, or as a result of serious diseases.
Reasons for development
Benign tumors of the ear localization are caused by pathogenetic processes that cause rapid cellular development and division. Usually these are fatty, skin, bone or cartilage, vascular tissues.
Formations of a malignant nature are associated with malignant metaplastic processes in tissues. In addition, cancerous processes in the ear often develop as a result of the degeneration of benign tumors.
Experts identify several pathogenic factors leading to ear cancer:
- Chronic eczema of the ear localization;
- Ear pathologies of advanced chronic form;
- Presence of precancerous diseases;
- Hereditary predisposition to cancer, the presence of blood relatives with ear cancer;
- Chronic form of laryngitis;
- Polyps in the ENT organs;
- Ultraviolet or radiation exposure;
- Lupus, psoriatic processes;
- Presence of post-traumatic scars in the ears.
The human papillomavirus infects the body through various microcracks in the human body. The virus does not manifest itself immediately and lives quietly in the human body.
A number of factors are described that cause warts to appear on human skin:
- Immunodeficiency;
- Chronic diseases;
- Eating too salty or spicy foods;
- Bad habits;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Taking antibiotics for a long time;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Stressful situations.
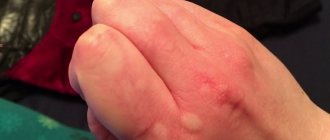
What does a lump in the ear area mean?
An ear tumor is a small-sized seal on the auricle, which is traditionally round in shape and has soft contents. Usually this phenomenon is not accompanied by feelings of discomfort and does not cause inconvenience to the person. In some cases, the formation of a lump above the ear may be evidence of a serious illness and pose a threat to health. After all, the appearance of a lump above, in or behind the ear can be evidence of a harmless cold or a serious phenomenon.
In no case should you engage in independent treatment; you should contact an ENT specialist. There are several common situations that involve the appearance of a hard lump in or above the ear.
Acute otitis of infectious nature
This pathology is accompanied by an acute pain sensation, which is popularly called “shooting.” In this case, body temperature rises to 37.5 degrees, and a transparent or yellow secretion is observed from the ear canal. Depending on the form of the disease, there are several characteristic symptomatic signs that accompany a tumor in the ear:
- slight itching or pain - this indicates the fungal nature of the lesion;
- the secretion has an unpleasant aroma - most often this indicates the progression of staphylococcus or streptococcus bacteria;
- prolonged development of symptoms and a gradual increase with the feeling that water is gurgling in the ear - we can talk about the allergic nature of otitis media.
How to treat if the appearance of a blister still cannot be avoided
To properly treat a blister, you need to know its origin. Therefore, if the cause of the formation is unknown, it is more appropriate to talk about pain relief, itching and swelling.
Modern pharmaceuticals and traditional medicine recipes come to the aid of the sick.
Medicines to combat illness
Broad-spectrum antimicrobial ointments such as Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Levomekol ointment, the root cause of the appearance of a blister is unknown, because they act on almost any group of bacteria.
Furacilin solution will help disinfect the surface of the skin.
Treatment of blisters caused by the herpes virus
Antiviral ointments are used to treat blisters caused by the herpes virus. They act precisely, reach the source of inflammation faster, and many of them have healing properties.
The most commonly prescribed are Oxolinic ointment, Viferon, Zovirax, Cycloferon.
Treatment of blisters - signs of allergies
In case of an allergic reaction, it is possible to use Suprastin, Zodak tablets and other antihistamines. For topical use, Fenistil gel is usually prescribed; herbal-based Gistan cream is also suitable.
Help with blisters formed at the site of a burn
Panthenol foam cream has proven itself to be effective in the treatment of blisters from burns; it has a light texture that allows you to apply the product without increased friction of damaged skin.
The well-known balm Rescuer, made from natural ingredients, helps to accelerate the restoration of the protective properties of the burned area of the skin.
OzhogovNet and Appolo gels are also effective; they not only have antiseptic properties, but also have a wound-healing and analgesic effect.
How to properly care for your ears, watch this video:
Treatment of blisters - symptoms of fungal ear disease
To get rid of a blister formed due to ear fungus, you must first cure the fungus itself. If the fungus is caused by taking antibiotics or hormonal drugs, you should stop using them.
Vitamin therapy will help boost immunity, a decrease in which could also lead to the formation of ear fungus and, as a result, a blister.
Antifungal agents should be prescribed by an ENT specialist depending on the type of fungus (yeast-like, mold, especially pathogenic). Nitrofungin and Econazole are usually prescribed.
The very prescription of antibiotic drugs for internal use in the treatment of any ailment is strictly prohibited. Remember, only your doctor can prescribe antibiotics. By self-medicating, you can cause serious harm to your health.
Traditional medicine comes to the rescue
If you don’t want to poison your body with medications, you can turn to traditional medicine. There are many recipes to get rid of various types of blisters.
Chereda is a natural antihistamine
The series has excellent antibacterial and wound-healing properties. In addition, this plant has long been known as a natural antihistamine.
To relieve itching and swelling from the blister, you need to gently wipe the affected area several times during the day with a cotton pad soaked in the infusion of the string. Lotions made from a concentrated infusion of herbs are also effective.
If you have allergies, you can also take the series orally. Brew 1 tablespoon of dried herb per glass of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes and drink warm. But this infusion should not be consumed more than 2-3 times a day.
Chamomile is an excellent anti-inflammatory agent
Truly a wonderful flower with a whole range of beneficial properties. Chamomile infusion has anti-inflammatory, antiviral and antimicrobial effects.
It is useful to use chamomile infusion lotions for blisters on the ears. This lotion will also relieve pain due to the soothing properties of chamomile. A crushed aloe vera leaf applied to the blister will have the same effect.
Apple Cider Vinegar - An Inexpensive Refrigerator Remedy
An antibacterial agent available to everyone. Using a cotton swab dipped in an aqueous solution of apple cider vinegar (1:1), you need to wipe the area of skin affected by the blister.
It is also useful for burns: diluted with cold water, vinegar will remove heat from the burn, thereby relieving pain and burning.
How to treat a lump in the ear area
If your ear is swollen and painful, you should pay attention to proven therapy methods; there are special instructions for this.
- The first thing to do is to determine the causative factor in the formation of an ear lump. If the manifestation of a ball near the ear does not itch or is accompanied by pain, most likely we are talking about an enlarged lymph node. The phenomenon indicates that perhaps the body is experiencing a severe runny nose, which does not always mean that a ball has appeared and it hurts. Sometimes otitis media becomes a causative factor. Sometimes patients feel a tingling sensation, but the inflammatory process continues.
- If lumps appear above the ear, and you are not sure that they act as an inflammatory process of the lymph node, you should not touch them. The fact is that only the causative factor in the occurrence of the phenomenon, and not the pain, is treated. If the painful sensation when pressing is bothersome, it is recommended to drip special anti-inflammatory compounds into the ears, and vasoconstrictor drops into the nose.
- If a ball appears on the ears, and the body temperature remains normal, you should refrain from using antibiotic compounds. However, in any case, it is worth visiting an ENT specialist who is competent in the rational selection of therapeutic tactics and will be able to prescribe the necessary medications. If the ear is swollen, this must be done without fail, otherwise the advanced process may lead to the phenomenon of chronic otitis media, which can pose a serious threat to hearing.
- If the formation appears gradually, is red in color and has an increased level of pain, most likely it is a boil formed in the outer ear. You should not squeeze it out, since the process is designed to lead to the formation of an infectious process. What to do is to moisten a piece of cotton wool with Vishnevsky’s special ointment and place it in the area of the external auditory canal. This action will ensure rapid maturation of the boil and drainage of pus.
- If a lump appears on the cartilage or in the area of the ear canal, which hurts when pressed, it is strictly forbidden to rub it with alcohol and other homemade products.
If a person’s ear is swollen, and it doesn’t matter whether the formation that appears hurts or not, this is a clear reason to pay a visit to a competent treating specialist. Only an otolaryngologist will be able to determine the exact causative factor due to which the lump appeared and the balloon inflated, and will also prescribe the appropriate remedy.
Remember that if you try to overcome swelling on your own, you may encounter diseases that will lead to serious inflammation that threatens hearing loss. Through diagnosis, it is possible to determine why a disease may appear and how to prevent the phenomenon.
Source
Photo of a growth on a person's ear
New growths of the auricle occur for a number of reasons and come in different shapes and types. But, despite their diversity, experts divide growths on the human ear into malignant tumors and benign formations
It is very important to see a doctor on time, get diagnosed and start treatment
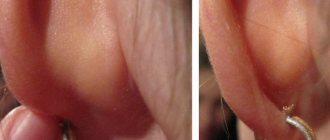
Benign formations of the auricle: causes and symptoms
Growths on the human ear that do not have cancer cells, photos of which are presented below, most often arise on the surface of the auditory organ, in the area of the middle ear or in the ear canal. They grow asymptomatically, for quite a long time, and do not make themselves felt in any way.
There are 10 main types of growths in the human ear:
- fibroma is light, often pedunculated. It grows due to a violation of epidermal cell division and is located outside at the beginning of the ear canal;
- hemangioma is a red vascular growth shaped like a small ball. Appears often in children;
- glomus growth - an accumulation of nerve endings in the middle ear, mainly in women;
- osteoma – consists of bone tissue, develops slowly, appears at a fairly young age;
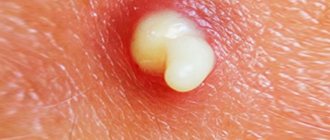
- lipoma (another name is a wen) is a small subcutaneous lump that does not cause any discomfort;
- papilloma is a consequence of the activation of HPV as a result of a decrease in the body’s defenses for a number of reasons. Usually pedunculated;
- A nevus is a mole that over time can degenerate into skin cancer – melanoma. A person can have such a growth on the ear from birth;
- chondroma is the result of pathology of cartilage tissue. It grows very slowly. Relapses may occur after surgery;
- atheroma - blockage of the sebaceous glands. Appears in the area of the lobe, round and regular in shape, painless;
- neuroma – associated with the auditory nerve. Occurs in women and in childhood. It is dangerous because it gradually causes deafness.
Such formations are diagnosed by external examination and histological examination of tissues.
Treatment mainly involves removal of the formation. For each type, one or another method is preferable. Radiation works well with papillomas and angiomas, but it is better to cauterize a lipoma using the cryotherapy method.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient usually undergoes a course of antibiotics.
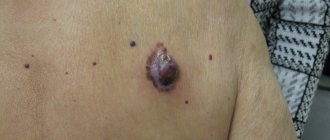
Malignant formations in the human ear: what are they called?
Growths have primary and secondary origin. The former develop from ear tissue, and the secondary arise as a result of metastasis processes from other organs.
There are 4 main types of malignant tumors:
- spinocellular epithelioma - looks like a wart, grows very quickly in depth and width. It appears most often in mature men on the lobe or at the beginning of the ear canal. Metastases spread to the salivary glands, the area of the skull and the middle ear;
- basal cell carcinoma – characterized by very slow growth, metastases in the later stages of development. It has the shape of a plaque or nodule with a pinkish tint. Outwardly it resembles an ulcer, which tends to bleed, crust over, and then peel off;
- sarcoma - appears mainly in children under 10 years of age, but is extremely rare. In an adult, its development depends on its location. External ones grow and develop slowly, internal ones - quickly, with metastases and destruction of the eardrum;
- melanoma - arises from pigment cells of the skin, grows rapidly, metastasizes through the blood and lymph to any internal organ, and is practically untreatable.
- strong, sometimes unbearable painful sensations that can radiate to the head;
- the pain is burning, fiery in nature, as if you had received a burn, at first it is periodic in nature, gradually intensifying, especially at night.
- mucus or pus may come out of the ear, as in acute otitis media;
- Patients experience tinnitus and hearing loss, which may disappear completely.
Basic methods for diagnosing pathology
The doctor diagnosing the tumor can be either an otolaryngologist or a dermatologist.
The diagnosis is made based on external examination and histological analysis. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe:
- otoscopy with pinching off a piece of tissue for biopsy;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance topography;
- X-ray;
- pharyngoscopy.
Based on the test results, the type, size and shape of the growth is determined, as well as the presence of metastases and their location.
For the most accurate determination of size, the best method is Doppler ultrasound using a contrast agent.
An accurate diagnosis is made after histology and tomography data arrive. It is the nature of the tumor that determines the treatment and its sequence.
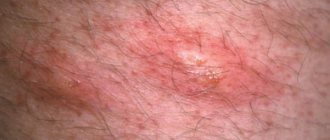
It’s as if bubbles are bursting in the ears: what is it?
Blisters are inflammations in the upper layer of the skin, which are characterized by clearly defined swelling, red or pinkish color, and the shape can be either blurry or clear.
Multiple vesicles - blisters, very similar to pimples, but with transparent contents, appear during an allergic skin reaction. But there are many more reasons when one or more blisters appear behind the ear:
- Insect bite: mosquito, midge, flea and others cause a slight swelling when bitten, which itches a lot
- Fungus: Fungal infections often cause a rash; if the infection occurs in the skin behind the ears, which is not uncommon, blisters and itching are likely.
- Miliaria: as on the fingers, in the armpits, behind the ears, where the skin often sweats under a warm hat, dyshidrosis can manifest itself.
- Friction: Sometimes a blister appears after intense rubbing of the skin behind the ear.
- Dermatitis: After contact with an irritating substance, contact dermatitis can appear behind the ear, where the skin is very delicate.
- Allergic reaction: hives after dyeing hair or changing shampoo or detergent appear and disappear within a few hours.
- Infection: chicken pox, measles, rubella and other infectious and highly contagious diseases occur with a rash in the form of blisters.
- Seborrhea: This disease can also affect the part of the scalp that is not covered with hair.
- Scrofula: many have not heard of this disease, meanwhile, grayish formations behind the ears, itchy and flaky - one of the most common diseases, it is caused by the tubercle bacillus, affects people (often children under 10 years of age, but sometimes adults), with a tendency to tuberculosis, weakened immune system.
- Neoplasms: often what a person mistakes for a blister does not go away for quite a long time; dense contents appear inside it, which keeps increasing, eventually forming not just a blister, but a huge “bump.” Such a blister may ultimately turn out to be either an epidermal cyst (benign tumor) or a malignant skin lesion.
- Otitis: inflammation can be both external and internal; itching and the appearance of a blister in the ear can also be the initial stage of otitis.
These and other reasons should force a person not to hesitate to contact a dermatologist, to follow his recommendations and advice regarding consultations with specialists - allergists, nutritionists, neurologists and venereologists.
Possible causes of sounds
The feeling as if bubbles are bursting in the ear is characteristic of the following factors:
- Sulfur plug. If accumulated wax has formed in the ear, the patient feels some discomfort. With a “fresh” plug, a person is bothered by the sound of shimmering water or the feeling of bursting bubbles. If we are talking about an old plug, then only ear congestion occurs;
- Foreign body. If there is a foreign body in the ear canals, a sensation of bursting bubbles may occur. This usually happens when turning the head or changing position;
- Otitis. This symptom is characteristic of otitis media, which is accompanied by purulent discharge. When fluid accumulates, the patient has a feeling of bubbles that periodically burst. It should be noted that this factor is accompanied by pain.
Also, the symptom can manifest itself in pathologies of the vestibular apparatus or in the presence of vascular pathology.
Prevention
To prevent the development of a pathology such as herpes in the ear, it is necessary not to neglect some simple rules, which are as follows:
- a healthy lifestyle at all times Walk more and spend more time in the fresh air. This will significantly strengthen your immune system.
- Nutrition must be correct. In order to work properly and perform a protective function, the body requires a constant supply of vitamins, proteins and microelements.
- Before eating vegetables and fruits, it is recommended to wash and heat treat them.
- It is better if bad habits are forgotten forever. Alcohol and nicotine primarily negatively affect human immunity.
- Personal hygiene must always be observed . Hands should be washed with soap as often as possible. If this is not possible, you can use antiseptics, for example, Miramistin or Chlorhexidine.
- room temperature In winter, it is important not to expose the body to hypothermia, and in the summer – to overheat.
Blister Treatment Options
If formations on the skin appear unexpectedly, and it is impossible to seek medical help, you need to remember about methods of help at home. You can alleviate the condition both with the help of medications and folk remedies.
Pharmaceutical ointments, plasters
- Having noticed a blister, treat the skin around it with an antiseptic;
- if the blisters are not damaged, carefully apply ointment with a cooling effect to a cotton pad, apply to the skin, and secure with a bandage;
- if the blisters burst, it is enough to lubricate them with anti-inflammatory ointment Solcoseryl, Methylurocil, oxolinic or tetracycline;
- repeat every 4 to 6 hours, carefully monitoring the patient’s condition.
For allergies and burns, you need to use products designed to treat them.
Treatment of blisters on the ear with traditional medicine
A lotion of soda with added water is applied to the affected area for insect bites to relieve itching.
Aloe juice, raw potatoes, carrots will help stop itching and inflammation.
Treatment
Treatment of ear herpes should only be carried out by a specialist in this field. Otherwise, you can only harm the health of the body. The treatment process must be constantly adjusted based on the results obtained. Therapeutic measures consist of several stages that require strict adherence to sequence.
First of all, it is better to completely isolate a patient diagnosed with ear herpes, since he is already a carrier of the pathological virus, and if a healthy person comes into contact with him, there is a high probability of infection.
Source: https://UralKozha.ru/bolezni/krasnyj-voldyr-za-uhom.html
The immune system and HPV
It should be noted that damage to HPV infection most often does not immediately manifest itself clinically. In people with good immunity, the virus is suppressed. It integrates its DNA into the DNA of locally located cells and is inactive. But once the immune defense weakens, the virus manifests itself by the appearance of growths - papillomas on the ear. Factors that provoke HPV activity may include:
- Severe stress.
- Taking antibacterial drugs.
- Hypothermia.
- Insufficient or inadequate nutrition.
- Chronic diseases.
- Immunodeficiency states.
- Bad habits.
Clinical manifestations of HPV are most often observed in older people, young children, and adolescents during puberty. If a benign tumor appears in the area where blood vessels are located, its strong growth can cause bleeding.
How to recognize and treat herpes in the ear?
The appearance of a small rash in the ears may be a symptom of the development of ear herpes. The disease can cause serious complications, as it is located near the organs of vision, hearing and brain. Immediate treatment will help avoid serious consequences.
All about the infectious agent
Herpes is a viral infectious disease characterized by the appearance of vesicular blisters on the affected area of the body.
Herpes in the ears can be caused by one of two types of virus:
- Type 1 virus. This is a herpes simplex virus, which is most often localized on the lips, less often on the mucous membrane of the nose and throat, the surface of the ear, and neck. It is present in the bodies of most people. People are first infected with the virus in childhood and remain carriers of this infection forever. It may not manifest itself for a long time, but if the immune system is weakened, its manifestations will not take long to appear.
- Virus type 3. It is also called Herpes Zoster. When it first enters the body (usually in childhood), it causes chickenpox. At an older age, when the immune system is greatly weakened, in a person who has had chickenpox, the virus will manifest itself in the form of shingles.
When the virus gets on a person’s skin or mucous membrane, it gradually begins to move to the internal organs. Then the herpes reaches the nerve endings, where it remains for some time until it disappears.
Possible routes of infection
You can become infected with the herpes virus:
- By airborne droplets. The virus can easily be transmitted by talking, sneezing, coughing, or kissing. The infection spreads through mucous membranes and microtraumas of the skin.
- Through contact and everyday life. Infection can occur through the use of household items of an infected person. Usually these are towels, cutlery, cosmetics, toothbrushes, etc.
- By transplacental route. In this case, the fetus becomes infected through the mother's umbilical cord.
Risk factors
The manifestation of herpes can be provoked by:
- hypothermia;
- overheating;
- pregnancy;
- menstruation;
- being under constant stress;
- alcohol abuse;
- public facilities;
- immunodeficiency states (HIV, AIDS).
Symptoms
Despite some similarities in the clinical picture, herpes viruses types 1 and 3 have characteristic differences in symptoms.
For herpes simplex virus
When the ear is affected by a simple type of herpes, the disease does not bring any particular trouble, passes without pain or complications, and the person feels well.
Herpes appears on the outer parts of the auricle, in the territory of the external auditory canal. Along with inflammation on the outside of the ear, infection can appear in the nose and lips.
The main symptoms of the herpes simplex virus:
- the affected area turns slightly red and swells slightly;
- itching appears;
- the skin of the ear becomes covered with small blisters filled with clear liquid;
- after a couple of days, the bubbles burst and then become covered with a dry crust, which falls off quite quickly, leaving no traces behind.
For shingles
The virus manifests itself not only on the outside of the ear, but also inside the ear canal. Severe pain in inflamed areas of the skin indicates that the nerve ganglia of the facial nerve are affected by the virus.
After opening the watery blisters, noticeable ulcers form in their place, and after healing, deep scars remain.
Shingles is more painful than the simple herpes virus:
- shooting pains appear at the sites of the rash;
- the person feels general malaise;
- body temperature rises;
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- herpes spreads to other areas of the skin.
If the disease proceeds without complications, then herpes zoster goes away in 1-2 weeks. Without proper treatment, the virus can progress to the next stage, which is called Ramsay-Hunt syndrome.
With this syndrome, the herpes rash spreads to:
- face;
- neck;
- tonsils;
- soft palate;
- eardrum;
- back;
- the back of the head.
Characteristic symptoms during the development of Ramsay-Hunt syndrome:
- dizziness and noise in the ears;
- hearing becomes dull;
- mild cramps appear;
- coordination of movements is impaired;
- there is excessive salivation;
- paresis of the facial muscles develops.
Treatment of the disease may take up to 1 year.
How to diagnose?
Infection of the ear with herpes requires immediate medical attention. The patient should contact a general practitioner, who, if necessary, will refer him to an infectious disease specialist, immunologist and dermatologist.
Diagnosis of herpes can be divided into 2 stages:
- medical examination;
- carrying out relevant laboratory tests.
To accurately determine the diagnosis, you cannot do without testing. Laboratory tests will help determine the type of virus, its concentration and phase of activity.
Classic laboratory diagnostic methods for determining herpes:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The simplest type of analysis that allows you to detect the virus even at the slightest presence in the body.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) . This analysis helps to calculate the presence of IgM and IgG antibodies and identify their concentration and determine the phase of the disease.
- Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF) . With this method, the biomaterial is treated with a special substance, under the influence of which the antigens begin to emit light, in which virus particles can be identified.
How to treat herpes in the ear?
Proper treatment will prevent the spread of the virus, alleviate symptoms and speed up the healing process. Therapy should begin immediately after the first signs of the disease appear.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies will help relieve symptoms and, in combination with medications, will contribute to a faster recovery:
- The areas where herpes is localized are wiped with essential oils of fir, lemon, tea tree, and eucalyptus.
- Aloe and Kalanchoe juice is effective. To do this, simply cut off the leaf and wipe the problem areas with it.
- To increase immunity, it is recommended to drink tinctures of echinacea purpurea and eleutherococcus.
- You can make antiseptic lotions from onion or garlic juice and apply to the ear until the liquid dries.
- Steam baths made from nettle and yarrow are effective.
Is herpes in the ear contagious?
Herpes is a highly contagious infection. A carrier of herpes simplex simply needs to sneeze to infect nearby people. 90% of the inhabitants of our planet are carriers of this virus.
Herpes type 3 is transmitted primarily by contact. The danger is liquid from bursting bubbles. The virus poses a threat only to people who have not previously had chickenpox.
Duration of the disease
The disease caused by the herpes simplex virus lasts on average 5-7 days, maximum 2 weeks.
Shingles lasts at best 1 month, on average 3-6 months, and in severe cases - up to 1 year.
If the case is advanced and cannot be treated at home, it is necessary to resort to the services of a hospital, where you will need to stay until complete recovery.
Complications
Herpes simplex is not dangerous, but herpes zoster can cause a number of complications:
- hearing loss;
- facial asymmetry due to severe inflammation of the facial nerve;
- musculoskeletal disorders (most often older people suffer from this);
- the addition of a bacterial infection - streptococci and staphylococci, which can cause pneumonia and inflammatory skin diseases.
Prevention methods
To prevent the risk of contracting herpes or to prevent the virus already in the body from becoming active, you should follow simple rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, move a lot;
- adhere to a proper, balanced diet (eat enough proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins);
- get rid of bad habits that reduce immunity;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- beware of hypothermia and overheating (dress appropriately for the weather);
- avoid stressful situations;
- treat all emerging diseases in a timely manner.
Compliance with these prevention methods will relieve many diseases for a long time and strengthen the immune system. In this case, it will be difficult for the virus to attack the body.
It is almost impossible to completely protect yourself from the herpes virus entering the body, but taking good care of your health will help reduce the risks of contracting this disease and ensure a speedy recovery and absence of complications in case of infection.
Source: https://kozh-med.com/kozhnye-bolezni/gerpes/v-uhe.html