Pigment spots on the face and body appear in almost every person with age. In medicine, this phenomenon is called lentigo. When localized on the face, pigmentation causes aesthetic and psychological discomfort. Pigment spots can indicate problems with the body, but in most cases, lentigo does not pose a serious threat to health. However, any neoplasm on the skin requires vigilance, since pigmented areas can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Classification of melanomas
Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor that develops from pigment cells. This is a dangerous type of tumor that can metastasize to almost all organs. Outwardly it looks like a nevus (birthmark), and sometimes grows out of it.
The following types of melanoma are distinguished:
- Superficial;
- Nodular or nodular;
- Lentiginous;
- Acral melanoma or acrolentiginous (subungual);
- Spindle cell;
- Achromatic.
Lentigo melanoma
Symptoms and stages of lentigo melanoma
The disease is protracted. It can take up to 20 years from the first symptoms to the stage of malignancy (malignancy). In the initial phase, the neoplasm looks like a pale, large freckle. The size increases gradually, the growth rate varies from a couple of mm to several cm per year. The freckle gradually turns into a pigment spot, whose distinctive feature is an irregular shape with clear boundaries and a smooth surface that does not extend beyond the intact skin.
The color takes on a number of different shades of red-pink, yellow-brown and white, but the pigmentation is uneven. Therefore, the formation resembles a blot or the outline of an island on a geographical map. This is how lentigo maligna (lentigo maligna), a precursor to melanoma, develops. This is the first stage with a clear clinical picture of the pathology. Transition to full-blown melanoma occurs in 50%.
During vertical growth, cancer cells penetrate beneath the epidermis and deeper. This phase is characterized by blurring of the tumor boundaries. They become wavy and not so clear. The tumor becomes bulging. The surface of melanoma also undergoes changes: cracks and nodes appear. The skin peels and the color darkens. At this stage, patients complain of itching at the site of formation and periodic bleeding.
The inflammatory process in the immediate vicinity of the tumor is a sign of the last stage and the formation of metastases. Melanoma becomes blue-violet. The patient’s well-being in this phase is characterized by the signs of any cancer:
- Severe fatigue;
- Heat;
- Sudden loss of body weight;
- Swelling of the lymph nodes;
- Weakness.
Malignant lentigo melanoma progresses slowly even in the vertical growth stage. Compared to superficial melanoma, the likelihood of metastases spreading is much lower.
Folk remedies
At home, folk remedies are an indispensable additional treatment, but only if lentigo maligna is completely excluded. Such methods can help if the spots are small and light.
For example, you can use products that contain acid on your facial skin:
- lemon, pomegranate, birch or rowan juice (just wipe the stains 1-3 times a day);
- strawberries (chop the fruits and make a mask for 15-20 minutes, rinse with warm water);
- fresh cucumber (vegetable slices should be applied to problem areas).
Such products are not harmful and can be used 1-3 times a day. They are safe for the skin and have no contraindications (except for allergies).
Causes
One of the causes of lentigo melanoma is the degeneration of a benign nevus due to constant trauma. Therefore, doctors recommend removing birthmarks in areas of regular friction - on the neck, shoulders, skin of the feet and palms. A large number of moles is a reason to be wary and closely monitor their appearance and condition.
The tumor occurs due to Dubreuil's melanosis, a precancerous skin disease characterized by an increased number of pigment spots of various colors and shapes. Risk factors include prolonged exposure to the sun and excessive dryness and dehydration of the skin. Sunburn received in early childhood or adolescence can play a decisive role. Women over 65 years of age and light-skinned and light-eyed people (Fitzpatrick types 1 and 2) are most susceptible to the disease.
Lentigo melanoma appears due to the same reasons as others. It differs in that before the development of malignant tumors, a characteristic change in the skin occurs.
Diagnostics
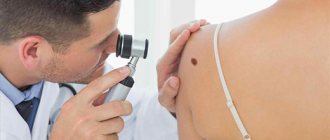
Timely diagnosis of lentigo reveals the disease at the stage of development, when the process of malignancy of melanoma has not begun. In this case, a complete cure is possible. The dermatologist examines the spot, measures it, and takes a photo. Non-invasive methods include dermoscopic examinations and computer diagnostics. The latter helps to analyze tumors over time. Dermatoscopy reveals structural features, which makes it possible to diagnose benign and malignant tumors.
A blood test shows the presence of tumor markers - enzymes that produce tumor cells.
Upon morphological examination, the initial stage shows atypical melanocytes - cells that produce melanin, which do not extend to the stratum corneum of the skin. When Dubreuil's disease transitions to lentigo-melanoma, changes affect all layers of the epidermis.
At the first signs of malignancy and vertical growth, a biopsy is performed. Part of the intact tissue is cut off and sent for biopsy. Examination of the site of the disease is not recommended, as this may cause uncontrolled growth of malignant cells. At this point, cancer cells penetrate the dermis and the inflammatory process begins.
Histology confirms the fact of a malignant tumor and determines the structure and stage of the process. It is carried out after excision. It reveals the proliferation and thickening of the epidermis.
Types of lentigo melanoma
The task of differential diagnosis is to distinguish pathology from diseases that are similar in external manifestations, but are not malignant. In this case, it is important not to confuse it with hyperkeratosis or actinic lentigo, which occur in the same areas of the skin as melanoma.
Symptoms
The benign form of lentigo, as a rule, does not cause physiological discomfort to humans. The clinical picture of this disease is characterized as follows:
- the presence of spots on the skin from light yellow to dark brown;
- the shape of the spots is round, no more than 2 centimeters in diameter;
- rashes are localized on exposed parts of the body, less often in the genital area and back;
- spots are not grouped;
- itching, peeling, and ulcer formation are not observed.
Lentigo maligna () manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- spots begin to grow;
- the boundaries of the neoplasm change shape, the edges become blurred;
- scars may form on the surface of the spot;
- the lesions are accompanied by itching.
If treatment for the malignant form of lentigo is not started in a timely manner, lentiginous melanoma may develop, which leads to the formation of cancerous metastases on the skin. In this case, grade 1 melanoma has the most favorable prognosis - metastasis to organs and lymph nodes is not observed, and the risk of developing a relapse of the disease is extremely low.
Treatment and prognosis
The type of treatment for lentiginous melanoma directly depends on the stage of the disease. The course of therapy is drawn up by the oncologist after an initial examination and consultation.
Surgical method
Surgery is the main method of treating melanoma. The neoplasm is removed, capturing adjacent tissues that have not undergone changes. This reduces the risk of relapse. It is recommended to perform surgery before the vertical growth stage begins, while the tumor affects only the top layer of skin cells. It is performed under local anesthesia, then stitches are applied. Subsequently, it is possible to carry out cosmetic surgery to eliminate the appearance defects that have arisen.
If the tumor has managed to metastasize, a regional lymphadenectomy is recommended, during which all malignant nodes in a specific organ are removed. For metastases in distant anatomical areas, treatment is tailored to the individual patient. The degree of development of the oncological process and the location of secondary foci are important. Individual metastases and those that threaten the patient’s life are removed.
Radiation therapy
If the size of the spot or the location of the tumor on the face makes surgical removal impossible, close-focus radiotherapy is performed. Lentigo melanoma is poorly responsive to chemotherapy and radiation therapy, so options are limited. The methods are justified in case of a significant number of metastases or as a step in combination therapy. Using X-rays, tumor development is stopped.
The average five-year survival rate for skin cancer was 92% in 2010 and rising. In the case of lentigo melanoma, due to the long period of horizontal spread, it is characterized as favorable. With the superficial growth of melanoma, it is 100%, but when the vertical growth phase is reached, it begins to rapidly deteriorate, and after surgery it drops to 15-25%, despite the fact that metastasis occurs only in 10% of cases.
Healing procedures
In most cases, benign age spots on the body do not cause noticeable discomfort, so they are not treated. Manifestations of lentigo on the face are especially troubling for women; this problem is of an aesthetic nature. To eliminate age spots, the following procedures are used:
- Laser resurfacing.
- Various types of chemical peels (azelaine, retinoic, salicylic).
- Diathermocoagulation (used for single spots).
- Photorejuvenation with pulsed rays.
- Brightening masks.
Along with cosmetic procedures, patients are prescribed medications that include vitamins and minerals, antioxidants, retinoids, and ascorbic acid. The combination of these substances normalizes the condition of the epidermis, increases its protective properties, and prevents the progression of pigmentation.
For malignant disease, surgical treatment is performed in combination with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Important advice: you should not try to treat lentigo using traditional methods. At the first signs of skin pigmentation, you should immediately make an appointment with a dermatologist or cosmetologist. If this is not done, you may miss the development of a serious disease; exposure to age spots using folk remedies can cause injury to the skin and accelerate the development of the pathological process.
Prevention
Measures to prevent skin diseases include constant protection from ultraviolet radiation. The UVI (UV Index) helps with this. It was developed by the World Health Organization as part of the international program to combat cancer and prevent cancer. This is a special indicator (0-10) characterizing the potential danger to a person in a specific geographical location during solar noon, i.e. between 12-14 noon. According to it, with a value above 3 (average radiation level), sun protection is required - cream with a high SPF factor, long sleeves and a hat. When the index is 8 or higher, it is recommended to stay in the shade.
If you have a large number of birthmarks, you should undergo regular examinations with a dermatologist to evaluate the condition of the nevi. Regular self-diagnosis helps to be alert in time if moles increase in size or change color.
Early detection of pre-melanoma formations is a type of prevention. Detection of lentigo melanoma in the radial growth stage leaves the possibility of a favorable outcome.