Cystic form of acne,
or
cystic acne
is a large acne in which the pores on the skin become blocked, leading to infection and inflammation. Acne mainly occurs on the face, but also on the upper torso and shoulders.
Acne most often affects teenagers and young adults, with approximately 80% of people between the ages of 11 and 30 having acne. Cystic acne is the most severe form and affects fewer people. All forms of acne can affect a person's self-esteem and mood.
Photo: Shutterstock/vialik
Causes
Adolescents are more susceptible to the disease; pathological processes occur less frequently in adults.
The development of inflammatory processes is based on two factors:
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- simultaneous active development of pathogenic bacteria in the ducts of the sebaceous glands.
When the sebaceous glands malfunction, excess sebum is produced. The sebaceous secretion becomes thicker and more viscous, and its outflow through the ducts becomes more difficult. Sebum, mixed with particles of keratinized cells, dust, and cosmetic residues, accumulates in the ducts of the sebaceous glands, becoming an ideal breeding ground for the development of bacteria, which, in turn, provoke inflammation and purulent processes.
The main reasons causing disruption of the sebaceous glands and the development of cystic acne are:
- Changes in hormonal levels. Hormonal changes in the body cause increased activity of the sebaceous glands, which ultimately leads to the development of acne. Most often, nodular cystic acne appears in adolescents during puberty, when active hormonal changes occur in the body. Also, sudden hormonal changes can cause acne in pregnant women and women who have had an abortion.
- Endocrine diseases. Disorders of the adrenal glands and ovarian diseases in women can lead to the development of cystic acne.
- Seborrheic dermatitis. The disease is caused by dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, changes in the rheological properties of sebum and the simultaneous development of fungal flora. In this case, cystic acne develops as a complication of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Hyperkeratosis. Thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis leads to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands, which can result in the formation of cystic acne.
- Taking hormonal drugs. Taking oral contraceptives, pharmacological agents based on insulin and some other medications leads to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands and the development of cystic acne.
Increase the likelihood of developing inflammatory processes in the skin:
- use of low quality cosmetics;
- insufficient skin care, as well as abuse of cleansing cosmetics;
- unbalanced diet;
- constant stress, physical fatigue;
- smoking;
- drinking alcoholic beverages.
According to statistics, cystic acne in men is more severe and lasts longer than in women.
Making a diagnosis for cystic acne
For treatment, it is first necessary to conduct a competent diagnosis.
When visiting a dermatologist, you must:
- Take a skin scraping to test for bacteria.
- Be examined using a microscope.
- Determine the acid level of the skin using a special test.
There is a possibility that you will have to additionally take a general blood test and be examined by a gastroenterologist and gynecologist. An analysis for hormone levels may also be prescribed.
Read how to get rid of blackheads on your face. What are conglobate globular acne? More details here.
Symptoms
In the cystic form of acne, pathological processes affect both the superficial and deep layers of the skin, which leads to the development of post-acne: scars form at the site of inflamed lesions, and pigmentation changes.
Cystic acne is most often localized on the face, in places of greatest accumulation of sebaceous glands (on the chin, forehead), and less often affects the skin of the chest and back. In the inflamed areas, redness of the skin is observed, enlarged pores are visible, and nodular-cystic structures are formed that fill with pus as they mature. The inflamed elements acquire a bluish-burgundy hue, cause noticeable pain, and can merge with each other, forming large lesions.
After stopping the pathological processes, the affected cells of the dermis are replaced by dense connective tissue, resulting in post-acne - scars remain in place of the inflamed foci.
Squeezing out blackheads is strictly prohibited. Squeezing can provoke the formation of even deeper and more painful subcutaneous cysts, scar formation, and the spread of infection throughout the body.
Stages of the disease
The disease is defined by three stages:
- In the first stage, the disease affects the surface layer of the skin, causing the appearance of so-called blackheads or acne.
- During the second stage, inflamed ulcers begin to appear on both the face and body (mainly in the back, chest, shoulders and forearms), characterized by pain and redness. The blackheads become deeper and larger, and when pressed, thick white pus comes out.
- At the third stage, purulent boils develop, which can be located both in groups and locally, take a long time to heal, after healing, pits, dark spots, and shallow scars remain on the skin.
Treatment
Cystic acne is characterized by a severe recurrent course and requires competent combination therapy, including:
- taking systemic retinoids and antibacterial drugs;
- use of local pharmacological agents;
- carrying out hardware procedures;
- nutrition correction.
For very large nodular cystic acne, they are incised and drained, but doctors rarely resort to this procedure.
Systemic drugs
A mandatory component of the complex treatment of cystic acne is antibiotic therapy and the use of systemic retinoids.
Antibiotics
Most often, nodular cystic acne is treated:
- Doxycycline;
- Minocycline;
- Minoleksin.
These are potent broad-spectrum antibiotics that are active against most pathogenic microorganisms. Their main advantage is the ability to penetrate the fat barrier and accumulate directly in inflamed areas, suppressing the development of bacterial flora and thus stopping pathological processes. The course of antibiotic therapy for cystic acne is long, lasting 1.5-2 months.
The doctor must select the optimal drug, as well as set the duration of the course, taking into account the type of pathogen, the severity of the pathological processes, the patient’s age, and the presence of concomitant diseases. The wrong choice of antibiotic can lead to worsening inflammation and deterioration of the skin condition.
Retinoids
If antibiotics do not have a sufficient therapeutic effect or the inflammatory processes are extremely severe, therapy with systemic retinoids is carried out. These are structural analogues of vitamin A, which can be prescribed independently, but more often they are used in combination with antibacterial agents.
Among the drugs of the retinoid group, the drugs of choice are:
- Acnecutane;
- Roaccutane;
- Will erase.
Retinoids are potent drugs, have a lot of contraindications, and can cause serious side effects, including hypervitaminosis, headaches, depression, anemia, dyspeptic syndrome, joint pain, liver dysfunction, decreased visual acuity, and others. That is why you should take medications from this group only as prescribed by a doctor. The specialist selects dosages and frequency of use for each patient individually.
In addition, retinoids have a teratogenic effect, and their use during pregnancy, even in minimal doses, can lead to the development of severe birth defects in the child. That is why it is important to exclude pregnancy a month before, during and a month after the end of treatment. Women of childbearing age should be sure to take a pregnancy test before starting retinoid therapy and one month after finishing treatment.
Local agents
In local therapy of cystic nodular acne, the most effective are ointments, gels and creams based on:
- azelaic acid (Skinoren, Skinoklir, Azix-Derm) – have a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and keratolytic effect, normalize the functioning of the sebaceous glands, suppress sebum production;
- benzoyl peroxide (Baziron AS, Eclaran) - exhibit pronounced bactericidal properties against epidermal staphylococcus and propionebacilli (most often causing acne), reduce inflammatory processes, suppress the production of sebaceous secretions, improve the absorption of excess sebum, promote skin hydration, reduce the risk of developing post-acne;
- retinoids (Adapalene, Klenzit) – normalize the processes of keratinization (cell division and keratinization), have a moderate anti-inflammatory effect, improve the rheological properties of sebaceous secretions, reducing its viscosity.
All local medications for acne are used in long courses, at least 3 months. Even if the inflammation has passed, therapy cannot be terminated prematurely, since the inflammation may worsen again.
Hardware techniques
Of the hardware techniques for the treatment of cystic acne, the following are most often recommended:
- laser therapy;
- phototherapy;
- darsonvalization.
These procedures help reduce inflammation, improve blood circulation in tissues, increase local immunity of the skin, and enhance the therapeutic effect of pharmacological drugs.
Correction of scars and spots formed after acne is carried out using the following procedures:
- mesotherapy;
- cryotherapy;
- laser peeling.
Procedures to eliminate scars are carried out only after the inflammatory processes have stopped.
Nutrition correction
The basis of the diet for cystic acne is the exclusion from the diet of foods that activate sebum production.
During the treatment period, it is recommended to completely stop using:
- semi-finished products;
- smoked meats;
- fried;
- fat;
- acute;
- baked goods and sweets;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- alcohol.
The basis of the diet should be plant and protein foods: vegetables and fruits, berries, fish, veal, poultry, dairy products. It is recommended to follow the diet for a long time, from a month to six months. In addition, it is important to drink enough liquid - proper drinking regimen helps cleanse the body of toxins.
Other methods
retinoids may be prescribed . Such medications fight the main cause of acne - increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, which provokes the appearance of a variety of elements of inflammation, including papules, pustules, nodules and some others.
Direct action on the gland itself significantly reduces the amount of sebum secreted.
This treatment is effective, even very effective, but only a doctor can prescribe it. Moreover, the dosage is strictly individual and depends on the severity of the inflammatory process. In addition, these drugs have many contraindications and side effects.
Treatment of nodular cystic acne with such drugs lasts up to 8 months. Medicines from the retinoid group should not be taken during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or if a woman plans to become pregnant within a year.
Before you start taking it, you should accurately establish the following information:
- Age.
- Floor.
- Duration of acne 4 degrees of severity.
- Individual specificity of the course of the disease.
- Condition of the affected area.
- Features of rashes, their number and type.
- Test results.
- The result of the inspection.
- Presence of hormonal disorders.
- Concomitant pathology.
It is very important to conduct an examination of the internal organs and understand exactly what caused the appearance of nodular cystic acne, although in most cases there is only one reason - the hormonal imbalance that occurs in the body during adolescence.
During treatment, not only careful skin care is required, but also the fight against side effects of therapy such as dryness and flaking. This can be done both using traditional methods and using special cosmetics - creams and gels.
With the right approach, it is quite possible to cure nodular cystic acne, even of the most severe severity, however, scars and other residual effects, which are called post-acne, may remain as complications. It will be quite difficult to get rid of them.
Author - Anna Mikhailova, dermatologist-cosmetologist of the first category, specialist at the Academy of Scientific Beauty. Especially for the site “Treating Acne”.
Folk remedies
When used independently, alternative medicine will not help cure cystic acne, but will speed up recovery when used in combination with medications.
The following have pronounced anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, and drying properties:
- aloe juice (apply fresh juice directly to inflamed areas several times a day);
- infusion of chamomile and calendula (pour a tablespoon of herbs with a glass of boiling water, leave, strain, use the solution to wipe the skin);
- tea tree or lavender oil (apply directly to acne 2-3 times a day);
- masks with turmeric (mix spice powder with sesame oil, apply the finished composition to inflamed areas, rinse with warm water after an hour);
- baking soda (mix a little product with water to a paste-like consistency, apply to inflamed areas, rinse after 20 minutes).
Photos before and after
See treatment methods for acne conglobata. About cleansing your face from acne at home. Find out further.
What are the symptoms of acne vulgaris? The answer is here.
Important! The use of certain retinol products and antibiotics increases skin sensitivity to sunlight. This can cause severe pigmentation. Therefore, on sunny days you cannot be outdoors without protective cream. In winter, a cream with SPF 15-20 will be enough; in summer, it is better to increase the degree of protection to 50.
Prevention of relapse
With cystic acne, it is important not only to stop inflammatory processes in the skin, but also to prevent re-exacerbation of the disease.
To do this, during the remission stage it is important:
- regularly use skin cleansers;
- give up comedogenic cosmetics with a high oil content, the use of which can clog pores (it is better to choose light water-based products);
- wipe the skin daily with antiseptic lotions;
- once a week, perform peelings and use scrubs (during an exacerbation, these procedures are prohibited);
- Be sure to remove makeup before going to bed;
- promptly treat pathologies of internal organs;
- strengthen the immune system (walking in the fresh air, taking vitamin and mineral complexes, a balanced diet, observing a work and rest schedule, getting enough sleep, regular moderate physical activity).
Cystic acne is an extremely severe form of acne. And only competent combined treatment, compliance with all medical recommendations, correction of diet and lifestyle will help cope with skin rashes and minimize possible complications. To choose the best medications and draw up a suitable treatment regimen, you need to consult a doctor, otherwise you can only worsen the condition of the skin. At the same time, you should be patient - treatment for cystic acne can last from several months to a year or more.
Differential diagnosis
A dermatologist is able to make the correct diagnosis. At the first examination, he always conducts dermatoscopy - a type of visual examination of skin formations using a special instrument. The device allows you to obtain a tenfold increase in acne, this provides the opportunity to study their structural features and understand how deeply the inflammatory process has spread.
Afterwards, pH measurements are performed and the acid-base balance is determined. The test results help differentiate acne from pyoderma.
To draw up an effective treatment regimen, the doctor must know what type of bacteria provoked the development of the pathological process, what susceptibility it has to modern antibacterial drugs. Bacteriological seeding of the contents of cysts and epidermal scales allows us to obtain an answer to these questions.
Isotretinoin
Isotretinoin is a very effective prescription medication for the treatment of cystic acne and is sold under many registered proprietary names in the United States (US), Europe, and the CIS.
Isotretinoin has significant side effects and is dangerous when used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Typically, the medicine is used in a dosage of 1 milligram per kilogram of body weight once daily for 16 to 20 weeks.
For cases of mild forms of acne, isotretinoin is not recommended by dermatologists, but is recommended as one of the best remedies for treating severe forms of acne.
Potential negative effects associated with the use of isotretinoin include:
- dry eyes
- chapped lips
- joint pain
- liver damage
- elevated lipid levels
Isotretinoin is a teratogenic drug, which means that its use during pregnancy (at any dose, even for a short time) can cause birth defects in the unborn baby.
Isotretinoin may also cause the loss of a baby or premature birth, which can cause the death of the newborn.
Women who may become pregnant are required to use direct contraception for 1 month before, while taking, and for at least a month after treatment with isotretinoin.
Pregnancy testing is also required before starting treatment with isotretinoin, and then 1 month after stopping the drug.
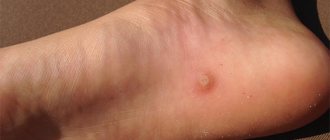
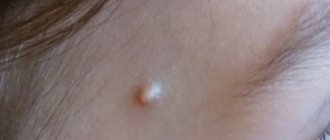
Sebaceous cyst near the eye
This is a small bump lying under the surface of the skin. It can appear anywhere, but most often it occurs on the face, neck and torso. The cyst usually does not cause any problems, so no treatment is required at all. It can be removed if it is causing discomfort or pain, or is infected or damaged.
These cysts develop when the sebaceous glands or ducts are blocked or damaged. Physical trauma such as a blow, abrasion, or skin conditions can cause damage.
Sebaceous cysts and epidermoid cysts are terms often used interchangeably. But in reality they are different. The former often arise from hair follicles, while the latter develop from skin cells. Sebaceous cysts arise from an inflamed hair follicle, which sometimes becomes swollen. Symptoms include:
- small round bump under the skin
- soft to the touch
- sensitivity, redness, swelling, if there is inflammation
- bumps that are painless unless they are infected or damaged
- small blackheads covering the central opening of the cyst.
Sometimes a malignant formation can be mistaken for a fatty cyst on the face. Sebaceous gland carcinoma is an aggressive skin malignancy. It can occur anywhere in the body, but in about 75% it appears in the periocular region (near the eyes). Diagnosis and treatment of these malignancies are often delayed because they are often mistaken for more common benign lesions.
Carcinoma (aggressive form of cancer)
Acne grades
Like any disease, acne varies in severity. Mild acne (blackheads or clogged pores) only needs to be treated with special products.
Photo 31 – Mild acne can be removed using special means Photo 32 – Mild acne
Mild acne is characterized by closed acne or acne (comedones); suppuration and pustular-papular lesions do not occur.
Photo 33 – Salicylic acid against acne
First degree rashes can be overcome with salicylic acid, zinc, sulfur ointment, masks with clay or sulsena.
Photo 34 – Zinc ointment before and after use
The appearance of a small number of pustules among the comedones indicates moderate severity of acne.
Photo 35 – Purulent pimples need to be dried
Treatment of second-degree rashes is carried out with the use of bactericidal agents: tea tree, lavender (spot on the pustule), preparations with azelaic acid, tretinoin, benzoyl peroxide, while continuing to use the listed products with sulfur or zinc, which dry and cleanse the skin.
Photo 36 – Tretinoin will dry out the pimple
Nutrition is controlled: sweets, fatty and fried foods are excluded.
Photo 37 – Watch your diet
When the severity of the disease increases - the appearance of suppuration - antibiotic ointments (Zinerit, Dalacin) are added. The occurrence of multiple foci of inflammation: papules, pustules with pus or cysts, in combination with comedones and sebaceous skin, indicates a severe degree of skin damage.
Photo 38 – Zinerit against acne
This is how the beginning of the third degree of acne (or even the fourth) appears. Systemic treatment will be required.
Photo 39 – In a complex case, treatment should be comprehensive
First of all, you need to consult several specialists (dermatologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist and immunologist) to identify the internal root cause.
Photo 40 – Get examined
Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe hormonal correction, birth control pills (Jess, Yarina), drugs to boost immunity (immunomodulators) or systemic antibiotics (tetracyclines, erythromycin, clindamycin, chloramphenicol), drugs with isotretinoin (Acnecutane or Roaccutane).
Photo 41 – The doctor will prescribe a drug, for example Roaccutane
A good effect is achieved by taking sorbents, preparations for the gastrointestinal microflora, and vitamin preparations. Externally, skin lesions are treated with antibacterial, disinfectant and regenerating agents with hyaluronic acid, zinc, and sulfur.
Photo 42 – The doctor will recommend effective treatment
Factors that increase the risk of developing acne
Elevated levels of testosterone (male sex hormone) lead to secondary sexual changes and reproductive development in boys. In girls, testosterone levels also increase during puberty, but to a much lesser extent, promoting bone and muscle growth. Increased levels of the hormone cause the glands to produce much more sebum than necessary.
The main factors causing acne:
- Heredity – those whose parents suffered from acne are more susceptible.
- Oily skin is the result of increased sebum secretion.
- Hormonal changes. Some women may break out with acne just before their period - this indicates a hormonal connection. Pregnant women can be prone to acne, especially during the first 3 months of pregnancy.
- Hormonal disorders. Women with hormonal conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome are more likely to experience acne.
- Acne can be the result of side effects of certain medications, such as steroids, lithium (taken for bipolar disorder or depression).
1 Acne is not caused by poor nutrition or a diet with lots of spices or oil. However, it is recommended to eat a healthy and balanced diet.
2 Acne is not caused by insufficient care. Although the lack of prevention of affected or inflammation-prone areas leads to the accumulation of sebum and dirt in susceptible people, increasing the risk of developing acne.
3 Acne is not associated with sexual activity or masturbation. The effects of the sun have not been proven, but tanning beds should be avoided as they increase the risk of skin cancer.
Who is at risk?
1 Acne is inherited. Hormonal changes during puberty and the menstrual cycle, as well as pregnancy, can increase the risk of acne. Almost 80% of people aged 1 to 30 years will experience inflammation.
2 Adolescents - among girls it most often occurs between the ages of 14 and 17 years, and among boys - between the ages of 16 and 19 years.
Symptoms may come and go, but the situation improves with age. Only 5% of women and 1% of men have acne over the age of 25.
Removal
A cyst on the face is usually harmless and goes away without treatment. But when it becomes swollen or sensitive, or irritating with its appearance, you can speed up its disappearance.
- A warm, moist compress may be applied to aid drainage.
- Apply a cloth or towel immersed in very warm water to the cyst and surrounding skin
- Leave until fabric cools
- Repeat the procedure two to three times a day
- For effective results, carry out the procedure described above several times a day.
- You must resist any urge to squeeze the cyst like a pimple . The inflamed lump can be removed by a doctor using a safe surgical procedure. It can be drained through an incision or steroid medications may be given to reduce swelling. If the cyst is infected or inflamed, squeezing it out on your own risks spreading the infection. The bag may still remain under the skin and grow back, refusing to go away even after treatment. An infected cyst can be treated with antibiotics.
- Surgical removal A cyst on the face can be removed through surgery. The doctor should do additional tests to find out if it is cancerous, which include:
- CT scan to help find the best path for surgery, identify abnormalities
- Ultrasound to identify cyst contents
- Biopsy to check for any signs or symptoms of cancer
Without surgery, the cyst is highly likely to return. Surgery can remove it completely and is the best treatment for this problem. Depending on the tests and the appearance of the lump, one of the following methods may be used:
- Conventional wide dissection: This is effective because the cyst is completely removed but a long-lasting scar is left.
- Minimal dissection: scarring is kept to a minimum, but there is a chance that the cyst will recur
- Laser removal: A small hole is created to remove the contents of the cyst using a laser. In addition, the outer walls are removed after about a month.
In addition to surgery, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic ointment to prevent infection. You may also need an anti-scar cream to reduce the appearance of scars.
Nodular cystic acne: features and consequences
Let's start with the simplest things.
Many people do not even suspect that they are faced with one of the most severe manifestations of acne, and continue to try to get rid of it with general methods. Of course, in the end they turn out to be ineffective, simply because getting rid of nodular cystic acne needs to be approached a little differently. Therefore, in this section we will tell you how to determine that you have this particular form of rash. We will explain the most common symptoms and talk about possible consequences.
But you should definitely remember that only a specialist, a dermatologist, can ideally diagnose the form of acne. Of course, theoretically, this can be done independently, but still one cannot count on high accuracy of such an approach.
What does cystic acne look like and how does it manifest?
How does a pimple like this even form? When the secretion produced by the sebaceous glands becomes too much (usually, this happens when the glands are hyperproductive - when more sebum is produced than the epidermis needs), the ducts through which it is brought to the surface of the skin begin to gradually become clogged with this same substance. Because of this, serious inflammation begins - bacteria actively multiply in the affected areas, which leads to the formation of pimples.
The cystic form of acne differs not only in the mechanism of formation, but also in its appearance. It definitely doesn't look like regular acne or feel like a standard pimple. Now let’s explain what the difference actually is.
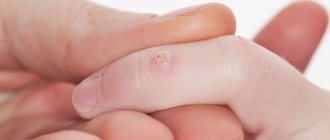
Unlike a regular rash, cystic acne looks like a kind of bubbles or nodules filled with white liquid in the center. Around the core, the acne is colored bright red - a clear sign that a strong inflammatory process has already begun and is fully undergoing in this area.
The sensations from such acne are unpleasant. They hurt when you try to put pressure on them and often itch if you don't touch them. And this, again, is due to the fact that everything in this area is inflamed. Squeezing out such a pimple is usually not difficult, although it, firstly, causes extremely painful sensations. And secondly, it doesn’t happen without a trace.
What are the consequences of such rashes?
Of course, cystic acne never goes away without leaving behind a few nasty reminders. This can happen either due to our intervention, or simply because the inflammation was too strong.
The fact is that such active inflammatory processes in the ducts of the sebaceous glands are considered harmful already in the process, and if they are not cured in time, then traces will remain on the skin in the form of scars and scars. If they did not arise due to, so to speak, human intervention, then the marks completely repeat the shape and size of the pimples - they are round and not too large. There will be no dents or depressions on the surface of the skin, but the marks will differ from healthy areas of the epidermis by a pinkish tint.
But the picture changes dramatically if you have abused the squeezing of cystic acne. In this case, everything is more serious. After poor-quality acne removal, large scars of all shapes and sizes, with indentations, usually remain on the surface of the skin. They differ from other areas of the skin not only in color, but also in their shape. Such scars look like small pits on the surface of the epidermis.
Such consequences no longer go away on their own. If the body takes about a year to regenerate ordinary marks, then it will never heal the pits on its own. They will have to be removed by a cosmetologist using a special laser.