Squamous cell skin cancer is a malignant neoplasm that forms from the spinous layer of the skin, which includes keratonocyte cells. It usually affects unprotected areas of the body that are more exposed to ultraviolet rays. Squamous cell carcinoma differs from similar pathologies in its aggressive course - intense infiltration of the lower layers of the skin and the spread of metastases occur. The disease is more often diagnosed in people aged 60 to 65 years. Small lesions of squamous cell carcinoma are treated with radiation therapy or surgery. The optimal treatment method is selected by a specialist based on the stage of the cancer process and its prevalence.
…
The life prognosis for squamous cell skin cancer is characterized by the following statistics: during the first 5 years, 90% of people whose tumor size is less than 1.5-2 cm survive, and if these sizes are exceeded and the tumor grows into the underlying tissue, only 50% of patients survive.
Causes
Decreased immunity and long-term regular exposure to solar radiation significantly affect the occurrence of a malignant process. Spinal cell carcinoma can also occur when:
- pigment xeroderma (develops in newborns);
- Bowen's disease;
- hereditary predisposition;
- Keir's erythroplasia;
- burns;
- taking immunosuppressants;
- chronic dermatitis;
- leishmaniasis;
- pyoderma;
- lupus erythematosus;
- Paget's disease;
- poor nutrition;
- various skin injuries;
- regular alcohol and nicotine intoxication of the body;
- frequent contact with chemicals, resins, arsenic, metal, tar.
Depending on the background against which the malignant process develops, the tendency for carcinoma to metastasize is different. Less often than others, formations that appear as a result of solar keratosis metastasize. More often than others, epitheliomas that form in the area of scars from burns, fistulas in chronic osteomyelitis and radiation-induced dermatitis, as well as tumors of the male genital organ, anus, and vulva metastasize.
Development mechanism
Experts distinguish four degrees of development of squamous cell carcinoma. Their division is made depending on the depth of tumor penetration into neighboring tissues, the presence of metastases and a number of other characteristics.
Stage 1. At the primary stage, the tumor strand penetrates only to the level of the sweat glands. Multiple formation of horny pearls occurs. Contact of healthy cells with the tumor leads to the formation of a zone around it in which inflammatory reactions occur.
Stage 2. Characterized by an abundance of cells with hyperchromic nuclei. The number of horn pearls is small.
Stage 3. A large number of atypical cells with mild keratinization are observed.
Stage 4. Signs of keratinization are completely absent, the inflammatory process is extremely weak or absent at all. All cells that make up the tumor are atypical.
How much does treatment for squamous cell carcinoma cost in Israel?
Squamous cell oncology develops from squamous epithelial cells, which are found in many organs, including the skin.
In Israel, all types of squamous cell cancer are treated, regardless of their location. The most common diseases are the following:
- squamous cell oncology of the skin;
- squamous cell tumor of the cervix;
- squamous cell lung cancer;
- squamous cell tumor of the larynx;
- squamous cell oncology of the esophagus.
Get an individual treatment price
1) Call the clinic right now on the Russian number 7-495-7773802 (your call will be automatically and free of charge transferred to a Russian-speaking doctor-consultant in Israel).
2) Or fill out the form below. Our doctor will contact you within 2 hours.
Varieties
Depending on the histological variants, the pathological process is divided into spindle cell, acantholytic, adenoid squamous, and verrucous cancer.
The disease is of two types: squamous cell keratinizing carcinoma (90% of cases) and non-keratinizing. The first option looks like a very dense formation, reminiscent of a particle of a nail. It is more difficult to diagnose because the skin growth is not intensely colored. It is considered a more aggressive form of the pathological process.
Carcinoma can have different degrees of cell differentiation:
- well-differentiated squamous cell skin cancer - the tumor is dense, hard to the touch with signs of keratinization. It spreads slowly, the prognosis with timely diagnosis is favorable;
- poorly differentiated - looks like a soft formation that develops quickly and is easily injured. It is characterized by a high level of metastasis and frequent relapses;
- undifferentiated - considered the most dangerous degree of the pathological process. The disease is rapidly progressing. Metastases appear soon after tumor formation. Usually detected on mucous membranes.
Most often, epidermoid cancer is highly differentiated.
Depending on the direction and nature of growth, there are 2 types of epithelioma:
- exophytic - a sedentary, dense, wart-like or nodular formation, usually red or brown, which very quickly increases in size and bleeds with minor injury. Sometimes the skin growth covers a layer of keratinized skin particles;
- endophytic is a small tumor surrounded by a dense ridge that grows quickly and ulcerates. It is dangerous due to rapid metastasis, destruction of bone tissue and blood vessels, and bleeding.
Pathology can be solitary (single) or multiple. Needs differentiation from:
- Bowen's disease;
- chronic inflammatory pathologies (tuberculosis, syphilis);
- basal cell carcinomas;
- melanoma;
- keratoacanthomas;
- sarcomas;
- pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia;
- Keir's erythroplasia;
- benign skin tumors (papillomas, atheromas, fibromas, lipomas).
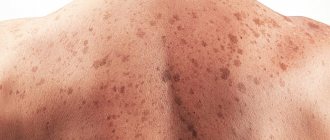
A malignant neoplasm is usually localized in the face and head, as well as in areas of the body exposed to sunlight. Tumors on the palms rarely appear.
Squamous cell skin cancer
This type of tumor has a relatively benign course. However, if left untreated, the advanced form of the disease can cause the death of the patient. Squamous cell skin cancer can occur at the site of keratosis (thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin), scars from wounds or burns, including sunburn, etc.
Treatment of squamous cell skin cancer in Israel is carried out mainly surgically. Along with traditional operations, Israeli surgeons are proficient in the Mohs operation technique. In this surgical procedure, the tumor is removed layer by layer and each removed layer is examined under a microscope. Cryotherapy (tumor destruction using liquid nitrogen at a very low temperature), laser therapy, electrocoagulation, as well as local treatment in Israel using cytostatic drugs can also be used.
Professor Ya. Shechter, one of the leading Israeli specialists in malignant skin tumors, brings treatment for squamous cell skin cancer to Top Ichilov.
The cost of surgery for squamous cell skin cancer is from $5,000.
Get exact price
Squamous cell skin cancer (squamous epithelioma, papillary cancer) is a malignant disease characterized by aggressive development and invasive (penetrating into tissue) growth. Squamous cell growth begins in the middle layers of the epidermis. The disease most often affects people over 60 years of age, but sometimes develops at a young age. This form of cancer is more common in people with fair skin.
Medicine does not know the direct causes that cause abnormal cell behavior and the formation of cancer. Doctors can only list the factors that significantly increase the risk of developing squamous cell skin cancer.
Ultraviolet radiation is considered the most significant factor influencing the development of squamous cell epithelioma. You can get an excessive dose of insolation from the sun during the period of its greatest activity (during the daytime) or, for example, in a solarium when visiting it frequently.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and IS NOT a guide to action! Only a DOCTOR can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS! We urge you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist! Health to you and your loved ones! Do not give up
Other influencing factors include:
- radioactive exposure; thermal or chemical burns; contact with carcinogenic substances (soot, tar, arsenic, some resins); genetic predisposition - the presence of skin cancer in a family history.
In addition, some skin diseases can cause squamous cell carcinoma:
- xeroderma pigmentosum (reticular melanosis) is a disease caused by skin hypersensitivity to solar radiation; Bowen's disease (epidermal carcinoma) - some doctors consider this pathology as the initial stage of squamous cell carcinoma; chronic dermatitis; constant inflammatory processes occurring in the skin layers; non-healing ulcerative lesions; skin injuries (chemical and sunburns); boils.
Recent studies have established a relationship between certain papilloma viruses and the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncological diseases arise from the joint (synergistic) action of physical (chemical) carcinogens and papilloma viruses. The immune mechanisms of the human body also play a role.
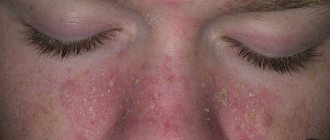
Squamous cell epithelioma can be localized on any part of the body - from the scalp to the external genitalia. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin of the nose or upper lip may develop, and there are cases of neoplasms forming in the perianal area.
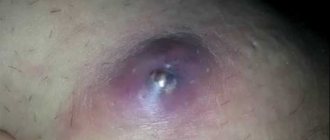
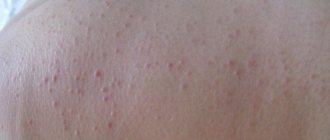
The initial stage of squamous cell carcinoma is quite variable. One of the first symptoms of the disease may be a reddish or white spot (wart or bulge) that forms on the skin on its own. The spot can quickly increase in size.
In other cases, the tumor may appear as a wound with raised edges that does not heal for a long time and bleeds for several weeks. Sometimes squamous cell carcinoma may appear as a dry, rough patch covered with keratinized scales of skin.
Usually a single lesion is formed, but sometimes there are multiple lesions.
In the first case, the tumor tumor rises above the level of normal skin, has a wide base and a dense consistency. Sometimes the tumor covers a layer of keratinized skin particles.
In the endophytic form of cancer (ulcerative), the initial lesion quickly undergoes ulceration. At the periphery of a crater-shaped ulcer, secondary elements can form, which gradually disintegrate and merge with the main focus. The tumor begins internal and external growth, destroying surrounding tissues (bones, blood vessels).
If cancer cells affect the lymph nodes, they first become denser, then become immobile, adhere to the skin and cause pain.
There are keratinizing and non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinomas. The first type sometimes takes the form of a very dense formation that resembles a particle of a nail (doctors call this formation a cutaneous horn).
A common symptom for all squamous cell tumors is their rapid development. Pain occurs as a result of secondary infection of the lesions. Squamous cell carcinoma metastasizes quite quickly - they usually occur when the tumor reaches more than 2 cm in diameter.
Like any other type of cancer, squamous cell carcinoma has 4 stages of development:
- At stage 1, the primary lesion does not exceed a diameter of 2 cm, the neoplasm spreads only to superficial areas of the skin, and the tumor itself is practically painless; At stage 2, the size exceeds 2 cm, the neoplasm penetrates all layers of the skin, but nearby tissues are not yet affected (at this stage, a single metastasis may appear in a nearby lymph node); Stage 3 is characterized by a significant increase in size, the tumor affects neighboring tissues, but does not yet reach bone and cartilage tissue (this stage is characterized by the presence of distant metastases); At stage 4, squamous cell carcinoma penetrates the bones and cartilage, and multiple metastases are diagnosed in distant areas of the body.
There are several forms of skin cancer, and the squamous cell type is one of the rarest. But at the same time it is also the most dangerous.
Timely treatment of the symptoms of squamous cell skin cancer will avoid many complications and prolong life for many years.
First of all, various damage to the skin can provoke a tumor.
Squamous cell carcinoma develops from cells of the spinous layer of the epidermis. Research conducted by scientists cannot yet give an exact answer to the question of what causes the symptoms of squamous cell skin cancer. However, doctors were able to identify several factors, the influence of which can provoke a tumor process in the skin:
- Solar and senile keratoses; Severe thermal and chemical burns of the skin; X-ray dermatitis; Xeroderma pigmentosum.
Not long ago, doctors established a clear connection between papilloma viruses and the symptoms of squamous cell skin cancer. The process of tumor formation occurs due to the synergistic effect of the virus with carcinogens, caused by genetic immune mechanisms.
What is the prevention of the disease?
- you need to be careful in the sun in summer, when it is most active;
- You should not overuse tanning in a solarium;
- if dermatitis occurs, they need to be treated promptly, as they are precancerous diseases;
- If you plan to go to the beach, you should use sunscreen. They should be applied approximately 20 minutes before the start of the procedure. This should be repeated every three hours;
- You need to carefully monitor the condition of your skin. If moles have acquired a strange shape, or some strange lumps have appeared, then you should urgently seek advice from an oncologist.
Stages of the disease
Like any oncological process, there are stages of development. There are 5 stages of epidermoid cancer:
- 0 – small, mobile and painless tumor located in the dermis or epidermis. There are no metastases;
- I – formation up to 2 cm, grows into all layers of the skin without affecting neighboring structures. There are no metastases;
- II – a malignant focus is more than 2 cm, but nearby tissues are not yet affected. A single metastasis may appear in a lymph node;
- III – the tumor grows, affects neighboring tissues (grows into the muscles, skin, and into the walls of vital organs). Distant metastases appear;
- IV – there are multiple metastases in bones and cartilage.
In the final stages, death usually occurs as a result of multiple organ failure.
Forms of the disease
In medicine, there are five stages that characterize skin cancer and its development.
- Zero stage. The formation is localized only on the surface of the body and does not affect deeper layers. At this stage, a visit to the doctor certainly ends in getting rid of the disease.
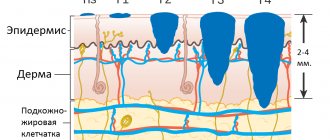
- First stage. The resulting tumor penetrates more deeply into the lower layers. At this stage, the neoplasm is fully formed and is two millimeters thick. This form is characterized by the fact that its metastases have not yet spread to the lymph nodes.
- Second stage. During this period, the tumor reaches almost four millimeters. Lymph nodes have not yet been affected by metastases. However, at this stage the patient may notice that the tumor is painful. As is known, with proper treatment, about 50% of patients are cured at this stage.
- Third stage. There is already damage to the lymph, but no other organs are yet affected by metastases. At this stage, skin cancer in humans causes a constantly high temperature. With proper treatment, doctors give a guarantee of survival of only 30%.
- Fourth stage. The tumor metastasizes throughout the body. The very first organs that are damaged by metastases are the lungs and liver. The fourth stage of the disease is accompanied by constant bleeding of ulcers. After a while, absolute intoxication begins. Only 25% of patients can save lives in such cases.
Stages of skin cancer development - features of the disease course
Squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix
This type of tumor accounts for 70-80% of all cervical tumors. Treatment of squamous cell cancer of the cervix in Israel in the early stages is carried out using organ-preserving methods, which allow preserving the uterus and the woman’s reproductive function. Such surgical interventions include, for example, conization surgery, in which the affected part of the cervix is removed along with the tumor.
At later stages, along with surgery, the patient may be prescribed chemotherapy and radiation therapy, including brachytherapy - irradiation of the tumor from a source located inside the body, near the tumor.
The treatment protocol for cancer in Israel is prescribed by leading Israeli oncologist Professor Moshe Inbar, head. Department of Oncology MC "Ichilov". The operations are performed by Prof. Dan Grisaro, manager dept. Oncogynecology MC "Ichilov". The cost of examination for squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix is from $3572
The cost of conization surgery is from $1498
Symptoms
At the initial stages of the malignant process, symptoms rarely cause concern to the patient. The formation becomes asymmetrical, lumpy, and increases in circumference (more than 6 mm). As the pathology develops, the following appears:
- pain in the area affected by the tumor;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- swelling;
- low-grade fever;
- itching and burning sensations;
- loss of sensation;
- pain at the site of skin growth formation;
- loosening or softening of the tumor;
- chronic fatigue;
- redness of the skin near the changed area;
- decreased appetite;
- bleeding when pressed.
Squamous cell lung cancer
The tumor is a form of non-small cell lung cancer. Compared to other malignant lung tumors, squamous cell carcinoma is characterized by slower growth. When this disease is detected early, the 5-year survival rate is about 80%.
In the early stages of the disease, surgery is usually performed. Its type depends on the location of the tumor. In inoperable patients, the main treatment method is radiation therapy, including brachytherapy and IMRT - intensity modulated radiotherapy, which allows targeted irradiation of the tumor with large doses of radiation without harming healthy tissue.
In late stages, targeted therapy using monoclonal antibodies can be used in the treatment of squamous cell lung cancer in Israel.
Folk remedies
When treating squamous cell carcinoma, you can alleviate the condition using traditional medicine recipes. However, you should not refuse traditional treatment from an oncologist.
Areas affected by squamous cell carcinoma should be treated with birch bud tincture. Verbena lotions to which table vinegar is added have also shown themselves to work well.
Also, to treat ulcers and plaques, an ointment is used, which is prepared from dried pomegranate seeds and honey.
Very useful for external use against this type of cancer, an ointment that is prepared on the basis of vegetable oil with powder from the inside of walnuts. The amount in the oil is added so that it becomes like an ointment.
Diagnostics
If disturbing symptoms appear, you should contact a specialist who will conduct a thorough examination of the affected area, collect anamnesis, and also prescribe a comprehensive examination. The initial examination is carried out using a dermatoscope - an optical device that allows you to obtain an enlarged image of a suspicious area of skin, analyze the condition of all layers of the epidermis, and study the structure of cells. The method allows you to see the tumor, assess the degree of cell differentiation and the depth of pathology growth into the layers of the skin.
A progressive method for studying skin tumors is siascopy. Performed using siascanners. A three-dimensional image of the tumor is displayed on the monitor screen and examined by a specialist. Siascopy allows you to examine a suspicious area of skin without the need to take a tissue sample for laboratory examination.
Another option for diagnosing carcinoma is triplex skin scanning. Performed without special training. Allows you to identify changes in the skin, assess the nature of the blood supply to blood vessels, and see signs of edema.
For the purpose of additional diagnostics, the following are used:
- biopsy of the changed area;
- instrumental studies;
- laboratory methods.
Instrumental diagnostics are used to search for secondary cancer foci and examine the lymph nodes that are primarily affected. MRI, as well as CT and radiography are usually used.
Laboratory tests include the study of blood and urine parameters. This allows you to assess the general health of the patient. A blood test is also performed to determine the concentration of the tumor marker SCC antigen. It is responsible for regulating the process of formation of healthy squamous epithelium and accelerates tumor growth in epidermoid carcinoma.
An increase in the concentration of SCC antigen in the blood can also occur when:
- skin diseases;
- liver failure.
The combination of all the procedures necessary for correct diagnosis allows the specialist to find out the type of carcinoma, the stage of the pathological process, and also decide on a plan for getting rid of cancer.
At the stage of identifying squamous cell carcinoma, doctors carry out differential diagnosis. It is necessary to exclude other types of cancer tumors, as well as diseases that resemble squamous cell epithelioma in symptoms and appearance.
The initial examination is carried out using a dermatoscope - an optical device that allows you to obtain an enlarged image of the affected area of the skin and illuminate the upper layer of keratinized skin.
Further research includes a cytological analysis, which is carried out for the ulcerative form of squamous cell carcinoma. A scraping is taken from the wound and studied in the laboratory. A histological analysis is also carried out - examination of tissues. This test is carried out after a biopsy - surgical removal of a sample from the site of the lesion.
The patient's lymph nodes, which are affected first, are also examined. To identify metastases, additional diagnostics are prescribed using ultrasound, MRI, and radiography.
Photo: Squamous cell skin cancer
For squamous cell skin cancer, complex treatment is used. The main type of therapeutic intervention is surgery, the purpose of which is to remove the tumor within healthy tissue.
- irradiation (radiation therapy); radiotherapy; laser therapy; photodynamic therapy; general and local chemotherapy; immunotherapy.
Radical techniques can vary: it all depends on the stage of the disease, the condition of the patient’s body and his age. Operations such as curettage, cryodestruction (exposure to ultra-low temperature liquid), electrocoagulation are used for small tumors that are at stages 1 or 2 of the development of the oncological process.
Modern clinics also use the Mosch method, developed in Israel. This type of surgical intervention makes it possible to achieve success in 95% of all operations and preserve a maximum of healthy tissue located at the tumor site.
Small tumors are sometimes suppressed with radiation therapy or local chemotherapy. Drugs are used that prevent tumor cells from mitosis (division) and the death of healthy cells.
The photodynamic method is based on the use of photosensitive compounds (photosensitizers) and light of a certain wavelength. The substances are injected intravenously and, when they reach the tumor, are exposed to light. This method of therapy is used when the tumor is localized in the eye or nose area, since other methods of exposure in this case can negatively affect vision and cartilage tissue of the nose.
Cryodestruction is used for small tumors that are not located on the scalp. Drug therapy is used in almost one hundred percent of cases as an addition to other treatment methods.
Chemotherapy and restorative therapy are necessary during the period of rehabilitation of the body after radical exposure. Medicines aim to restore tissue and prevent relapses.
In the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma, due to the aggressive nature of the tumors, early and correct diagnosis is important. The prognosis of treatment depends on how soon the patient goes to the clinic for examination.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx
Squamous cell tumors are the most common malignant tumors of the larynx. In Israel, this disease is treated primarily surgically, including using radiosurgery. During the operation, the larynx may be completely or partially removed. In this case, an operation is performed to restore the removed tissue, which allows the patient to maintain speech and swallowing functions.
The treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx at Top Ikhilov is led by the head. dept. otolaryngology MC "Ichilov" Professor Dan Fliss.
Treatment
Treatment of squamous cell carcinoma is directly dependent on the size of the tumor, location, age characteristics of the patient and the stage of development of the malignancy.
Most often, surgical treatment is used to completely remove the tumor , after which the patient undergoes radiotherapy to completely remove the metastases. X-ray therapy is also carried out in case of tumor localization on the lips, in the oral cavity and other areas in which surgery cannot be performed.
It is often prescribed to elderly patients for whom surgery is contraindicated due to their health condition. It is also possible to use photodynamic therapy and cryodestruction - targeted cooling of the tumor using liquid nitrogen to destroy its cells.
This video demonstrates the actual operation:
How much does treatment for squamous cell carcinoma cost in Israel?
For epidermoid cancer, therapy is selected taking into account the location of the tumor, the stage of development of the disease, the presence or absence of metastases, the patient’s health status, and his age. The most effective methods of treating malignant lesions of this type are considered:
- surgical intervention;
- cryotherapy;
- radiotherapy;
- chemotherapy;
- X-ray therapy;
- laser vaporization;
- PDT.
Simultaneously with medical prescriptions, restorative procedures that increase the protective functions of the immune system and improve the general condition of the patient should be carried out.
The surgical method is the most used. It is selected for extensive, deeply penetrating lesions, as well as at advanced stages of development of squamous cell carcinoma. Skin pathologies up to 2 cm are excised with a reserve of healthy epithelium of 4 mm. Larger, as well as low-grade formations that are localized in dangerous areas (scalp, ears, eyelids, wings of the nose, lips) require excision with a margin of 1-2 cm of intact skin.
Cryodestruction
Therapy with liquid nitrogen is prescribed for the presence of numerous lesions, as well as for small skin tumors and relapses of spinalioma.
This treatment allows you to quickly, painlessly and effectively destroy the tumor. The tumor is treated using a special applicator with liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of extremely low temperatures (-1960 degrees), the cells of formation are frozen and destroyed. Within a few weeks, the carcinoma is rejected and replaced by a scar.
Radiation treatment
Radiotherapy is used in the initial stages of epidermoid carcinoma until the tumor completely disappears, or in the later stages of the pathological process to reduce the tumor to a size that allows surgical intervention.
Treatment may be recommended as adjuvant therapy after surgical removal of squamous cell carcinoma.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy helps to preserve as much as possible the intact surface near the affected area, since the effect is only on the epidermoid carcinoma itself. Small tumors are treated with injections. Ointments may be prescribed to prevent the growth of the tumor. In cases of relapses, in advanced stages of cancer, in cases of significant tumor size, as well as in the detection of metastases, systemic drugs are used.
Laser treatment
Laser vaporization is prescribed for diagnosing spinocellular cancer of the skin of the face (eyelids, lips, wings of the nose and mouth), and for elderly patients. Elimination of metastases when treating altered areas is also carried out. The technique allows you to remove the tumor quickly, painlessly and effectively. This creates a thin, elastic scar.
Treatment of cancer localized on the wings of the nose and in the eye area is difficult, since most treatment methods can damage the lens and cartilage tissue. In such cases, low-intensity laser radiation in combination with photosensitizers is recommended. This treatment option is called photodynamic.
After completing the course of treatment, the person must undergo dispensary observation by a specialist at his place of residence. The first examination, including examination of the skin, palpation of lymph nodes and ultrasound, is required after 1.5 months, then after 3, 6 months and 1 year. Then an annual visit to the doctor will be enough.
The main goal in the treatment of skin cancer is radical removal of the tumor, which is carried out by excision of the primary tumor to healthy tissue. Currently, there are several methods of surgical treatment.
Classic excision. This method is applicable to any form of tumor in the early stages of development. The surgeon removes the tumor, capturing 1-2 cm of adjacent healthy skin. It is subsequently examined under a microscope for the presence of cancer cells in intact tissue.
Microsurgery MOHS. This method is most effective in the development of basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. The peculiarity of this operation is the layer-by-layer removal of the tumor and instant microscopic examination of each layer for the presence of cancer cells. Sections are made until healthy tissue without cancer appears under the microscope. Microsurgery is performed to minimize the removal of healthy tissue and preserve the cosmetic effect.
Fulguration (electrocoagulation) and curettage. This simple method is also suitable for removing small squamous or basal forms. The operation is performed using a curette, a small spoon-shaped instrument. When damaged tissue is removed, an electrical current is applied to the area to destroy any remaining cancer cells and prevent bleeding. For complete removal it is necessary to carry out several stages of treatment.
Cryotherapy. This method is used to remove Kaposi's sarcoma, melanoma, basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma when the tumor is small. The essence of the operation is to remove the cancerous tumor with liquid nitrogen, which is applied directly to the site of the lesion.
As a result of shock freezing of a tumor, cancer cells are destroyed, but along with them, nerve damage can occur, which often leads to loss of sensitivity in this area.
Laser therapy. Removing cancer cells with a laser is a modern and highly effective method, since during layer-by-layer removal of affected tissue, which is carried out with high precision, healthy tissue is not injured. Laser therapy is performed quickly and under local anesthesia.
Forms
Conventionally, there are two forms of squamous cell carcinoma: exophytic and endophytic. There is also a combination of them, the so-called mixed form.
- Exophytic form. It is characterized by the formation of a dense nodular formation of a skin tone at the beginning of the disease. The surface of the neoplasm is often covered with a yellowish horny mass.
The node quickly grows in height, while its base is inactive and wide due to the fact that, simultaneously with the increase in size, the tumor grows deep into the tissue. The surface has a bumpy structure. At an advanced stage, it is possible for this form to transform into an infiltrative-ulcerative form.
- Endophytic form. It is characterized by the presence of a small dense node at the initial stage, which ulcerates during development. Around the neoplasm, the formation of secondary nodules is possible, eventually merging with each other and the main nodular formation. The tumor grows both in width and depth.
Prevention
Timely treatment of skin diseases is important. Other preventive actions include:
- regular self-examination, visiting a specialist at least once a year (especially if there is a hereditary predisposition);
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle - moderately intense sports, long walks in the fresh air, a balanced diet, minimizing the impact of stress factors;
- the use of ointments containing retinoids;
- Regular use of 5-fluorouracil cream.
Forecast
The prognosis for squamous cell epithelioma is favorable. Metastases form less frequently than in other types of malignant pathologies. Large and deeply penetrating cutaneous carcinomas are more likely to metastasize.
If spinalioma is treated at the third or fourth stage of development, then the prognosis for the next 5 years of life is approximately 60%, and with well-chosen and correctly administered therapy at the initial stages of the disease - about 90%.
Squamous cell skin cancer is a malignant disease that is not very common. Detection of pathology at an early stage, timely determination of the type of cancer and the background against which the malignant process developed are important elements of effective treatment. Lifestyle correction, as well as regular visits to a specialist for examination, will help to successfully stop a relapse, which is possible in 30% of cases.
Degrees of differentiation and their differences:
In order to make a diagnosis, the oncologist refers the patient to histology, to analyze biopsies, scrapings from the affected areas of the skin or ulcers. Based on the results of the histological examination, the type of squamous cell skin cancer is revealed.
- Undifferentiated squamous cell carcinoma (non-keratinizing) . The most malignant form is characterized by rapid growth. The mutation occurs in the cell of the spinous layer, after which its development stops, and all subsequent clones have a similar structure. Keratin does not accumulate in cancer cells and the process of their death does not occur.
- Differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (keratinizing). In this case, the mutation also occurs at the level of the cell of the spinous layer, but after several divisions the resulting clones, on the contrary, begin to accumulate large amounts of keratin. Cancer cells gradually lose cellular elements and die, which is externally manifested by the deposition of crusts (keratin masses) on the surface of the tumor, which have a yellowish color. Unlike normal keratinization, with keratinizing cancer this process is accelerated several times.