Psoriasis is a non-contagious chronic disease that until recently was considered simply a skin disease. A peculiarity of the inflammatory process in certain areas of the skin in patients with psoriasis is that the life cycle of normal skin cells is approximately 30-40 days, when, as with psoriasis, it is 4-5 days, that is, after 4 days, skin cells gradually die, forming plaques , dryness, flaking of the skin, etc.
The problem of treating this complex and difficult-to-treat disease today is pressing not only for dermatologists; many doctors of other specializations are often involved in determining the causes of psoriasis in a patient, and are also directly involved in the complex treatment of this disease. Today, medicine views psoriasis from the point of view of a systemic failure in the body, and not just as a skin inflammatory process. Even its name has changed, now it is psoriatic disease. Why is psoriasis a systemic pathology? Because patients exhibit several different disorders in the functioning of the body as a whole - nervous, endocrine, immune. In medicine, there are several types of psoriasis; there are also a large number of causes for this disease, mostly theories, since there is no convincing evidence of these alleged causes, let’s consider them in more detail.
A few facts: Psoriasis is not a contagious disease, as it is believed to be caused by a malfunction in a person's immune system, namely overactive T cells in the skin. Psoriasis is classified as a hereditary disease; if one parent has psoriasis, the risk of developing psoriasis in a child is 25%, and if both parents have it, the risk is 65%. In addition to the hereditary factor, the trigger for the debut of psoriasis or relapse is the use of antibiotics, NSAIDs, B vitamins, as well as stress, alcohol, and skin injuries.
Why does psoriasis appear?
Psoriasis is a non-infectious disease.
The cause of its appearance is not yet known for certain, but most doctors claim that it is hereditary, and people with a genetic predisposition are especially at risk. This disease occurs with its own periods of complications and remissions. Throughout life, it haunts a person, bringing negative aspects that affect life activity and ability to work.
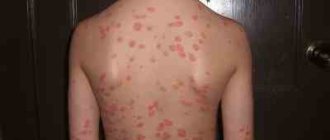
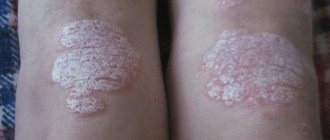
Psoriasis (squamous lichen) manifests itself in the form of skin rashes: red, white, silvery spots protruding on the surface of the skin. Normally, skin cells grow sequentially and die within 4 weeks.
With this disease, cells tend to grow at an accelerated pace, resulting in plaques that become covered with silvery scales. The spots may initially cover small areas of the skin. When complicated, they can spread to a large area of skin.
Psoriasis is an abnormal reaction of the body to external irritants, which results in rapid death of the upper layer of skin in certain areas of the body. Normally, the duration of the cycle of cell division and subsequent maturation is 21-28 days; in the case of psoriasis, the period is reduced to 3-5 days.
Today, most experts tend to consider psoriasis a multifactorial disease of hereditary etiology. There are several theories about the origin of the disease.
According to the first, there are two types of lichen:
- the first is a consequence of poor functioning of the immune system, affects the skin and is inherited, appearing at a young age;
- the second makes itself felt after 40 years, affects joints, nails, is not genetically determined and is not associated with a malfunction of the immune defense.
Causes of psoriasis
Experts in this field are primarily inclined to believe that the cause of the disease is an overreaction of the immune system, which begins to act aggressively towards its own cells.
But there are other reasons for the appearance of this insidious disease:
- Heredity;
- Nervous breakdowns and mental stress;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Metabolic disorders in the body;
- The presence of parasites in humans;
- Viral diseases;
- Allergy;
- The reaction is not medication;
- Surgical intervention;
- Excessive weight and obesity.
Usually, a doctor diagnoses psoriasis by visual examination of the skin, as well as by the condition of the nail plates. Sometimes it is possible to take a sample for testing to rule out an infectious or fungal disease.
What causes the disease? I’ll tell you this: doctors have not yet established the true cause of the development of this pathology. There are several proven reasons, which I will now describe. Maybe you will find yours among them.
In order to determine why psoriasis appears, you need to consider theories that prove the influence of certain factors on the development of the disease.
Considering that doctors still cannot reliably find out what exactly causes psoriasis, many say that any unexplained rashes on the skin are a release of negative energy. This can be a manifestation of accumulated irritation and dissatisfaction that has been suppressed for a long time.
This is what makes a person touchy, he becomes suspicious, excessively withdrawn. And sooner or later, all the accumulated internal conflicts manifest themselves in the form of skin rashes.
Among the favorable factors for the appearance of psoriasis are the following:
- Excessively thin skin. It contributes to a greater extent to the appearance of psoriatic plaques;
- Constant contact with chemical reagents, and especially with alcohol solutions of chemically aggressive substances;
- Fascination with antibacterial soap: it helps to destroy the natural protective barrier of the skin;
- Alcohol and smoking abuse;
- Excessive consumption of hot and spicy foods, as well as chocolate;
- Sudden change in climate zone.
Why does the immune system fail?
The causes of malfunctions in the functioning of immune cells have not been fully established. During research, it was proven that there are many provocateurs for psoriasis.
Often close relatives of patients have a similar problem. Hence the genetic theory of the origin of psoriasis. Sometimes pathology develops due to chronic intoxication of the body. It is believed that improper functioning of the intestines (increased permeability of its cells) contributes to the accumulation of waste and toxins in the body. There are suggestions that skin inflammation is caused by hormonal changes. Psoriasis is often diagnosed in people with diabetes and obesity. Women are at risk during menopause.
Unanticipated immune reactions can cause systemic and skin infections. Untreated dermatitis and chronic allergic rashes, as well as severe viral infections, end with psoriasis.
It has been proven that the disease is associated with neuroses and stress. Psycho-emotional stress, severe shocks and stressful situations can activate autoimmune reactions. If the disease has already begun, nervousness worsens its course.
Psoriasis is diagnosed equally often in men and women. Pathology also has no age restrictions. Most often, the first manifestations of psoriasis occur in young people 16-23 years old, as well as in older people - 57-60 years old.
Classification of the disease
How psoriasis begins, how it manifests itself, what its effect on the body is - all these points are determined by the specific type of pathology. Today there are several classifications of the disease. One of the most common divides psoriasis into two types:
- non-pustular;
- pustular.
The non-pustular (or simple) form is a chronic pathology characterized by a stable course. This group also includes erythrodermic psoriasis, the main symptom of which is damage to most of the skin.
The pustular variety includes:
- annular pustulosis;
- Barber's psoriasis;
- von Zimbusch psoriasis;
- psoriasis of the palms and soles.
A separate category are:
- drug-induced form;
- seborrheic;
- Napkin psoriasis;
- “inverse psoriasis” (develops on the flexor surfaces).
Depending on the localization of the pathological process and the characteristics of the manifestation of the first symptoms of psoriasis, the following are distinguished:
- Vulgar or in other words - plaque psoriasis. This is the form of the disease I see most often in my office. Plaques appear on the patient’s body, which are covered with grayish scales.
- Pustular, in which pustules are observed in the affected area.
- Teardrop-shaped, affecting every tenth patient. Characteristic scales may form throughout the body.
- Exudative psoriasis, characterized by sticky scales that change color. This occurs due to the fact that yellow liquid leaks from the body, which saturates the scales.
- Palmoplantar variant, in which the lesions are located on the palms and soles.
- Erythroderma, which is a severe form of the disease, during which almost all skin integuments become affected. Moreover, the pathology is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes, increased body temperature, and poor blood tests.
- Psoriatic arthritis, which affects the joints.
The disease has several stages - stable, progressive, regressive.
Currently, dermatologists distinguish two types of psoriasis. The first of them develops mainly in children and young people due to poor heredity. Transmitted genes with weakened immunity cannot resist the development of the disease. Scientists believe that about 70% of patients suffer from this type of illness.
The essence of the disease
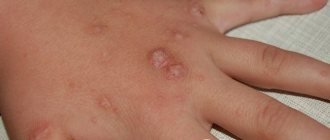
With psoriasis, areas of inflammation form on the skin. They are represented by a papular (nodular) rash. Papules have a flat surface, rise above the skin, feel dense to the touch, and look like red or pink spots. The disease begins with one spot. It increases in size. Smaller ones form around the first outbreak.
In psoriasis, skin cells divide too quickly
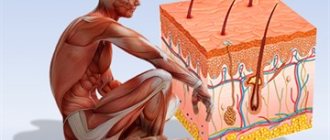
Due to active division in the inner layers of the dermis, the stratum corneum of the skin is constantly renewed. Dead scales imperceptibly peel off from the surface and are replaced by other cells. The update cycle takes 28 days. With psoriasis, this process is reduced by 7 times. A new layer of dead cells forms in 4 days. Superficial dead cells do not have time to exfoliate from the skin during this time. Dead cells accumulate on inflamed spots, forming large dry scales.
Pathological changes occur due to attacks on skin cells by the immune system. Psoriasis is of an autoimmune nature.
What to do if you have psoriasis?!
|
Dependence of symptoms on the stage of the disease
The manifestations of psoriasis vary depending on the specific season and stage. Many patients experience a “winter” version of the disease, in which periods of exacerbation occur in late autumn or winter. In the warm season, due to the intensity of ultraviolet radiation, improvement occurs. The “summer” type is quite rare. During the pathology, three stages are distinguished:
- Progressive, in which new elements constantly appear, the active growth of existing plaques, the presence of a pink zone around them, severe peeling, and itching are recorded.
- Stationary – the growth of papules stops, new rashes do not form, small folds are noticeable on the top layer of skin, around the plaques.
- Regressive - there is no peeling, plaques begin to disappear, and as the disease subsides, areas with increased pigmentation remain in their place.
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)
This molecule is one of the most important factors in protecting the body from bacteria and viruses. TNF-α is produced by immune cells. The molecule activates immune cells and stimulates the production of substances (including interleukins ) that regulate inflammation and the immune response. Scientists believe that TNF-α is one of the key links in the formation of psoriasis, since its excess causes inflammation. Indeed, patients with psoriasis have elevated levels of TNF-α. In addition, TNF-α can increase the severity of depression in patients with psoriasis.
Provoking factors
When treating this disease, a person’s inner peace is also very important. Psoriasis is a very serious and mysterious disease, but it is necessary to treat it not as a diagnosis, but as a way of life.
What causes psoriasis? Doctors still cannot explain the true reasons for the development of dermatosis and put forward several versions.
Psoriasis is a complex, practically incurable skin disease. The disease has a chronic course and is manifested by the formation of extensive reddish-whitish rashes of various localizations on the surface of the skin.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CncBAs4zgTM
At the initial stage, psoriasis is characterized by round redness on the elbows and knees. Less commonly occurs on the scalp.
Over time, psoriatic plaques appear on almost the entire body. It is important to note that at an advanced stage, the affected areas can occupy from 70 to 80% of the total skin surface.
Among the direct factors why psoriasis appears, there may be various triggers, but the most common and convincing among them are mechanical or chemical injuries, sunburn, infections, medications, psychological stress, smoking and obesity.
Causes of psoriasis in childhood
The symptoms of psoriasis in children have some differences, especially in infants. The first signs are not typical.
A delimited area of redness appears in the skin folds, which is accompanied by maceration and gradual peeling of the stratum corneum (starting from the periphery). Outwardly, it resembles eczematitis, diaper rash or candidiasis.
In young children, rashes continue to appear in places uncharacteristic for psoriasis (on the skin of the face, mucous membranes of the genital organs, in natural skin folds). Very often, rashes first develop on the head, under the hair.
Here, accumulations of crusts form against the background of moderate infiltration. Another common area for rash localization is areas of the skin exposed to constant friction from clothing or exposure to aggressive medications.
The papules that form on the body gradually merge into plaques with irregular outlines. Their sizes can vary from a lentil grain to a child's hand.
With a drop-shaped form, papular elements are small in size. They appear unexpectedly, quickly covering the body, face, neck, scalp and extensor areas of the arms and legs.
Psoriasis in children has a long and persistent course. The only exception is the teardrop type, which is characterized by a milder course with long periods of remission.
As in the case of adults, there are three stages, or stages, in the development of the disease.
- In the progressive stage, small itchy papules with a red rim of peripheral growth appear. A feature of symptoms in infancy is the weak severity of pinpoint bleeding, terminal film and the phenomenon of stearin stain. In children, the lymph nodes enlarge and thicken, sometimes they become painful (especially with erythroderma and exudative psoriasis).
- Upon transition to the stationary stage, peripheral growth stops, the infiltrate in the center of the plaque becomes flattened and desquamation decreases.
- The regressive stage is characterized by resorption of the rash elements. Sometimes a characteristic depigmented rim can be seen around them. Areas of the former rash lose pigment or, conversely, undergo hyperpigmentation. Lymph nodes become soft and decrease in size.
Diffuse lesions are observed on the child's palms and soles. Cracks and infiltration of the skin are also noted. In the case of common forms of dermatosis, the nails are affected: pinpoint indentations or longitudinal grooves form on them. Severe psoriasis leads to deformation of the nails.
Pustular psoriasis is very rare in children. It can occur in older adults. This disease is characterized by a severe course with a noticeable deterioration in the condition and an increase in temperature.
Arthropathic varieties do not occur in childhood. In rare cases, small patients indicate the presence of joint pain.
Symptoms of the disease
Psoriasis is a systemic pathology that, in addition to spreading to the skin and nails, can affect the spinal column, joints, tendons, immune, endocrine, and nervous systems. Damage to the liver, kidneys, and thyroid gland often occurs. The first symptoms of psoriasis are most often:
- general weakness;
- feeling of chronic fatigue;
- depressed state or depression.
As I already said, this disease is characterized by scaly elements. If you scratch the affected area, the peeling will intensify, and a shiny, moist area will remain where the scales were torn off. If you continue to itch, drip bleeding will form.
With psoriasis, an atypical reaction of the body to any irritant is observed. Psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of itchy plaques of varying sizes. Normally, skin cells mature within 3 weeks, but with psoriasis they slough off after 5 days, which leads to severe itching, especially on the head (with seborrheic psoriasis) or palms. Adequate treatment is prescribed to relieve acute symptoms.
The most characteristic symptoms of psoriasis include:
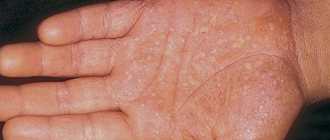
- the appearance of pink-red psoriatic plaques with dry whitish scales (pictured). As a rule, they are most often localized in the knees, elbows, arms and scalp;
- With nail psoriasis, there is degeneration of the nail plate on the hands, a violation of the shape and color of the nails. In severe forms, dystrophic changes may develop;
- itching and dandruff on the head (under the scalp);
- cracking of the skin followed by suppuration of areas of the body affected by psoriasis;
- Sometimes hyperthermia and deterioration of the patient’s general condition are possible.
In most cases, dermatovenerologists can establish a diagnosis of psoriasis only on the basis of an external examination. Photos of people with similar problems and knowledge of how this disease looks and spreads will help everyone independently identify it in themselves. After all, doctors only take cells for biopsy in exceptional cases.
In the initial stages, only small areas of the skin are affected. As a rule, they are located on the scalp, elbow and knee bends. Over time, the affected areas become larger and spread to other parts of the body.
Psoriasis is diagnosed by pale pink papules that rise above the surface of the skin. Each of them has clear boundaries, and they peel off. In addition, the areas affected by the disease are itchy, and people complain of a feeling of skin tightness.
Prevention
Prevention of psoriasis, as well as measures to prevent exacerbations, are as relevant as the treatment itself:
- It is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of the skin very carefully; use moisturizing creams based on natural ingredients.
- Monitor your general health, especially if you have problems with your immune system. Taking multivitamin complexes is a mandatory component of psoriasis prevention.
- Regular massage improves lymph flow and blood circulation, due to which decay products are removed faster and the skin is better cleansed.
- Any contact with household chemicals should be limited to the maximum. Gloves and household respirators are mandatory means of protection if it is not possible to delegate household chores to other family members. When choosing household chemicals, pay attention to the presence of dyes, chemicals and fragrances. The Christmas tree level should be equal to the natural level. It is also worth minimizing the use of skincare products and decorative cosmetics.
- Often the first signs of illness appear after nervous overstrain, so it is important to master different methods of relaxation and self-control. The benefits of healthy sleep should not be ignored. For frequent stress, it is permissible to take herbal soothing tinctures and teas.
- Smoking is a direct provocateur of both exacerbations and the disease itself initially. We are talking about smokers who consume more than 20 cigarettes per day. Under the influence of cigarette smoke, immunity decreases, blood vessels are affected, and the body's antioxidant defense is weakened. As for alcohol, it does not affect the onset of this skin pathology, but can aggravate its course.
Diagnosis of psoriasis
The diagnosis of psoriasis is made by a dermatologist after an in-person examination of the entire skin. There are a number of skin diseases from which psoriasis rashes should first be distinguished. These include eczema, lichen planus, contact dermatitis, toxicoderma and other diseases.
The first symptoms of psoriasis may be nonspecific, modified by self-administration of medications at home, and require long-term observation of the rash to make a correct diagnosis or a skin biopsy.
What factors can trigger psoriasis?
In addition to theories of the origin of the disease, several provoking factors can be identified. These include:
- Poor nutrition, eating allergens, insufficient amounts of vitamins and microelements.
- Bad habits such as alcohol and cigarettes, as well as taking drugs.
- Incorrect intake or untimely discontinuation of medications.
- Various dermal injuries.
- Violation of the hormonal balance of the body.
Heredity and a combination of several provoking factors can lead to a disease such as psoriasis. It is very important to diagnose the pathology in a timely manner and begin adequate treatment. This will help avoid many negative consequences in the future.
Can you get psoriasis?
Until now, doctors cannot confidently say why psoriasis appears. Therefore, it is impossible to say 100% whether it is possible to become infected with this disease through the use of common household items or other ways. Today, the disease is considered non-contagious, and patients with psoriasis can visit public places: solariums, saunas, swimming pools, etc.
Health experts from many countries conducted studies that confirmed the safety of communication with such patients and refuted the theory about the possibility of contracting psoriasis through airborne droplets, household or sexual contact.
Important! Psychological comfort is very important for people with this diagnosis, so society needs to reconsider its views on the disease and try to accept it, realizing that the pathology will not harm them or others.
Viral theory of origin
The disease can occur at any age - in children and adults, the elderly, and does not depend on gender. The prevalence is the same in both sexes.
A number of scientific studies in dermatovenerology have led to the conclusion that the disease is of a viral nature, because against the background of pathology, changes occur in the peripheral lymph nodes. Doctors suspect that it is retroviruses, transmitted by inheritance, that are one of the causes of the disease.
However, to confirm this theory, the virus must be identified. And in order to do this, the virus needs to be isolated and a favorable habitat must be selected. Science is not yet able to do this.
The problem is that retroviruses are characterized by the ability to transform the genetic year of the carrier. Through the enzyme reversese, they produce special DNA, which leads to the formation of a false program in cells, which changes the human genome.
But it has been definitely proven that blood transfusion from a sick person to a healthy one does not lead to infection and, accordingly, psoriasis. Therefore, the viral theory has not been proven.
How is psoriasis treated?
Treatment of nervous psoriasis requires varied therapy. To get rid of discomfort, you will need to use not only topical medications, but also sedatives.
Many doctors prescribe their patients the use of B vitamins, which have a positive effect on the central nervous system. Keep in mind that the treatment of this disease is quite an expensive procedure, since insufficient therapy can easily lead to an exacerbation.
Psoriasis is an incurable disease, but all treatment methods for this disease are aimed at reducing the number of periods of complications and increasing the duration of remissions.
The difficulty of treatment lies in choosing a drug that will be effective for the manifestations of the disease. Each patient is recommended to have a purely individual approach in the treatment of psoriasis.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes local treatment using various creams, ointments, lotions, which are directly applied to the affected areas of the skin. If this method does not produce positive results, phototherapy or photochemotherapy with direct irradiation of the skin is prescribed.
If this does not provide effective progress in treatment, then medication is prescribed orally or by injection. This method is called systemic.
Over time, the disease may become resistant to one or another treatment method, then the doctor changes the drugs and prescribes a different course of treatment. Such changes in the treatment of psoriasis are called rotation.
Antibiotics are not usually prescribed to treat this disease. But in case of acute complications of the disease and repeated relapses, the doctor may prescribe a course of treatment with antibiotics.
You can read about treating psoriasis at home in a special section. I’ll tell you this: to eliminate a disease, you need an integrated approach. Self-medication is inappropriate here.
For people with this pathology, an individual therapeutic course is developed that reduces inflammation, itching, and reduces peeling.
Various ointments and creams containing urea, salicylic acid, dithranol, pyrithione and other components help with this. Preparations with naphthalene and tar have also proven themselves well.
The drug Methotrexate is prescribed as a systemic treatment. To suppress active division of skin cells, this solution is injected intramuscularly once a week. The course lasts seven weeks. You can read more about the drug Methotrexate in this article.
To strengthen the immune system, the immunosuppressant Cyclosporine is prescribed. It is taken only under the supervision of a doctor.
Photochemotherapy, or otherwise known as PUVA, has also worked well. This is ultraviolet irradiation with waves of 360 mm. This procedure will slow down cell division and improve autoimmune processes.
Well, perhaps the most pleasant “cure” for psoriasis is spa treatment. A holiday in Israel at the Dead Sea will be 100% effective. Expensive, I don’t argue, but if a disease poisons your life, you won’t pay that much money just to get rid of it.
For budget options, I can suggest Matsest or Pyatigorsk. The “Salt Caves” have also proven themselves well, which are now, perhaps, located in every city. Two courses per year are enough to maintain the disease in a stable condition or in remission.
Conventionally, all methods can be divided into two groups:
- external therapy;
- systemic treatment.
There is no point in trying to get rid of a disease such as psoriasis on your own with the help of medications. After all, only a doctor can assess whether you have complications and determine the form and stage of the disease.
Also, treatment is selected depending on the age of the patient. At the same time, there is no point in hoping for a quick recovery.
Typically, treatment lasts about 1.5-2 months, provided that the patient does not find himself in stressful situations and does not have a weakened immune system.
In all cases, even in a state of stable remission, patients should use salicylic ointment and any fatty creams with Vaseline and lanolin. This helps prevent exacerbations of the disease over a long period of time.
Treatment
Getting rid of psoriasis involves an integrated approach using the following categories of medications and drugs.
Creams and ointments
Ointments and creams can fight psoriasis quite effectively with minimal side effects. These products are usually applied directly to inflamed areas:
- Hormonal ointments are among the most effective; they eliminate the main symptoms and block the proliferation of keratinocytes. The most powerful products in this category can irritate the skin and cause dryness and thinning of the epidermis.
- Salicylic acid eliminates psoriatic plaque by cleansing the skin. Dosage when using this product is extremely important, since excessive use leads to hair loss and irritation of the skin.
- Retinoids are an active form of vitamin A; they are almost as effective as hormonal ointments, but the clinical effect takes longer to achieve. Hypersensitivity to ultraviolet radiation is the most common side effect.
- Tar ointments reduce the severity of negative symptoms and block the growth of skin cells. Side effects include alopecia, acne or folliculitis.
- Calcipotriol is a form of vitamin D that comes in the form of an ointment or gel. Combined use with hormonal agents gives maximum effect.
- Moisturizing creams help eliminate negative side symptoms such as dryness and itching of the skin, but they should not be used as the main method of treatment.
- Anthralin in ointments helps eliminate scales and blocks the proliferation of keratinocytes. After applying to the inflamed area, the product must be washed off after some time.
Tablets for psoriasis
Since it is not always possible to defeat psoriasis through local therapy, there is a need to supplement the treatment strategy with a tablet form of medication. Side effects can become significantly more frequent, so constant monitoring of your general health through testing and visiting a doctor is a must:
- Systemic glucocorticosteroids reduce inflammation, swelling and itching, and block increased activity of skin cells. Side effects are extremely numerous, so tablets of this group are rarely prescribed.
- Psoriasis throughout the body can be treated with Methotrexate, which demonstrates effective cytostatic and anti-inflammatory effects. The body reacts quite positively to low dosages. Rare side effects include increased fatigue, decreased appetite, and digestive problems.
- Retinoids are effective in cases where the skin disease psoriasis cannot be treated with other means. Side effects include alopecia and inflammation of the lip area. After using tablets of this group, you should not give birth for 3 years, since retinoids provoke the occurrence of birth defects.
- Cyclosporine has many similarities with methotrexate and is classified as an immunosuppressant. Increased blood pressure and the occurrence of renal pathology are the most common side effects.
- If the listed drugs cannot be used due to the characteristics of the patient’s body, it may be advisable to prescribe hydroxyurea or Thioguanine.
Methotrexate
Tar ointments
Calcipotriol
Injections
Medicines that help get rid of psoriasis can be presented in the form of injections with the following components:
- Antihistamines instantly block acute itching;
- Glucocorticosteroids in the form of injections are used if tablets and ointments with this component are not effective;
- Biological drugs are the result of the synthesis of human and animal proteins. They have a beneficial effect on the body's immune system, but their price is too high for many patients.
Using shampoos
It is also worth considering special medicated shampoos, since only they can remove psoriasis on the head:
- Antifungal shampoos, for example, Nizoral, are effective if the causative agent of pathological inflammation is a fungal infection;
- Shampoos containing corticosteroids, such as Sarech, Clobex and Etrivex;
- Tar shampoo or soap is used to eliminate psoriatic scales, as well as reduce burning and itching. Examples include Tana, 911 tar and Algopix shampoos. It is also permissible to add birch tar directly to the shampoo that the patient usually uses.
Medications
If the appearance of psoriasis is diagnosed in time, the following medications can bring the desired result:
- The ASD2 fraction has been used since USSR times, mainly by veterinarians, but the use of this drug also helps with psoriasis in humans. This is an antiseptic whose action is aimed at immunomodulation. The use of compresses is acceptable. Lotions, topically or even internally. The treatment method in question is not recognized by official medicine.
- Infliximab is a biological drug for intravenous or subcutaneous administration.
- Dexazone, Metypred and Prednisolite belong to the category of hormonal drugs, which, despite their effectiveness, are accompanied by unpleasant side symptoms.
- Methotroxate, a member of the group of cytostatics, is usually used under the close supervision of a physician and with maximum caution. At the beginning of the course, you should take no more than 5 g per week; further dosage is determined by your doctor.
- Neotigazon is relevant if the pathology is severe. Complex therapy with drugs containing vitamin A, methotrexate and retinoids is prohibited.
Biologically active substances
Since it is rarely possible to quickly get rid of psoriasis, it is worth taking dietary supplements as additional maintenance therapy:
- Vitamin D is useful because calcium is one of the most important minerals in the fight against the skin disease in question, and vitamin D is needed for its absorption. The use of this supplement at the stage of transition from the active phase to the stationary phase is most effective.
- Silicon in the composition of vitamin-mineral complexes plays the role of a sorbent, attracting antigens, and also improves the condition of the skin.
- Lecithin is able to quickly restore epithelial cells that die in this pathology. The integrity of the skin is restored much faster, and the inflammatory process becomes less pronounced.
- Omega-3 acids and fish oil also help eliminate inflammation.
Traditional approaches to treatment
To increase the effectiveness of medications, complex therapy can be supplemented with traditional methods of treatment, but remember that psoriasis on the back and other areas may be sensitive to allergenic substances, so you should first consult with your doctor:
- Chinese green tea helps reduce discomfort due to skin itching, plaques lighten. Application is possible internally as a drink or externally in the form of masks on affected areas.
- Sunbathing can reduce the manifestations of psoriasis, especially in combination with sea water. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation should not be direct; sunbathing is better in the shade. If you ignore this recommendation, the manifestations of psoriasis will only be eliminated temporarily, but soon the disease will return with even more pronounced negative symptoms.
- An ointment made from birch tar, salicylic alcohol and sea buckthorn oil should be applied directly to the affected areas for 2 hours. If the psoriasis on the stomach or back is quite extensive, you should place gauze over the ointment. After washing off the ointment, you need to apply celandine tincture in the form of oil.
- An infusion of flaxseed allows you to eliminate the clinical symptoms of the disease in question within a week. Soak a spoonful of seeds in a glass of boiling water for a day, then boil, cool and strain, take in the morning before meals in combination with activated carbon (1 tablet for every 10 kg of weight). The course should be continued for 20 days, even if the manifestations of psoriasis have disappeared. Products containing caffeine are prohibited.
- Propolis and butter in the form of an ointment in a ratio of 1:20. Mix the ingredients, boil for 15 minutes, strain and apply to the affected areas. The product must be stored in the refrigerator.
- Celery decoctions can be taken orally once a day, and a compress can be applied for 2 hours for 21 days. Three courses with a break a week will be enough to forget about the disease for several years.
- Celandine powder and petroleum jelly in the form of an ointment must be used for 3 days, applied to inflamed areas of the skin. After a break of 4 days, the course continues until external manifestations completely disappear. To prepare the product, all components are mixed in equal proportions.
Birch tar ointment
Flaxseed infusion
Celery decoctions
Celandine powder
Psoriasis - how to get rid of a deadly autoimmune disease?
Judging by the fact that you are reading these lines now, victory in the fight against psoriasis is not yet on your side...
Have you already thought about radical treatment methods? This is understandable, because psoriasis can progress, resulting in the rash covering 70-80% of the body surface. Which leads to a chronic form.
Red blistering blisters on the skin, itching, cracked heels, peeling skin... All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand. But perhaps it would be more correct to treat not the effect, but the cause? We found an interesting interview with a dermatologist at the Russian Dermatology Center. Read the interview
Psychosomatic theory
Initially, you should accept that any skin disorders are not only a consequence of internal problems, but also a signal from the body about its condition. This is confirmed by the fact that even after skin transplantation to a sick person, it soon acquires dermatous qualities.
That is, the skin is a “screen or mirror” that reflects changes in the body, not only physical, but also psychological. From this point of view, traditional methods of treating psoriasis seem pointless, because the source of the problem is not affected. But on the other hand, the causes of psoriasis have not been established, which means that doctors still cannot influence them.
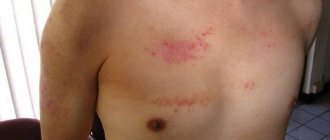
Important information: What psoriasis looks like on the chest and nipples: causes and treatment
Some scientists who adhere to the psychosomatic theory of the etiology of the disease believe that the cause of psoriasis is the mother’s excessive care, or, conversely, her detachment. This is what shows up as symptoms on the skin.
The reason may lie in an excess of care on the part of the woman, or the lack thereof. Thus, overprotection, which is disguised as a desire to keep the child close to you at any cost, provokes ambivalent feelings in the child. At the same time, he tries to pull away, but also feels the need for her.
Conflicting emotional experiences leave an imprint on the personality and cause the development of psoriasis and other dermatological diseases.