Streptodermia is one of the very dangerous skin diseases that is caused by exposure to streptococcal microflora. The causative agent is group A b-hemolytic streptococcus. The problem is common among children who have delicate skin that is more susceptible to various infections. However, it can also affect adults, developing against the background of other skin diseases that cause a weakening of the functions of the immune system.
In the latter case, the course of the disease is much easier than in children, so there is no risk of additional complications. With timely treatment, the symptoms disappear after a few days, but if you treat them negligently and do not take radical measures on time, this can lead to rapid spread and coverage of large areas of the body.
Massive outbreaks of infection occur in closed groups (military unit, correctional facility), since this is facilitated by contact and household communication.
Causes of the disease
On the skin of every person there is a large number of bacteria, including pathogenic ones, which form the microflora of the body and do not cause harm to it. When favorable conditions arise, they begin to multiply, which leads to the development of the disease.
Streptoderma refers to diseases caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus bacteria. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to act actively when the skin ceases to perform protective functions.
Streptoderma is infectious in origin, so it can spread in different ways. More often, the disease is transmitted through contact with a sick person through household items: towels, dishes, bedding, clothing.
You can become a carrier of streptococcus if you hold onto handrails in public transport or stair railings at the entrance.
The causes of infection with a dangerous skin disease are:
- open wound surfaces, thermal burns, bites of blood-sucking insects;
- weakened immune system;
- diabetes;
- phlebeurysm;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- prolonged overheating or hypothermia of the lower extremities;
- metabolic disease;
- renal or liver failure;
- poor nutrition, alcohol consumption;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- nervous overstrain, frequent stress, overwork.
Forms of streptoderma in adults
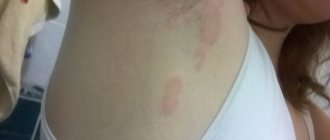
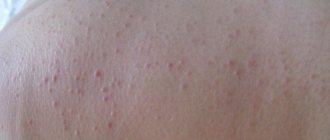
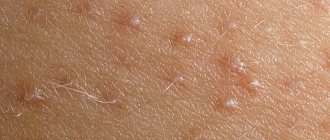
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of rashes on the skin, which have different structures and localizations. Depending on the nature of the damage to the skin, experts distinguish the following types of disease :
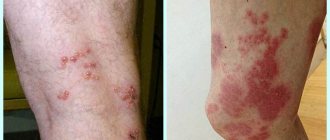
- Impetigo . Rashes form in places where the skin is damaged: on the face, arms or legs. The site of damage first becomes inflamed, then a small bubble filled with liquid forms, which bursts. The resulting wound has uneven, flaky edges. Over time, the rashes dry out and become covered with yellowish crusts. The rash is accompanied by severe itching. When scratching, skin damage quickly spreads to other areas of the body, resulting in the formation of several foci of inflammation;
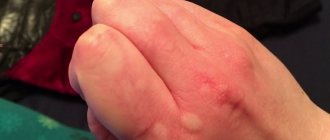
- Tourniol . With this form of skin lesions, the rashes are very dense, small in size, and open very poorly. Most often, lesions are located near the fingernails;
- Ringworm simplex . In adults, this form of the disease is very rare. It is characterized by small spots, painted pink, covered with white or grayish scales of different sizes;
- Staphylococcal diaper rash or intertriginous streptoderma. People who are overweight are susceptible to the disease. The rashes are located in the skin folds and appear as weeping wounds. In this case, signs of inflammation, redness, and swelling are observed on the skin. Over time, deep cracks form at the site of erosion, which cause severe pain;
- Streptococcal ecthyma . The disease is characterized by deep damage to the layers of the skin. The rashes are blisters filled with purulent exudate, which burst within a short time and become covered with a yellow or greenish crust. After healing, scars remain. The most common location of the rash in adults is on the legs;
- The chronic form of streptoderma develops with prolonged exposure to external factors. These may be high and low temperatures or skin injuries in the same place. The rashes have a permanent localization (most often it is streptoderma on the hands). Between periods of exacerbation, large areas of flaky skin form at the site of the rash.
The disease has many manifestations that require immediate contact with a specialist who will prescribe competent treatment.
Locations
Streptoderma can occur on any part of the human body. However, the most “favorite” locations are:
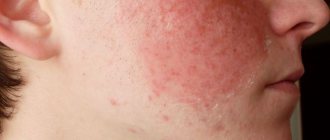
On the face
- area under the nose;
- chin;
- cheeks;
- upper lip;
- corners of the mouth;
- area around the ears.
On the body
- Hands;
- periungual fold;
- feet;
- shins;
- buttocks and intergluteal space;
- inguinal-genital area;
- armpits;
- under the breasts (in women);
- large folds on the abdomen;
- small of the back.
The localization of streptoderma foci depends on the form of the disease. In some cases, especially if hygiene measures are not observed, starting in one place, the disease can spread to large areas of the body.
Main symptoms of the disease
Many skin diseases have similar symptoms. Signs of streptoderma can be determined independently before visiting a dermatologist.
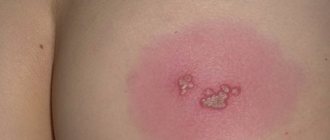
At the initial stage of the disease, small pink spots appear. Their formation is accompanied by itching and slight flaking of the skin. Then, bubbles filled with a yellowish liquid form at the site of the lesion. If left untreated, they merge with each other, forming large areas.
After some time, the rashes dry out and scales form on the surface. Streptoderma can appear on the arms, back, scalp, abdomen, face, lips. .
If in childhood there may be signs of intoxication in the form of general weakness, vomiting, swollen lymph nodes and fever, an adult may not have these signs. Streptoderma on the butt occurs in severe cases in children.
Potential Complications
Symptoms of streptoderma usually disappear within a few days, so complications are quite rare - but can nevertheless become quite serious.
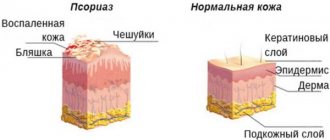
Therefore, if you notice a change or worsening of symptoms, it is best to seek medical help. The most likely complications of streptoderma in the absence of proper treatment include: Damage to the deep layers of the skin - streptococcal infection, spreading into the deep layers of the skin, causes symptoms such as pain, fever, and the appearance of red, inflamed areas of the skin. This condition can be treated quite effectively with antibiotics, and paracetamol is recommended to suppress pain and high fever. Guttate psoriasis is a non-infectious skin disease that can develop in children and adolescents after a bacterial infection.
Most often, this type of psoriasis is observed after bacterial throat infections, but in some cases it also appears after streptoderma. Scalp psoriasis causes small (less than one centimeter) inflammations to appear on the chest, arms, legs, and scalp.
Scarlet fever is a fairly rare bacterial infection that causes a pink rash to appear throughout the body, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and a general feeling of malaise. Antibiotics are used to treat scarlet fever, a highly contagious disease. Septicemia is a bacterial blood infection that occurs after streptoderma in rare cases.
Blood poisoning is accompanied by fever, nausea, low blood pressure, and breathing problems. Septicemia is a potentially life-threatening disease that requires immediate treatment.
Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is a very rare and dangerous complication of streptoderma, a kidney infection accompanied by symptoms such as changes in the color of urine, the appearance of blood in the urine, increased blood pressure, swelling of the face, ankles, feet, and abdomen.
Source: beautynet.ru
Diagnosis of streptoderma
If you notice the first signs of the disease, you should consult a dermatologist. After a visual inspection, a mycological analysis is required, and the contents of the rash can be taken for bacteriological culture.
To confirm the diagnosis, a general and biochemical blood test, coprogram, and ultrasound of the abdominal organs are performed.
If the diagnosis of streptoderma is confirmed, how to treat it in adults, the necessary recommendations will be given by the attending physician.
Treatment methods
It is not enough for patients to know how the disease manifests itself externally and what causes it. It is important to understand what drugs are used to treat streptoderma in adults. Treatment at home should be agreed with a specialist. You should not limit yourself to traditional medicine, since they can only complement the main therapy.
In order for the treatment to bring a positive result, medications are used that have an antibacterial and antiseptic effect.
To prevent the spread of lesions, rashes should be treated twice a day. Cotton-gauze wipes soaked in aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and resorcinol have a drying effect. Single rashes are treated with iodine and ichthyol ointment. Treatment of pustular lesions is carried out with antibacterial ointments. This will help stop the infection from developing.
In severe cases of the disease, the use of glucocorticosteroids is recommended, which quickly heal skin damage. These drugs should not be used for a long time, as they are addictive and reduce the therapeutic effect.
Physiotherapy has a positive effect: ultraviolet radiation, heliotherapy, UHF, electrophoresis, phonophoresis.
In addition to external remedies, the doctor may prescribe treatment with antihistamines, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and vitamin complexes.
As additional remedies, lotions with decoctions of medicinal plants that have a drying effect can be used. The most commonly used infusions are chamomile, oak bark, celandine, and string.
It should be remembered that during the period of exacerbation of streptoderma, baths are contraindicated for the patient. To keep the skin clean, wipe healthy skin with napkins containing chamomile or calendula infusions.
Patients should reconsider their diet. It is recommended to exclude fatty and spicy foods, limit the consumption of salt and sugar, carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea. To prevent skin irritation, you need to wear clothes made from natural materials that absorb moisture well and allow air to pass through.
Levomekol
| Levomekol | |
| Laevomecolum | |
| Chemical compound | |
| IUPAC | Dioxomethyltetrahydropyrimidine + Chloramphenicol |
| Classification | |
| Pharmacol. group | Antimicrobial combination agent |
| Dosage forms | |
| • ointment for external use; | |
| Other names | |
| "Levomekol" |
Levomekol (lat. Laevomecolum, international name - Chloramphenicol + Methyluracil) is a white ointment for external use. Developed at the Kharkov Pharmaceutical Institute (now called the National Pharmaceutical University) in the late 1970s. The ointment does not contain auxiliary (formative) substances, so all the components participate in the formation of the therapeutic effect.
Levomekol is a combined composition for topical use. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and is also active against gram-positive and gram-negative microbes (staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli). The ointment penetrates into tissues without damaging biological membranes and stimulates regeneration processes. The antibacterial effect of the drug in the presence of pus and necrotic masses is preserved.
Indications for the use of the ointment are purulent wounds (including those infected with mixed microflora) in the first (purulent-necrotic) phase of the wound process. Contraindications include hypersensitivity.
It is necessary to soak sterile gauze pads with ointment and loosely fill the wound. It is also possible to administer it into purulent cavities through a catheter using a syringe (pre-heating the drug to 35-36 C°). Dressings are performed daily until the wound is completely cleansed. Side effects include allergic reactions (skin rashes).
Before using Levomekol, you should consult your doctor.
Disease prevention
Streptoderma is difficult to treat. The recovery process can take a very long time. To prevent the development of infection, you should follow a number of simple rules :
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- use antibacterial agents to treat exposed areas of the body;
- treat minor skin lesions with aseptic means;
- promptly treat infectious and viral diseases;
- strengthen the body's defenses.
It is very difficult to cure the disease, but strict adherence to hygiene rules, a healthy balanced diet and strengthening the immune system will help avoid the development of such a dangerous disease as streptoderma.