Most often, people turn to surgeons with damaged skin on their legs. If bacteria and other microorganisms enter the wound, it becomes infected and suppurates. This condition must be treated to avoid the development of undesirable consequences.
Treatment should be comprehensive, which includes treatment, regular dressings, antibacterial therapy and symptomatic therapy. In this article you will learn what to do if a wound on your leg is festering, how it can be cured and how to properly treat it to avoid re-infection.
Causes
Violation of the integrity of the skin, accompanied by inflammatory symptoms and the formation of purulent exudate, is usually called a purulent wound. Any injury with damage to the skin is an entry point for the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms, which are present everywhere.
The penetration of pyogenic bacteria complicates the course of the pathological process, complicating treatment and increasing the recovery period.
Factors predisposing to the formation of a festering wound:
- violation of sterile conditions during dressing;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules leads to the proliferation of microbes on the skin;
- decrease in the body's defenses;
- getting sand or earth into an open wound;
- contact of the damaged surface with dirty clothing;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus);
- being in polluted, dusty places;
- hormonal changes (menopause in women);
- involutive (age-related) processes in elderly people.
Clinical picture
With purulent wounds on the legs, pronounced local symptoms are observed; in severe cases, a deterioration in the general condition is possible.
A purulent infection caused by aerobic or anaerobic microorganisms, if the rules of asepsis are not observed, can develop on any wound surface, and a small scratch can develop into an abscess (ICD code 10 - L02).
An uncomplicated wound on the leg shows mild redness and does not cause significant clinical manifestations.
But there are also complications:
- swelling appears, which increases throughout the purulent process;
- a festering wound on the foot or lower leg turns red to a bluish tint;
- the temperature of the skin over the inflamed area increases;
- severe pain in the foot becomes throbbing;
- severe forms of suppuration can lead to limitation of motor ability of the lower limb.
At the initial stage, when the wound on the leg festers, the inflamed area looks like a small hyperemic elevation above the skin. Over time, the compaction increases, and the skin at the top of the abscess becomes thinner and a white-yellow head appears under it in the center.
As the pus matures, the skin on the foot breaks and the contents spill out. After opening the abscess, the pain subsides, the swelling decreases, and the general condition improves.
Athlete's foot
Foot fungus - athlete's foot. One contact with the affected area is sufficient for infection. But is it that easy to get rid of? How to do this with traditional recipes and medicines?
It's very easy to get foot fungus
Causes of athlete's foot
Athlete's foot is caused by the fungus trichophyton (Trichophyton mentagrophytes, in ICD-10 code B35.3 Mycosis of the feet). For some time, the pathogen was called Epidermophyton Kaufmann-Wolf, which gave rise to the disease epidermophytia.
It is transmitted through household contact and is more often infected in public hygiene establishments and places where it is customary to walk barefoot:
- showers;
- swimming pools;
- saunas and baths;
- sports and dance halls.
The fungal spores are tenacious. It is enough for the patient to walk barefoot on the floor to fill every trace with mycotic cells. A person whose feet touch this place risks not only getting athlete's foot, but also spreading the infection further.
Transfer methods:
- household (through contact of bare feet with an infected surface indoors);
- through common shoes, socks, stockings;
- hygiene items (washcloths, scissors, towels, soap);
- close contact with sore feet or nails.
You can become infected with a fungus through contact with an infected surface.
The ideal situation for the transmission of fungus is steamy, sweaty, hot feet. The patient sweats in excess at such moments. The probability of infection in a healthy person approaches 100% when the pores of the skin are open - the fungus easily penetrates the epithelial layer.
The protective resources of the skin lose ground when the foot is in uncomfortable conditions or weakened by disease..
Prerequisites for infection:
- wearing tight, uncomfortable, low-quality shoes;
- synthetic hosiery;
- frequent foot injuries (a scratch, scratching, chafing or blister is enough);
- specific working conditions (high temperatures, closed shoes, profuse sweat);
- chronic diseases.
High risks for those who have been diagnosed with atherosclerosis, vegetative-vascular dysfunction, varicose veins, thrombosis and other circulatory disorders. Diabetes mellitus, problems with the nervous system, vitamin deficiency, and decreased immunity are no less damaging to the body’s defenses.
Read: Treatment of mycosis of the feet
Trichophyton is also the causative agent of inguinal athlete's foot in men and women. This increases the risk of unwittingly increasing the area of infection.
Forms of the disease and their symptoms
Athlete's foot is divided into clinical forms of the disease, characterizing the location and features of manifestation:
- squamous form;
- intertriginous;
- dyshidrotic;
- epidermophytosis of nails.
Squamous form
The most dangerous form of fungus, as the symptoms are unobtrusive and do not cause concern . Peeling of the feet, redness at the arch, rare mild itching.
Doctors note that over the years, patients tend to coexist with this form, to be a carrier of mycosis due to their own inattention to health.
Dyshidrotic and squamous epidermophytosis tend to flow in both forms alternately.
The squamous form is the most dangerous type of fungus
Intertriginous form
Develops against the background of untreated penetrating epidermophytosis. Itching and peeling spreads to the interdigital area and the bends of the toes. The little and ring fingers are especially affected. Weeping wounds, erosions and cracks form. Characteristic is the detachment of whitish crusts of the epidermis.
The exacerbation occurs in the summer; in winter the disease is inactive.
The intertriginous form of the fungus affects the interdigital area of the feet
The skin becomes loose, cracked and weak against infections. Characteristic of a neglected form. For example, streptococcus in combination with epidermophytosis is dangerous for erysipelas of the lower leg or thrombophlebitis.
Dyshidrotic form
Clusters of small bubbles form on the sole of the foot. Over time, they merge into a single area. The foot becomes painful. Removing the top layer means opening ulcers and erosions. The vesicular layer rises to the sides of the foot. When the skin has healed and the blistering has gone away, it is believed that the squamous form has returned.
It worsens in spring and summer. Accompanied by elevated body temperature and malaise, allergy-type rashes are possible. The acute form lasts 1-2 months, but timely therapy at such stages is more effective than ever.
The dyshidrotic form of the fungus is characterized by the appearance of small blisters on the skin
Secondary infection is also dangerous. The liquid in the blisters becomes cloudy, whitish in color - this is suppuration. This is how lymphadenitis and lymphangitis develop.
Read: What does foot fungus look like?
Erased form
Apart from a modest area of peeling on the feet and rare cracks between the toes, there are no symptoms. These signs also rarely indicate the presence of disease. Patients argue that this is irritation or vitamin deficiency.
The erased form occurs in the initial stages of the disease and flows into another.
When the form of foot fungus is erased, peeling and cracks form between the toes.
Athlete's nails
It affects the nail plate only. The big toes and little fingers have an advantage. The nail becomes yellow, visible stripes, separations and thickenings are visible. The plate crumbles, breaks or separates from the finger on its own, as in the photo.
Athlete's nails most often affect the little fingers and big toes
Hands are out of danger. This is not a reason to use one manicure set for legs and arms. Keep separate tools for sick and healthy nails. After treatment, get rid of the infected.
Diagnosis of athlete's foot
The combination of symptoms and laboratory tissue examination (under a microscope) provide information about the future diagnosis. For analysis, take the exfoliated layer of the epidermis and soak it in alkali. Under the influence of the reagent, you can see the threads of the mushroom.
To study the stage of the fungus, a piece of infected skin is examined under a microscope.
Foot treatment
Antimycotic therapy and folk remedies can destroy epidermophytosis. Complex cases with concomitant diseases and secondary infections will not respond to self-medication. The patient will only worsen the course of the disease.
The drugs are indicated for informational purposes.
Medicines
Treatment takes place in 2 stages:
- Removal of the stratum corneum, puncture of blisters.
- Relieves inflammation, heals wounds, destroys fungus.
The improvement of nails begins with the complete removal of the infected plate. Therapy takes about 2 months in total.
In standard cases, athlete's foot is treated with external antifungal drugs in the form of a gel, ointment, solution or cream:
- Itraconazole;
- Terbinafine;
- Fukortsin;
- Clotrimazole;
- Castellani paint;
- Boron-zinc-naphthalan ointment;
- Lamisil;
- Tinactil;
- Arievich ointment.
Terbinafine is a good remedy for foot fungus
The latter is designed to remove the dry layer of skin. It is applied immediately after a softening soda foot bath. Generously lubricate the sore spots, wrap them in cellophane or parchment, and put on socks. Removed in a day.
Usually the layer of skin comes off easily with a little help from your fingers. If this does not work, then the compress is extended for another day. The softening effect is due to the presence of lactic and salicylic acid.
The lion's share of fungal spores is removed from the old layer of affected skin.
Complicated forms of secondary infection, damage to large areas of the skin (for example, the groin area and legs), as a consequence of the disease, are treated in a hospital.
Inside they prescribe:
- antihistamines - Diphenhydramine, Tavegil, Suprastin;
- antibiotics – Erythromecin, Cephalosporin;
- multivitamins - according to individual prescription;
- calcium chloride intravenously.
Read: How to cure foot fungus: pharmacy and folk remedies
To remove dead skin cells, lotions made of copper, zinc, and baths with decoctions of herbs and soda are recommended.
Tavegil is used to treat complex forms of fungus
Treatment with folk remedies
Homemade recipes are sometimes as effective as medical remedies. Some ingredients are purchased at the pharmacy.
Lactic salicylic collodion
Milk-salicylic collodion is prepared at home. Take 10 g of lactic and salicylic acid and 80 g of collodion. Mix thoroughly and store in the refrigerator. In the morning and before bedtime, lubricate your feet. The best effect is with the simultaneous use of 5% salicylic ointment. Course – 7-10 days.
Lactic acid has a detrimental effect on fungus
Salicylic acid prevents the spread of fungus along the leg by inhibiting the work of the sweat glands. Softens the stratum corneum with thousands of fungal cells and allows skin detachment to remove it along with the parasite.
Celandine compress and lotions
Dry celandine herb (3 tablespoons) is steamed with half a liter of boiling water and boiled for several minutes. Leave for an hour, then apply a compress overnight. Course – 10 days.
In addition, you can lubricate the wounds with pure juice of the plant for speedy healing.
Celandine is an old remedy for treating fungus.
Herbal decoction for baths
Basil and larch (100 g each) are mixed into one collection. For half a liter of boiling water take 3 tbsp. l. and boil for a couple of minutes. Soak your feet in the broth for 12 days.
Basil has antifungal properties
Classification
An infected wound on the leg may have various signs of suppuration, which are taken into account during treatment. In addition to symptomatic manifestations, the classification is based on the etiology and route of entry of the pathogen.
Types of purulent lesions:
- boil - purulent inflammation in a limited capsule, more often manifested in people with reduced immunity;
- carbuncle - suppuration with several purulent “rods”, limited by a fibrous membrane;
- phlegmon is an unlimited large abscess that can develop when the periosteum is damaged;
- hidradenitis – inflammation of the sweat glands, found in the groin area;
- abscess - a purulent process that develops as a result of incorrect injection, when the leg is punctured with a sharp object;
- panaritium - purulent inflammation is fixed on the toes near the nail bed.
Treatment of purulent wounds at home
What to do if the wound has already been opened by a doctor and a bandage has been applied? You can treat leg wounds at home yourself. Daily disinfection is necessary for rapid healing and to prevent the spread of infection. Treatment of a limb with a purulent wound should be carried out 1–2 times a day. Please note that you can make dressings yourself only in mild cases of the disease.
To carry out the procedure, the following conditions must be met:
- Mandatory disinfection of hands and tools. Most often this is done with alcohol.
- The old bandage must be carefully removed; if it is strongly stuck to the wound, the bandage is moistened with hydrogen peroxide.
- Remains of pus should be removed from the cavity, the edges should be treated with an antiseptic, sometimes they are lubricated with iodine or brilliant green.
- The inside is treated with a drug or a napkin soaked in the drug is placed. If the damage is very deep, a rubber drainage is inserted inside to remove pus.
- The wound on the leg is covered with several layers of bandage and carefully secured. It is imperative to ensure that there is no air access to the affected area. This may lead to the development of an anaerobic infection.
If the injury is very severe, treatments must be done at least four times a day. In this case, you need to leave the wound in the air for 20 minutes during each treatment.
Primary processing
The appearance of an injured area on the leg often leads to inflammation of the wound. Infection is an integral part of the process; microorganisms are found everywhere, including on the skin.
With accompanying factors (decreased immunity, living in unsanitary conditions), pyogenic bacteria invade the unprotected damaged area.
To prevent suppuration of the wound, it is necessary to treat the damaged area with antiseptic solutions, followed by applying a bandage of sterile dressing material to the injured area. This measure will clean the wounded surface and protect against future infection.
Treatment tactics
Having discovered an infected wound of the lower leg or other part of the leg, it is necessary to take therapeutic measures. To do this, it is important to correctly assess the severity of the damage.
Differential diagnosis when visiting a doctor will help not only make the correct diagnosis, but also avoid such a life-threatening complication as general blood poisoning (sepsis).
If the abscess is small in size, without significant swelling and is not accompanied by general intoxication, self-treatment at home is possible. A medical specialist will tell you during a consultation how to treat a festering wound, how to treat purulent lesions.
The patient performs therapeutic procedures at home under the supervision of the attending physician.
In severe cases, hospitalization, opening the abscess in an inpatient setting, installing drainage, and regular dressings may be necessary. Local treatment must take place in parallel with general therapy; for this purpose, antibacterial and immunostimulating drugs are prescribed.
Possible complications
The most dangerous consequence of self-treatment of a boil is an incorrect diagnosis.
Often, under the guise of a boil, tumors are hidden, which are not always benign. In this case, all methods aimed at treating the boil will cause deep harm to the body.
If you open an abscess on your own, there is a high risk of infection of the blood and surrounding tissues. The spread of infection can cause an abscess, erysipelas, and phlegmon. Find out what phlegmon is from here.
The fusion of two boils develops into a dangerous purulent inflammation - a carbuncle. We wrote more about what a carbuncle is here.
Boils on the leg near the groin should be kept under special control due to the location of the lymph nodes nearby.
If the infection spreads to the venous and lymphatic tissue, this is fraught with the development of lymphadenitis and thrombophlebitis.
The knee, ankle and other periarticular areas are a dangerous location for a boil.
The concern is the proximity to the joint and its possible inflammation. This occurs especially often in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Severe conditions are caused by the spread of infection through the blood. Sepsis and inflammation of the brain are dangerous and cause death.
Antibiotic therapy
An inflamed wound on the leg is most often treated using antimicrobial therapy methods. Antibiotics for wound suppuration are used topically for irrigation, washing the affected surface, piercing around the suppurating areas, as well as for general treatment, the purpose of which is to prevent re-suppuration.
Relapses after apparent well-being are quite common; re-inflammation of the wound occurs as a result of an incomplete course of treatment.
An antibiotic for purulent wounds is prescribed by a doctor after laboratory tests. If there is no specific infection, broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs of the penicillin, tetracycline and cephalosporin series are prescribed.
The dosage and duration of treatment are determined by the attending physician; independent uncontrolled use can lead to negative consequences. In addition to the general course in the form of oral administration, local exposure to an antibiotic solution is used during dressings. When prescribed, this method can also be used at home.
After opening the abscess and removing the purulent exudate, an antibacterial ointment with an antibiotic is prescribed for purulent wounds. The product fights the causative agent of pyogenic infection at the local level, preventing repeated suppuration.
How to treat an abscess, boil, abscess on a leg or finger
An abscess on the toe is an infectious disease accompanied by purulent melting of tissue. In most cases, the causative agents of such pathologies are staphylococci and streptococci, but sometimes they can be caused by other types of pathogenic microflora.
Furuncle, abscess, carbuncle and other types of ulcers are very unpleasant diseases. Their main manifestation is severe pain in the area where the source of inflammation is located.
What could be an abscess on the big toe? What are the symptoms of such a neoplasm, and how to treat it? In some cases, therapy can be carried out at home, but sometimes the patient may need a minor operation to open the abscess. In this situation, only a surgeon can help.
to the table of contents?
Abscess on the leg: what is it and what are its causes?
A pimple on the leg with redness around it - what could it be? There are several options and reasons why such ulcers appear. Let's look at them separately.
Furuncle
A furuncle on the leg, or boil, is a purulent formation that forms in the area of the hair follicle.
The cause of its appearance, as noted earlier, is a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection.
Its penetration into the underlying layers of the skin can be facilitated by numerous factors, ranging from wounds and scratches to dangerous diseases - AIDS, diabetes and others.
How do purulent acne appear on the legs? The boil does not form immediately, but some time after the penetration of the bacterial infection. First, redness appears in the affected area, possibly a slight burning sensation and itching. Then the inflamed area begins to hurt and “tug” from the inside. This is precisely the first signal that pus begins to accumulate in the hair follicle.
After 2-3 days, a rod is formed in the affected area - a capsule filled with pus. After its appearance, the site of inflammation must be treated with an antiseptic (Chlorhexidine or Miramistin) and covered with a sterile gauze bandage.
Depending on the situation, you can speed up the release of pus using folk remedies. But if this was not possible, you must immediately make an appointment with a surgeon.
to the table of contents?
Abscess
An abscess on the leg in most cases is a complication of an untreated boil. This is a very painful and more dangerous disease, which is also caused by pathogenic microflora. Read more about abscesses at the link https://skinadvice.ru/abstsess.html
On a note. It is important to distinguish between the concepts of “boil” and “abscess”. Abscesses on the legs, which are boils, have a core and clearly defined boundaries. At the same time, elevated body temperature is not always observed. If it rises, then its values do not exceed 38 degrees.
An abscess of the lower leg or other part of the leg is a diffuse purulent inflammation that does not have clear boundaries. The affected area also varies. With furunculosis, inflammation develops in the hair follicle, sebaceous and sweat glands.
But with an abscess, the pathological process affects the soft tissues of the lower limb.
to the table of contents?
Carbuncle
Pus on the leg that has accumulated in the form of grouped boils is called a carbuncle. It has the same symptoms as boils, but is more difficult for patients to tolerate. It is usually treated surgically, but special ointments or folk remedies can be used to speed up the maturation of ulcers.
to the table of contents?
Felon
Panaritium, or paronychia, is an abscess that is an abscess on the leg. It occurs only on the fingers, but can spread further. Unlike carbuncles and boils, which form exclusively in the area where hair follicles are present, panaritium appears on any part of the finger. However, the most common place for its localization is the periungual area.
Paronychia is a very painful, excruciating condition. It often develops due to the presence of hangnails on the finger. However, such suppuration on the toe often occurs when wounds and cracks in the skin become infected.
When touching the abscess, severe pain is felt. The formation has a white, yellow or green tint. There is a halo of inflammatory skin around it. Such festering of a wound on the leg is fraught with serious consequences. In the absence of timely treatment, purulent tissue melting can reach the bone of the sore finger.
to the table of contents?
How to treat ulcers on the legs?
How to treat an abscess on the leg? Despite the fact that ulcers affect different parts of the body and differ in the mechanism of their development, in many ways the principles of therapy are similar to each other. Treatment methods can be:
- conservative (use of ointments or folk remedies);
- surgical.
But surgery is a last resort, so first let’s look at the question of how to treat a purulent abscess at home.
to the table of contents?
Medications
Ointments with antibacterial, analgesic, bacteriostatic and antiseptic effects can help the release of pus or accelerate the process of maturation of the abscess. So, how to treat an abscess on your toe? This will help you:
- ointments Levomekol, Levosin, Levomycetin;
- Liniment Vishnevsky;
- Tar ointment;
- Oxolinic ointment;
- Ichthyol ointment.
Read about ointments that are used for purulent wounds and boils at the link https://skinadvice.ru/mazi-dlya-vytyagivaniya-gnoya-iz-rany.html
How to use these drugs for an internal pimple on the leg? First, the abscess must be treated with an antiseptic solution. After this, you need to apply the selected ointment to the surface of a sterile napkin and apply it to the surface of the pathological focus. Wrap a bandage on top and leave for 8-12 hours. The dressings must be changed until the abscess opens.
If there is an abscess of the foot or other part of the leg, or a boil that does not go away for a long time, grows or multiplies, then in this case local treatment alone will not be enough. You will have to resort to the systemic use of antibiotics, preferably penicillin: Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, etc. However, it is not recommended to cancel local treatment.
to the table of contents?
Folk remedies
If your toe breaks out, but you don’t have any pharmaceuticals at hand, how can you treat the disease? To speed up the process of boil maturation, as well as to promote the rapid discharge of pus from felon or carbuncles, you can turn to alternative medicine methods. The following products are effective:
- Onion-soap mixture. If an abscess appears on the heel or other part of the leg, the following recipe will help speed up the release of pus or the maturation of a boil/carbuncle. Peel a medium-sized onion and bake in the oven. While the vegetable is cooking, you need to grate a small piece of laundry soap on a fine grater. Then mix the ingredients, you can add a little tar. Apply the composition to the abscess, cover with sterile gauze and wrap with a bandage. Keep the compress for up to 6 hours, after which rinse off any remaining residue and, if necessary, apply the mixture again.
- Warm baths with sea salt or soda. These products are excellent at drawing out pus, disinfecting, and accelerating wound healing. It is necessary to dissolve 1 tbsp in hot water (1 l). l. sea salt or baking soda, cool the liquid to body temperature and lower the sore leg into it so that the abscess is completely covered with the solution. Hold for 5 minutes, then remove the affected limb and gently wipe dry.
It is very useful to combine such procedures with medications - ointments and creams. They will not interfere with systemic administration of antibacterial agents.
to the table of contents?
Surgery
Surgical treatment of an abscess on the toe is indicated when conservative methods are ineffective. It is based on opening the abscess, emptying it and introducing antibiotics and/or antiseptics into the resulting cavity.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. In the area where the purulent focus is located, injections of Lidocaine, Novocaine or Ultracaine are made.
After this, using a scalpel and under conditions of strict asepsis and antiseptics, the doctor dissects the abscess and drains it. The entire manipulation lasts about a quarter of an hour.
After this, the patient is sent home, having previously (again, if necessary) been prescribed systemic antibacterial drugs.
If sutures were placed at the incision site, they are removed 10-14 days after the operation. The patient spends the entire postoperative and rehabilitation period on an outpatient basis. That is, at home.
To avoid the formation of ulcers on the legs, it is necessary to promptly treat any wounds and abrasions. It is important to monitor the state of the immune system and avoid vitamin deficiencies or anemia. If a boil, abscess or panaritium has already formed, and home or local medications do not help, you should immediately seek help from a surgeon.
Source: https://skinadvice.ru/naryv-na-noge.html
Treating an abscess at home
If treatment is carried out at home, the speed of recovery depends on proper treatment of the abscess. Successful therapy consists of following the treatment steps, creating antiseptic conditions during dressing so that a secondary infection does not occur.
How to properly treat a purulent wound yourself at home? Processing and dressing algorithm:
- Wash and wipe your hands with a disinfectant solution. Alcohol wipes and antiseptic hand gels are used as an antiseptic.
- Remove dressing material. It is forbidden to tear off the bandage so as not to injure the affected area. The bandage is cut with scissors, a gauze cloth can be moistened with an antiseptic solution and wait a little, then carefully remove the old bandage.
- Wipe the area around the inflammation with a cotton pad soaked in antiseptic. Movements during processing should be directed from the periphery to the cut.
- Apply liberally to the damaged surface with hydrogen peroxide or an aqueous solution of chlorhexedine.
- Accumulated pus and necrotic tissue should be carefully removed using cotton pads.
- Dry the affected surface with blotting movements using sterile gauze wipes.
- Prepare an antibacterial solution, moisten a napkin in it and apply it to the abrasion, cover with clean napkins on top and secure with an adhesive plaster or bandage.
The frequency of treating infected cuts at home depends on the amount of purulent discharge. Dressings are carried out at least twice a day; if there is heavy discharge from the wound, the number of manipulations increases.
What to do if inflammation on the foot festers for a long time, despite all medical procedures? For non-healing wounds, it is recommended to have additional consultations with an endocrinologist and an infectious disease specialist and to take a blood sugar test.
When to see a doctor
If the patient has an extensive wound, then you should consult a doctor immediately after its appearance. Since this situation requires emergency assistance from specialists who will properly treat the wound, stop the bleeding if necessary and prescribe adequate treatment.
If the wound is small and shallow, you can treat it at home.
However, you should know the situations in which you should consult a doctor:
- Increased purulent discharge from the wound. If the bandage begins to get wet faster or a large volume of pus is visually detected during prolonged treatment, then an immediate consultation with a surgeon is required. In this case, a thorough examination of the wound and adjustment of treatment is necessary;
- Increased or onset of pain . They are usually pulsating in nature;
- Long-term non-healing damage – when no tendency to healing is visible within 7 days;
- Severe swelling and redness in the wound area;
- General hyperthermia, that is, an increase in body temperature. This may be a signal of the spread of infection.
Treatment of an abscess
How to heal a wound if there is no pus coming out? Therapeutic actions depend on the stage of suppuration. In the initial manifestations, when the swelling is just beginning to appear, it is recommended to apply a compress, which can have a resolving effect on the beginning purulent process.
If time is lost and the abscess has already formed, the medicinal composition will help speed up the maturation and natural evacuation of purulent exudate.
For the medicinal base of the compress you will need: 2 ml of Analgin, 2 ml of Diphenhydramine, 5 ml of Dioxidine, 5 ml of Dexamethasone. All components are mixed, a gauze napkin must be placed in the medicinal composition and distributed on the abscess.
Using a spatula or spatula, apply a thin layer of ointment that draws out pus from a closed wound (Vishnevsky’s liniment) onto a gauze napkin soaked in the medicine, fixing it with cling film on top. Bandage the compress on top and leave for several hours.
How to treat a wound after opening an abscess? While pus or clear liquid continues to flow from the wound, it is recommended to apply an ointment that draws out pus (Ichthyol ointment) during dressings. When the wound is completely clean, you can use antibacterial ointments (Levomekol), which promote healing of the purulent wound.
Traditional treatment
Recipes from traditional healers have long been used to treat purulent formations at home. Medicinal herbs and bee products were used as a medicinal base. The effectiveness of some recipes has been tested for years, but such treatment may not always be safe.
The likelihood of allergic reactions and individual intolerance to natural components can lead not only to rashes like urticaria, but also to more severe forms: Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock.
Therefore, before use, it is advisable to consult a doctor and conduct a preliminary sensitivity test. Traditional methods are most often used to “pull out” pus from a closed wound; the use of non-sterile drugs for an open wound surface is not recommended.
Popular recipes:
- Kalanchoe has long been known for its powerful bactericidal effect. Kalanchoe juice and homemade ointment - how to treat a festering wound. During the daytime, a napkin is moistened in freshly squeezed juice from the leaves of the plant. Ointment for smearing a purulent wound at night: mince the leaves to make 1 tablespoon of gruel, add 1 tablespoon of honey and sea buckthorn oil. Store the resulting mass in a dark container in a cool place.
- Honey can be used in its pure form. To do this, apply melted honey to the site of suppuration or on a sterile napkin and apply to the abscess. The procedure can be performed up to several times a day.
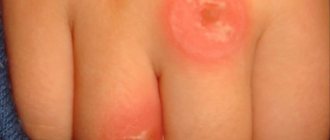
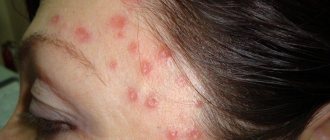
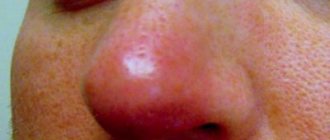
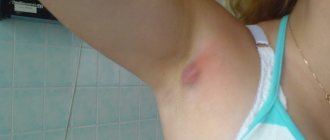
Furuncle (boil) on the leg: 8 reasons, as it looks in the photo, 5 ways to treat, prevention
A furuncle (boil) is a specific purulent formation localized around the hair follicle.
Caused by an opportunistic bacterium that lives on the skin and mucous membranes. A boil on the leg can be located in any place where there is hair (fingers, thighs, legs, knees, groin area), with the exception of the soles. Read more about what a boil is here.
The main reasons why boils appear on the leg
Purulent inflammation is provoked mainly by Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus), which under normal conditions is constantly present on the body, but does not cause discomfort to a person.
It begins to actively reproduce when conditions favorable to it arise. Typically, a boil appears during a period when the body is weakened. If the immune system functions normally, it quickly suppresses the development of Staphylococcus aureus.
8 main reasons for the formation of boils:
- Weakening of the immune system due to past illnesses. After exposure to a viral or bacterial infection, the body resists weaker, so a favorable environment for the development of staphylococci is formed. Hypothermia often becomes a catalyst for boils. People with HIV and rheumatoid diseases are also susceptible to the appearance of boils.
- Damage to the skin. A boil between the legs is often caused by friction on the inner thighs, especially in hot weather. In the groin, purulent formations appear due to rubbing of the skin with synthetic fabric, too tight or uncomfortable underwear. The “entry gates” for infection are cuts, scratches, and cracks.
- Disruption of the endocrine system. Hormonal imbalances provoke the appearance of boils, especially in patients with diabetes. Diabetics have reduced sensitivity to pain, so they do not notice breaks in the skin through which infection penetrates. Due to insufficient blood circulation, purulent formations often cause complications in them, which is fraught with serious skin problems.
- Alcohol abuse. People who drink reduce their body's resistance due to constant intoxication.
- Neglect of personal hygiene. The combination of excessive sweating and dirt creates ideal conditions for the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. At the same time, the hair follicle becomes clogged, and the bacteria in the hair follicle begin to act even more actively. As a result, pus collects there and an abscess forms.
- Poor nutrition. Throughout the year, it is necessary to include fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet, which are rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements, complex carbohydrates, and animal protein. In their absence, purulent formations often occur. Eating large amounts of sweets especially sharply activates the proliferation of staphylococcus.
- Taking medications. Medicines from the group of antibiotics, immunosuppressants, cytostatics, glucocorticoids can provoke excessive development of Staphylococcus aureus against the background of weakened immunity.
- Psychosomatics. Psychologists agree that furunculosis sometimes occurs due to certain emotional states. The appearance of boils is provoked by anxiety, fear, irritation, and anger.
What it looks like in the photo, special symptoms and signs
A boil can appear anywhere on the leg, but more often an abscess forms in the groin fold, under the knees, on the inside of the thigh, that is, where there is moisture and friction, and, therefore, an environment favorable for the corresponding bacteria. It is also common for a boil to appear on the toes.
The first signs of a boil formation:
- itching, redness;
- the formation of a hard lump that is painful when pressed and quickly increases in size.
After 5-7 days, the ripening stage begins, a purulent core forms in the area of the hair follicle, and a pustule with purulent contents appears on the surface.
At this time, pain increases, which quickly disappears after the boil breaks through and the purulent contents come out. Sometimes the abscess breaks out 10-15 days after formation.
Squeezing out pus yourself is strictly prohibited.
During ripening, a boil on the leg can cause the temperature to rise to 37-39 degrees; some patients feel pulsation, tingling and itching in the area of the abscess.
After the boil breaks through, a crater-shaped depression remains, which heals after 3-10 days. Scars form at the site of particularly deep boils.
Identifying a boil is quite simple: to do this, you need to look at how it looks in the photo and compare it with your own formation. A boil is a compacted red or bluish area, in the center of which there is a head with white or yellowish contents (appears after a few days). The diameter of the redness can vary: from 5 mm to 5 cm or more.
Can it be confused with a lymph node compaction?
At the initial stage, you can confuse the compaction of the lymph node with a boil: it increases in size (from a large pea to a chicken egg), becomes harder, and the skin in the area of the inguinal lymph node turns red.
Next, sharp pain occurs, swelling appears, and the temperature rises to 40 degrees (not always). In this case, a purulent head does not form.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor as serious treatment is required. Sometimes any purulent formation in the groin area can cause inflammation of the lymph nodes.
How to distinguish from other formations
It is almost impossible to confuse a boil with a regular pimple. Pimples do not have a dense infiltrate, they do not have a purulent core, and the skin around the purulent head is more pink than red or blue. A pimple takes an average of 3 days to ripen, while a boil can ripen up to 15 days (and sometimes longer).
The difference between a lipoma (wen) and a chiryak is that it is a round, soft tumor that does not hurt or itch. But when infected or rubbed by clothing, it turns red and can fester.
How to get rid of a boil on or between your legs: 5 effective remedies
At home, dry heat is used to treat abscesses in the legs. You can warm the boil with warm salt in a bag, a boiled egg, or a salt heating pad. Warming accelerates the maturation and release of the purulent core. Frequency: 3-5 times a day, for 15 minutes, until the pus comes out.
At the stage of compaction formation, you can get rid of the boil (by interrupting its development) with the help of iodine or brilliant green, generously lubricating the reddened area (up to five times a day). The best folk remedies have already been written about on our website in this article.
How else to treat a boil in order to speed up its breakthrough and prevent complications: ointments, solutions, balms.
Ichthyol ointment
Action:
- draws out purulent contents;
- reduces inflammation;
- relieves pain;
- disinfects.
For treatment, you need to take a small amount of ointment (the size of a grain of corn or a little larger), apply it to a cotton pad or gauze, and apply it to the abscess. A bandage is applied on top. The procedure is carried out three times a day until complete healing.
Price: 75 rubles for 25 g (10%).
Balsamic liniment according to Vishnevsky
Action:
- accelerates the separation of purulent contents;
- has an antiseptic effect;
- stimulates the regeneration process.
The ointment should be spread in a thin layer over the entire surface of the boil. The affected area is covered from above with a multilayer gauze bandage. The procedure should be carried out twice or thrice a day, for 5-10 days.
Cost: 65 rubles for 30 g.
Dimexide
Action:
- accelerates the ripening of the boil;
- resolves the infiltrate;
- reduces pain;
- produces an antiseptic effect.
Treatment of a boil on the leg is carried out with a compress at a concentration of 40%; to obtain a solution, 20 ml of Dimexide are diluted with 30 ml of purified water.
The gauze is dipped into the solution, wrung out, applied to the affected area, covered with polyethylene and cotton cloth, and fixed with a bandage or plaster. Leave the compress on for 20-30 minutes.
The procedure is carried out once a day (until the abscess is completely treated).
Price: 90 rubles per 100 ml.
Elon K
Action:
- removes inflammation;
- disinfects;
- promotes rapid ripening of the abscess;
- completely removes pus.
A strip of ointment 2-3 cm long is evenly distributed over the area of the boil. The top of the abscess is sealed with an adhesive plaster or a sterile bandage is applied. The procedure is carried out 1-2 times a day. You need to repeat until a breakthrough + 1-3 days.
Cost: 300 rubles for 25 g.
Vinylin
Action:
- helps cleanse pustules from pus;
- accelerates regeneration;
- has an antimicrobial effect.
The composition of Shostakovsky balm is applied to fabric napkins, which are applied to the affected area 3-5 times a day, for 10-15 minutes. This must be done from the period after the breakthrough until the wound is completely healed.
Price: 75 rubles for 50 g.
IMPORTANT: all products cannot be used together. You need to choose 1 or 2 (preferably after a face-to-face consultation with a surgeon or dermatologist).
The most effective ointments for boils are described here. In general, all methods of treating abscesses can be found here.
Which doctor should I contact if nothing helps or the boil cannot be treated?
The treatment of boils is mainly carried out by a surgeon; he will recommend conservative therapy or perform surgery if the pus does not come out and complications arise.
As a last resort, if there is no surgeon in the clinic, you can contact a dermatologist, internist or family doctor, or in the case of a child, a general practitioner.
Is a boil on the leg treated promptly and how exactly?
A boil on the skin of the leg, in principle, is not dangerous, but it still cannot be started (especially if it is localized in the groin area).
Basically, with a large boil or when the pus does not break out on its own, the surgeon quickly removes the boil by cutting the skin, piercing the formation and cleaning the boil. This is followed by treatment with an antiseptic and regular dressings. In some cases, antibiotic therapy is prescribed (the active substance and form of the antibiotic are prescribed by the doctor depending on each specific situation).
Is a boil on the leg dangerous: consequences and complications
Possible complications of a boil on the leg:
- Carbuncle. Multiple inflammations of the hair follicles occur, which merge together. The radius of damage is large - 10 centimeters or more.
- Vascular pathologies. Arteritis or thrombophlebitis may occur. They cause severe pain. In advanced cases, death is possible.
- Lymphadenitis. Occurs when an abscess is localized in the groin area. It is an inflammation of the lymph nodes, sometimes purulent.
- Phlegmon. An inflammatory process occurs in the subcutaneous and intermuscular tissue. Characterized by rapid spread.
- Abscess. The accumulation of purulent contents under the skin affects many tissues and can spread to adjacent muscles and even to nearby organs.
- Sepsis. A severe inflammatory disease that occurs due to purulent contents entering the blood. Possible death.
If the leg is swollen, the temperature has risen, severe pain is present, and a white purulent dot does not appear near the boil, you should consult a doctor (surgeon or dermatologist) in person. He will tell you what to do and how to treat the formation.
Prevention
Preventive measures aimed at preventing the formation of boils, including on the legs:
- proper nutrition with an abundance of vitamins and nutrients;
- careful hygiene, especially in the groin area, fingers, under the knees;
- avoiding hypothermia;
- blood sugar control for diabetics and patients with hormonal imbalances;
- preventive therapy for constant relapses of furunculosis (use of vitamin supplements, hardening, systemic strengthening of the immune system).
Furuncle on a child’s legs: recommendations
What causes boils in children:
- poor skin care;
- hormonal imbalance during puberty;
- hypothermia.
The peculiarity of the course of the disease is that due to the immaturity of the immune system, a boil in a child often turns into phlegmon or sepsis. He might even die.
Accordingly, only a doctor should determine how to treat a boil in a child, even on the leg. Especially in the presence of high temperature.
In general, therapy in children is practically no different from treatment in adults. Preventive measures are the same.
Source: https://netpryshi.ru/furunkuly/furunkul-na-noge.html
Prevention
To prevent infection of the damaged skin surface, you must follow simple rules:
- if the skin on the legs is injured, carry out antiseptic treatment;
- do not manipulate with dirty hands;
- cover the wound surface with a plaster or bandage to prevent contact with pathogenic microbes.
If large abscesses appear, general condition deteriorates, or body temperature rises, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and qualified treatment.
Tags: abscess, hidradenitis, pus, abscess, diabetes, infection, infected wound, carbuncle, honey, open wound, panaritium, wound, phlegmon, boil About the author: Andrey Stepanovich
« Previous entry
Varieties of felon
An abscess most often begins near the nail, but its course can vary. It is customary to distinguish several types of abscess on the finger.
- Superficial cutaneous panaritium often occurs on the back of the finger.
- Subcutaneous.
- Paronychia is an abscess that forms only around the nails.
- The subungual form is characterized by the appearance of fairly deep inflammation in the corresponding area.
- Articular - develops in the area of the phalanx of the finger as a result of injury. If complicated, it can develop into osteoarticular.
- Bone panaritium. Develops as a consequence of damage to bone structures or complications of previous types.
- If treatment is not started in time, the most severe form, pandactylitis, may appear as a complication. In this case, the inflammation spreads to adjacent tissues, ligaments and tendons.