Human papillomavirus is a virus that causes pathological changes in skin cells in the form of warts and papillomas. It can manifest itself not only by the appearance of neoplasms, but also by other more dangerous diseases. The insidiousness of this virus lies in the fact that there are many ways of infection, and the incubation period takes quite a long time. Unfortunately, at the moment there are no methods of complete cure, so you need to at least know exactly what HPV type 35 in women is?
According to doctors, the number of people infected with HPV is 70-80% of the population. It is not difficult to become infected with papillomaviruses. To prevent this from happening, you need to be extremely careful.
It is not just HPV that leads to dangerous diseases, but certain types of it. Today, more than 100-150 types are known and their number continues to grow.
What is HPV type 35 and its features
There are about 170 types of human papillomavirus, the 16th strain is most often identified.
Manifestations of HPV are typical for all types; only a specialist doctor (dermatologist, dermato-oncologist, gynecologist, urologist, oncologist) can determine the danger of a malignant process and the level.
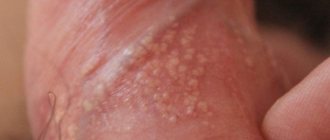
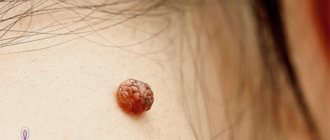
A type of papillomavirus, strain hpv 35, provokes the development of condylomas, genital warts, which have a high level of oncogenicity.
It is found in cancer of the cervix and labia, cancer of the penis, malignant tumors of the vagina and anal area.
When it enters the body, papillomavirus type 35 provokes the growth of cells in the epidermal layer of the skin.
When diagnosing oncological processes of the reproductive organs in women and men, in 60% of cases exactly type 35 is detected. The development of easily traumatic polyps on the mucous membranes of the anogenital area is often provoked. Such growths bleed, form long-term non-healing wounds, and stimulate the aggression of cancer cells inside the body.
A prerequisite for the development of lesions from HPV is a weakened immune system of the body.
Immunomodulators
The most effective means of this group are:
- Immunal;
- Amiksin;
- Reaferon;
- Polyoxidonium.
In the complex treatment of HPV, traditional medicine can be used. Tinctures of aloe, echinacea, ginseng and mumiyo. They have a negative impact on the growth and development of formations.
It must be remembered that with any treatment method, a woman must visit a doctor and follow all prescribed recommendations from a specialist. If you have type 35 virus, self-medication is strictly prohibited, since without professional help there is a high probability of the formations degenerating into cancerous tumors.
How dangerous is the type for men and women?
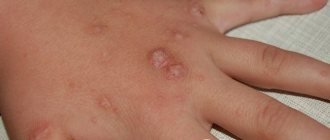
Under the influence of the formation of papillomas of the HPV 35 genotype, men and women may experience various characteristic manifestations, complications of the reproductive sphere, damage to the external skin, internal organs:
| In men | Among women |
| In men, the HPV 35 strain increases the risk of developing a complication of papillomatous growths - bowenoid papulosis. The disease affects the entire anogenital area, the normal process of urination is disrupted, libido decreases up to impotence, neuroses and psychological discomfort appear (depression, stress, psychosomatic disorders). | In women, the formation of giant papillomas of the genital area is often provoked, which, when fused, form characteristic warts in the form of a cauliflower inflorescence, a bunch of broccoli, or a chicken scallop. The formations are easily injured during sexual intercourse and grow quickly. |
| Infection in men can spread to the mucous membrane of the urethra. The danger of the appearance of filamentous papillomas in the urethra is the risk of provoking urethritis, cystitis, and prostatitis if the infection spreads. Therapy requires surgical intervention with the complex effect of immunostimulating agents. | A secondary infection often occurs, which causes foul-smelling vaginal discharge. |
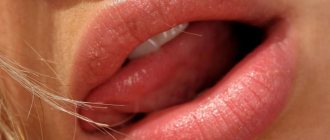
| With the development of pathology in men, more often than in women, the intestines are retracted: the process of defecation is disrupted, papillomas appear in the anus, on the rectal mucosa. Due to constant traumatization by feces, malignancy is virtually inevitable. | The female population is prone to developing oral condylomas when infected with HPV 35 (loose mucous membrane, oral types of sexual contact). Oral papillomas are injured when chewing food or brushing teeth. |
How does infection occur?
We can highlight the main ways the virus enters the body.
- Sexual path . Sexual contact with a man who is a carrier of the infection will be the easiest route of infection. The virus circulates throughout the body and penetrates fluids: saliva, urine, semen. These fluids are exchanged during sexual intercourse. And even a single contact risks infection. Frequent changes of partners can cause genital papillomatosis.
- Domestic. The mechanism of such infection is not yet fully understood. The method and time of infection are very difficult to track. Viral cells can enter the blood through skin lesions: wounds, cracks. Even a kiss becomes a cause of infection if the oral mucosa is affected by papillomas.
- Hereditary path . The birth canal of a pregnant woman transmits the virus to the baby at the time of birth. The risk of infection is not very high, but if a woman has genital warts, the risk increases.
Infection occurs without obvious signs of infection. The process is sluggish and develops very slowly until the final manifestation. Unless, of course, it is destroyed by the body.
- Incubation period. The development of HPV 35 lasts almost 3 months. During this period, the virus replicates, that is, the infection multiplies and penetrates healthy cells.
There are cases that the latent stage lasts only two weeks, and sometimes a whole year.In many young women, the body eliminates the infection on its own, but in some, the virus becomes more active and the disease becomes chronic.
- Active stage. Signs are already visible to the naked eye: skin formations appear that grow quickly.
The period is accompanied by vaginal lesions with unbearable itching. Sometimes a woman does not realize she has the virus until after menopause. At this time, the virus begins to damage healthy cells. Therefore, you should visit medical facilities regularly for check-ups.
Causes and symptoms of HPV 35
The main etiological factors of occurrence, triggers of the disease:
- Transmission of HPV from a sexual partner in the presence of warts on the skin of the anogenital area in a carrier partner and microtraumas on the mucous membranes and skin in a healthy partner, even during protected sexual intercourse.
- Skin injuries in adults and children during everyday contact with a carrier of the disease. There may be sharing of towels, razors, bed or underwear, visiting public bathing places (baths, showers, swimming pool).
- Transmission of HPV when a child passes through the birth canal from a carrier mother, during breastfeeding. The first signs of the development of papillomatosis appear by the age of 1-2 years of the baby’s life.
Features of human papillomavirus infection
HPV type 35 is a sexually transmitted infection. The diseases it causes are widespread throughout the world, both among women and their partners. In some infected people they are asymptomatic, but in most cases they are accompanied by the formation of genital warts. A characteristic feature of HPV 35 is the ability to cause accelerated cell division of the skin and mucous membranes, which causes malignant neoplasms.
Virus replication does not occur in cell cultures, so information about them can only be obtained through molecular genetic processes. The causes of HPV type 35 are different; most often, infection occurs through unprotected sexual intercourse.
Methods for diagnosing the virus
The diagnostic complex consists of a number of studies and tests to determine the HPV 35 strain. The examination regimen is prescribed by the doctor after examining the skin lesion:
- genotyping of the virus with determination of DNA identity using polymerase chain reaction (taking biomaterial from the papilloma for analysis);
- a general blood test to determine disorders in the body (anemia, bacterial or viral infection, the presence of inflammatory reactions, the norm of leukocytes, lymphocytes is determined to determine the functioning of the immune system);
- examination of the genital organs, mucous membranes of the mouth (frequent localization) and the skin of the body;
- cytological scraping from the cervix, smear from the urethral canal;
- positive digest test;
- histological examination of papilloma biopsy to identify cancer cells.
Treatment of pathology
The human papillomavirus - you now know what it is - can be destroyed by the human immune defense. That is why, when HPV DNA is detected, the patient is prescribed immunostimulating drugs and antiviral agents. The following medications show good results:
- Panavir;
- Allokin-alpha;
- Isoprinosine;
- Epigen;
- Immunal;
- Polyoxidonium;
- Reaferon.
In addition to strengthening the immune system and reducing viral activity, treatment for HPV also involves removing genital warts. And if medications are used to fight viruses, then genital warts must be removed using hardware methods. The most commonly practiced methods are:
- Laser therapy. The most effective and safe option for removing genital warts. The laser beam is directed onto the surface of the tumor. The destruction of papilloma occurs literally in a matter of seconds: it simply disappears. After laser treatment, the affected epithelial cells are completely removed, so the risk of relapse - re-growth of the wart - is completely eliminated. The procedure is painless, bloodless, and therefore there is no rehabilitation period after laser removal of condylomas. There are no scars or cicatricial formations left in the area of the former wart. The formation of a small pit is possible, but later the surface of the skin is leveled.
- Electrocoagulation. The technique involves treating skin tumors with high-frequency current. After exposure, the condyloma dries out and falls off. The obvious disadvantages of this method of exposure include pain.
- Cauterization with liquid nitrogen. The method is based on the effect of low temperatures on the affected tissue. The genital wart is treated with liquid nitrogen. As a result of cooling, it slowly dies and eventually falls off. The technique is completely painless and is a budget method. But it also has its downside: at least 10 days pass between treatment and the death of the papilloma.
If genital warts have merged into one and have covered too much of the skin, the patient will be recommended to have the tumor surgically removed. The minimum size of a genital wart for which a surgical scalpel will be used is 1 cm.
The obtained tissue samples are necessarily sent for histological examination. At the very beginning of the development of the disease, when the warts are still very small in size, special medications can be used to remove them - ointments, gels and aerosols.
Their action is based on tissue necrosis: over time, they dry out and fall off, leaving no scars or scars. To independently remove skin tumors, you can use the following drugs:
- Cryopharma;
- Cocoderil;
- Dermavit;
- Verrucacid;
- Veregen;
- Collomak.
When processing, the product must be applied strictly to the surface of the neoplasm. The surface of healthy skin should not be touched.
Traditional methods of treating HPV
The main treatment method can be supplemented with traditional methods. The main goal of therapy for infection with HPV genotype 35 is to increase the body’s immune defense. Strengthening the immune system helps suppress viral activity.
Traditional medicine recommends preparing decoctions of nettle, blackcurrant leaves and dandelion roots. Herbs can be combined in equal proportions. Then brew 1 teaspoon of the resulting mixture in a glass of boiling water (200 ml) and leave for fifteen minutes.
Before use, the drink must be filtered and drunk three times a day warm. To remove papillomas - warts that have formed on the face and hands, you can use the following recipes:
- the garlic-vaseline mixture is applied to the surface of the wart, sealed with a band-aid and left overnight;
- Using a pipette, table vinegar is applied to the surface of the skin formation; healthy skin can be protected by treating it with a layer of Vaseline;
- green walnuts must be chopped and the jar filled 2/3 full. Pour kerosene and leave for 3 weeks to infuse. Use the resulting liquid to treat warts.
Human papillomavirus is an insidious disease prone to frequent relapses. That is why an integrated approach is recommended in the treatment of human papillomavirus infection caused by genotype 35.
Treatment methods for HPV type 35
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
If HPV strain 35 is detected, treatment should include complex treatment with antiviral drugs and surgical removal of external manifestations using hardware techniques. Elimination with folk remedies or cauterization with pharmaceutical preparations (supercelandine, condiline, verrucacid) is unacceptable due to the high risk of injury to the formation.
Taking antiviral and immunostimulating drugs helps the body cope with the aggression of strain 35 and prevent relapses.
Oral administration and intravenous administration of drugs are used: interferon, viferon, genaferon, proteflazid, immunoflazid.
Removal of condylomas using surgical intervention includes the following techniques:
- surgical excision of growths and affected tissues, used for large papillomas, combined with antiviral medications;
- laser coagulation allows you to quickly and painlessly eliminate all condylomas; inconvenience is caused by hard-to-reach condylomas on the genitals and the risk of burns to the genital mucosa;
- cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen (freezing apparatus) allows you to get rid of warts most effectively in several sessions, even with deep localization;
- radiosurgical method with the creation of a radioactive field for the destruction of papilloma. A new, effective method for removing formations.
The selection of an elimination method and further therapy to suppress the activity of HPV 35 in the body is prescribed by the attending physician based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Features of treatment of human papillomavirus
How is the virus treated? Type 35 virus does not require special treatment. Usually the immune system is able to cope with the infection on its own. This process can fail if the virus is strong enough and the immune system is weakened.
The risk of infection in case of secondary infection is very high.
Successful treatment will require a combination of two methods:
- antiviral therapy;
- elimination of external symptoms of the disease.
Antiviral therapy consists of taking a whole range of medications that help the body resist the virus. They also strengthen the immune system.
It should be honestly noted that treatment does not guarantee a 100% positive result , but it will prevent serious consequences.
Although HPV 35 has a low oncogenic risk, a malignant tumor can develop. The probability is high if condylomas are localized in the genital area and cervix.
Papillomas must be removed . The virus itself is destroyed by medications, and hardware methods are used to destroy condylomas.
- Electrocoagulation. The neoplasm is exposed to current. The papilloma dries out and disappears over time. There is a greater disadvantage - painful sensations.
- Laser therapy .
The method is considered the safest and most effective. The laser beam destroys the papilloma, which instantly disappears. Infected cells are completely removed. This prevents the reappearance of formations in this place. Removal is painless, and there is almost no rehabilitation. There are no scars left. There may be a small hole that will quickly disappear. - Cryodestruction. The papilloma is cauterized with liquid nitrogen. The method is almost painless and cheap, but quite lengthy. It will take about 10 days to process the growth.
- If the papilloma reaches a large size, you have to resort to surgery . After removal, the formation is sent for examination.
- In the initial stage, when the growth is still small, elimination is carried out using ointments or aerosols. The components of these products kill papillomas tissue, which then disappear.
These drugs include: Panavir, Immunal. They will prevent the virus from multiplying.
Life prognosis and prevention of degeneration
There is no specific prevention for strain 35. To prevent infection and prevent the activation of the virus, you must follow the following rules:
- avoid casual sexual contacts;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, do not use public items;
- support the body's defenses;
- carry out sanitation of chronic foci of infection;
- undergo preventive examinations with a therapist once a year.
With timely diagnosis and the appointment of an adequate treatment regimen, the prognosis is favorable, cure occurs in most cases. With the development of an oncogenic process, degeneration into a malignant formation, treatment is carried out by an oncologist with chemotherapy drugs that suppress the body’s immune forces.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
How the virus is transmitted
For a long time, the papillomavirus may not manifest itself at all, but at the same time a person becomes a carrier of this infection and infects the people around him. The virus is transmitted sexually, and the form of intimacy does not matter - infection occurs with equal frequency during vaginal, oral or anal sex.
A condom does not provide 100% guarantee of protection against pathogenic microorganisms, since it does not cover all mucous membranes. Moreover, you can become infected with the papilloma virus without even having direct sexual contact - intimate caresses, kisses and touches can also cause infection. Most often, a person’s immune system repels the virus, but with a weakened immune system, the infection still settles in the tissues and begins to develop.
The domestic route of infection is much less common, but this possibility cannot be completely discounted. In this case, the virus can enter the human body through wounds, scratches and cracks in the skin.
The virus can also sometimes be transmitted from mother to fetus during childbirth. The likelihood that an infected person will transfer the infection from one area of skin to another is extremely low, but the spread of the virus activated on the genitals is quite possible. This is due to the fact that the mucous membrane is not as dense as the skin and is more susceptible to injury.
If the virus is in the human body in an inactive state, it may not manifest itself for a long period of time; the activation of the virus occurs at a time when the status of the immune system changes.
Provoking factors that can “awaken” the virus and bring it out of its latent state are the following:
- depression and stress;
- hormonal disorders;
- pregnancy, in which there is almost always a decrease in the functionality of the body’s defenses;
- chemotherapy;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives, as well as other hormonal drugs;
- hypothermia;
- exacerbation of chronic ailments.
Reference! The incubation period of the virus ranges from six months to several years.