The word “nevus” translated from Latin means birthmark. Most often it is benign in nature. On the skin, a mole can be seen as a spot, often colored brown or flesh-colored. In the skin itself, different types of cells can divide and then grow. Among them there are melanocytes. These are specialized skin cells that produce pigment such as melanin. At the same time, melanocytic nevus is the most common neoplasm on the skin. Such moles can be found on any part of the body surface. Against the background of such a neoplasm, the manifestation of malignant tumors of both the epidermis and its appendages is possible.
Melanocytic nevus
Etiology of the disease
Scientists have proven that age spots, which are classified as nevus, appear due to congenital disorders of the epidermis. The appearance of congenital melanocytic nevi is caused by hormonal imbalance, pregnancy, diseases of the genitourinary system, radiation, and genetic disorders. Against the background of pathological processes, improper formation of melanoblasts is observed - cells that are the source of the development of melanocytes.
Their stagnation leads to the appearance of age spots. Factors provoking the development of secondary growth:
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- frequent visits to the solarium;
- menopause;
- uncontrolled use of contraceptives;
- prolonged inflammation of the skin.
Why is melanoma nevus dangerous?
Extracutaneous melanoform neoplasm has a high risk of bleeding. It can cause anemia and the need for transfusion therapy. If the tumor is damaged and the infection spreads, there is a risk of death.
Other complications include:
- necrosis of the intestinal mucosa;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- visual impairment;
- disorders of the musculoskeletal system;
- volvulus;
- pathologies of the lungs, liver, spleen, bladder.
The malignant potential of melanoform neoplasms is still unknown: there is no data on cancer mutations of this pathology in medical statistics. Cases of the disease involving the musculoskeletal system are dangerous due to its dysfunction, as well as the need for amputation. Damage to the central nervous system due to a nevus can be fatal.
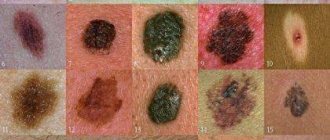
As with other skin formations, the risk of malignancy of a melanoma spot is determined by the following criteria:
- a sharp increase in size;
- discomfort, pain on palpation;
- peeling, tingling, itching;
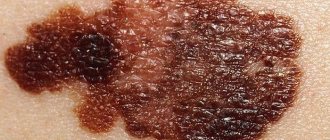
- change in color, especially to black or dark blue;
- the appearance of tubercles or roughness on the surface;
- blurring contours;
- frequent bleeding;
- separation of sputum, pus on the surface of the skin.
If one or more symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Criteria for classifying entities
The disease can be congenital and acquired, primary and secondary. Pigment spots are divided into several types.
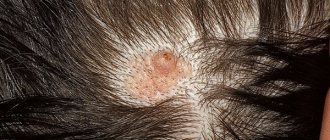
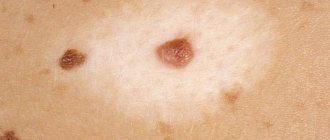
Borderline melanocytic nevus of the skin has clear boundaries and is brown in color. More often the disease is primary, acquired. The neoplasm is covered with hair, and its diameter does not exceed 1 cm. This type of disease is diagnosed in adults and adolescents.
Complex melanocytic nevus differs from borderline nevus in its location - the scalp. It has a uniform color and is similar to a papule.
Galonevus, unlike previous types, has a pigment rim, which occurs against the background of an autoimmune process. The spotted form protrudes slightly above the skin. It can be acquired or congenital.
The dysplastic appearance manifests itself independently or is transformed from other neoplasms. A mole with unclear boundaries and irregular shape can develop into a precancerous state.
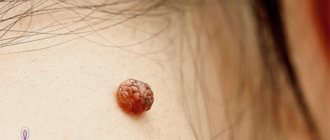
Blue formation is another type of melanocytic papillomatous intradermal nevus. It can be cellular or ordinary. Most often localized on the neck and face, fingers and lower back.
Other types of disease:
- Mongolian spot. The neoplasm is round in shape with a dull tint and a volume of more than 10 cm. The pathology does not develop into a cancerous process.
- Lentigo. The spot does not contain nevus cells. It can appear in any part of the body and on mucous membranes.
- Atypical. A rare type of spots that are characterized by the appearance of a fibrous papule in the nasal area.
- Lentiginous. Education can provoke melanoma.
Mixed papillomatous melanocytic nevus rarely develops, which is accompanied by the simultaneous appearance of several types. 5% of newborns are diagnosed with moles. If they cover a significant area of the body, melanoma may develop.
In adolescents, a melanocytic mole occurs in 90% of cases. People over 25 years old have more than 40 spots. Up to 20 moles can be seen on the body of people over 30 years of age. In older people, growths are absent, since their appearance is associated with hormonal imbalance.
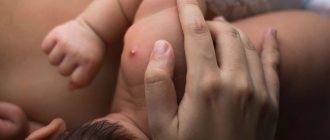
Melanocytic nevus in children
In newborns and children of the first year of life, birthmarks rarely appear; they are found in only 1% of babies.
This type of mole is called “congenital”. However, their number can increase significantly during adolescence. The number of moles (and their size) may increase until age 18. They appear not only as spots or nodules, but sometimes look like a warty formation.
Signs indicating the need for medical consultation are:
- the appearance of a new mole in a child before the age of one year;
- congenital nevus grows very quickly;
- the child is bothered by tingling, itching or pain;
- the mole has turned blue or black;
- hair has begun to grow on the pigment spot or it has become lumpy;
- the contours of the mole have become fuzzy and blurred;
- the nevus constantly gets wet or bleeds periodically;
- the surface of the stain begins to peel off.
To reduce the likelihood of a birthmark degenerating into a malignant neoplasm, it is necessary to prevent it from rubbing on clothing, not to allow the nevus to come into contact with aggressive substances, and not to allow the child to remove hairs from the birthmark (if any).
Clinical picture
Apart from spots, nevus has no other clinical symptoms. It does not cause pain or burning, there is no discomfort. Multiple or single hairs denser than the body hair may appear on the body. Formations that are prone to a malignant process acquire the following symptoms:
- rapid growth of spots;
- change in the outlines of moles;
- the formation of a dark rim around the formations;
- inflammation, redness and swelling of the skin;
- tingling with itching;
- peeling of the skin.
Factors that can trigger the cancer process are associated with injury, thermal or chemical damage to the nevus. The most dangerous complication of the disease is melanoma with metastasis. In 70% of cases, melanoma occurs as a result of degeneration of a mole. Persons with melanoma-dangerous nevi are required to avoid factors that stimulate their malignant transformation. Those at risk of developing the disease are those who have:
- giant congenital nevi;
- numerous moles on the skin;
- the appearance of nevi in places exposed to insolation and mechanical influence;
- neoplasms in elderly people.
It is necessary to be constantly examined in order to detect the cancer process in a timely manner. If you identify signs that indicate cancer, you should consult a dermatologist or oncologist.
Stages of changes in nevi
Melanocytic nevi , both acquired and congenital, are characterized by staged changes throughout life. The classic path of development includes 3 stages, which differ in the depth of the formation:
- a simple nevus or borderline nevus is a superficial flat brown spot;
- a complex or combined nevus is located deeper and looks like a brown spot or raised formation on the skin;
- An intradermal nevus is a light-colored, raised formation located deep in the skin.
Diagnosis and treatment
To make a diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory tests are carried out. During the initial examination, the doctor collects anamnesis and examines the skin. When signs of malignancy appear, CT and MRI are used. If the nevus bleeds, it is necessary to take a scraping. Additionally, the patient donates blood for tumor markers.
The disease is differentiated from all other pigmented tumors of the skin. The formations differ from seborrheic keratosis. They do not have a rough surface or horny cysts. Unlike dermatofibromas, nevi have a dense consistency. Neurofibromas are characterized by a flesh-colored tint and the presence of a stalk. The typical form differs from the dysplastic formation in size and symmetry.
Treatment tactics are determined by several parameters:
- Clinical picture: type, size, risk of malignancy of the nevus.
- Availability of medical equipment for medical procedures. Some clinics do not have equipment for removing tumors using the modern method. In such institutions, a classic operation is performed.
To remove a melanocytic mole, cryodestruction is used. Freezing of the formation is carried out with liquid nitrogen or carbonic acid. After treating the problem area, a crust appears, under which healthy skin grows. Cryodestruction is considered a minimally invasive method for treating nevus, so it does not cause discomfort.
You can remove a mole with laser beams. The procedure is considered painless. After surgery, the nevus is completely eliminated. No scars remain, but the epidermis under the mole will be lighter than the shade of the skin.
Which moles are dangerous?
Despite the fact that some types of nevi are considered more dangerous and some less, any of these formations can degenerate into melanoma. Therefore, they cannot be ignored. The main sign of melanoma is a change in the shape and size of the nevus. The following are symptoms that indicate you need to see a doctor immediately:
- The mole is located in a place that is constantly injured (neck, back, head).
- The appearance of new formations and nodules next to the nevus.
- Itching and tingling in the affected area.
- Changes in the color, shape and size of a mole.
- The emergence of new formations.
Even if only one new mole appears, do not be lazy and consult a doctor. Perhaps this will save your health from much more serious troubles.
ul
Operations and prevention
To remove the growth, electrocoagulation is prescribed. The manipulation is carried out using electric current. The operation is considered minimally invasive, since the healthy epidermis is not affected. Bleeding is excluded, but during the procedure the patient may complain of pain and other discomfort. The main contraindication to electrocoagulation is a large nevus.
To remove the tumor, dermatologists also use radiosurgery. A special knife has a direct effect on the nevus tissue. After the intervention, no scars remain on the body. If the patient has giant nevi, the use of a radioknife is contraindicated. The classic surgical method for removing a mole is surgery using a scalpel.
After anesthesia, the tumor is excised along with nearby healthy tissue. The technique is effective if numerous growths of nevi are detected or their localization in hard-to-reach places. After surgery, dressings and wound treatment with an antiseptic are indicated. There are no special preventive measures for the appearance of nevi.
You can reduce the likelihood of developing the disease by avoiding prolonged contact of the skin with sunlight or radiation. It is recommended to treat the skin with protective products while tanning. If there are numerous age spots, solarium is contraindicated. It is necessary to be examined by a dermatologist annually. The prognosis of the disease in most cases is favorable, even after surgery to remove the malignant growth.
How are nevi treated in the Rassvet blade?
The doctor will examine the patient's skin completely to eliminate the risk of missing melanoma or other skin cancer. Suspicious formations are further studied using a device that allows you to examine the skin with 10 times magnification - a dermatoscope. The patient's chart describes nevi that require observation. The doctor will suggest surgical removal of suspicious nevi, followed by histological examination of the removed material (sent to an expert laboratory). Removal of nevi for aesthetic reasons can be performed at the request of the patient.
Recommendations of a dermatologist for patients with nevi:
- avoid excessive ultraviolet irradiation of the skin (tanning, sunbathing, solariums, ultraviolet drying of manicure and pedicure coatings); when staying outdoors for a long time, use a broad-spectrum photoprotective cream with SPF 30 or higher, clothing that covers the skin, a hat and glasses with an ultraviolet filter;
- try not to injure nevi when shaving, combing, changing clothes;
- undergo an annual preventive examination of nevi with a doctor;
- independently examine nevi according to the ABCDE rule;
- if there are a large number of nevi (50-100 or more), especially in combination with the presence of risk factors (sunburn, visits to a solarium, melanoma and skin cancer previously identified or in close relatives, the presence of atypical nevi), undergo a digital skin mapping procedure.
Author:
Voronina Vera Removna dermatologist
Causes
Nevus can be congenital or acquired. The exact causes of pathological proliferation of melanocytes have not been established. Congenital nevi are considered a hereditary disease. Acquired pathology occurs against the background of exposure to external and internal provoking factors. These include:
- pancreatic diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- frequent allergic skin diseases;
- constant mechanical trauma to the skin;
- prolonged exposure to sunlight.
Under the influence of these factors, melanocytes accelerate their proliferation and actively produce pigment substances. An accumulation of cells and their staining of the skin is a mole.