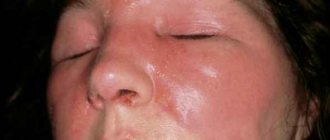
Causes of allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis is irritation of the skin due to prolonged contact with a facultative irritant, that is, a substance that normally should not cause an allergic reaction.
Allergic dermatitis develops in individuals with excessive sensitivity to irritants. The most common cause of allergic dermatitis is contact with various chemicals, including:
- medications - neomycin, gentamicin, novocaine, lidocaine, sulfonamides, furatsilin, ethacridine lactate, synthomycin, which are used in the form of solutions, ointments, etc.;
- paraphenylenediamine - black and other dark dyes for fabrics, printing inks;
- Peruvian balsam - perfume;
- turpentine - solutions, shoe polishes, printing inks;
- nickel sulfate - metal, metallized fabrics, jewelry, catalysts;
- cobalt sulfate - cement, galvanizing solutions, machine oils, eye shadow, refrigerants;
- tiuram—rubber products;
- formaldehyde - disinfectants, polymers, formidron;
- chromates - cement, antioxidants, machine oils, matches;
- parahydroxybenzoic acid esters - food preservatives;
- latex - gloves;
- keratin - hair from guinea pigs.
During the process of pathogenesis, the antigen (allergen) is captured by Langerhans cells, in which it is partially broken down and binds to molecules. Langerhans cells migrate from the epidermis to regional lymph nodes, where antigen presentation to T lymphocytes occurs. T-lymphocytes become sensitized, proliferate, and are released from the lymph nodes into the blood. Thus, the entire skin is sensitized to this antigen.
T lymphocytes release cytokines and influence other cells that also produce cytokines when they encounter this antigen. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs only in individuals who are sensitized to it.
The concentration of the allergen does not matter; the severity of dermatitis is determined by the degree of sensitization. It can last for months and years to certain allergens. Dermatitis develops no earlier than 1-2 weeks after contact with a strong allergen, sometimes months and years after contact with a weak allergen.
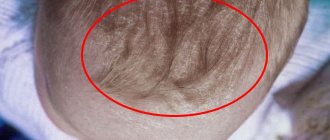
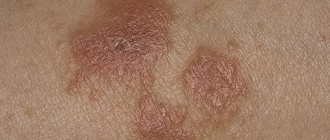
As the name itself suggests, the rash occurs primarily at sites of contact with certain substances. This may be erythema, erythema-squamous, papular, vesicular, bullous elements in various combinations, erosion, crusts, peeling, lichenification (in cases of chronicity).
Clinical features that distinguish allergic contact dermatitis from simple allergic contact dermatitis:
- dermatitis develops after repeated contact with substances after a certain latent period necessary for the development of sensitization;
- the rash is localized not only at sites of contact with certain substances, but also in distant areas of the skin (mainly erythema-squamous, papular, of varying severity);
- allergic contact dermatitis is accompanied by signs characteristic of eczema - microvesiculation, true polymorphism, exudate, tendency to relapse;
- dermatitis does not always regress after eliminating contact with the substances that caused its development.
The course can be acute, subacute and chronic.
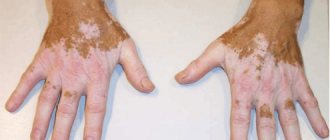
Intercellular edema in the epidermis, hyperplasia and hypertrophy of endothelial and perithelial elements of blood vessels, narrowing of their lumen, perivascular infiltration. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by metals is usually provoked by chromium salts contained in cement (cement eczema), household powders, pastes, nickel (nickel-plated jewelry, buckles, etc.), cobalt. In cases of sensitization to nickel, the so-called “nickel scabies” may develop, which is accompanied by intense itching.
Possible skin lesions during metal osteosynthesis. In orthopedic and traumatological practice, metal prostheses that contain steel, nickel, chromium, cobalt, titanium, molybdenum and other metals are widely used. The components of prostheses and rods undergo partial diffusion around the metal material. In the form of ions and corrosion products, they penetrate into neighboring tissues, causing an inflammatory process. In areas of osteosynthesis, skin manifestations can occur several weeks and months after surgery. The frequency of skin lesions is small. Clinically, the process can occur as nummular dermatitis (eczema), lichen simplex chronicus, purpura on the skin of the lower extremities, generalized vasculitis, bullous dermatitis, erythema multiforme. In all cases, patients are bothered by itching, which does not stop even under the influence of local or general corticosteroids.
Allergic contact dermatitis caused by cosmetics occurs due to the use of creams, powders, shampoos, deodorants, perfumes and the like. Initially, the rash appears directly at the points of contact, and subsequently can spread to other areas.
Allergic contact dermatitis caused by adhesive substances develops after the use of adhesive plasters and cleol, various household adhesives. In most cases, the process is limited to the point of contact.
Allergic contact dermatitis caused by drugs usually results from taking drugs such as furacilin, ethacridine lactate, novocaine, syntomycin, anesthesin, penicillin and other drugs. It should be remembered that some of them (syntomycin, anesthesin) are included in ointments, liniments, and often combined.
Allergic contact dermatitis caused by plants is called phytodermatitis. It can be caused by hogweed (a strong allergen that causes bullous dermatitis, and in cases of large areas of damage, symptoms of intoxication and fever also develop), primrose, parsnip, tobacco (tobacco dermatitis) and other plants. A higher risk of phytodermatitis exists when contacting wet plants (in dew or after rain). They are often linear in nature or leaf shaped. Erythema with clear contours, edema, papules, vesicles, bullous elements and a rash develop on distant areas of the skin that have not been in direct contact with plants.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis
As already mentioned, the symptoms of dermatitis can be local or general, differing in acute and chronic course. Local symptoms include itching, rashes of various types, and redness. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, a strong inflammatory process can be noticed. The affected dermis turns red and swells, then small blisters or pimples appear on the skin. They often burst, leaving crusts behind. Capable of covering large areas and even the entire body. So, the main symptoms of the disease and what allergic dermatitis looks like:
- redness of the skin, which is called erythema;
- burning and severe itching;
- peeling of the skin;
- blistering rash with allergic dermatitis, containing a clear liquid inside;
- feeling of heat in the affected area;
- pain syndrome (occurs rarely).
The pictures show what dermatitis looks like in this case: the skin pattern becomes more pronounced, often accompanied by pigmentation.
Children or people with weakened immune systems may experience symptoms of intoxication. It will be indicated by an increase in body temperature, severe weakness, nausea or vomiting, and headache. Patients may also complain of watery eyes or a runny nose if the allergic reaction was caused by phytodermatitis.
How to treat allergic dermatitis?
Treatment of allergic dermatitis is to identify and eliminate the influence of the allergen. Shown:
- general hyposensitizing therapy sodium thiosulfate,
- calcium chloride,
- intravenous gluconate;
- fenistil,
Local therapy has a secondary effect and is usually symptomatic. In the presence of severe erythema, edema, and bullous elements, cold lotions are used, then corticosteroid ointments. An indifferent shaken mixture is applied to large areas of the allergic rash.
It is advisable to exclude food allergens (chocolate, mushrooms, honey, cocoa, oranges) and extractive substances (broths, jellied meat) from the diet. In order to prevent relapses during the inter-relapse period, courses of treatment with histaglobulin can be carried out.
Corticosteroids
This group of drugs is often used for atopic dermatitis in adults. They contain hormones and have an anti-inflammatory effect. However, their long-term use is not recommended, as this will lead to skin atrophy. The most effective are:
- Prednisolone is a synthetic drug with moderate strength. The product is used for severe allergic diseases, including dermatitis. Do not use for systemic fungal infections, as well as for hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. A special feature is that it can also be used to treat children under the strict supervision of a doctor.
- Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticosteroid that has anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. Available in the form of an injection solution. Indicated for severe allergic reactions. There are many contraindications if it is used as a systemic drug, so it is not recommended to treat the disease yourself.
- Fluticasone comes in the form of a nasal spray. Included in the list of vital medications. It is indicated for the prevention and treatment of allergic rhinitis and dermatitis in adults and children. Can be used to treat children from 4 years of age. The therapeutic effect occurs with regular use.
In addition to the indicated systemic drugs (most often prescribed are Zyrtec, Ketotifen and others like them), there are also special complex ones that include several active components from each of the listed groups. Additionally, they may include antibiotics. In some cases, NSAIDs are used as nonspecific therapy.
Sodium thiosulfate deserves special attention. This drug helps eliminate toxins. This is why sodium thiosulfate is used in combination with other medications to treat allergies.
When treating with any drug, you need to change your diet. A sick body needs vitamins every day.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis at home
Treatment of allergic dermatitis is usually carried out at home; hospitalization is not necessary at all. An exception may be cases of dermatitis that develops against the background of other more complex diseases and specific conditions.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis at home should occur in parallel with the exclusion of contact with the allergen itself; diet is not the least important - it is important to exclude spicy foods that irritate the gastrointestinal tract, as well as potential allergens - alcohol.
Prevention
Dermatitis is chronic, so it is worth taking measures to prolong periods of remission and prevent exacerbations. Prevention is as follows:
- contact with allergens - substances that cause inflammatory reactions of the skin - should be excluded or at least minimized.
Advice! Before you start using a new cream, be sure to conduct an allergy test by applying a small amount of cream to the skin of your wrist. If there is no negative reaction, then you can apply the product to your face and neck.
- eat rationally, take vitamin supplements.
- use emollients or hypoallergenic moisturizers, since the skin of the neck is dry and thin and needs special care.
- try to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, since dermatitis is most often a consequence of allergic reactions. A strict diet is prescribed for the period of exacerbation, and after the symptoms subside, it will be possible to gradually expand the list of permitted products, after consulting with a specialist.
- be physically active, walk more, do physical exercise and sports.
So, dermatitis on the neck can be caused by various reasons. It is unlikely that it will be possible to identify them on your own, so the patient needs to consult a specialist. It is necessary to consult a dermatologist; in addition, you may need to consult an allergist and gastroenterologist.
What medications are used to treat allergic dermatitis?
Medicines that reduce general sensitivity to the identified allergen:
- sodium thiosulfate - 5-50 ml intravenously, depending on the severity of the allergic reaction;
- calcium chloride - 5 ml of the substance intravenously in a stream (slowly, over 3-5 minutes);
- calcium gluconate - 1-3 g 2-3 times a day intravenously or intramuscularly;
Antihistamines:
- fenistil - a small amount of cream is squeezed onto the fingertip and applied to the affected area every 2 hours for 4 days;
- terfenadine - 60 mg (one tablet or 2 measuring spoons) 2 times a day or 120 mg (one tablet of terfen forte) in the morning;
- astemizole - orally, on an empty stomach, 10-30 mg once a day for a week and no more;
- fenkarol - 25-50 mg 3-4 times a day over the next 10-20 days;
Diuretics:
- furosemide - intramuscularly or intravenously, 40-120 mg daily;
Enterosorbents:
- polysorb - the average daily dose for adults is 0.1-0.2 g/kg body weight (6-12 g);
- enterosgel - 1 tbsp. (15 g) 3 times a day 1-2 hours before meals or taking other medications, washed down with water.
Diet food
During treatment of dermatitis, it is important to normalize your diet and completely eliminate foods that can cause an allergic reaction.
Related article:
Symptoms and treatment of contact dermatitis on the face
These include:
- Citrus.
- Chocolate and coffee.
- Alcohol.
- Dairy products.
- Eggs.
- Preservatives.
- Seafood.
- Honey.
- Nuts.
Sweet, salty and fatty foods can only be consumed in limited quantities. Processing food in the form of frying should be avoided.
The diet should include:
- Cereals.
- Vegetables and fruits.
- Lean meat and broths.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis with traditional methods
The use of folk remedies for the treatment of allergic dermatitis is effective at the stage when it is necessary to alleviate symptoms. Antihistamines in combination with neutralizing the action of the allergenic factor have the greatest effect against allergic reactions, however, traditional methods are appropriate in combination with conservative treatment. Discuss with your doctor the following ways to soothe affected areas of the skin:
- herbal infusions for drinking - string, currant bark, tricolor violet, viburnum bark, chamomile, licorice root;
- homemade ointments - from sea buckthorn oil, pork, chicken or goose fat;
- compresses with infusions - from elecampane roots, oak bark, horsetail herbs, lemon balm, calendula, felt burdock;
- baths - from nettle, oregano, chamomile flowers, blue cornflowers, valerian, wild rosemary leaves;
- aromatherapy - using lavender, geranium, sandalwood oils.
Carrying out treatment
When the first signs appear, you must know how to treat dermatitis on the neck, since untimely or incorrect treatment can lead to various complications. Treatment is prescribed only after a comprehensive diagnosis, so you need to take tests to determine the type of pathology.
Treatment of dermatitis on the neck involves following a diet. It is important to exclude from your diet foods that contain harmful animal fats, as well as allergens. In addition, you need to strengthen the immune system by using special vitamin complexes.
It is important to choose the right ointment for dermatitis on the neck, which will not only eliminate the inflammatory process, but also promote skin healing. It is worth remembering that the skin in the neck area is quite delicate and thin, which is why the ointment must contain moisturizing components.
A photo will help determine the presence of dermatitis on the neck. Treatment involves the use of medications, in particular antihistamines. Basically, the doctor prescribes to patients:
- "Diazolin";
- "Zodak";
- "Erius".
Treatment of allergic dermatitis during pregnancy
The course of any allergic reactions, and allergic dermatitis is no exception, can be especially acute during pregnancy, but the opposite often happens, the condition of some patients improves during pregnancy.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis in a pregnant woman follows a standard regimen. The goal is still to quickly stop the immune system's response to the allergen, which means there is a need to identify it and prescribe antihistamines. Treatment will not be as effective as possible if contact with the identified allergen is not excluded.
Preparations for topical use are especially relevant; they relieve symptoms, reduce itching, discomfort, disinfect and soothe the affected area of the skin. Of all the medications for which allergic dermatitis is indicated, you need to choose only safe ones, which means you can’t do without a doctor’s recommendation. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Antihistamines
They are the ones most often used to solve this problem due to their high efficiency. These medications can fight both external and internal manifestations of allergies, in particular, they can reduce the impact of an ingested allergen on the body. However, there is one drawback - excessive drowsiness during treatment.
Antihistamines are divided into three groups:
- First generation drugs. Relieves swelling and inflammation quite quickly. Different forms are used. They can cause nausea, headache, drowsiness, and a feeling of euphoria, therefore they are used only in case of outpatient treatment. First generation antihistamines include Clemastine, Chloropyramine, Promethazine, Meclozine, Dimetindene and others.
- Second-generation antiallergic drugs are contraindicated in elderly people, as well as in patients who suffer from cardiac diseases, since these drugs negatively affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system. For everyone else, they are good because they affect physical and mental activity. These are Astemizole, Loratadine, Akrikhin, Ebastine, Ketotifen and others.
- Third generation drugs against allergic dermatitis are indicated for people with chronic diseases, since they have virtually no side effects. This group includes Fexofenadine, Hifenadine, Cetirizine, Zyrtec.
Zyrtec is available in the form of drops, which is very convenient for eliminating the symptoms of dermatitis in children older than 6 months. Zyrtec is indicated for allergic dermatitis, which is accompanied by itching and rash. Loratadine is indicated for various manifestations of allergies, including dermatitis. Has antipruritic effect. These anti-dermatitis tablets begin to act within half an hour after administration, and the full therapeutic effect occurs within 24 hours. To consolidate it, you must complete a full course using Loratadine, the duration of which is from 10 to 15 days. This is relatively little, since if you use Ketotifen, the treatment will last at least 3 months.
Which doctors should you contact if you have allergic dermatitis?
- Dermatologist
- Infectious disease specialist
Diagnosis is based, in addition to clinical data, on indications of the patient’s contact with certain allergens, as well as positive skin allergy tests (patch tests).
For metal allergic dermatitis, epidermal and intradermal skin tests with any suspected substance are not sufficiently informative because they give different results. Often, the correct diagnosis is made only after the rash disappears as a result of removal of osteosynthesis materials.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - a
| Treatment of lung abscess |
| Treatment of brain abscess |
| Treatment of liver abscess |
| Treatment of splenic abscess |
| Treatment of overuse headaches |
| Treatment of pituitary adenoma |
| Treatment of adnexitis |
| Treatment of acromegaly |
| Treatment of alcoholism |
| Treatment of alcoholic hepatitis |
| Treatment of alcoholic liver disease |
| Treatment of alopecia |
| Treatment of alveolitis |
| Treatment of amoebiasis |
| Treatment of liver amyloidosis |
| Treatment of renal amyloidosis |
| Treatment of sore throat |
| Treatment of aneurysm |
| Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis |
| Treatment of anuria |
| Treatment of kidney aplasia |
| Treatment of aplastic anemia |
| Treatment of ovarian apoplexy |
| Treatment of appendicitis |
| Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis) |
| Treatment of ascariasis |
| Treatment of ascites |
| Treatment of pulmonary atelectasis |
| Treatment of atherosclerosis |
| Treatment of atypical pneumonia |
| Treatment of autoimmune hepatitis |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.