Causes of fungal dermatitis
It has been clinically proven that yeast-like fungi are one of the components of the natural human microflora. Under the influence of unfavorable conditions, the body loses the ability to control the growth and reproduction of pathogens, resulting in the development of fungal dermatitis. One of the reasons for the appearance of mycoses may be a hereditary predisposition.
Provoking factors:
- reduction of general and local resistance of the body;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis;
- poor, one-sided nutrition, strict diets;
- stress, overwork, physical strain;
- long-term use of antibiotics.
Atopic dermatitis is often a predisposing factor to the appearance of mycoses. In this case, fungal infection occurs as a complication of allergic dermatosis and is accompanied by the manifestation of allergies.
The development of mycosis in infants is facilitated by an insufficiently developed immune system, as well as errors in caring for the baby. Wet diapers, poor hygiene, prolonged contact with feces - all this provokes diaper dermatitis.
Skin fungus is highly contagious. Primary infection can occur during contact with a sick person, when using the same hygiene products, toys, clothes and shoes. People especially often become infected with mycosis in bathhouses, swimming pools, and industrial locker rooms.
How to prevent the development of the disease?
Fungal eczema is not easy to get rid of. Even if all traces of the disease have disappeared, it can remind itself at any moment, as soon as favorable conditions appear. To avoid this, you need to adhere to certain preventive measures:
- avoid stress and emotional stress;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- promptly disinfect wounds, cuts and scratches on the body;
- do not use other people’s hygiene products;
- do not walk barefoot in public places;
- do not take antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription;
- consume enough vitamins and minerals.
You should also wear clothes made from natural fabrics, eat a balanced diet, and exercise. At the same time, you should not overuse sunbathing, you should avoid contact with household chemicals, and try to avoid injuries, colds and infectious diseases. If you detect the slightest signs of skin pathology, you should immediately consult a doctor, since self-medication is likely to be ineffective and will only worsen the situation.
Copying site materials is possible without prior approval if you install an active indexed link to our site.
The information on the site is provided for general information purposes only. We recommend that you consult your doctor for further advice and treatment.
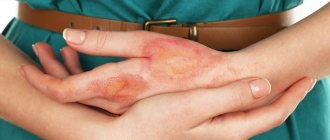
Symptoms of fungal dermatitis
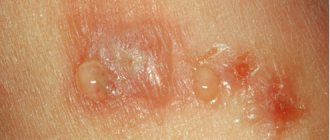
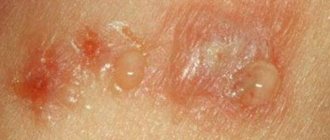
A distinctive feature of fungal dermatitis is mykids - allergic-type skin rashes resembling eczema or scaly lichen. They appear as a response to the effects of a particular mycosis.
The appearance of pustules and papules is accompanied by the following manifestations of fungal dermatitis:
- soreness and itching of the affected areas;
- increased skin moisture;
- redness and swelling.
Burst blisters become covered with a dry, flaky and itchy crust.
In addition to the rash, fungal dermatitis is characterized by accompanying symptoms of damage to body systems:
- weakening of skin resistance;
- decreased general immunity;
- endocrine disorders.
Fungal dermatitis in adults is usually localized on the skin, nails and scalp. In babies, mycoses most often affect the oral mucosa (thrush) and the area of the inguinal folds (diaper dermatitis).
A fungal infection in the chronic phase is characterized by severe skin deformation. Sick pustules leave behind noticeable scars and cicatrices, which can only be removed with the help of a cosmetologist.
Symptoms
With dermatitis caused by fungi, the following symptoms are noted:
- the affected areas turn red or bluish;
- peeling and itching;
- rashes may form in the form of bubbles with clear liquid;
- With candidiasis, a white coating forms on the affected areas.
If fungal skin infections are not treated, the disease can become chronic. With chronic dermatitis, the deeper layers of the skin are affected, and after the rashes heal, scars remain.
Features of the course in children
A newborn baby most often develops diaper dermatitis caused by improper skin care. With this disease, the skin becomes inflamed and a fungal infection can easily develop. The following factors provoke dermatitis in infants:
- artificial feeding, according to statistics, children who receive breast milk get sick less often;
- poor skin care - infrequent bathing, improper use of skin care products;
- incorrect choice of clothing that rubs the baby’s delicate skin.
The disease manifests itself in an infant by the following factors:
- large areas of reddened skin;
- the appearance of bubbles filled with cloudy liquid;
- formation of surface erosions;
- crusts;
- peeling.
Forms of fungal dermatitis
The symptoms of fungal dermatitis largely depend on the type of pathogen and the location of the mycosis. On this basis, it is customary to distinguish several types of disease.
Keratomycosis
The fungal infection is found in the upper layers of the dermis. Multiple foci of inflammation can be located on the back, abdomen, chest, neck, and calves. They look like a pinkish blurry spot with slight flaking. Accompanied by itching and tissue irritation.
Keratomycosis is more often diagnosed in young people 18–45 years old. Patients with diabetes mellitus and tuberculosis, people with weakened immunity and excessive sweating, and workers in hazardous industries (flour mills) are at risk.
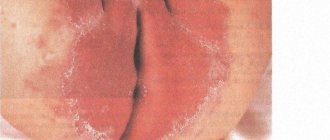
Candidiasis
The pathogen prefers to settle on the dermis and mucous membranes. It is often localized in the oral cavity, on the genitals, and in skin folds. A striking example is diaper dermatitis.
Candida fungi penetrate deep into the tissue, causing irritation, redness and unbearable itching. The danger of mycoses of this group lies in their ability to affect the mucous membrane of internal organs. Pathology is caused by insufficient hygiene, stress, and adverse environmental influences. It is this type of fungus that is most often infected.
Dermatomycosis
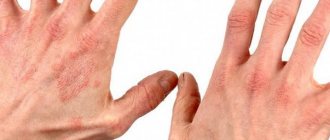
The most commonly diagnosed and extensive group of dermatitis. This type of mycoses has a variety of symptoms depending on the location of the source of inflammation. It is found in the interdigital spaces, on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, in the axillary and groin areas, under the hair, on exposed skin and nails.
Dermatomycoses include seborrheic dermatitis, manifested by irritation and peeling of tissue, severe itching. Mycosis is often mistaken for dry dandruff. When the nails are affected, a change in the color of the horny plate, its deformation and detachment from the bed are observed.
When localized on the skin, fungal dermatitis manifests itself as itchy spots and plaques, papules with purulent contents, and tissue swelling. Inguinal mycosis in men is characterized by rapid spread of infection to the scrotum and penis.
Sporotrichosis
The most dangerous type of fungal dermatitis. Invades the limbs and groin area; in case of complications, it spreads to the internal organs and lymph nodes. Treatment is long and difficult. As a rule, it occurs after serious illnesses, operations, or long-term antibiotic therapy.
Pathogenesis
Violation of the barrier function of the skin leads to increased permeability to fungi. Initially, pathogens penetrate the surface keratin layer, softening and loosening it. If this occurs in areas with increased keratinization, the patient may notice a change in the thickness and texture of the skin. In all other zones, this stage occurs quickly and unnoticeably.
By actively multiplying and plunging deep into the dermis, fungi contribute to the appearance of local skin changes and the activation of immune mechanisms. Cellular immunity is primarily used to counteract mycotic infection. True, in many cases it remains incomplete and does not lead to the complete destruction of the pathogen.
Additional inclusion of humoral protection is not able to have a clinically significant effect on the course of fungal dermatitis and does not protect against re-infection. The antibodies produced are type-nonspecific. Because of this, false-positive reactions to fungi that are not detected in a given patient are quite common. Cross serological reactions to some epidermal factors and even to group IV blood isoantigens are also possible.
Imperfect immune reactions and a high probability of allergization are factors contributing to the recurrent course of the disease.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing fungal dermatitis is not very difficult. The disease has a number of specific signs, which the doctor pays attention to at the first examination.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed additional procedures:
- examination of the affected areas under a Wood's lamp;
- microscopic examination of scrapings of the upper layers of the dermis;
- blood chemistry;
- HIV testing.
In addition to carrying out diagnostic procedures, the doctor is interested in all the medications the patient is taking, finds out living and working conditions, and clarifies compliance with hygiene skills.
Treatment of fungal dermatitis
The main direction of successful fight against mycosis is the continuity of therapy, which corresponds to the period of complete renewal of the skin and is 28 days.
The treatment regimen for fungal dermatitis includes the use of systemic and local agents:
- antimycotics in the form of tablets - Lamisil, Nizoral, Fluconazole, Diflucan. The drugs are taken after meals;
- local antifungal agents - Bifosina, Mycozoral, Kanizoan;
- antihistamines for itching - Erius, Zyrtec, Suprastin;
- sedative medications - tincture of valerian or motherwort, Novopassiat;
- immunomodulators and vitamin complexes - Lykopida, Lymphomyosot.
If fungal dermatitis is of the allergic type, the patient is prescribed corticosteroid ointments (Prednisolone) and prescribed a diet.
To avoid relapses and cleanse the skin, use Skin-cap gel, shampoo or spray. The medication has antimycotic and antimicrobial activity, accelerates tissue regeneration.
Content
In most cases, the disease occurs after injury or any damage to the integrity of the skin as a result of the development of various types of mycoses, candidiasis, and lichen.
Initially, fungi penetrate into wounds or cracks in the skin and, if favorable conditions exist, begin to multiply in it. Since the microorganisms themselves, the toxins and waste products they secrete, are foreign to the human body, it begins to actively fight them, which can lead to sensitization and, accordingly, allergic reactions in the form of eczema. That is why fungal eczema in most cases occurs in those parts of the body that are most often affected by fungi after a weakened immune system, stress, or problems with the endocrine and nervous systems.
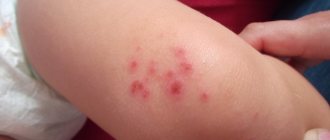
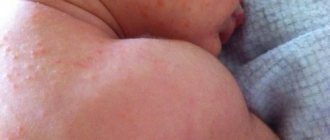
Fungal dermatitis in children
Fungal dermatitis in children often develops against the background of reduced immunity, dysbacteriosis, poor nutrition and insufficient care. Often, mycosis occurs after infectious diseases as a reaction to excessive use of medications.
In childhood, the following types of fungal dermatitis are most often diagnosed:
- thrush (damage to the oral mucosa). It manifests itself as a cheesy coating and increased sensitivity, which is why the baby refuses food;
- diaper dermatitis. Affects the skin of a newborn baby and is characterized by irritation and redness in the groin, swelling, itching;
- perianal dermatosis (rash near the anus). Develops against the background of dysbacteriosis;
- seborrheic mycosis. It is most often localized in the head area, strewing the scalp with yellow, greasy scales.
Dermatitis in infants is often accompanied by fever, deterioration in general health, sleep disturbances, vomiting, and intestinal disorders.
To treat mycotic infections in children, cutaneous agents are used: Clotrimazole, Miconazole. If a bacterial pathogen is associated with dermatitis, Tetracycline ointment is prescribed. All medications are used only after the approval of the attending physician.
Preventive measures
Unfortunately, the child’s body does not develop immunity to skin fungi. Therefore, it is necessary to adhere to simple preventive measures:
- The child must be clean - hygiene measures must be taken after each bowel movement. As a last resort, if it is not possible to use water and soap, wipe with sanitary napkins for babies.
- Diapers for boys and girls are different in shape, as they are designed taking into account physiological differences. Purchase them accordingly.
- Use baby soap to wash your baby.
- After bathing, do not rub your baby’s skin under any circumstances – gently pat dry with a soft towel.
- Do “air baths” for half an hour every day. At the same time, the room should be warm, but not hot.
Attentive attention to the condition of the baby and his body will allow you to notice the problem in advance and begin treatment in a timely manner.