- July 8, 2018
- Dermatology
- Bukataya Olga
Children are more likely than adults to experience allergic reactions on the skin caused by exposure to external factors. However, the causes of dermatitis are completely different. Each type is accompanied by certain characteristics. However, their symptoms may be similar. For example, cold dermatitis is very similar to allergic dermatitis. Moreover, it is often accompanied by a runny nose and non-infectious conjunctivitis. In extremely rare cases, cold dermatitis causes asthma attacks triggered by inhalation of cold air.
Main reasons
Why does cold dermatitis occur? The reasons for this pathology can be completely different. Most often, this type of dermatitis occurs as a result of hypothermia. Doctors identify several other factors leading to such violations:
- Too dry skin. In this case, there is a lack of natural fat coverage. This leads to rapid loss of moisture, as well as deterioration of the elasticity of the upper layers of the epidermis.
- The occurrence of abnormal protein reactions in skin cells. This happens due to exposure to low temperatures. Experts suggest that the resulting compounds turn into strong irritants, which in their effects are similar to allergens. This increases the production of histamine.
- Hypertrophied reaction of blood vessels (capillaries) of the skin. In other words, their spasm. As a result of this violation, the blood circulation of the upper layer of the epidermis significantly worsens, cell starvation and dehydration of the integument begin.
Factors provoking pathology
Experts have not yet identified the main factors that can provoke the development of cold dermatitis. However, it was found that such a disease develops when there is a disruption in the human immune system.
Almost any source of infection increases the risk of developing such dermatitis. This can be pyelonephritis, caries, sinusitis, as well as metabolic disorders in the human body and disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. It is for this reason that when making a diagnosis such as cold allergy or dermatitis, it is recommended to conduct a thorough examination to identify diseases that negatively affect the state of the immune system. Therapy, as a rule, is intended not only to eliminate unpleasant symptoms, but also to rid a person of the disease.
Who is at risk?
It is impossible to clearly determine who is at risk for this disease. Experts confidently say that women suffer from cold dermatitis twice as often as representatives of the stronger sex. The first signs of the disease may appear before the age of 30. Due to age-related deterioration of the skin, allergies to cold bother many older women.
Often young children also suffer from the disease. The risk group primarily includes those who are prone to allergic reactions. But as practice shows, in many children, cold dermatitis disappears over time in the same way as diathesis. The process proceeds much faster if timely and correct treatment is carried out.
Localization
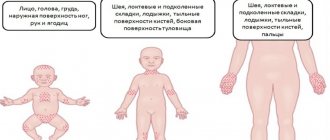
The localization of cold dermatitis depends on which parts of the body were exposed to prolonged exposure to the irritant. Most often, symptoms of the disease appear on the neck, arms, ears and face. It is these areas that remain open, and it is difficult to protect them from allergies.
However, in some cases, signs of cold dermatitis can be seen on closed parts of the body. Often in the cold there is itching in the area of the bends of the joints in the knees and elbows. Allergy foci can also be seen on the inner surface of the lower leg and thigh.
Symptoms of cold dermatitis
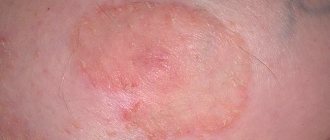
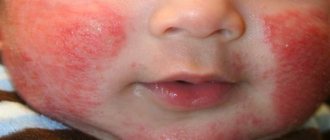
The main symptom of HD is the formation of dry, flaky spots on the skin that have a red or dark red tint. Their size does not exceed 2-5 cm and are accompanied by itching and burning.
Over time, cracks appear on the surface of the new growths, and subsequently a dry crust appears. Parts of the body most often affected by the disease are the face, neck, hands and ears. That is, those that are constantly open, which allows unhindered exposure to the cold. In rare cases, signs of HD may appear in the knees and upper thighs. They are quite easy to identify; these spots look like the one shown in the photo below.
Main symptoms of the disease
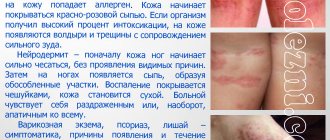
The symptoms of cold dermatitis are similar to the manifestations of foodborne or atopic dermatitis. With this disease it is noted:
- itching;
- redness of the affected areas;
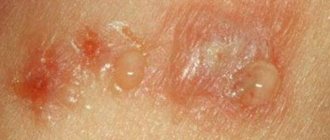
- urticaria: blisters of various sizes that look like a nettle burn or an insect bite, accompanied by severe itching;
- violation of the integrity of the skin, cracks;
- the formation of bubbles, which subsequently causes the appearance of weeping areas;
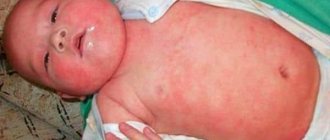
- swelling of the mucous membranes and skin.
Other signs of illness
Allergy to cold is manifested not only by skin rashes and swelling. With this disease you may:
- increased lacrimation;
- body temperature rises to 37-37.5˚C;
- acute rhinitis occurs;
- drowsiness, dizziness appear;
- dry vomiting occurs;
- appetite worsens.
Extremely rarely, the disease causes bronchospasm, loss of consciousness and Quincke's edema. This disease occurs in both children and adults. In the latter, the disease can progress rapidly. However, some symptoms may be pronounced, while others may be invisible.
Tablets for allergies to cold. Allergy to cold
Allergist-immunologist Yegor Batorov about urticaria, which occurs when exposed to low temperature
The saying “it’s better to be covered in sweat seven times than frost once” is especially true for people suffering from cold urticaria. In severe cases of this disease, the figurative meaning of this joke can quickly become literal.
Is there an allergy to cold? What are its symptoms? Cold urticaria (CU) is a disease characterized by the appearance of blisters and/or angioedema after general or local exposure to cold, one of the forms of physical urticaria. ICD-10 code: L50.2 (urticaria caused by exposure to low or high temperature).
Classification
- Acquired HC
- primary (contact, idiopathic)
- secondary (with cryoglobulinemia, infectious diseases, tumors; occurring after taking medications, insect bites, etc.).
- Hereditary HC
- Cryopyrin Associated Periodic Syndromes (CAPS): familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome, Muckle-Wells syndrome (urticaria, deafness, amyloidosis), Chronic Infantile Onset Neurologic Cutaneous Articular Syndrome/Neonatal Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disease – CINCA/NOMID)
- Familial atypical HC.
Epidemiology
Allergy to cold can occur in both adults and children. However, it is more common in young people (18–25 years old). This is a relatively rare condition, with an incidence of about 0.05–0.1% of all cases of urticaria. In cold climates it naturally develops a little more often. More than half of patients with chronic hyperplasia suffer from other allergic diseases.
In most cases (> 90%), primary acquired CU develops. Hereditary forms are extremely rare (≤1: 360,000–1,000,000), inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, and persist, as a rule, from early childhood.
Causes of cold allergies
The significant factors and causes of primary acquired cold urticaria are unknown. Secondary acquired chronic disease can develop in patients with infectious diseases (viral hepatitis, HIV infection, infectious mononucleosis, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, borreliosis, etc.), tumors, after the use of medications, including serums and vaccines, hymenoptera bites. Cryoglobulins (serum proteins that change their structure and precipitate when the temperature drops; are formed in tumor, infectious and systemic inflammatory diseases) were detected in the blood of 3–4% of patients with chronic chronic disease. Isolated cases of secondary CC that arose against the background of allergen-specific immunotherapy and after allergological skin tests have been described.
Hereditary CC develops as a result of mutations in the gene encoding the cryopyrin protein, which is involved in the regulation of the production of proinflammatory cytokines, primarily interleukin-1 (IL-1).
Pathogenesis
Local and/or general exposure to cold on the skin or mucous membranes leads to changes in tissue antigens and/or antibodies. Contact of these altered molecules with mast cell receptors leads to the release of histamine and other allergy mediators from the latter. Under their influence, capillary permeability increases, swelling and inflammation quickly develop.
In hereditary forms of CC, an uncontrolled increase in the expression of IL-1 leads to the development of a systemic inflammatory process in many organs and tissues of the body.
Symptoms of an allergy to cold
How does an allergy to cold manifest itself? The triggering factor is general or local cooling: cold air, in severe cases, sometimes a draft or flow from an air conditioner is enough, immersion in cold water, ingestion of cold food and drinks, contact with a cold object. Cold-induced cholinergic urticaria develops after exercise in the cold.
Patients with cold allergies complain of symptoms such as:
- typical urticarial rashes,
- rounded or irregularly shaped elements rising above the surface of the skin, accompanied by itching or burning,
- possible swelling of the lips, mucous membranes of the oral cavity,
- itching in the mouth, throat.
A rash with an allergy to cold usually appears within a few minutes on the arms, legs, face or other areas of the skin exposed to cold, less often around them or on “insulated” parts of the body (reflex CU). With cold erythema, there are no characteristic urticarial elements, the cooled area turns red, and pain appears.
In warm conditions, skin manifestations usually regress within 1–24 hours, but may persist for up to several days.
In severe cases of the disease, disturbances of consciousness, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, difficulty breathing, vomiting, and abdominal pain are possible.
In addition to the individual sensitivity of the patient, the severity of cold symptoms proportionally depends on the operating temperature, the cooled area and the duration of exposure.
Diagnostics
In most cases, characteristic complaints, medical history and examination results are sufficient to make a clinical diagnosis of CU. To confirm it, a provocative test is performed: an ice cube packed in polyethylene is placed on the skin of the anterior surface of the forearm for 10–20 minutes, after which one or more urticarial elements appear at the site of contact or around it for 30 minutes. Antihistamines must be discontinued at least 48 hours before the test.
In case of a negative ice test, it is possible, but modern guidelines do not recommend - due to the risk of developing systemic reactions - a modified cold test: the forearm is placed in very cold water (5 ° C) for 10 minutes.
For the same reason, as well as from humanism, the third test is not recommended for use: a person stripped to his underwear is placed in a room with a refrigerator temperature of +4 °C for 20–30 minutes. This truly Gestapo method allows you to identify HC, which manifests itself only with general cooling.
In civilized countries, to assess the severity of chronic cold, the temperature sensitivity threshold is also determined using a special device, but it is not used in the daily practice of domestic allergists.
Using laboratory and instrumental methods, the presence of pathological conditions that may be associated with the development of secondary chronicle disease is excluded or confirmed.
Treatment of cold allergies
How to treat allergies to cold? Patients with HC should, if possible, avoid exposure to low temperatures: dress warmly, wash with warm water, do not drink cold drinks, swim with great caution or not swim at all. During the cold season, it is recommended to use cosmetics.
The main remedy for the treatment of cold allergy symptoms is H1‑. If necessary, it is possible to increase the daily dose up to 4 times, but for this it is necessary to obtain the informed written consent of the patient.
The effectiveness of leukotriene antagonists is not shown in all cases. Systemic glucocorticosteroids are often ineffective.
Tolerance induction with the patient's own serum is used to a limited extent due to the relative complexity and labor-intensive nature of the procedure. From a patient with an exacerbation - usually after a walk in the cold - 20 ml of blood is taken, the serum is isolated, diluted with saline and gradually increasing concentrations are injected subcutaneously over two weeks. In some cases, this method has a good temporary or permanent clinical effect in the treatment of cold urticaria.
In rare cases, when life-threatening conditions occur and the disease is severe, hospitalization is indicated. In case of secondary chronic disease, treatment of the underlying disease is necessary.
Is the pathology dangerous?
Most often, signs of cold dermatitis appear on the face and hands. In any case, treatment for the disease is required. This disease is not included in the list of fatal pathologies. However, in the absence of therapy, problems may arise, including a strong feeling of discomfort, an unattractive appearance of the affected areas of the skin, their cracking, an increased risk of infection through small wounds, and so on. In this case, there is a need for additional treatment. Especially if tissue infection occurs.
According to experts, if you are allergic to cold, the risk of developing age spots increases, as well as noticeable scars in places where damaged skin has not healed for a long time. Eliminating such symptoms of a disease is much more difficult than curing the disease itself.
Diagnostic methods
If symptoms of cold dermatitis appear, it is recommended to consult a specialist. A dermatologist treats such diseases. The first step is to examine the patient. The doctor should also interview the patient about his well-being. Only after this are other studies prescribed.
Modern techniques suggest the use of a diagnostic method such as ph-metry. In other words, the procedure allows you to establish the acid-base balance of the skin. This study makes it possible to exclude the possibility of developing fungal tissue infections and psoriasis. With such diseases, indicators change significantly.
Dermatoscopy is also used. In this case, examination of the skin is carried out using special equipment. The study allows us to exclude the development of oncological pathology.
In some situations, a dermatologist may prescribe a consultation with a gastroenterologist for the patient. A specialist in this profile conducts an examination of the gastrointestinal tract. Consultation with an otolaryngologist and urologist may also be required. These specialists determine the presence of chronic infections.
When carrying out diagnostic measures, there is often a need for laboratory tests of stool, blood, and urine.
How to treat
Treatment of cold dermatitis is complex. It should include:
- use of external means;
- taking antihistamines by mouth;
- hypoallergenic diet;
- folk therapy.
In advanced situations, physiotherapy may be required. It is also important to cure any chronic diseases, caries.
Drug therapy is based on taking antiallergic drugs. At the first symptoms of dermatitis, you need to take one tablet of Suprastin, Loratadine, Tavegil or other antihistamines and consult a dermatologist. He will prescribe further treatment with a detailed regimen for using a particular drug:
- antibiotics for various types of infections;
- vitamins A, E, C, PP to strengthen the immune system;
- prebiotics for the treatment of dysbiosis;
- for parasites - antiparasitic drugs.
If pancreatic or liver diseases are detected, it is necessary to take choleretic medications and enzymes.
Doctors often prescribe medications that improve peripheral circulation.
Vitamin therapy is used - ascorbic acid, vitamins A, E and PP are often prescribed. The most effective traditional medicine recipes are:
- Horsetail decoction. A teaspoon of herb is poured into 200 ml of hot water, infused, and filtered. Drink the decoction on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Herbal infusion. A large spoonful of the mixture (elecampane, marshmallow root, licorice in equal parts) is poured with 400 ml of hot water, infused for 10 hours, filtered, and taken 1/3 cup three times a day.
- Raspberry root decoction. 40 g of the plant is poured into 400 ml of boiling water, left for half an hour, and filtered. Drink 1/4 glass at night and before planning to go out into the cold.
- Horsetail decoction. The herb is poured with 200 ml of boiling water, and after cooling it is filtered. Drink a little in the morning on an empty stomach.
How to treat cold dermatitis?
After a thorough examination, the dermatologist prescribes treatment. First of all, it is aimed at eliminating the most unpleasant symptoms of the pathology. Most often, antihistamines are prescribed in the form of tablets orally, as well as in the form of a spray for external use. Such drugs can relieve swelling and redness of the skin, as well as reduce the risk of the formation of small wounds and cracks. Treatment of cold dermatitis on the hands and face requires special attention.
A dermatologist may recommend the use of special creams that can:
- significantly improve the condition of capillaries located in the skin;
- protect the skin from adverse factors;
- accelerate the adaptation of the skin to unfavorable environmental conditions;
- maintain and restore the fat (lipid) barrier that protects the skin and retains moisture in the tissues.
Treatment of cold dermatitis is carried out comprehensively. Among the medications for this disease: “Tavegil”, “Suprastin”, “Fenistil”. In addition to eliminating unpleasant symptoms, therapy may be prescribed to combat the underlying disease. Those who are prone to an allergic reaction to cold are advised not to go outside at low temperatures unless absolutely necessary. Also, if any dermatitis occurs, it is necessary to optimize the diet.
Treatment
In order to reduce the symptoms of this disease, it is necessary to resort to the following methods of drug treatment.
First of all, you should take medications that improve skin condition. For these purposes, vitamin complexes with a high content of ascorbic acid (Vit. C), retinol (Vit. A), rutin (Vit. P), nicotinic acid (Vit. PP), and tocopherol (Vit. E) are suitable. All medications that improve microcirculation in organs and tissues (riboxin, meldonium) have a positive effect.
In order to help directly during the development of manifestations of cold dermatitis, the use of fast-acting antihistamines, which include diazolin and tavegil, is indicated.
Prevention of infectious complications plays an important role. To do this, if cracks form on the skin, the affected areas should be treated with antiseptics. It is possible to use both special combined disinfectants and chlorhexidine and furatsilin directly. You should avoid using alcohol solutions and iodine, as they dry out the skin.
Prevention
If a tendency to cold dermatitis has been identified, the patient is recommended to take preventive measures. He should be careful when outdoors when the temperature drops. If there is a risk of hypothermia, the skin should be warmed immediately. It is not recommended to rub it.
It is also worth using therapeutic and protective cosmetics. These products should be applied approximately 30 minutes before going out into the fresh air.
It is recommended to follow a balanced diet. The diet should be enriched with beneficial components for the skin and vitamins. You should approach the issue of hardening with extreme caution. Even washing with cold water can lead to illness. In severe cases, iced drinks and ice cream should be avoided.
Folk recipes
Home treatment begins with the selection of caring and protective equipment. Cleansing creams are chosen from the category of gentle care for sensitive skin. Fat creams are suitable for nutrition and protection from the flow of cold air. They are applied 30 minutes before leaving.
The action of folk remedies is aimed at strengthening the body, increasing resistance, and restoring skin cells.
- An ointment made from elecampane root will help with frosty dermatitis. It is crushed into powder and added to a mixture of equal parts lard (preferably pork), fish oil, petroleum jelly, calculating 2 parts of the mixture to 1 part elecampane. The ointment is distributed in a thin layer over the inflamed spots once a day. After recovery, washing with a warm decoction of elecampane is carried out for another 1.5 weeks.
- Infuse 40 g of crushed raspberry root in 2 cups of boiling water for half an hour. The expressed extract is taken in portions of 3 tablespoons before going outside and at night.
- Yarrow tea is a natural antihistamine. A tablespoon of dried herbs is poured into a glass of boiling water and left for an hour. The strained drink is taken one third of a glass three times before meals.